当前位置:网站首页>Notes on advanced points of C language 2
Notes on advanced points of C language 2
2022-04-23 06:41:00 【~Ha】
Catalog
- Four 、 The pointer
7、 Strings and pointers
8、 Array pointer
9、 Array name and address
10、 The difference between pointer variables and array names
11、 Conversion of pointers in multidimensional arrays
12、 The pointer is used as the parameter of the function
- Four 、 The pointer
7、 Strings and pointers
a、 char string[100] = “I love C!”
Defines a character array string, Used to store multiple characters , And use ”I love C!” to string Array initialization
character string “I love C! ” Store in string in
b、 char *str = “I love C!”
A pointer variable is defined str, Only character address numbers can be stored ,
So I love C! The characters in this string cannot be stored in str In pointer variables .
str Just stored characters I The address number of , “I love C! ” Stored in the text constant area
c、 char *str =(char*)malloc(10*sizeof(char));// Dynamic application 10 Bytes of storage space , First address to str assignment .
strcpy(str, "I love C"); // The string “I love C!” copy to str Point to the memory
A character array : In the memory ( Stack 、 Static global area ) It opens up a space for storing strings
Modifiable , Can be initialized directly
String pointer : stay Text constant area Opened up a space to store strings , Pay the first address of the string to str
Do not modify the , Can be initialized directly
Pile up : Use malloc The function requests space in the heap , Copy the string to the heap
Modifiable , Cannot initialize directly
Whether the memory pointed to by the pointer can be modified depends on the position pointed to by the pointer , Pointing to the text constant area is not modifiable , Pointing stack 、 Pile up 、 The static global area can be modified
A character array : Use scanf perhaps strcpy
buf_aver="hello kitty"; // error , Because the name of the character array is a constant
strcpy(buf_aver,"hello kitty"); // correct
scanf("%s",buf_aver); // correct Pointer to string :
buf_point="hello kitty"; // correct ,buf_point Point to another string
strcpy(buf_point,"hello kitty"); // error , read-only , Can you copy the string to buf_piont The memory pointed to depends on buf_point Where to point .8、 Array The pointer ( Is a pointer )
Concept : Itself is a pointer , Point to an array , Add a jump to an array , That is, point to the next array
Define methods : The type of array pointed to (* Pointer variable name ) [ The number of elements of the array pointed to ]
int (*p)[5];// Defines an array pointer variable p, p Pointing to an integer, there are 5 Array of elements , That is, each small array has five integer variables
p+1 Point down 5 An integer , Skip one with 5 Array of integer elements .
difference Array pointer :int (*p) [5] Is a pointer , Only four bytes
int *p[5] It's an array , There are five shaping pointers
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int a[3][5];// Defined a 3 That's ok 5 A two-dimensional array of columns
int(*p)[5];// Define an array pointer variable p, p+1 Jump one with 5 An integer array of elements
printf("a=%p\n",a);// The first 0 Row address of row
printf("a+1=%p\n",a+1);// The first 1 Row address of row , a and a +1 Bad 20 Bytes
p=a;
printf("p=%p\n",p);
printf("p+1=%p\n",p+1);//p+1 Jump one with 5 One dimensional array of integer elements
return 0;
}$ One dimensional array pointer int(*p)[5] ; There are... For each line 5 individual int A two-dimensional array of type elements
$ Two dimensional array pointer int(*p)[4][5]; Use with a three-dimensional array , A three-dimensional array consists of several 4 That's ok 5 A two-dimensional array of columns
$ ...
Confusing content :
Pointer array : Is an array , A collection of pointers of the same type
int *p[10];
Array p Yes 10 individual int * Pointer variables of type constitute , Namely p[0] ~p[9]
Array pointer : Itself is a pointer , Point to an array , Add 1 Jump an array
int (*p)[10];
P It's a pointer , p Is an array pointer , p Add 1 Point to the next array , jump 10 A plastic .
The pointer of the pointer :
int **p;//p It's the pointer of the pointer , It can be saved int * Type of address
int *q;
p=&q;
9、 Array name and address
The pointer : Variable takes address
The pointer of the pointer : The pointer variable takes the address
Array pointer : Array name and address
int a[10];
a+1 Jump an integer element , yes a[1] The address of
a and a+1 One element apart , 4 Bytes
&a It becomes a one-dimensional array pointer , yes int(*p)[10] Type of .
(&a) +1 and &a The difference is an array, that is 10 The elements are 40 Bytes .
c Language policy , Array name and address , Becomes an array pointer . Add 1 Jump an array
10、 The difference between pointer variables and array names
int a[10];
int *p;
p = a;
The same thing :a and p Point to the same address , Equivalent when referring to array elements
Difference :a Is a constant ,p It's a variable. ;p You can assign ,a Can't assign a value
Yes a The fetch address is an array pointer , Yes p Take a pointer whose address is a pointer
11、 Conversion of pointers in multidimensional arrays
In a two-dimensional array , Line address take * Not worth it , It means that the pointer is degraded , By line address ( Array pointer ) Become the first in this line 0
Addresses of elements . take * The front and back still point to the same place , But the types of pointers are different
#include <stdio.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int a[3][5];
printf("a=%p\n",a);
printf("a +1=%p\n",a+1);
printf("*a =%p\n",*a);// *a Became the second 0 Xing di 0 The address of the column element
printf("(*a)+1 =%p\n",(*a)+1 ); // The result is 0 Xing di 1 The address of the column element
return 0;
}12、 The pointer is used as the parameter of the function
When calling a function, pass the address of the variable , Pass... In the called function *+ The address changes the value of the variable in the stagnation function
To change the value of the variable in the main function , The address of the variable must be passed in , And you have to pass *+ Address To assign , No matter what type this variable is
void fun(char **q)
{
*q="hello kitty";
}
int main()
{
char *p="hello world";
fun(&p);
printf("%s\n",p);// The result is : hello kitty
}When passing an array to a function, you can't pass all the array in at one time , Can only pass the address of the array
When passing a one-dimensional array :void fun(int p[]) perhaps void fun(int *p) // The two are equivalent , It's all pointers
When transmitting a two-dimensional array :void fun(int p[][4]) perhaps void fun(int (*p)[4])
When passing pointer array :
void fun(char **q) // char *q[]
{
int i;
for(i=0;i<3;i++)
printf("%s\n",q[i]);
}
int main()
{
char *p[3]={"hello","world","kitty"}; //p[0] p[1] p[2] char *
fun(p);
return 0;
}
版权声明
本文为[~Ha]所创,转载请带上原文链接,感谢
https://yzsam.com/2022/04/202204230548245455.html
边栏推荐
- 【UDS统一诊断服务】二、网络层协议(2)— 数据传输规则(单帧与多帧)
- [UDS unified diagnosis service] i. diagnosis overview (1) - diagnosis overview
- C语言输入和输出(printf和scanf函数、putchar和getchar函数)
- 相机标定:关键点法 vs 直接法
- 搭建openstack平台
- 非参数化相机畸变模型简介
- C语言的浪漫
- [UDS unified diagnostic service] II. Network layer protocol (1) - overview and functions of network layer
- C#【文件操作篇】按行读取txt文本
- Dynamic creation and release, assignment and replication of objects
猜你喜欢
Detailed arrangement of knowledge points of University probability theory and mathematical statistics

【UDS统一诊断服务】一、诊断概述(2)— 主要诊断协议(K线和CAN)
Opencv uses genericindex for KNN search
Graduation project, viewing screenshots of epidemic psychological counseling system
【UDS统一诊断服务】(补充)五、ECU bootloader开发要点详解 (2)
C#【文件操作篇】PDF文件和图片互相转换
在visual stdio中运行qt程序
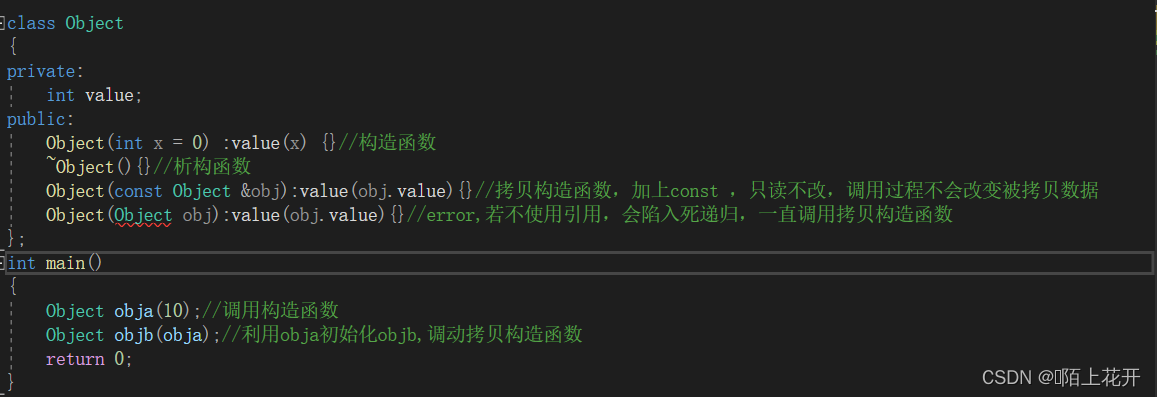
copy constructor

【UDS统一诊断服务】四、诊断典型服务(5)— 功能/元件测试功能单元(例行程序功能单元0x31)
![[UDS unified diagnostic service] IV. typical diagnostic service (5) - function / component test function unit (routine function unit 0x31)](/img/98/becd691d3d46f74f7666f5cb323eaf.png)
[UDS unified diagnostic service] IV. typical diagnostic service (5) - function / component test function unit (routine function unit 0x31)
随机推荐
友元函数,友元类,类模板
爬取彩票数据
大学概率论与数理统计知识点详细整理
在visual stdio中运行qt程序
C语言循环结构程序
【UDS统一诊断服务】五、诊断应用示例:Flash Bootloader
Vscode custom comments
SSH 公钥 私钥的理解
Dynamic creation and release, assignment and replication of objects
C语言进阶要点笔记4
Qt 给应用程序加图标
cartographer_node 编译没问题,但是运行直接挂掉的bug
Completely clean up MySQL win
爬虫之requests基本用法
实现一个计算m~n(m<n)之间所有整数的和的简单函数
共用数据的保护
【UDS统一诊断服务】一、诊断概述(4)— 基本概念和术语
函数的调用过程
【UDS统一诊断服务】二、网络层协议(1)— 网络层概述与功能
【学习一下】HF-Net 训练