当前位置:网站首页>虫子 二叉树OJ
虫子 二叉树OJ
2022-04-21 14:06:00 【华为云】
二叉树OJ淬体
例1:单值二叉树
题目
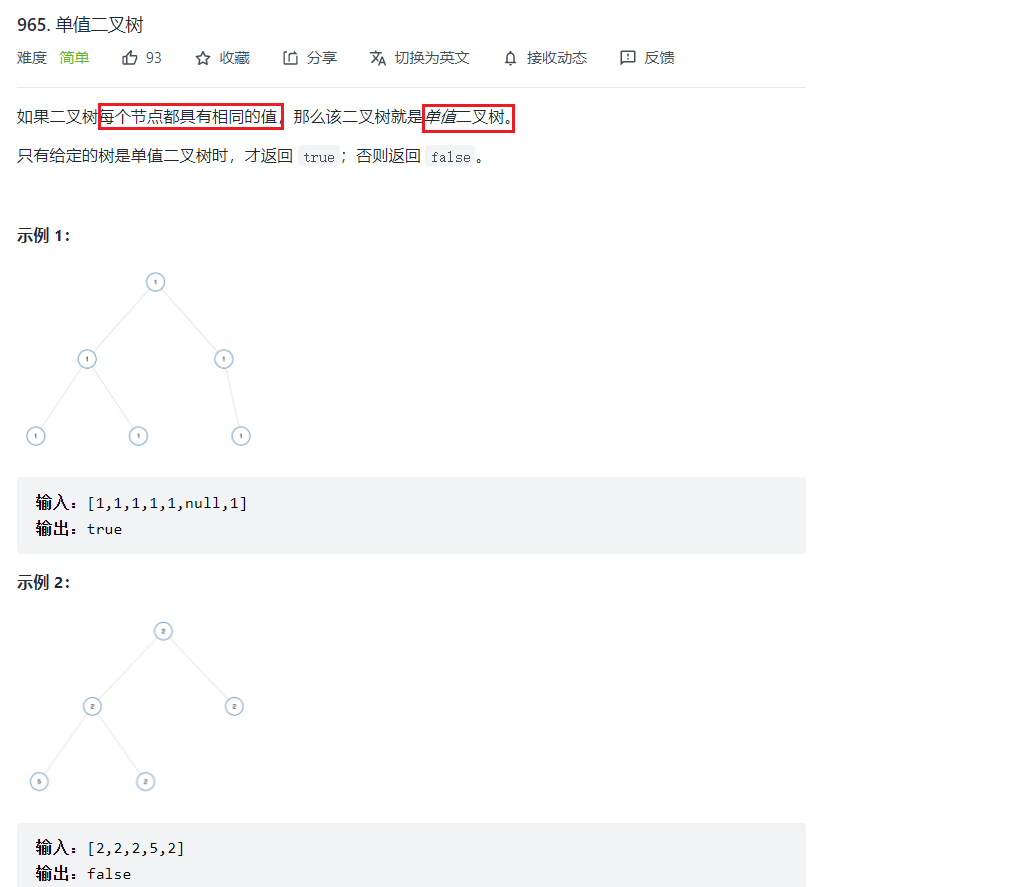
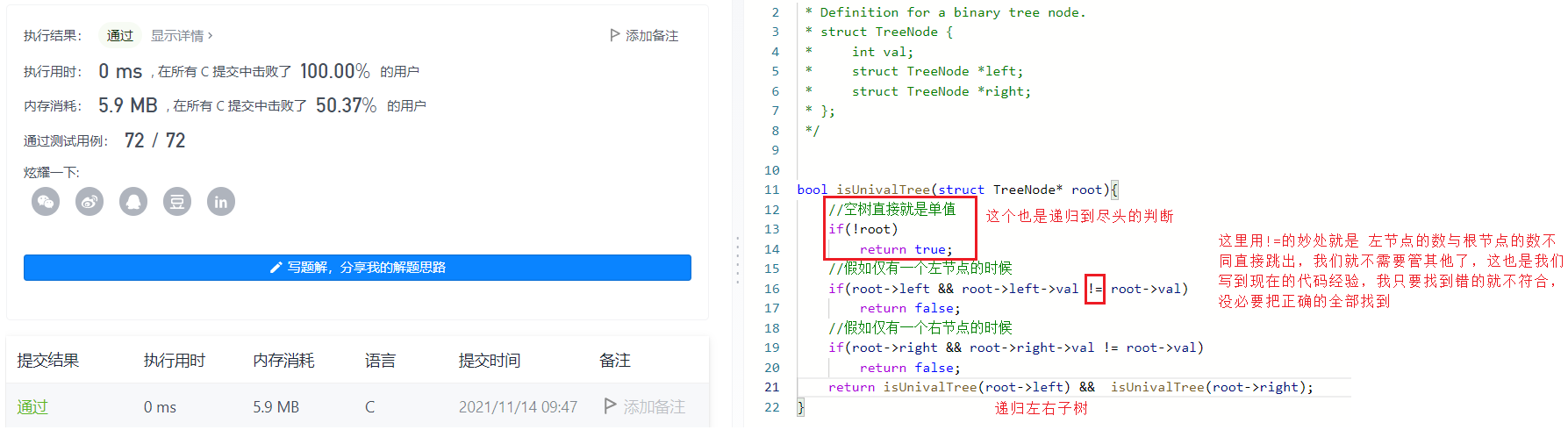
bool isUnivalTree(struct TreeNode* root){ //空树直接就是单值 if(!root) return true; //假如仅有一个左节点的时候 if(root->left && root->left->val != root->val) return false; //假如仅有一个右节点的时候 if(root->right && root->right->val != root->val) return false; return isUnivalTree(root->left) && isUnivalTree(root->right);}例2:二叉树的前序遍历
题目
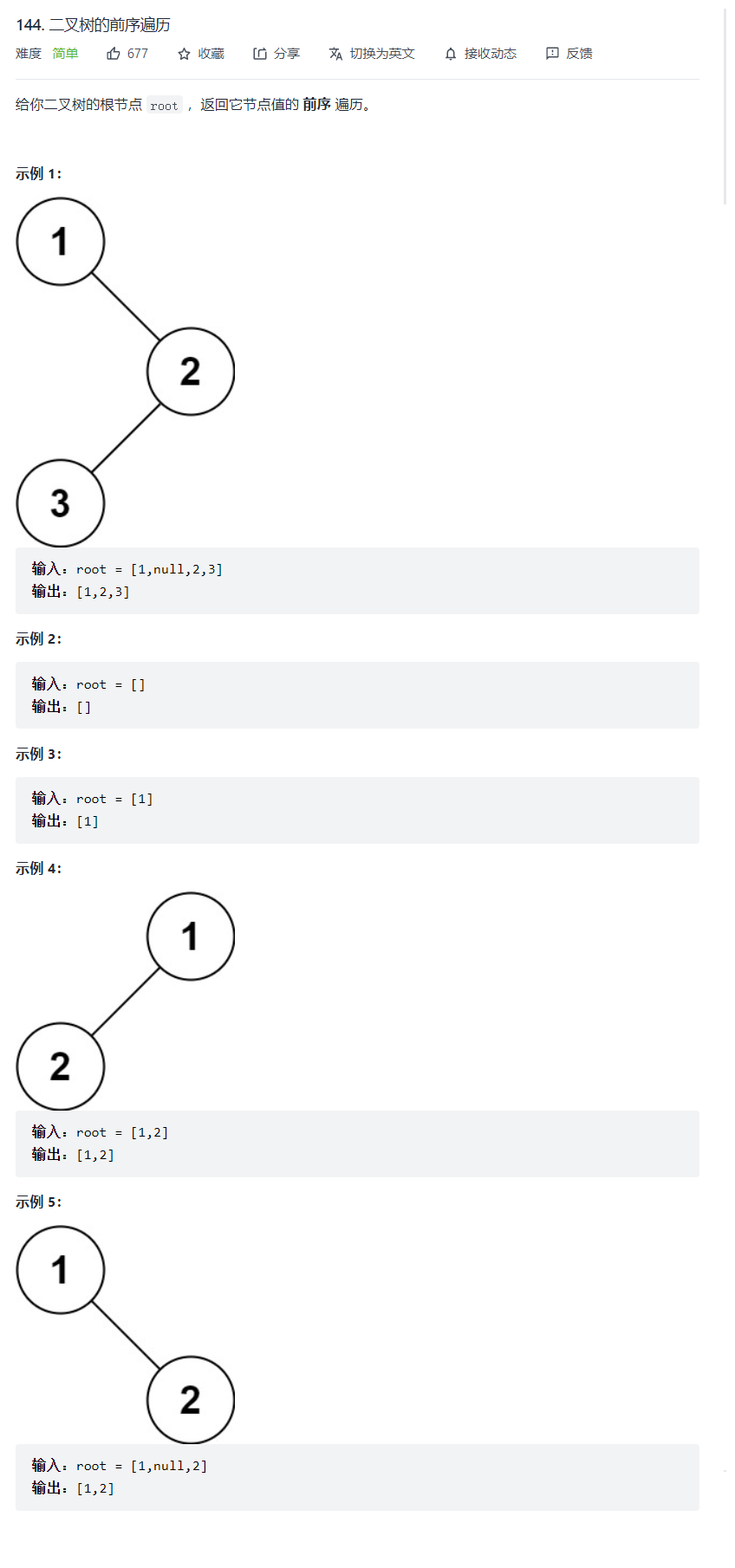
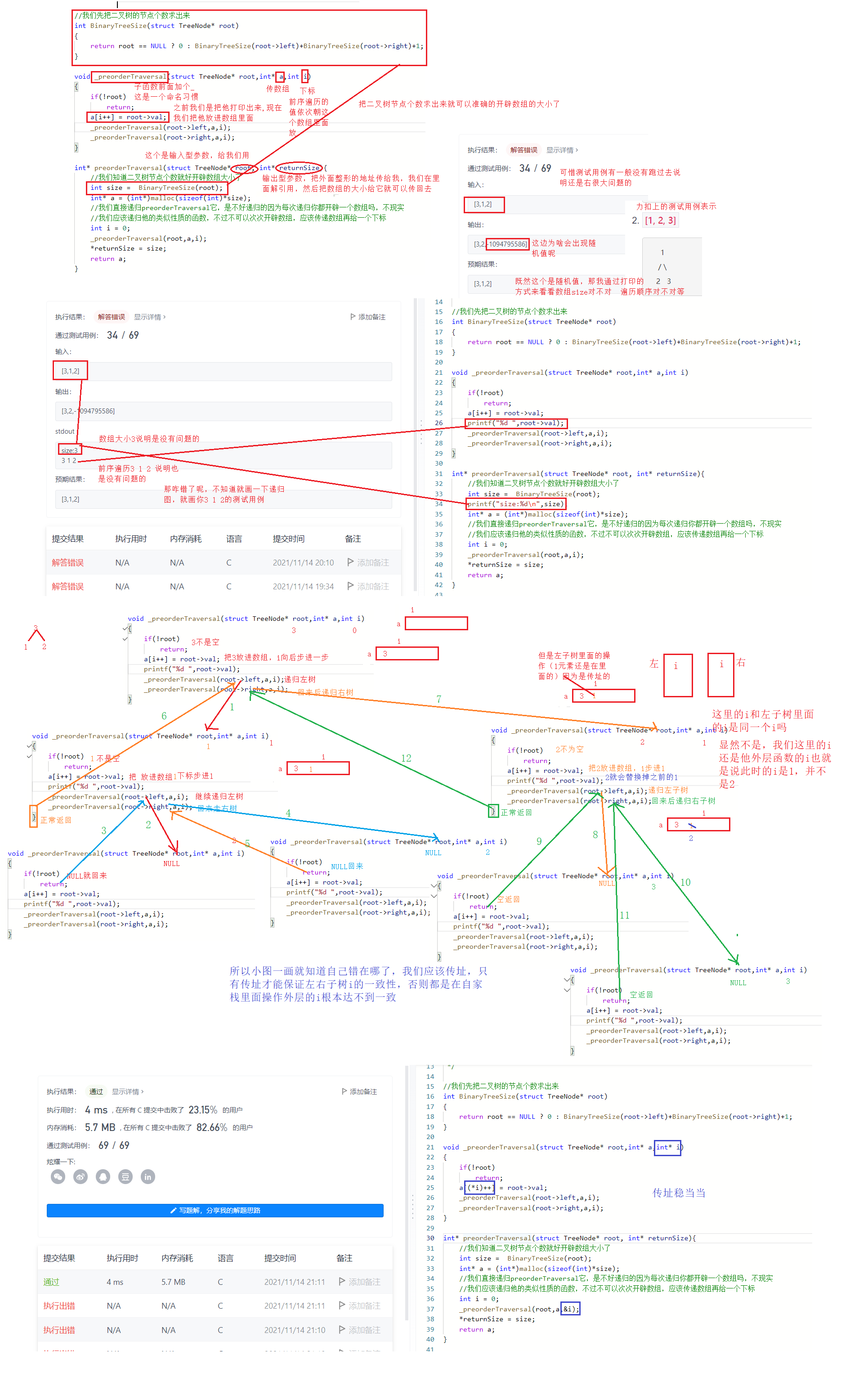
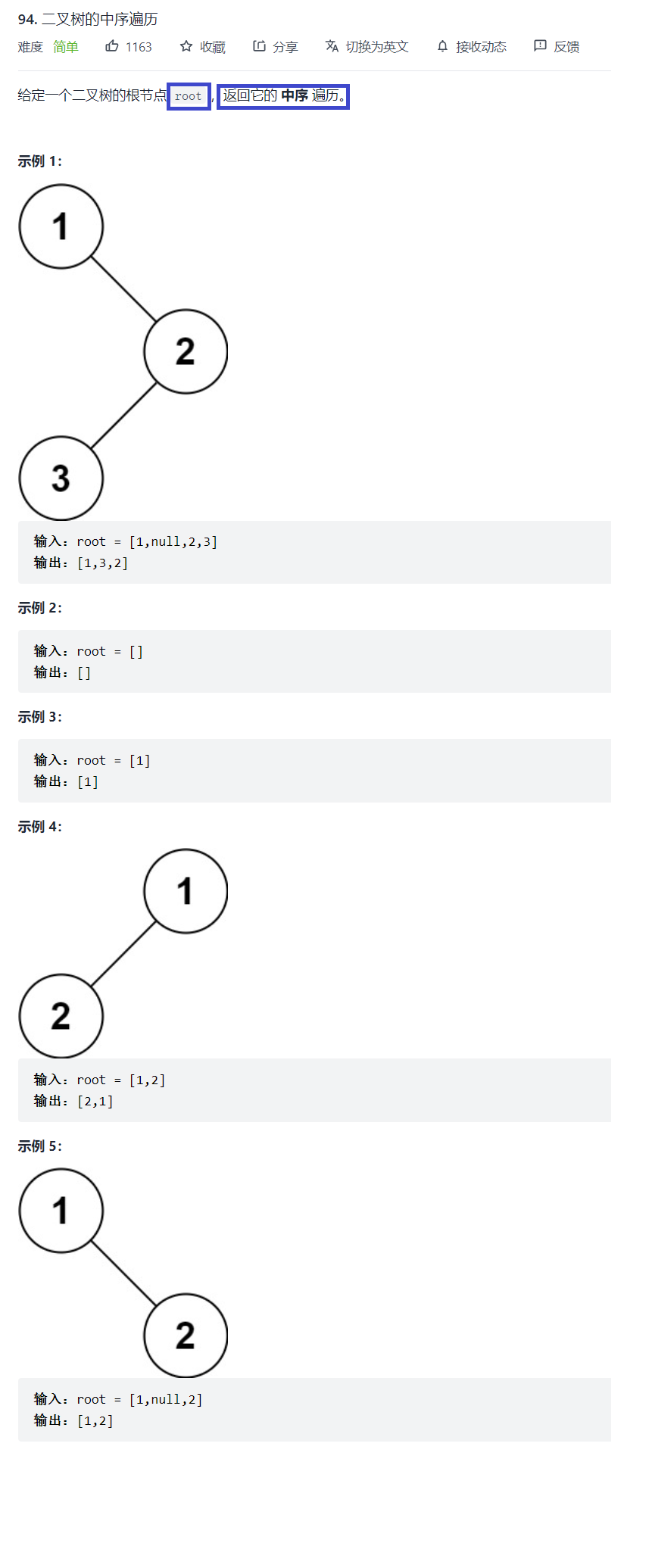
//我们先把二叉树的节点个数求出来int BinaryTreeSize(struct TreeNode* root){ return root == NULL ? 0 : BinaryTreeSize(root->left)+BinaryTreeSize(root->right)+1;}void _preorderTraversal(struct TreeNode* root,int* a,int* i){ if(!root) return; a[(*i)++] = root->val; _preorderTraversal(root->left,a,i); _preorderTraversal(root->right,a,i);}int* preorderTraversal(struct TreeNode* root, int* returnSize){ //我们知道二叉树节点个数就好开辟数组大小了 int size = BinaryTreeSize(root); int* a = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*size); //我们直接递归preorderTraversal它,是不好递归的因为每次递归你都开辟一个数组吗,不现实 //我们应该递归他的类似性质的函数,不过不可以次次开辟数组,应该传递数组再给一个下标 int i = 0; _preorderTraversal(root,a,&i); *returnSize = size; return a;}例3:二叉树的中序遍历
题目
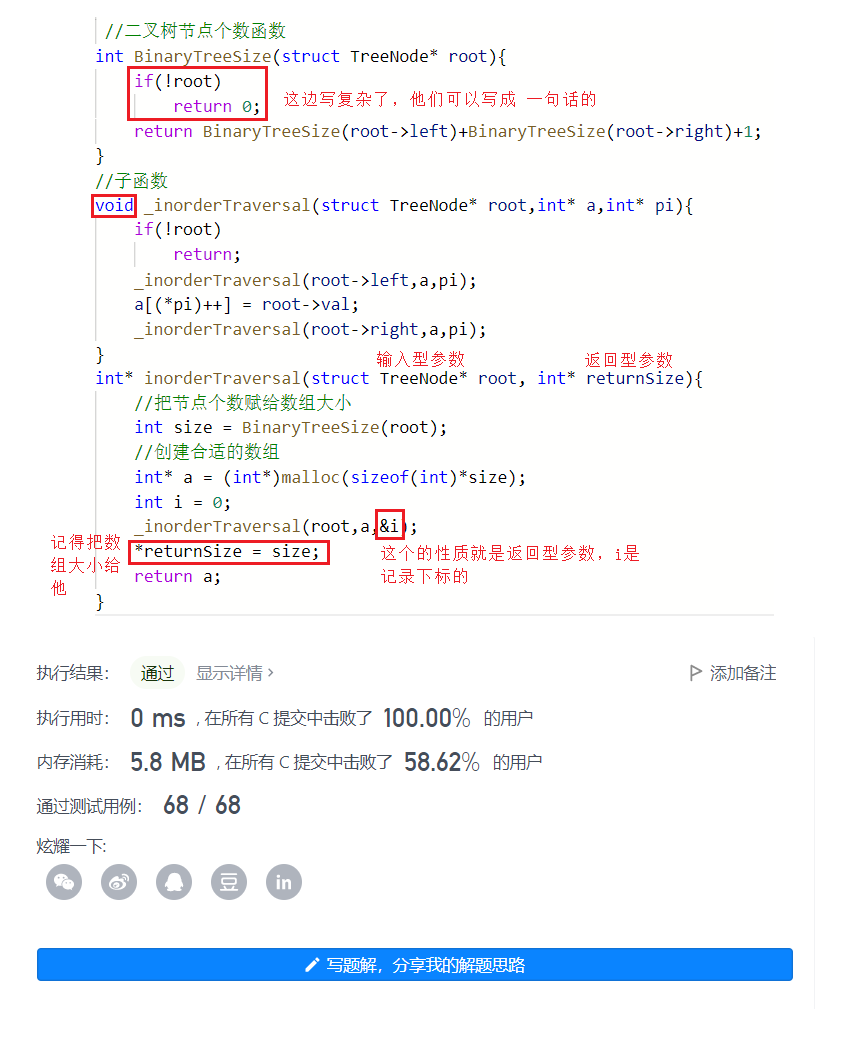
//二叉树节点个数函数int BinaryTreeSize(struct TreeNode* root){ if(!root) return 0; return BinaryTreeSize(root->left)+BinaryTreeSize(root->right)+1;}//子函数void _inorderTraversal(struct TreeNode* root,int* a,int* pi){ if(!root) return; _inorderTraversal(root->left,a,pi); a[(*pi)++] = root->val; _inorderTraversal(root->right,a,pi); }int* inorderTraversal(struct TreeNode* root, int* returnSize){ //把节点个数赋给数组大小 int size = BinaryTreeSize(root); //创建合适的数组 int* a = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*size); int i = 0; _inorderTraversal(root,a,&i); *returnSize = size; return a;}例4:二叉树的后序遍历
题目
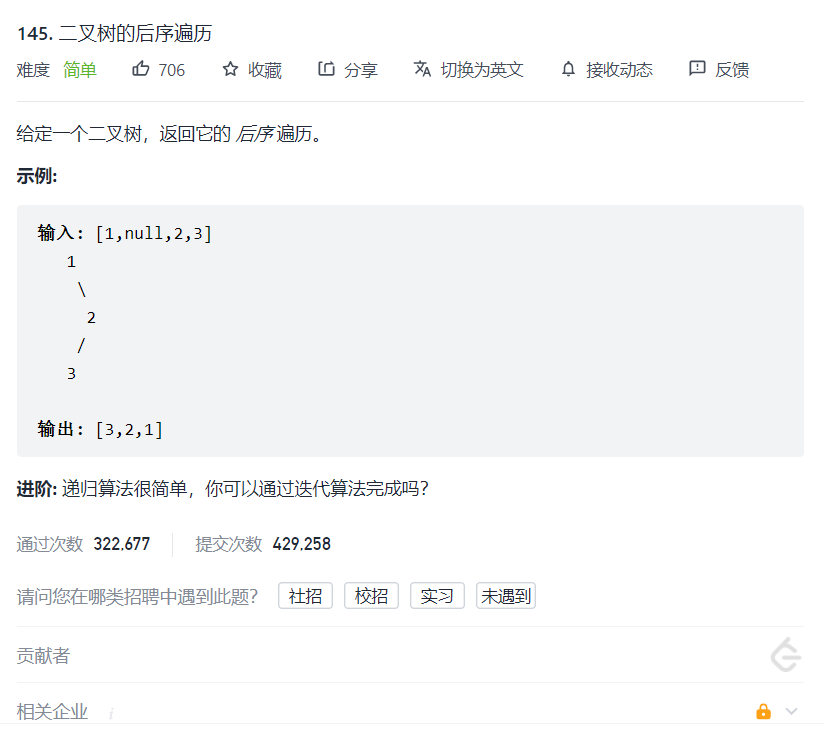
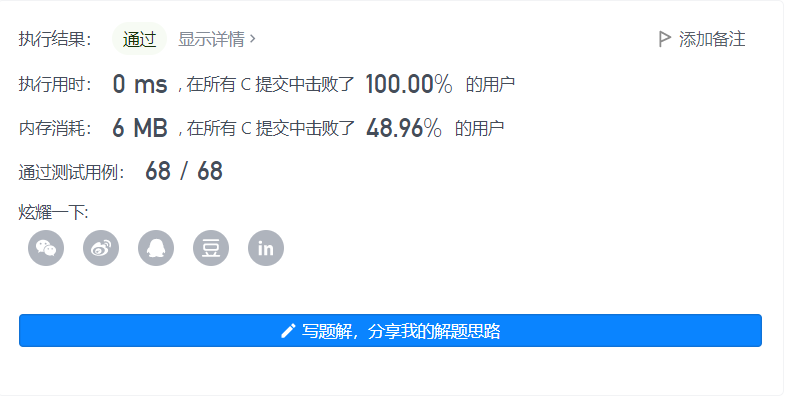
//二叉树int BinaryTreeSize(struct TreeNode* root){ return root == NULL ? 0 : BinaryTreeSize(root->left)+BinaryTreeSize(root->right)+1;}//子函数void _postorderTraversal(struct TreeNode* root,int* a,int* pi){ if(!root) return; _postorderTraversal(root->left,a,pi); _postorderTraversal(root->right,a,pi); a[(*pi)++] = root->val;}int* postorderTraversal(struct TreeNode* root, int* returnSize){ //数组大小传过来 int size = BinaryTreeSize(root); //创建合适的数组 int* a = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*size); int i = 0; _postorderTraversal(root,a,&i); *returnSize = size; return a;}例5:相同的树
题目
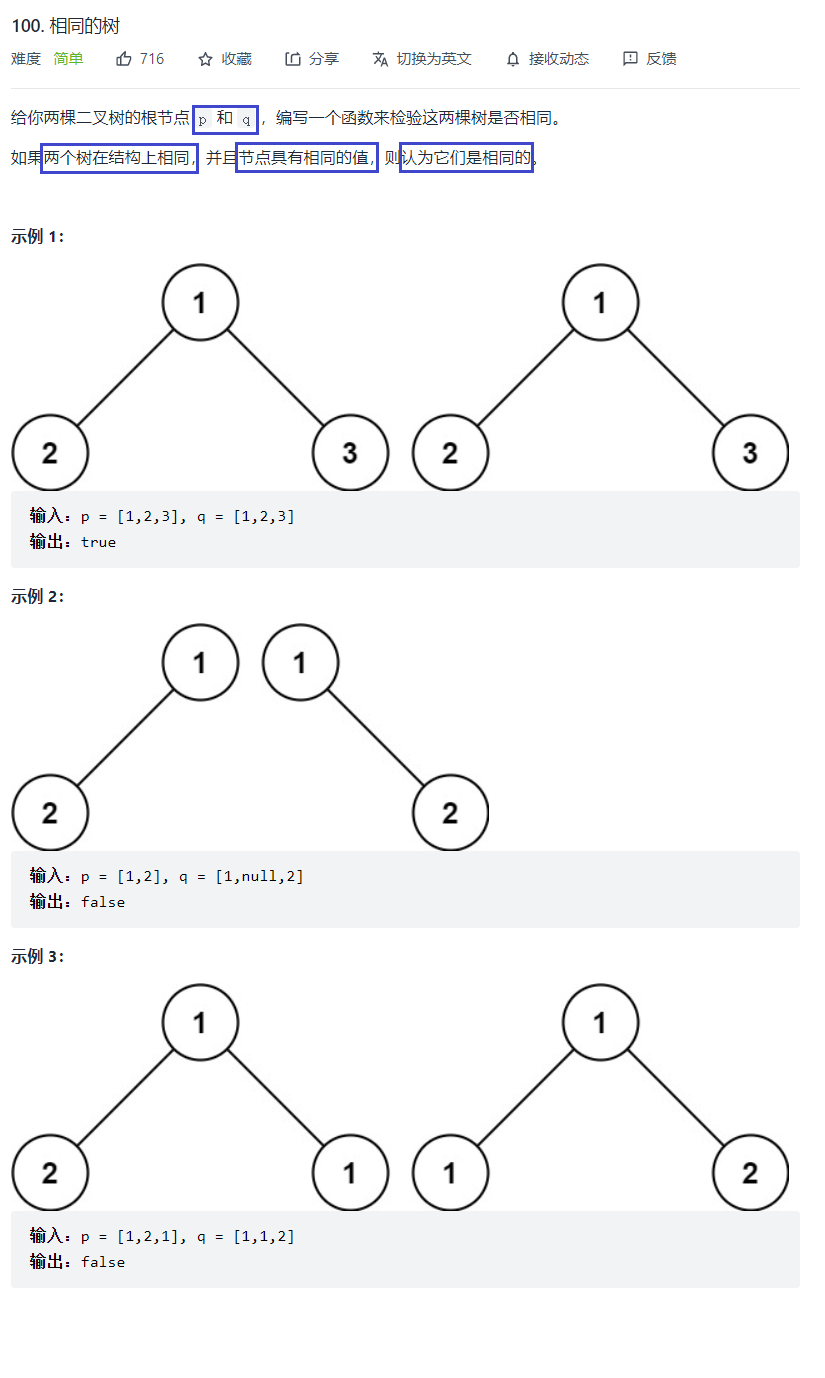
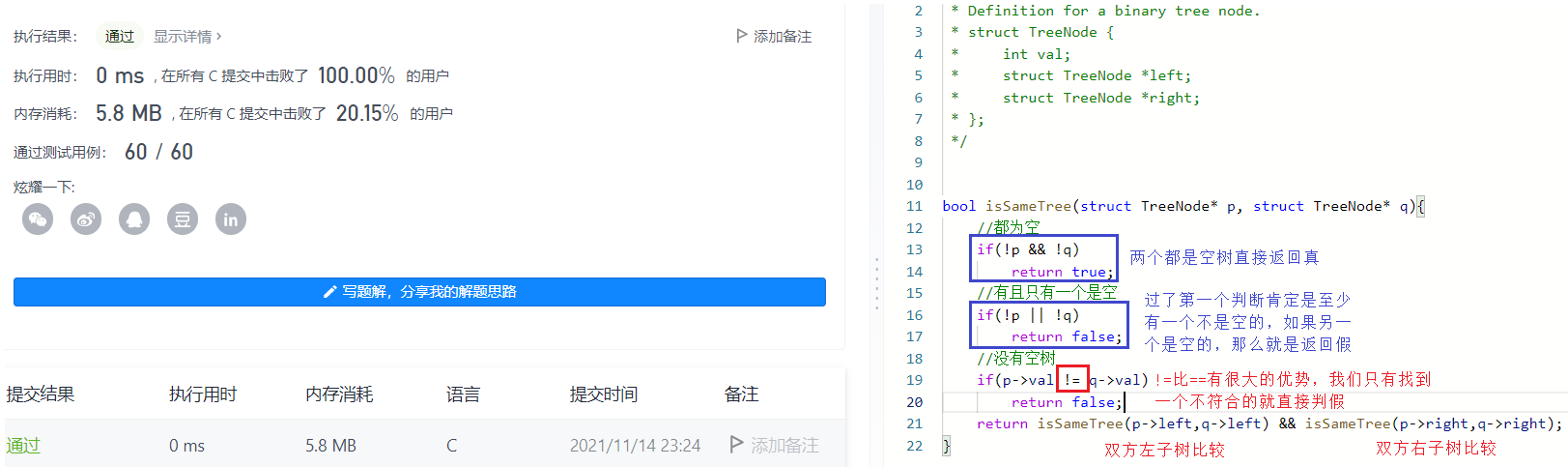
bool isSameTree(struct TreeNode* p, struct TreeNode* q){ //都为空 if(!p && !q) return true; //有且只有一个是空 if(!p || !q) return false; //没有空树 if(p->val != q->val) return false; return isSameTree(p->left,q->left) && isSameTree(p->right,q->right);}例6:对称二叉树
题目
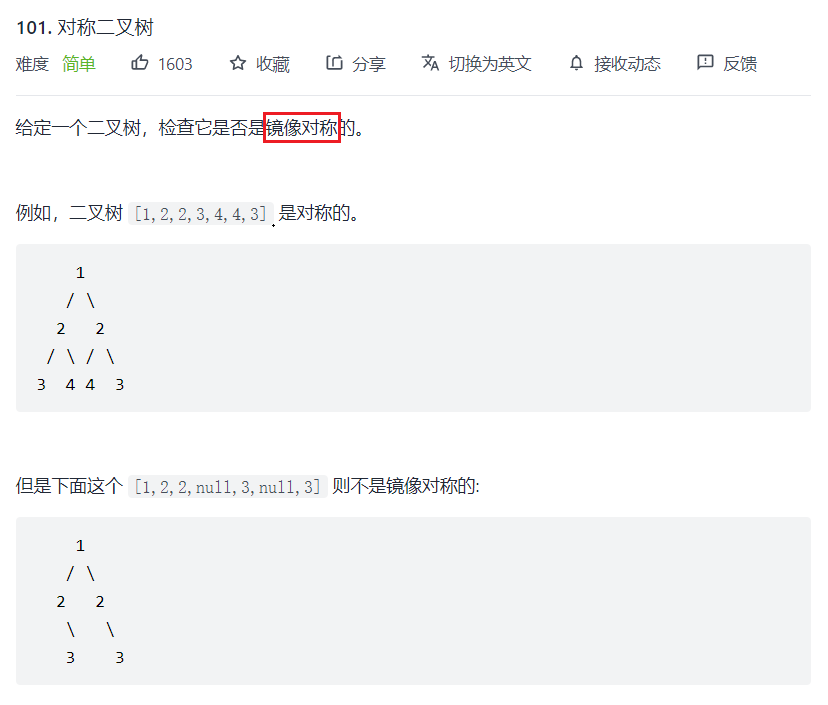
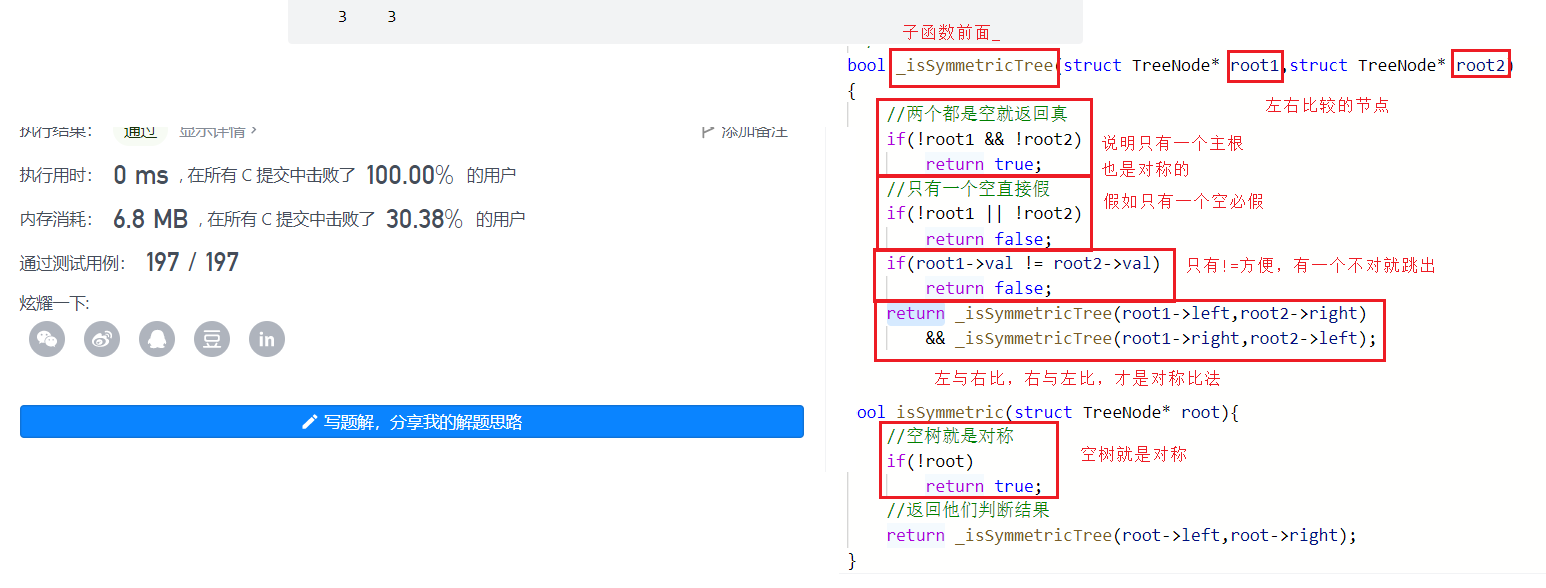
bool _isSymmetricTree(struct TreeNode* root1,struct TreeNode* root2){ //两个都是空就返回真 if(!root1 && !root2) return true; //只有一个空直接假 if(!root1 || !root2) return false; if(root1->val != root2->val) return false; return _isSymmetricTree(root1->left,root2->right) && _isSymmetricTree(root1->right,root2->left);}bool isSymmetric(struct TreeNode* root){ //空树就是对称 if(!root) return true; //返回他们判断结果 return _isSymmetricTree(root->left,root->right);}例7:另一棵树的子树
题目
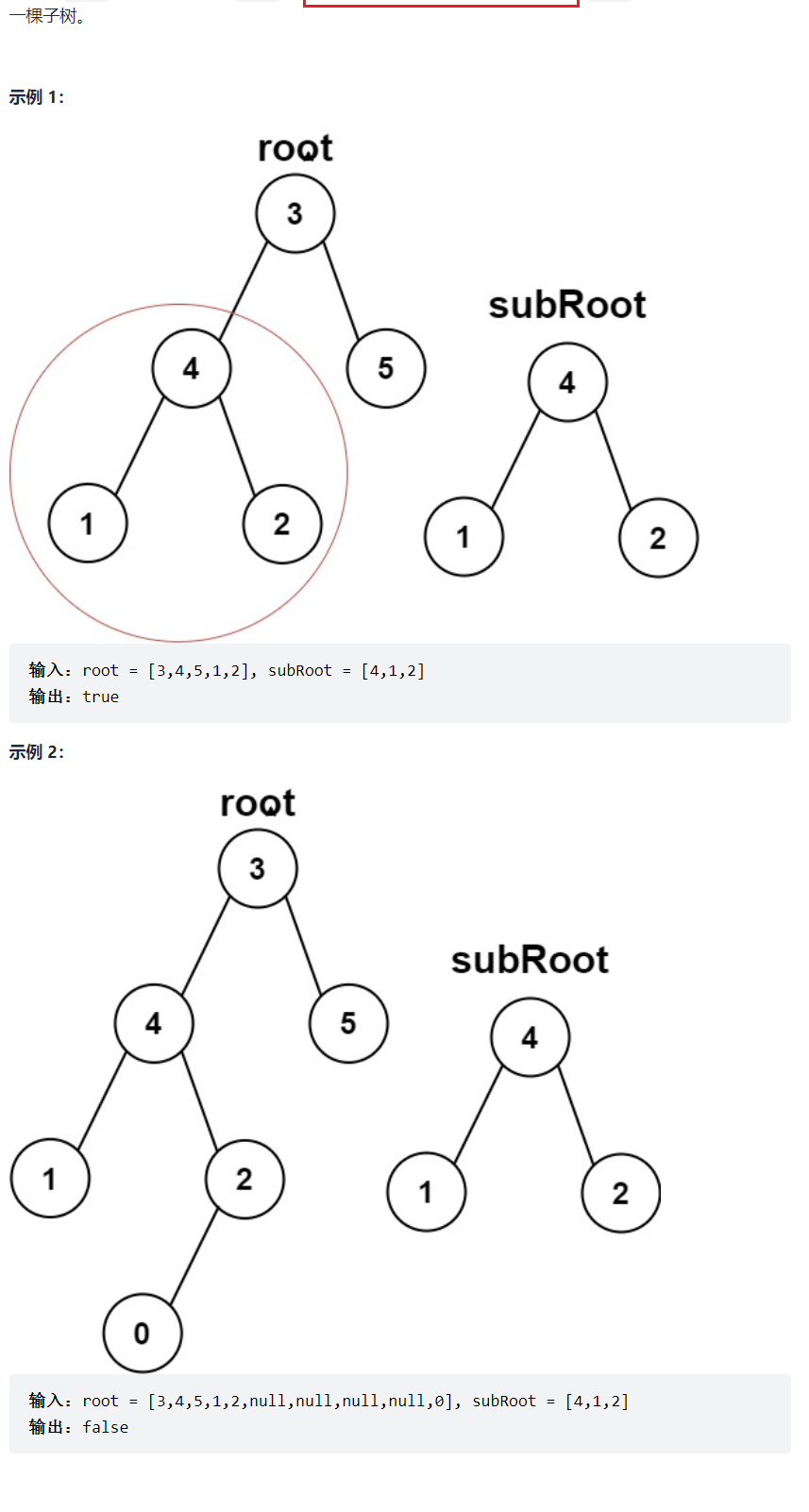
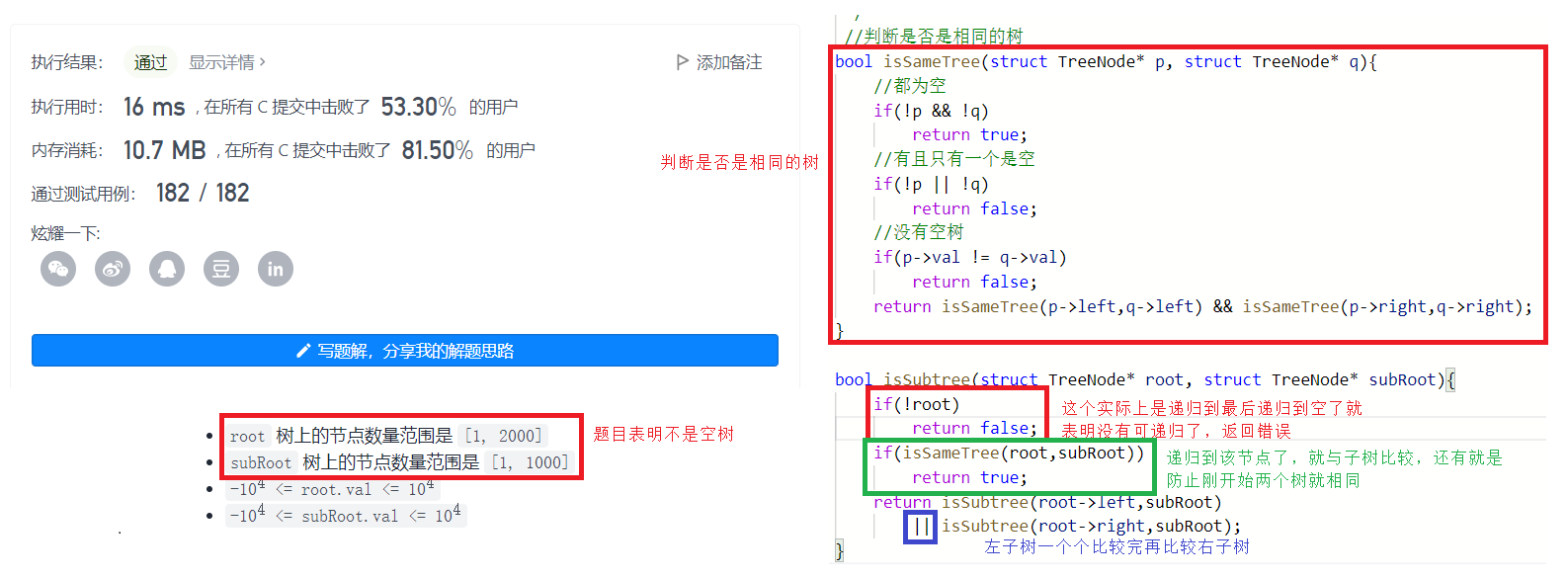
//判断是否是相同的树bool isSameTree(struct TreeNode* p, struct TreeNode* q){ //都为空 if(!p && !q) return true; //有且只有一个是空 if(!p || !q) return false; //没有空树 if(p->val != q->val) return false; return isSameTree(p->left,q->left) && isSameTree(p->right,q->right);}bool isSubtree(struct TreeNode* root, struct TreeNode* subRoot){ if(!root) return false; if(isSameTree(root,subRoot)) return true; return isSubtree(root->left,subRoot) || isSubtree(root->right,subRoot); }例8:二叉树遍历
题目
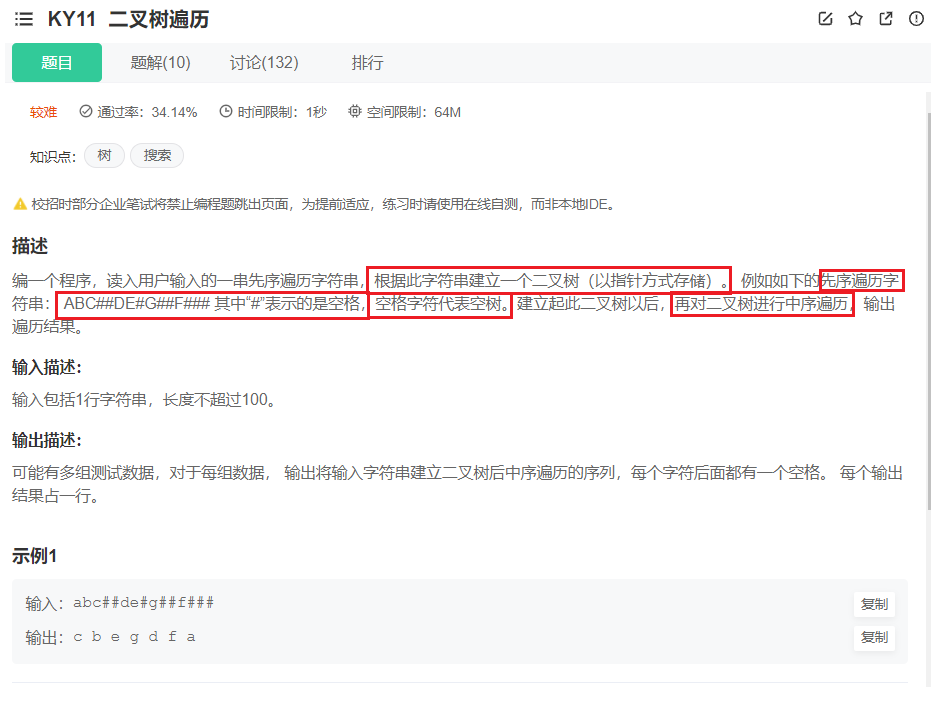
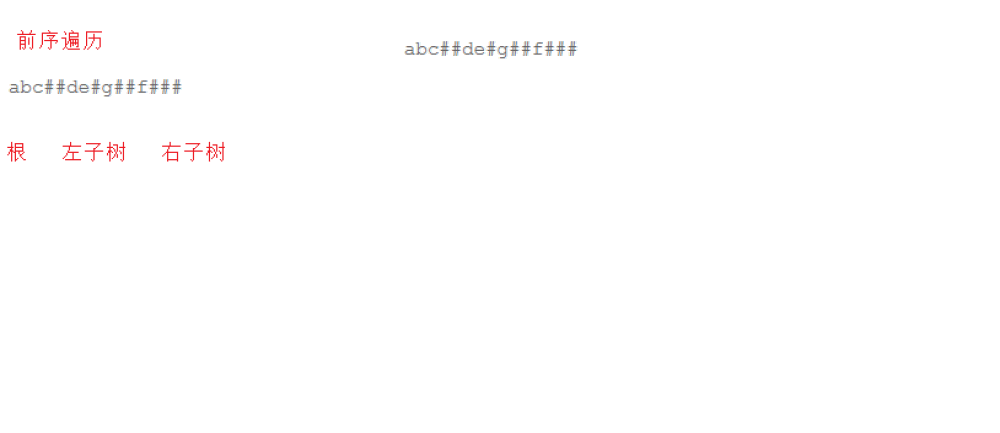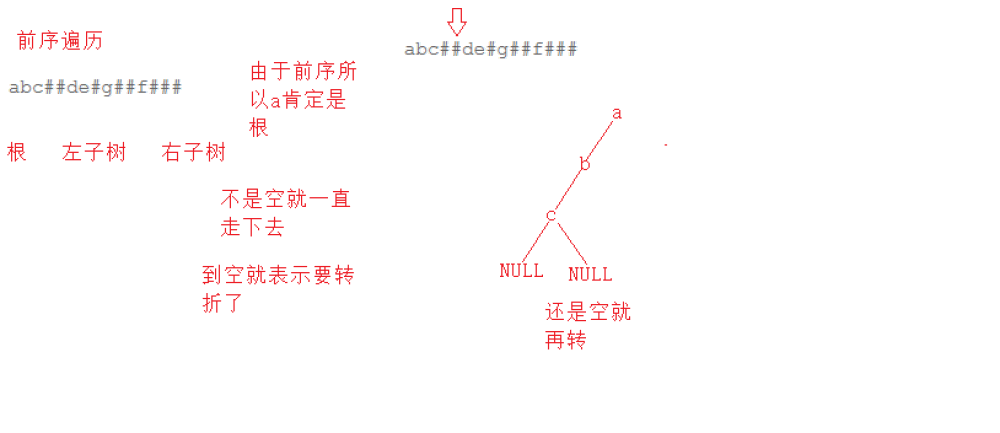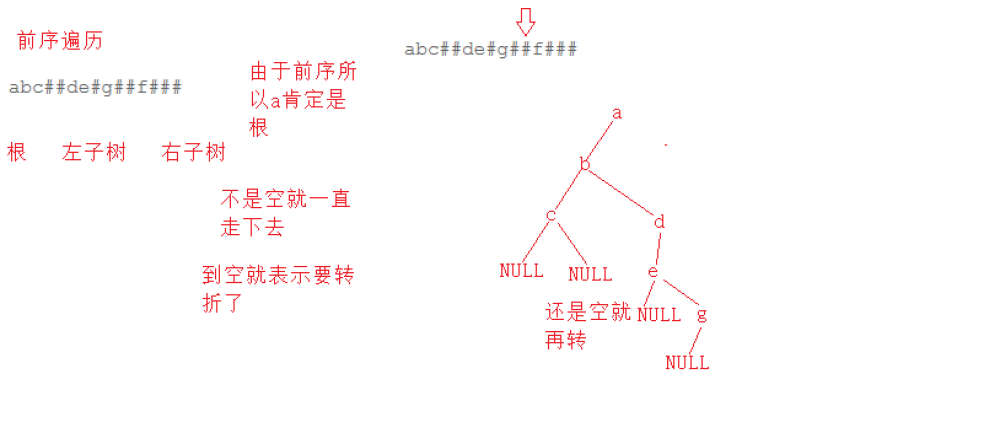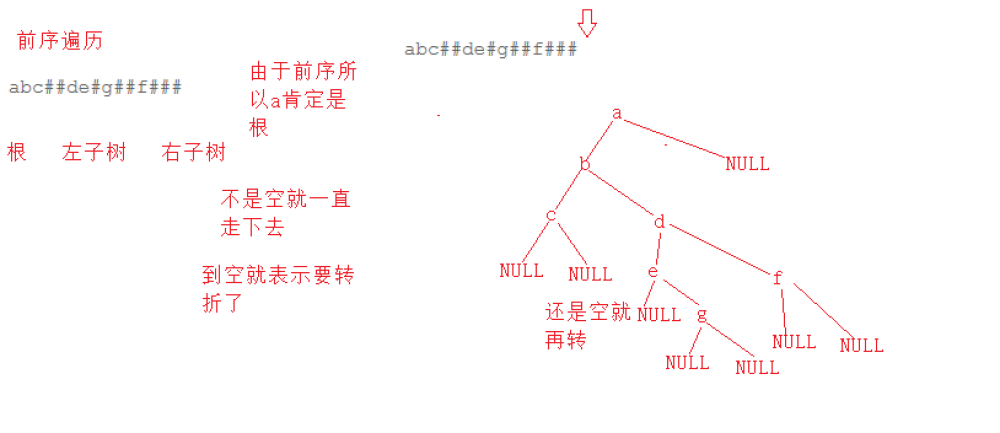
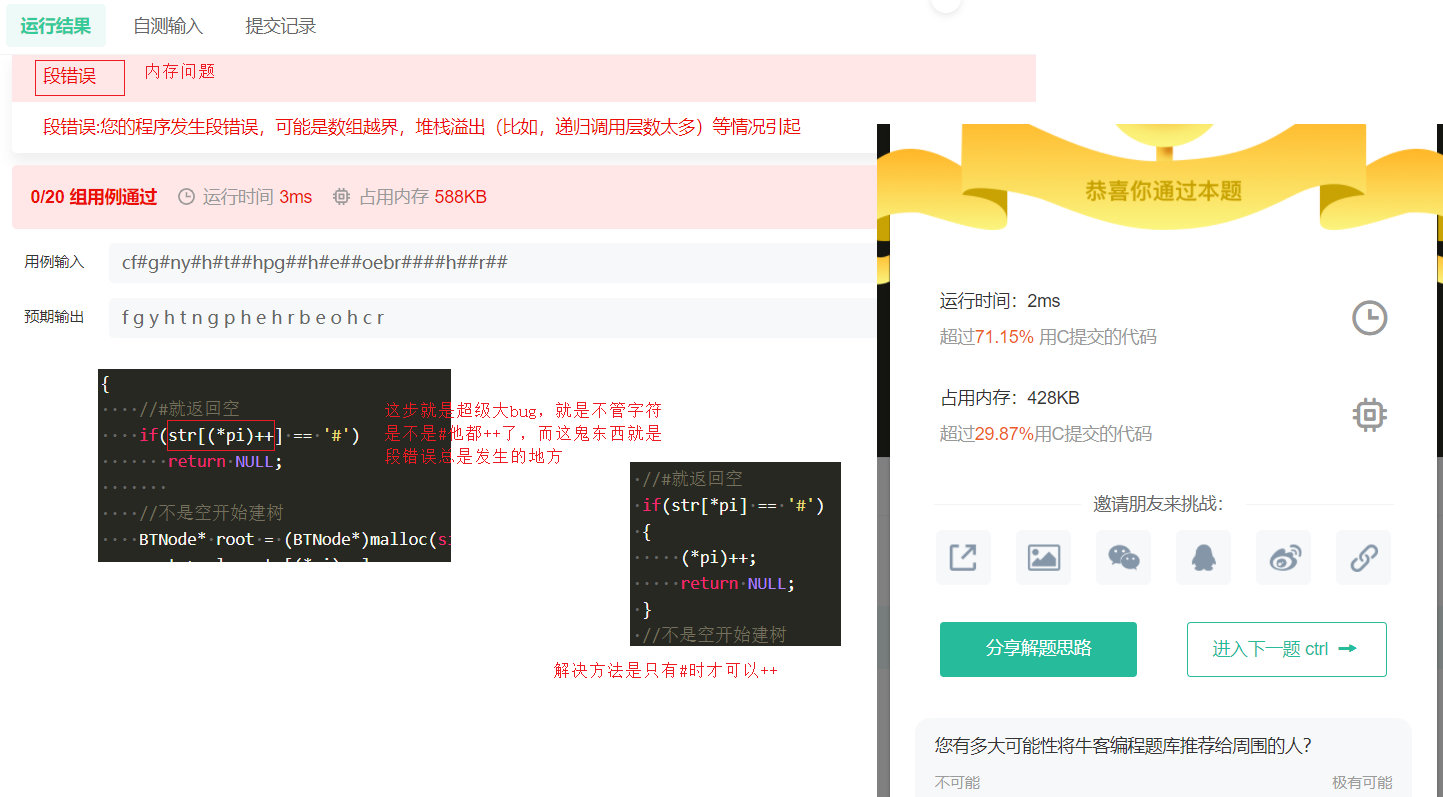
#include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h>//树节点typedef struct BinaryTreeNode{ struct BinaryTreeNode* right; struct BinaryTreeNode* left; int val;}BTNode;//创建树BTNode* CreateTree(char* str,int* pi){ //#就返回空 if(str[*pi] == '#') { (*pi)++; return NULL; } //不是空开始建树 BTNode* root = (BTNode*)malloc(sizeof(BTNode)); root->val = str[(*pi)++]; //递归创建 root->right = CreateTree(str,pi); root->left = CreateTree(str,pi); return root;}//中序遍历void InOrder(BTNode* root){ //空就返回 if(!root) return; //先走左 InOrder(root->right); //打印中 printf("%c ",root->val); //再走右 InOrder(root->left);}int main(){ //因为不超过100 char str[100] = {0}; //多组输入 while(scanf("%s",str) != EOF) { //创建树 int i = 0; BTNode* root = CreateTree(str,&i); InOrder(root); } return 0;}版权声明
本文为[华为云]所创,转载请带上原文链接,感谢
https://bbs.huaweicloud.com/blogs/348955
边栏推荐
- 腾讯二面:MySQL的半同步是什么?
- C语言每日一题——小乐乐改数字(牛客网)
- How to turn off vs Code eslint verification? Let's have a look
- glusterfs存储搭建初步测试
- MySQL storage engine
- 应用打包还是测试团队老大难问题?
- Take you to play c language functions easily
- 无人驾驶虚拟仿真(十五)--障碍物检测与识别1
- 原来升职加薪的测试工程师都擅长做接口测试
- Congratulations to EDG for winning the 2021 hero League global finals
猜你喜欢

一篇文章带你初步了解c语言操作符基础知识
Tcpdump packet capture and nmap are easy to use
![C语言每日一题——[NOIP2008]ISBN号码(牛客网第76题)](/img/a5/d6869747e2a61d076b4763021be123.png)
C语言每日一题——[NOIP2008]ISBN号码(牛客网第76题)

English word memory method based on anki + vocabulary

RedisJSON:一个可以存储 JSON 的 Redis

ROS2学习笔记(三)-- 采集虚拟仿真环境图像并发布

程序员想在深圳扎根,除了去腾讯,还可以考虑一下这些公司

从源码里的一个注释,我追溯到了12年前,有点意思
C语言每日一题——小乐乐改数字(牛客网)

Definition of Derivative
随机推荐
C language selection and circulation classic exercises
There are two important limits of the limit existence criterion
一篇文章带你初步了解c语言操作符基础知识
ROS2学习笔记(六)-- 自定义消息和服务实现控制指令优化以及在线换图
A quietly rising domestic software
C语言选择和循环经典习题
Ros2 learning notes (XI) -- ros2 bag data recording and playback
手把手教你使用rand函数实现猜数字游戏
MySQL read / write separation server -- maxscale service
利用库函数qsort()来进行排序,实现及原理分析
一个悄然崛起的国产软件
Introduction to redis cluster construction and management
ROS2学习笔记(五)-- ROS2命令行操作常用指令总结(一)
无人驾驶虚拟仿真(十五)--障碍物检测与识别1
Ros2 learning notes (8) -- road recognition and debugging based on the application of ros2 parameters
Getting started with redis
2021.10.24 程序员(媛)节日快乐!!!
阿里二面:main 方法可以继承吗?
面了个腾讯拿 38K 出来的,让我见识到了基础的天花板
Ros2 learning notes (10) -- ros2 launch startup file