当前位置:网站首页>Internal class instructions (static, instance, local)
Internal class instructions (static, instance, local)
2022-04-22 07:33:00 【Enjoy sir】
List of articles
Concept
java In , By Defined in another class or method The class of is called inner class
Classification of internal classes
1、 Member inner class
2、 Local inner classes
2.1、 Anonymous inner class
3、 Static inner class
Member inner class
1、 Grammar format :
Member inner class is the most common inner class , Its definition is inside another class :
class Outer {
// Member inner class
class Inner {
}
}2、 How to instantiate a member inner class ?
Instantiate the external object first
Outter outter = new Outter();And then the external object to (new) Instantiate inner member class :
External class . Inner class Inner class object name = External class objects .new Inner class ();
Outter.Inner inner = outter.new Inner();3、 characteristic :
Member inner classes can Unconditional access to all member properties and member methods of an external class ( Include private Members and static members )
4、 Be careful :
When the inner class of a member has the same name as the outer class Dd Member variables or methods , There will be hiding ,
namely By default, members of inner classes are accessed .If you want to access a member of an external class with the same name , It needs to be accessed in the following form :
External class .this. Member variables
External class .this. Member method
chestnuts
package com.blog.innertClassTest;
/** * @Author jinhuan * @Date 2022/3/23 17:42 * Description: * Local inner classes */
public class InnerClass01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Instantiate a local inner class object
InnerClass01 innerClass01 = new InnerClass01();
InnerClass01.Inner01 inner01 = innerClass01.new Inner01();
// Merge steps
//InnerClass01.Inner01 inner01 = new InnerClass01().new Inner01();
// Call internal test Method Be careful , It's modified num Value , After calling, we check whether the modification is successful
inner01.test();
// Check the private properties of the external class num Whether the value of has changed
System.out.println(" Internal class modified num The value is :"+innerClass01.num);
}
/** * Private properties of external classes num * */
private int num = 10;
/** * Of an external class say Method * */
private void say(){
System.out.println(" I'm a Outter Class! ");
}
/** * Inner class Ineer * */
class Inner01{
// The inner class instance accesses the private properties of the outer class
private void test(){
System.out.println(" External private properties num The value of is "+num);
num += 10;
System.out.println(" External private properties num The modified value of is "+num);
// Call the method with the same name of the inner and outer classes It is found that the default call is the internal member's own method ( Nearby principle )
System.out.print(" Called by default say The method is :");
say();
// How to use the inner class object to call the member method of the outer class
System.out.print(" Call an external with the same name say Method :");
InnerClass01.this.say();
}
/** * Method with the same name of external class * */
private void say(){
System.out.println(" I'm a Inner Class! ");
}
}
}

Local inner classes
1、 Grammar format :
[ List of modifiers ] return type Method name ( List of formal parameters ){
class Local inner classes {
}
}2、 How to instantiate a local inner class ?
In its Within the scope of the method , adopt new Keyword creation
3、 Be careful :
A local inner class is like a local variable in a method , yes Can not have public、protected、private as well as static Modifier Of .
4、 Applicable scenario
The creation of a class Just use it once When
Or when we have to instantiate a useless class or its implementation class in order to use a method
chestnuts 1
package com.blog.innertClassTest;
/** * @Author jinhuan * @Date 2022/3/24 11:13 * Description: */
public class InnerClass02 {
static int num01 = 11;
private int num02 = 12;
public static void main(String[] args) {
int num03 = 13;
/** * Local inner classes Inner02 * */
class Inner02{
int num04 = 14;
/* The difference between a local inner class and a member inner class is Access to local inner classes is limited to methods or scopes , Private properties of external classes cannot be accessed directly */
public void test(){
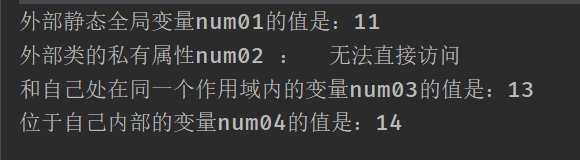
System.out.println(" External static global variables num01 The value of is :"+num01);
//System.out.println(" Private properties of external classes num02 :"+ num02);
System.out.println(" Private properties of external classes num02 : No direct access ");
System.out.println(" Variables in the same scope as themselves num03 The value of is :"+num03);
System.out.println(" Variables inside themselves num04 The value of is :"+num04);
}
}
// Instantiate a local inner class
Inner02 inner02 = new Inner02();
// Call the local inner class test Method
inner02.test();
}
}
chestnuts 2( Use scenarios )
Interface class
package com.blog.innertClassTest;
/** * @Author jinhuan * @Date 2022/3/24 13:23 * Description: * Simulate a development scenario , * Interface oriented programming : Now a human interface is defined according to the requirements * The abstract methods in it represent the common characteristics of mankind , Human “ Realize ” Should be able to eat */
public interface Person {
void eat();
}
Test class
package com.blog.innertClassTest;
/** * @Author jinhuan * @Date 2022/3/24 13:26 * Description: Test class * */
public class Test01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/* * Now suppose you have a requirement * We have to call the following use Method * But we didn't person Implementation class of , And we only use this method once * What do I do ? The interface cannot be instantiated directly ! * To create an interface implementation class ! * It's inevitable , But is it necessary for us to create a single class ? * It's not necessary , Local inner classes are enough * */
/** * Local inner classes * */
class PersonImpl implements Person{
@Override
public void eat() {
System.out.println(" I'm eating !");
}
}
PersonImpl person = new PersonImpl();
// A successful call use Method
use(person);
}
/** * Called method use * */
public static void use(Person person){
}
}
Local internal classes and final keyword ( a key )
stay jdk1.8 Before , Only... Can be accessed in local inner classes final Variable of type ( Except for global variables )
however 1.8 After the version , If a variable that can be accessed is accessed in the local inner class A, take The default is to add final keyword To embellish
however , Once you are right A It's reassignment , Then the previous visit will go wrong !
because final Variables of type cannot be reassigned , This and local inner classes can only access final There is a conflict between types of data !
chestnuts


Anonymous inner class
1、 Grammar format :
With reference :
Parent class Parent class reference = new Parent constructor ( parameter list )| Implementation interface (){
// The body part of the anonymous inner class , If it's an interface , Need to implement it
};Without reference :
new Parent constructor ( parameter list )| Implementation interface (){
// The body part of the anonymous inner class , If it's an interface , Need to implement it
};2、 How to instantiate an anonymous inner class ?
Anonymous inner classes are created directly through new Keywords are instantiated
3、 matters needing attention :
Using anonymous inner classes must also Only one parent class or interface can be inherited , You can't have both
Anonymous inner classes do not class keyword
This is because anonymous inner classes are used directly new To generate a reference to an object . Of course, the reference is implicitIn the anonymous inner class is Cannot define constructor Of
Anonymous inner class There cannot be any static member variables or static methods
Anonymous inner classes are local inner classes , So all restrictions on local inner classes also apply to anonymous inner classes
Anonymous inner class It can't be abstract , It must implement all the abstract methods of the inherited class or implemented interface
Anonymous inner class Only access final The local variable of type
chestnuts
Interface class
package com.blog.innertClassTest;
/** * @Author jinhuan * @Date 2022/3/24 13:23 * Description: * Simulate a development scenario , * Interface oriented programming : Now a human interface is defined according to the requirements * The abstract methods in it represent the common characteristics of mankind , Human “ Realize ” Should be able to eat */
public interface Person {
void eat();
}
Test class
package com.blog.innertClassTest;
/** * @Author jinhuan * @Date 2022/3/24 13:42 * Description: */
public class Test02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/** * Anonymous inner class * */
// The first way to create it polymorphic
Person person = new Person() {
@Override
public void eat() {
}
};
System.out.print(" Anonymous classes created using the first method use Use Method ");
use(person);
// The second way
System.out.print(" Anonymous classes created in the second way use Use Method ");
use(new Person(){
@Override
public void eat() {
}
});
}
/** * Called method use * */
public static void use(Person person){
System.out.println("USE Called !!!");
}
}

Static inner class
1、 Concept :
Static inner classes are also defined in another class
But there is one more in front of the class static keyword2、 Format :
class Outter {
public Outter() {
}static class Inner { }}
3、 How to instantiate :
External class name . Static internal class name Static internal class reference name = new External class name . Static internal class name ();
( Unlike local inner classes You don't have to instantiate external objects first )4、 Be careful :
Static inner classes do not need to depend on outer class objects , Similar to static member properties
it Out of commission Of an external class Not static Member variables or methods
class Test{
// Static variables
static int num01;
// This class is inside the class , So it's called an inner class
// Because there is static, So called “ Static inner class ”
static class Inner01{
}
// Instance variables
int num02;
// This class is inside the class , So it's called an inner class , No, static It's called an instance inner class .
class Inner02{
}
// Method 01
public void method01(){
// local variable
int num03 = 100;
// This class is inside the class , So it's called an inner class
// Local inner classes .
class Inner03{
}
}
// Method 02
public void method02(){
// dmethod01() Method num03, stay method02() You can't use
// Empathy ,dmethod01() Method Inner03, stay method02() You can't use
// Local * Can only be used in its scope
}
// main Method
public static void main(String[] args) {
/** * Anonymous inner class * */
// The first way to create it polymorphic
Person person = new Person() {
@Override
public void eat() {
}
};
System.out.print(" Anonymous classes created using the first method use Use Method ");
use(person);
// The second way
System.out.print(" Anonymous classes created in the second way use Use Method ");
use(new Person(){
@Override
public void eat() {
}
});
}
/** * Called method use * */
public static void use(Person person){
System.out.println("USE Called !!!");
}
}
// Human interface
interface Person{
// Abstract method
void eat();
}
The above are my personal views , To share . In case of carelessness , Please criticize and correct ! I would appreciate it and revise it at the first time !

版权声明
本文为[Enjoy sir]所创,转载请带上原文链接,感谢
https://yzsam.com/2022/04/202204220613115796.html
边栏推荐
- L1-064 估值一亿的AI核心代码 (20 分) 格式错误
- L1-064 AI core code valued at 100 million (20 points) has wrong format
- 快排与归并排序
- HDU Ice_cream‘s world I (并查集判环)
- P1095 [noip2007 popularity group] escape of the catcher
- 并发编程的艺术(3):深入理解Synchronized的原理
- CodeTON Round 1 (Div. 1 + Div. 2, Rated, Prizes)
- Codeforces Round #780 (Div. 3)
- LeetCode - 6 - (字符串相乘、下一個更大元素<ⅠⅡⅢ>、k個一組翻轉鏈錶)
- 并发编程的艺术(5):ReentrantLock的使用
猜你喜欢
Cannot find interface mapping after updating HDF
![P1095 [noip2007 popularity group] escape of the catcher](/img/5e/0437bdee83b6b66626e535e382b84b.png)
P1095 [noip2007 popularity group] escape of the catcher

In the process of class loading, the allocation area of class variables is different from that of instance variables

LeetCode - 6 - (字符串相乘、下一個更大元素<ⅠⅡⅢ>、k個一組翻轉鏈錶)

系统日志文件过大优化

The art of concurrent programming (11): introduction to tool classes in JUC

Leetcode - 7 - (nearest common ancestor of binary tree, rotation array, direct of binary tree, next permutation, combined sum)

I.Jam-packed (均分/最大最小值) (2021年度训练联盟热身训练赛第五场)

HDU Ice_cream‘s world I (并查集判环)

L2-001 emergency rescue (extension of shortest Dijkstra - number of shortest paths & maximum weight of paths)
随机推荐
119 · 编辑距离
I.Jam-packed (均分/最大最小值) (2021年度训练联盟热身训练赛第五场)
L2-004 这是二叉搜索树吗?(先序输入&判断搜索二叉树&后序输出)
Art de la programmation simultanée (9): utilisation finale et principes
C language | pointer
Recursive reverse linked list
系统日志文件过大优化
L2-005 set similarity (set judgment)
Cannot find interface mapping after updating HDF
Codeforces Round #776 (Div. 3)
Codeforces Round #588 (Div. 2) C D
Educational Codeforces Round 125 (Rated for Div. 2)
1242 · 无重叠区间
LeetCode - 8 - (三数之和、Z字形变换、两数之和<链表>、盛最多水的容器、电话号码的字母组合)
843 · 数字翻转
Leetcode - 8 - (sum of three numbers, zigzag transformation, sum of two numbers < linked list >, container with the most water, letter combination of telephone number)
76 · 最长上升子序列
Educational Codeforces Round 125 (Rated for Div. 2)
L1-071 前世档案 (20 分) (类似二分)
Codeforces Round #780 (Div. 3)