当前位置:网站首页>牛客SQL刷题记录
牛客SQL刷题记录
2022-04-22 15:56:00 【REN_林森】
SQL刷题
1、group by 可加select后的别名
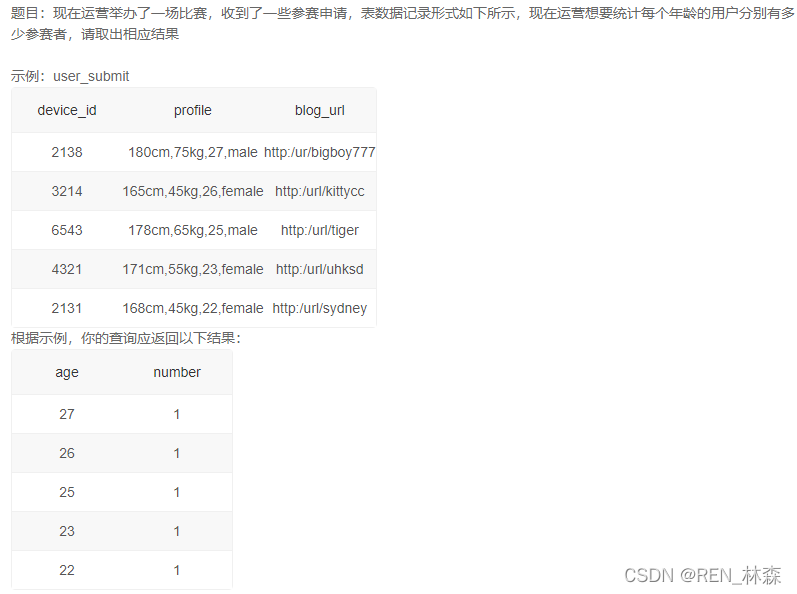
select
substring_index(substring_index(`profile`,',',-2),',',1) as age,
count(device_id) as number
from user_submit
group by age
# 注:不能count(age),age字段不存在,不知道为啥。
2、substring_index使用

/* select 'male',count(device_id) from user_submit where `profile` like '%,male' union select 'female',count(device_id) from user_submit where `profile` like '%female' */
# 变形
/* select if(`profile` like '%female','female','male') as gender, count(1) as number from user_submit group by gender */
# 采用文本分隔函数,substring_index(str,substr,第几次出现,负数表示倒数 to 字符串末尾)
/* select substring_index(`profile`,',','-1') as gender, count(1) as number from user_submit group by gender */
# WHEN THEN 练习
select
CASE
when profile like '%female' then 'female'
when profile like '%,male' then 'male'
end
as gender,
count(1) as number
from user_submit
group by gender
3、自表的笛卡儿积就是for循环
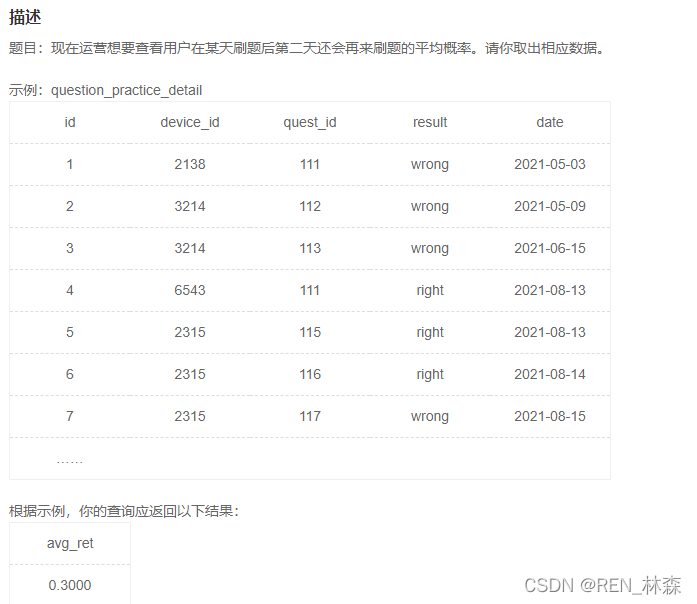
# 1-如何确定总人数?2-如何确定前后两条都在刷题的人数?
# 1-总人数?不分组,直接去重计算device_id的个数。
# 2-前后两天都在刷题的人数?
/*select count(date2) / count(date1) from ( select distinct qpd.device_id, qpd.date as date1, qpd2.date as date2 from question_practice_detail as qpd left join question_practice_detail as qpd2 on qpd.device_id = qpd2.device_id and 1 = timestampdiff(day,qpd.date,qpd2.date) ) as next_time */
select
distinct qpd.device_id,
qpd.date as date1,
qpd2.date as date2
from question_practice_detail as qpd
left join question_practice_detail as qpd2
on
qpd.device_id = qpd2.device_id
and
1 = timestampdiff(day,qpd.date,qpd2.date)
4、select 后不能接与group by无关字段(一对多问题)+多变量in操作

# 不能直接在外层select中取device_id
/* select u1.device_id,u1.university,u1.gpa from user_profile u1 inner join ( select university,min(gpa) as gpa from user_profile group by university ) as u2 on u1.university = u2.university and u1.gpa = u2.gpa order by u1.university */
# 直接以in的方式
select
device_id,university,gpa
from user_profile
where
(university,gpa)
in
(
select university,min(gpa) from user_profile
group by university
)
order by university
5、子查询练习
子查询把哪些必须分开的查询分开变成view,然后结合,再查出自己想要的字段。
毕竟group by 会和 一对多的字段冲突。
毕竟group by 会和 不同条件计数冲突。


/* device_id 和question_id有一对多问题,在统计时就不能一起查出来。 所以, 第一步:先统计question_cnt,right_question_cnt。 第二步,再统计device_id,university */
select
u1.device_id,u1.university,
if(u2.question_cnt is null,0,u2.question_cnt),
if(d1.right_question_cnt is null,0,d1.right_question_cnt)
from user_profile u1
left join
( select device_id,
count(question_id) as question_cnt
from question_practice_detail
where
MONTH(date) = 8
group by device_id ) as u2
on
u1.device_id = u2.device_id
left join(
select device_id,count(result) as right_question_cnt
from question_practice_detail
where result = 'right'
group by device_id
) as d1
on
d1.device_id = u2.device_id
where u1.university = '复旦大学'
/* 两个子查询所产生的衍生视图,三表左外连接。 左外?因为8月份有复旦大学个别同学没有参加答题,题目要求记为0,内联会导致该用户丢失。 左外2?因为有同学答题全是错的,题目要求记为0,内联会导致没有用户答题记录,毕竟全错。 衍生视图1-2?答题数量肯定不能会答对数量一起count出来, 所以只有竖着拆出两表记录count(question_id),count(result_right_cnt) 两个count建立在不同的条件,所以肯定分开查询再联合成表之后,再查自己想要的字段。 */
6、count+if+null可完成同表不同值的计数
1)成长需要过程,需要迭代的版本,不可能是一步登天的人。
2)count不统计null,所以可count+if+null或者sum|avg + if + (0,1)来完成不同条件的统计,减少多个子查询以及其中的重复表操作。

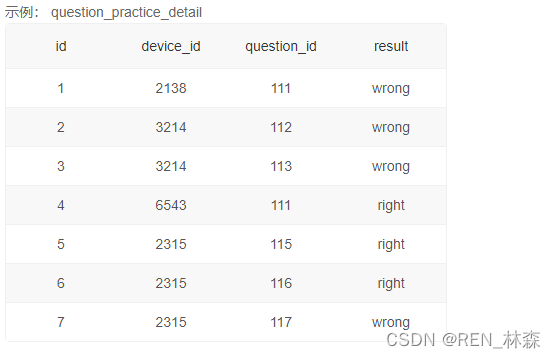

/* 取 浙大用户回答题目不同难度的个数 m 取 浙大用户回答题目不同难度的正确个数 n 得 正确率 = n / m 排 按正确率升序输出 */
# 取1
/* select difficult_level, count(qpd.question_id) as question_cnt from user_profile u inner join question_practice_detail qpd on u.device_id = qpd.device_id right join question_detail qd on qpd.question_id = qd.question_id where university = '浙江大学' group by difficult_level */
# 取2
/* select difficult_level, count(qpd.question_id) as question_right_cnt from user_profile u inner join question_practice_detail qpd on u.device_id = qpd.device_id inner join question_detail qd on qpd.question_id = qd.question_id group by difficult_level where university = '浙江大学' and result = 'right' */
# 得 + 排 t1 left join t2表,毕竟分子可能为none,但也要记录下来。
/* select t1.difficult_level, if(t2.question_right_cnt is null,0,t2.question_right_cnt) / t1.question_cnt as correct_rate from ( select difficult_level, count(qpd.question_id) as question_cnt from user_profile u inner join question_practice_detail qpd on u.device_id = qpd.device_id inner join question_detail qd on qpd.question_id = qd.question_id where university = '浙江大学' group by difficult_level ) as t1 left join ( select difficult_level, count(qpd.question_id) as question_right_cnt from user_profile u inner join question_practice_detail qpd on u.device_id = qpd.device_id inner join question_detail qd on qpd.question_id = qd.question_id where university = '浙江大学' and result = 'right' group by difficult_level ) as t2 on t1.difficult_level = t2.difficult_level order by correct_rate */
# 注:count不统计null
# 改进:取正确的个数和取总个数可以一起取,用if+null来完成。
select
difficult_level,
count(if(b.result = 'right',b.question_id,null)) / count(b.question_id) as correct_rate
/* 除了count(),还可以用sum()和avg()来实现。 sum():sum(if(b.result = 'right',1,0)) avg():avg(if(b.result = 'right',1,0)) */
from
(
select device_id
from user_profile
where university = '浙江大学' #提前把表变小
) as a
inner join
(
select device_id,question_id,result
from question_practice_detail # 提前把表变小
) as b
on
a.device_id = b.device_id
inner join question_detail as c
on b.question_id = c.question_id
group by difficult_level
order by correct_rate
7、substring细节

select cust_id,
cust_name,
upper(concat(substring(cust_name,1,2),substring(cust_city,1,3))) as user_login
from Customers
# 注:substring(str,第几位而不是从0开始的index,截多少)
8、子查询好处
子查询可以生成轻量级table–view,这样可以where、distinct、select 指定字段等筛选条件来完成数据源table的瘦身。然后再用小的view去join 其它 table,不仅可以减少很多不必要的连接,而且还可以小表驱动大表,除此之外,逻辑分明,删选条件出现在自己的table中,而不是影响延申到整个大表。
总:子查询三点好处
1)逻辑分明,筛选条件在自己的table中,不影响其它表。
2)数据源的瘦身,减少接下来不必要的连接等所带来的时空开销。
3)如果存在索引,还可以小表驱动大表,减少时空开销。
当然,有时候子查询甚至是解题的关键,而不是提升时空效率的辅助。


# 非子查询方法
/* select distinct o2.cust_id from OrderItems o1 inner join Orders o2 on o1.order_num = o2.order_num where o1.item_price >= 10 */
# 上述方法-缺点:要先连表,再筛选,所以会很大的表,浪费时间和空间,可子查询为小的view解决。
# 拿 OrderItems的小view,且去重了,避免没必要的连接
/* select distinct order_num from OrderItems where item_price >=10 */
# 用小view来inner join Orders表,这样小view来驱动大表,减少很多不必要的连接。
select distinct cust_id
from (
select distinct order_num
from OrderItems
where item_price >= 10
) as OI
inner join
Orders o1
on
OI.order_num = o1.order_num
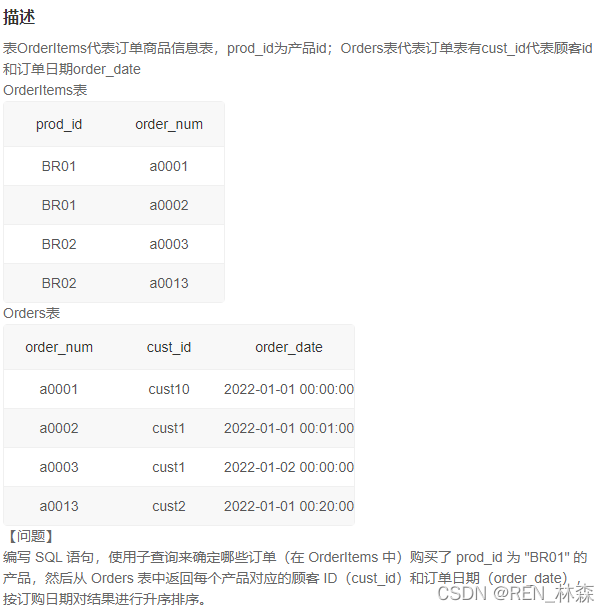

/* 取哪些用户什么时候买了prod_id为BR01品牌的产品 注:BR01有多种产品;取了之后还需对购买日期进行升序排序 M1:直接inner join 两表,然后取买了prod_id为BR01的哪些用户和买的时间 */
/* select o.cust_id,o.order_date from OrderItems oi inner join Orders o on oi.order_num = o.order_num where oi.prod_id = 'BR01' order by o.order_date */
/* M1-defect:筛选逻辑不分明;有很多不必要的连接;没有小表驱动大表。 M2:采取子查询,筛选逻辑限定在各自的表之内,不忘外延申。 */
# 取prod_id为BR01的商品名order_num
/* select order_num from OrderItems where prod_id = 'BR01' */
# inner join Orders来取出对应order_num的记录中的cust_id和order_date,并对order_date进行排序
select cust_id,order_date
from
(
select order_num
from OrderItems
where prod_id = 'BR01'
) as T1
inner join Orders o
on T1.order_num = o.order_num
order by order_date
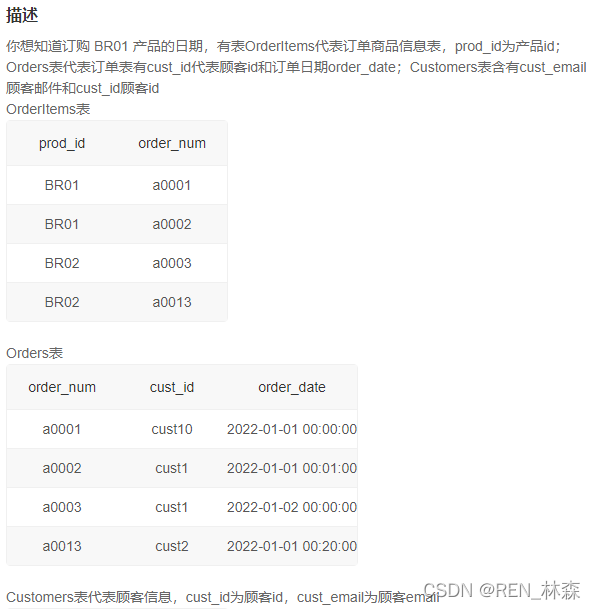

/* 取购买了BR01产品的用户信息--cust_email。 注:用户信息和OrderItems中有个Orders表相连,而不是直接相连。 M1:直接三表相连,取对应条件--prod_id = 'BR01'; 注:可小表驱动大表,用用户表来驱动order表。 */
/* select cust_email from Customers c inner join Orders o on c.cust_id = o.cust_id inner join OrderItems oi on o.order_num = oi.order_num where oi.prod_id = 'BR01' */
/* M1-defect:筛选逻辑不分明;很多不必要的连接;小表驱动可以再明显点,即用小的view来驱动。 M2:用筛选逻辑分明的子查询来生成小的view,再进行驱动其它表,可以减少不必要的时空开销。 */
# prod_id='BR01'的限定属于OrderItems表,所以先生成一个小view
/* select order_num from OrderItems where prod_id = 'BR01' */
# M2:三表相连,用小view驱动,再取出需要的记录即可,没有额外的筛选条件
select cust_email
from
(
select order_num
from OrderItems
where prod_id = 'BR01'
) as T1
inner join Orders as T2
on T1.order_num = T2.order_num
inner join Customers as T3
on T2.cust_id = T3.cust_id


/* 取用户购买商品的总金额? 总金额?item_price * quantity as total 当个用户的总金额?sum(total) as total_ordered + group by cust_id M1:两表相连,以cust_id分组,求总金额。最后降序排序。 注:可小表Customers来驱动其它表 */
/* select T1.cust_id, sum(T2.item_price * T2.quantity) as total_ordered from Orders as T1 inner join OrderItems as T2 on T2.order_num = T1.order_num group by T1.cust_id order by total_ordered desc */
/* M1-defect: total_ordered是再T2表中计算出来的,再在T1表中进一步,所以计算逻辑需分层。 M2:子查询将计算逻辑限制在各自的表内 */
# 取total_ordered & order_num
/* select order_num,sum(item_price * quantity) as total from OrderItems group by order_num */
# view join Orders,拿到cust_id & total_ordered,并对total_ordered。
select cust_id,
sum(T1.total) as total_ordered
from
(
select order_num,sum(item_price * quantity) as total
from OrderItems
group by order_num
) as T1
inner join Orders T2
on T1.order_num = T2.order_num
group by cust_id
order by total_ordered desc
子查询将各自的查询、计算等逻辑限制在各自的表内


/* 取prod_id对应订单的总额度。 M1:连接Products和OrderItems表,以prod_name(不唯一)为组,对应的prod_name,以及sum(quantity) 注:不能以prod_id为组,因为我们取的是prod_name。虽然prod_id与prod_name一对一。 */
/* select T1.prod_name,sum(quantity) as quant_sold from Products T1 inner join OrderItems T2 on T1.prod_id = T2.prod_id group by T1.prod_name */
/* M1-defect:sum(quantity)求和逻辑应该限定在OrderItems表内,而不是延申到相连的大表中。 M2:用子查询将各自计算逻辑限定在各自的表中。 */
# 在OrderItems表体现计算逻辑
/* select prod_id,sum(quantity) as quant_sold from OrderItems group by prod_id */
# 将Products与子查询view相连,直接体现查询数据字段逻辑。
select prod_name,T2.quant_sold
from Products T1
inner join
(
select prod_id,sum(quantity) as quant_sold
from OrderItems
group by prod_id
) as T2
on T1.prod_id = T2.prod_id


/* target:取Customers表中的cust_name,再取其用cust_id对应到Orders表中order_num字段。 M1:Customers join Orders表,再在该view基础上实现取字段逻辑。 注:Customer表相对于Orders表肯定小很多,需要进行小表驱动大表。 注:取出元素之后,还需对顾客名称和订单号进行升序 */
/* select cust_name,order_num from Customers T1 inner join Orders T2 on T1.cust_id = T2.cust_id order by cust_name,order_num */
/* M1-defect:对顾客名称的排序逻辑应该限定在view中,因为是先按顾客名排的; 对order_num的排序应该限定在Orders中。 M2:采用子查询来将逻辑限定到自己的表中。 */
select cust_name,order_num
from
(
select order_num,cust_id
from Orders
order by order_num
) as T1
inner join Customers as T2
on T1.cust_id = T2.cust_id
order by cust_name
/* 注:由于MySQL会进行联表优化,所以会小表驱动大表. 所以无论把那个表写在前面,MySQL都会选一个小表来驱动。 所以这里采用单个子查询,让Orders的衍生出表操作先完成,再配合Customers表 */
参考文献
限定逻辑在特定范围内+子查询为我们想先操作逻辑(不会被MySQL优化)



/* target:取三表连接view中的cust_name,order_num,以及OrderTotal = quantity * item_price 注:结构需要对顾客名称及订单号进行升序。 M1:三表相连--cust_id + order_num,再升序即可 */
/* select cust_name,T2.order_num, quantity * item_price as OrderTotal from Customers T1 inner join Orders T2 on T1.cust_id = T2.cust_id inner join OrderItems T3 on T2.order_num = T3.order_num order by cust_name,T2.order_num */
/* M1-defect:一些操作逻辑应该限定在最小范围的表或view中, 如: 1-乘法计算quantity * item_price 应限定在OrderItems中, 这样不仅计算逻辑操作不延伸,而且不暴露多余的field到接下来的view中。 2-对order_num的排序逻辑就该限定在Orders表中,毕竟order_nums是后排字段。 M2:子查询来将逻辑限定到特定的范围内。 */
# 乘法逻辑
/* select order_num,quantity * item_price as OrderTotal from OrderItems */
# 外层排序逻辑,即对order_num排序
/* select cust_id,T1.order_num from Orders as T1 inner join ( select order_num,quantity * item_price as OrderTotal from OrderItems ) as T2 on T1.order_num = T2.order_num order by T1.order_num */
# M2
select cust_name,T2.order_num,OrderTotal
from Customers as T1
inner join
(
select cust_id,T1.order_num,OrderTotal
from Orders as T1
inner join
(
select order_num,quantity * item_price as OrderTotal
from OrderItems
) as T2
on T1.order_num = T2.order_num
order by T1.order_num
) as T2
on T1.cust_id = T2.cust_id
order by cust_name


/* target:查询Orders表中的cust_id和order_date字段。 当然这些记录的order_num字段必须所属prod_id为BR01的。 M1:OrderItems表和Orders表以order_num字段相连得到view。 当然要还要以prod_id=BR01来筛选,再生成的这个view。最后取出需要的字段。 注:需要根据购买日期进行升序。 */
/* select cust_id,order_date from OrderItems as T1 inner join Orders as T2 on T1.order_num = T2.order_num where T1.prod_id = 'BR01' order by order_date */
/* M1-defect:逻辑溢出到联结表中; M2:子查询将prod_id = BR01条件限定到OrderItems表中,且取一个只带order_num的字段暴露给其它表。 然后轻量级view驱动大表。 子查询也可把对order_date升序逻辑限定到Orders表中。 */
# 筛选逻辑
/* select order_num from OrderItems where prod_id = 'BR01' */
# 排序逻辑
/* select * from Orders order by order_date */
# M2:将生成好的view连接,最后实现取字段逻辑
/* select cust_id,order_date from ( select order_num from OrderItems where prod_id = 'BR01' ) as T1 inner join Orders as T2 on T1.order_num = T2.order_num order by order_date */
# 注:MySQL做了优化,两个子查询时|两个表时,根本就不知道谁驱动了谁。
# 由于第一个子查询生成的view只有一个字段,所以用where来替代。
select cust_id,order_date
from Orders T1
where exists (
select 1 from OrderItems where prod_id = 'BR01' and T1.order_num = OrderItems.order_num
)
order by order_date



/* target:返回订单总结不小于1000的客户名,订单号。然后对总额进行排序。 客户名在Customers表中,总额在OrdersItems表中,由中间表Orders表<order_num,cust_id>关联。 M1:三表关联生成view,计算订单额度,并进行大于等于1000筛选,最后取出客户没,订单号字段。再对总额排序。 */
/* select cust_name,sum(item_price * quantity) as total_price from OrderItems as T1 inner join Orders as T2 on T1.order_num = T2.order_num inner join Customers as T3 on T2.cust_id = T3.cust_id group by cust_name having total_price >= 1000 order by total_price */
/* M1-defect: 1-计算逻辑和筛选逻辑没有限定到OrderItems表中,而且OrderItems表中由重复order_num。 2-Orders表可以先和Customers表连接,生成只带order_num和cust_name这样的view。 注:不知道谁驱动谁,Mysql做了优化,所以不把排序逻辑限定再OrderItems表中,再连接可能就乱了。 */
# 计算逻辑
/* select order_num,sum(item_price * quantity) as total_price from OrderItems group by order_num having total_price >= 1000 */
# 获取只带cust_name和order_num的view
/* select cust_name,order_num from Orders as T1 inner join Customers as T2 on T1.cust_id = T2.cust_id */
# M2:逻辑限定在各自的子查询中,然后连接view,实现取字段逻辑和排序逻辑
select cust_name,total_price
from
(
select order_num,sum(item_price * quantity) as total_price
from OrderItems
group by order_num
having total_price >= 1000
) as T1
inner join
(
select cust_name,order_num
from Orders as T1
inner join Customers as T2
on T1.cust_id = T2.cust_id
) as T2
on T1.order_num = T2.order_num
order by total_price
常见count(非null)、计数逻辑在内、排序逻辑在外、ifnull()置0


/* target:取Vendors表中的vend_id;取Products表中以vend_id为组的产品数量。 转义:取Vendors表中的vend_id,以及该公司对应Products表中的产品有多少种。 M1:将Vendors表与Products表左连,然后以vend_id为组,取出vend_id,即产品种类数量。 注:count()聚集函数不统计为null的值。 */
/* select vend_id,count(prod_id) as prod_id from Vendors left join Products using(vend_id) group by Vendors.vend_id order by Vendors.vend_id */
/* M1-defect:计数逻辑应该限定再Products表中 M2:采用子查询先对Products表中以vend_id为组进行计数。 再right join Vendors表,最后对vend_id升序 注:应为right join 会出现none值,所以配合ifnull()函数来置0 */
# 计数逻辑
/* select vend_id,count(prod_id) as prod_id from Products group by vend_id */
/* M2:Vendors left join view + 取vend_id + ifnull()置0 + order by vend_id 注:排序逻辑防止最后的view上,因为MySQL的优化,不知道谁驱动谁,所以限定再某表内,再连接可能会乱。 */
select vend_id,ifnull(prod_id,0)
from Vendors left join
(
select vend_id,count(prod_id) as prod_id
from Products
group by vend_id
) as T
using(vend_id)
order by vend_id
9、left、right join + union实现MySQL不能实现的outer join


/* target:取Products表中的prod_name字段;取OrderItems表中的order_num字段。再对产品名升序。 M1:用Products表左联OrderItems表,取出Products表中的prod_name,及OrderItems表的order_num字段。 注:题目要求使用Outer join来连接,但是不肯可能有订单里的产品id在Products表中找不到, 只可能,Products的商品没有被下单,毕竟Products是主表,订单表是从表。 */
/* select prod_name,order_num from Products as T1 left join OrderItems as T2 using (prod_id) order by prod_name */
/* M1-defect:没有做到题目的要求进行full outer join,但是Mysql不支持outer join。 target:MySQL如何实现outer join? S:可以通过left join + union + right join M2:通过left join 取Products全记录+OrderItems连接记录, union right join 取OrderItems没有与Products匹配上的记录,即Products.prod_id is null。 最后再对prod_name升序。 */
# left join
/* select prod_name,order_num from Products left join OrderItems using(prod_id) */
# right join + OrderItems.prod_name is null
/* select prod_name,order_num from Products right join OrderItems using(prod_id) where Products.prod_name is null */
# M2:union view + 对prod_name升序
select prod_name,order_num
from
(
select prod_name,order_num
from Products left join OrderItems using(prod_id)
union
select prod_name,order_num
from Products right join OrderItems using(prod_id) where Products.prod_name is null
) as T
order by prod_name

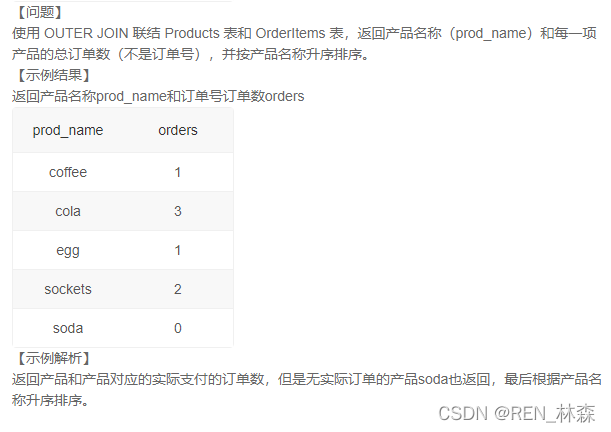
/* target:取出Products表中的prod_name字段; 取出OrderItems表中的订单数量,根据prod_name分组, 当其必须是一对一时--unique key,这里需要取prod_name字段。 最后对prod_name升序。 注:需要进行outer join,考虑到Products是主表,所以采用主表Products left join 从表OrderItems。 M1:将Products表与OrderItems根据prod_id left join相连,以prod_id分组,计算总订单数。 注:1-需要对prod_name升序;2-left join会产生none情况,直接count()聚集,它会忽略null值。 */
/* select prod_name,count(order_num) from Products left join OrderItems using(prod_id) group by prod_name order by prod_name */
/* M1-defect: 1-理论上应该以prod_id来分组,而不是prod_name。 2-计数逻辑应该限定在OrderItems表范围类。 M2:采用子查询来完成计数逻辑在OrderItems表中--生成view,再和Products表right join,完成字段的取出。 */
# 计数逻辑
/* select prod_id,count(order_num) as orders from OrderItems group by prod_id */
/* M2:通过计数逻辑生成view,right join上Products表,取出prod_name和orders字段。 注:1-右连就有none,需要if来置0;2-还需对prod_name进行排序。 */
/* select prod_name,ifnull(orders,0) from Products left join ( select prod_id,count(order_num) as orders from OrderItems group by prod_id ) as T using(prod_id) order by prod_name */
/* M2-defect:没有按照题目考察的要求来,需要进行outer join。 MySQL如何进行outer join? S:left join + union + right join + filed is null M3:采用union + 再排序来解决。 */
# left join + 子查询
/* select prod_name,ifnull(orders,0) from Products left join ( select prod_id,count(order_num) as orders from OrderItems group by prod_id ) as T using(prod_id) */
# right join + field is null
/* select prod_name,ifnull(orders,0) from Products right join ( select prod_id,count(order_num) as orders from OrderItems group by prod_id ) as T using(prod_id) where Products.prod_name is null */
# M3:union + order by prod_name
select prod_name,orders
from
(
select prod_name,ifnull(orders,0) as orders
from Products left join
(
select prod_id,count(order_num) as orders
from OrderItems
group by prod_id
) as T using(prod_id)
union
select prod_name,ifnull(orders,0) as orders
from Products right join
(
select prod_id,count(order_num) as orders
from OrderItems
group by prod_id
) as T using(prod_id)
where Products.prod_name is null
) as T
order by prod_name
10、union 生效在 order by之前
union 生效在 order by之前,order by 是对union后的view进行排序。要想order by在union 之前生效,只能子查询替代。

/* M1:union + order by */
/* select prod_name as name from Products union select cust_name as name from Customers order by name */
/* M1-替代 M2:将连接成的view 作为 table,然后实现取字段逻辑 和 排序逻辑 */
select ne
from
(
select prod_name as ne
from Products
union
select cust_name as ne
from Customers
) as T
order by ne

SELECT cust_name, cust_contact, cust_email
FROM Customers
WHERE cust_state = 'MI'
order by cust_name
UNION
SELECT cust_name, cust_contact, cust_email
FROM Customers
WHERE cust_state = 'IL' ORDER BY cust_name;
版权声明
本文为[REN_林森]所创,转载请带上原文链接,感谢
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_43164662/article/details/124057727
边栏推荐
- JSP echo
- sql语句———多表联查
- CASIA webface of dataset: a detailed introduction to the introduction, installation and use of CASIA webface dataset
- 【合泰HT32F52352定时器的使用】
- Immundiagnostik IDK TurbiPEL测定分析
- 每周推薦短視頻:存量時代如何重構企業核心競爭力?
- Graphics 101 matrix transformation (sections 2-4)
- jsp回显
- [二叉数]相同的树
- [Kunpeng training camp] Chongqing 2022 developer competition
猜你喜欢

NFT 平台安全指南

Fourier analysis and filtering

Build your own web site (8)

Future development direction of construction industry: digital chemical plant management system

redis简单存储建立文件夹

Graphics 101 matrix transformation (sections 2-4)
理想与集度的技术之争:激光雷达究竟装哪儿更安全?

想做自媒体运营却不会写作?4个珍藏的运营技巧

Servlet基础

343-Leetcode 反转字符串中的元音字母
随机推荐
redis优化系列(一)基于docker搭建Redis主从
Xcode 13 How to use the local swift package
LeetCode每日一题——824. 山羊拉丁文
悟空的私藏「架构』书籍推荐
制作的自媒体短视频很模糊?教你3个方法,让视频变清晰
【Altium Designer10详细安装】
Altium designer generates PCB production files and proofing process (taking jialichuang mall as an example)
SAP UI5 数据类型(data type) 学习笔记
阿里云国际版设置电子邮件托管教程详解
腾讯云堡垒机开启OTP认证
单选按钮选中
Shell script attempt
【洛谷】P1036 [NOIP2002 普及组] 选数(DFS)
bluetoothGatt.disconnect()无效,还是保持着连接
Sending non-protected broadcast
eltable样式修改。父子组件传值。模糊查询
7个月,158家单位参编,《2021网信自主创新调研报告》来了
【鲲鹏训练营】重庆2022开发者大赛
Spark basic learning notes 23: dataframe and dataset
短链接生成器,adf.ly、shorte.st、ouo.io、adfoc.us哪个更好,有哪些区别
