当前位置:网站首页>OneFlow源码解析:算子指令在虚拟机中的执行
OneFlow源码解析:算子指令在虚拟机中的执行
2022-08-10 10:21:00 【InfoQ】
1 、Op在虚拟机里的执行
1.1 PhysicalRun和InstructionsBuilder
JUST(PhysicalRun([&](InstructionsBuilder* builder) -> Maybe<void> {
return builder->Call(xxx);
}));oneflow/core/framework/instructions_builder.h// Make VM instructions with instruction builder and run instructions with physical/local view.
template<typename CallbackT>
Maybe<void> PhysicalRun(const CallbackT& Build) {
vm::InstructionList instruction_list;
InstructionsBuilder instructions_builder(&instruction_list);
JUST(Build(&instructions_builder));
JUST(vm::Run(instructions_builder.mut_instruction_list()));
return Maybe<void>::Ok();
}Maybe<void> Run(vm::InstructionList* instruction_list) {
auto* virtual_machine = JUST(SingletonMaybe<VirtualMachine>());
JUST(virtual_machine->Receive(instruction_list));
return Maybe<void>::Ok();
}1.2 InstructionsBuilder
// 用于lazy mode(nn.Graph)
// Build VM execution instructions with NNGraph's inputs/outputs/parameters for NNGraph execution.
Maybe<void> LaunchLazyJob(const vm::EagerBlobObjectListPtr& inputs,
const vm::EagerBlobObjectListPtr& outputs,
const vm::EagerBlobObjectListPtr& parameters,
const std::shared_ptr<NNGraphIf>& nn_graph);
// 用于全局同步,同步等待所有指令调用完成
Maybe<void> GlobalSync();
// 用于Tensor内存释放(归还allocator)
Maybe<void> ReleaseTensor(const std::shared_ptr<vm::EagerBlobObject>& eager_blob_object);
// 操作Tensor实际内存(blob)
template<typename T>
Maybe<void> AccessBlobByCallback(
const T tensor,
const std::function<void(ep::Stream*, const std::shared_ptr<vm::EagerBlobObject>&)>& callback,
const std::string& modifier);
// 最常用的指令构建方法,用于构造op执行所需的OpCall指令
Maybe<void> Call(const std::shared_ptr<one::StatefulOpKernel>& opkernel,
vm::EagerBlobObjectList&& input_eager_blob_objects,
vm::EagerBlobObjectList&& output_eager_blob_objects,
const one::OpExprInterpContext& ctx, Symbol<Stream> stream);1.3 InstructionPolicy
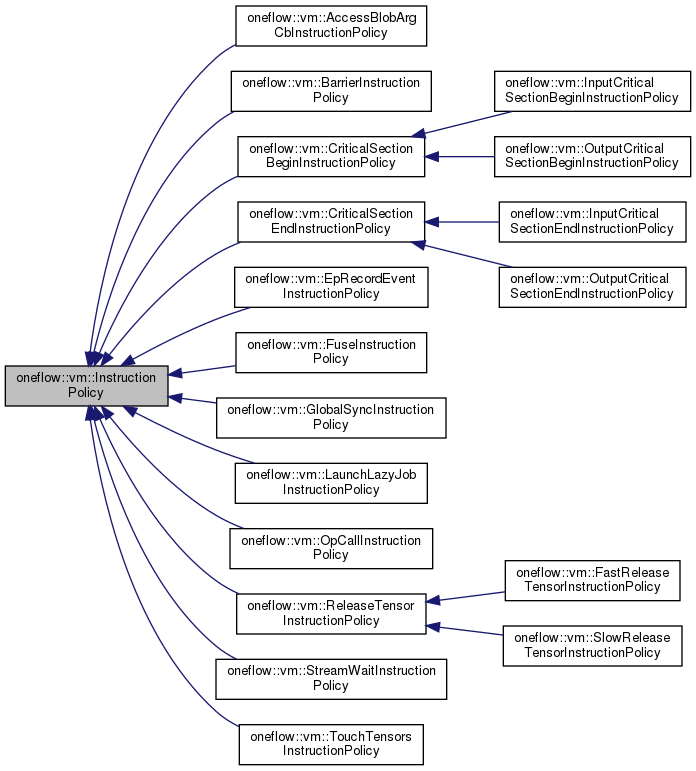
OpCallInstructionPolicyReleaseTensorInstructionPolicyBarrierInstructionPolicyJUST(PhysicalRun([&](InstructionsBuilder* builder) -> Maybe<void> {
return builder->Call(xxx);
}));Maybe<void> InstructionsBuilder::Call(
const std::shared_ptr<one::StatefulOpKernel>& opkernel,
vm::EagerBlobObjectList&& input_eager_blob_objects,
vm::EagerBlobObjectList&& output_eager_blob_objects,
const std::shared_ptr<const one::GlobalTensorInferResult>& global_tensor_infer_result,
const one::OpExprInterpContext& ctx, Symbol<Stream> stream) {
...
...
// 获取当前vm stream
auto* vm_stream = JUST(Singleton<VirtualMachine>::Get()->GetVmStream(stream));
// 通过OpCallInstructionPolicy初始化OpCall指令
auto instruction = intrusive::make_shared<vm::Instruction>(
vm_stream, std::make_shared<vm::OpCallInstructionPolicy>(
vm_stream, opkernel, std::move(input_eager_blob_objects),
std::move(output_eager_blob_objects), global_tensor_infer_result, ctx,
*one::CurrentDevVmDepObjectConsumeMode()));
// 指令入列表
instruction_list_->EmplaceBack(std::move(instruction));
return Maybe<void>::Ok();
}2 、虚拟机的运行原理
2.1 VM初始化
VirtualMachineScope::VirtualMachineScope(const Resource& resource) {
Singleton<VirtualMachine>::New();
}VirtualMachine::VirtualMachine() : disable_vm_threads_(false), scheduler_stopped_(false) {
// Class VirtualMachineEngine only cares the basic logical of vm, while class VirtualMachine
// manages threads and condition variables.
// In order to notify threads in VirtualMachineEngine, a notify callback lambda should be take as
// an argument for VirtualMachineEngine's constructor.
engine_ = intrusive::make_shared<vm::VirtualMachineEngine>();
OF_PROFILER_NAME_THIS_HOST_THREAD("_Main");
std::function<void()> SchedulerInitializer;
GetSchedulerThreadInitializer(&SchedulerInitializer);
schedule_thread_ = std::thread(&VirtualMachine::ScheduleLoop, this, SchedulerInitializer);
transport_local_dep_object_.Reset();
}void VirtualMachine::ScheduleLoop(const std::function<void()>& Initializer) {
SyncVmModeGuard guard(SyncVmMode::kEnable);
Initializer();
MultiThreadScheduleCtx schedule_ctx{};
while (pending_notifier_.WaitAndClearNotifiedCnt() == kNotifierStatusSuccess) {
OF_PROFILER_RANGE_GUARD("VirtualMachine::ScheduleLoop");
auto start = std::chrono::steady_clock::now();
static constexpr int kWorkingMicroseconds = 1000;
// Every time this thread wakes up, engine_ is scheduled for about `kWorkingMicroseconds`.
// The cost of os thread switching is about 5-10 microseconds. Doing more scheduling in
// a single waiting up can reach higher performance.
do {
do {
const size_t total_inserted = engine_->total_inserted_instruction_cnt();
const size_t total_erased = engine_->total_erased_instruction_cnt();
engine_->Schedule(schedule_ctx);
if (ThreadLocalEnvBool<ONEFLOW_VM_ENABLE_SCHEDULE_YIELD>()
&& total_inserted == engine_->total_inserted_instruction_cnt()
&& total_erased == engine_->total_erased_instruction_cnt()) { // nothing handled.
std::this_thread::yield();
}
} while (!engine_->SchedulerThreadUnsafeEmpty());
} while (MicrosecondsFrom(start) < kWorkingMicroseconds);
}
ScheduleUntilVMEmpty(engine_.Mutable(), schedule_ctx);
CHECK_JUST(ForEachThreadCtx(engine_.Mutable(), [&](vm::ThreadCtx* thread_ctx) -> Maybe<void> {
thread_ctx->mut_notifier()->Close();
return Maybe<void>::Ok();
}));
{
std::unique_lock<std::mutex> lock(worker_threads_mutex_);
for (const auto& worker_thread : worker_threads_) { worker_thread->join(); }
}
scheduler_stopped_ = true;
}ScheduleLoopScheduleLooponeflow/oneflow/core/common/notifier.hclass Notifier final {
public:
OF_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_MOVE(Notifier);
Notifier() : notified_cnt_(0), is_closed_(false) {}
~Notifier() = default;
NotifierStatus Notify();
NotifierStatus WaitAndClearNotifiedCnt();
void Close();
private:
size_t notified_cnt_;
std::mutex mutex_;
bool is_closed_;
std::condition_variable cond_;
};engine_->Schedule(schedule_ctx)while (pending_notifier_.WaitAndClearNotifiedCnt() == kNotifierStatusSuccess) {
auto start = std::chrono::steady_clock::now();
...
do {
do {
...
engine_->Schedule(schedule_ctx);
...
} while (!engine_->SchedulerThreadUnsafeEmpty());
} while (MicrosecondsFrom(start) < kWorkingMicroseconds);
}2.2 VM指令调度
void VirtualMachineEngine::Schedule(const ScheduleCtx& schedule_ctx) {
// Release finished instructions and try to schedule out instructions in DAG onto ready list.
if (unlikely(mut_active_stream_list()->size())) { ReleaseFinishedInstructions(schedule_ctx); }
// Try run the first barrier instruction.
if (unlikely(mut_barrier_instruction_list()->size())) { TryRunBarrierInstruction(schedule_ctx); }
// Handle pending instructions, and try schedule them to ready list.
// Use thread_unsafe_size to avoid acquiring mutex lock.
// The inconsistency between pending_instruction_list.list_head_.list_head_.container_ and
// pending_instruction_list.list_head_.list_head_.size_ is not a fatal error because
// VirtualMachineEngine::Schedule is always in a buzy loop. All instructions will get handled
// eventually.
// VirtualMachineEngine::Receive may be less effiencient if the thread safe version
// `pending_instruction_list().size()` used here, because VirtualMachineEngine::Schedule is more
// likely to get the mutex lock.
if (unlikely(local_pending_instruction_list().size())) {
HandleLocalPending();
} else if (unlikely(pending_instruction_list().thread_unsafe_size())) {
// MoveTo is under a lock.
mut_pending_instruction_list()->MoveTo(mut_local_pending_instruction_list());
if (local_pending_instruction_list().size()) { HandleLocalPending(); }
}
// dispatch ready instructions and try to schedule out instructions in DAG onto ready list.
if (unlikely(mut_ready_instruction_list()->size())) {
DispatchAndPrescheduleInstructions(schedule_ctx);
}
// handle scheduler probes
if (unlikely(local_probe_list_.size())) {
HandleLocalProbe();
} else if (unlikely(probe_list_.thread_unsafe_size())) {
probe_list_.MoveTo(&local_probe_list_);
if (local_probe_list_.size()) { HandleLocalProbe(); }
}
}InstructionMutexedList pending_instruction_list_;
// local_pending_instruction_list_ should be consider as the cache of pending_instruction_list_.
InstructionList local_pending_instruction_list_;
ReadyInstructionList ready_instruction_list_;
LivelyInstructionList lively_instruction_list_;
BarrierInstructionList barrier_instruction_list_;- pending相关的instruction_list是悬挂/待处理的指令列表;
- lively相关的instruction_list是活跃的正在执行中的指令列表;
- ready相关的instruction_list则是已完成准备工作(指令融合、指令DAG构建等)待执行的指令列表;
- 将已完成准备工作的指令放入ready_instruction_list_中维护;
- 尝试运行barrier指令列表(barrier_instruction_list_)中的第一条指令;
- 如果本地pending指令列表(local_pending_instruction_list_)非空,则通过
HandleLocalPending方法处理这些悬挂指令(指令融合、指令执行DAG图构建、插入ready列表)
- 如果ready指令列表非空,则通过
DispatchAndPrescheduleInstructions方法进行指令派发和预调度处理。
DispatchAndPrescheduleInstructionsDispatchAndPrescheduleInstructionsDispatchInstruction2.3 VM指令派发
template<void (VirtualMachineEngine::*OOMHandler)(vm::Stream*, const ScheduleCtx&)>
void VirtualMachineEngine::DispatchInstruction(Instruction* instruction,
const ScheduleCtx& schedule_ctx) {
auto* stream = instruction->mut_stream();
// Prepare
{
// 指令的Prepare
const auto& ret = TRY(instruction->Prepare());
if (unlikely(!ret.IsOk())) {
// 处理指令Prepare过程中的OOM的逻辑
if (ret.error()->has_out_of_memory_error()) {
// 让allocator释放不必要的cacahe,再重新执行指令的Prepare
(this->*OOMHandler)(stream, schedule_ctx);
...
}
}
}
// 将当前指令放入running_instruction_list
stream->mut_running_instruction_list()->PushBack(instruction);
if (stream->active_stream_hook().empty()) { mut_active_stream_list()->PushBack(stream); }
// Compute
if (OnSchedulerThread(*stream)) {
// StreamPolicy的Run方法触发指令的实际执行——Compute
stream->stream_policy().Run(instruction);
} else {
stream->mut_thread_ctx()->mut_worker_pending_instruction_list()->PushBack(instruction);
schedule_ctx.OnWorkerLoadPending(stream->mut_thread_ctx());
}
}- 执行指令的Prepare
- 执行指令的Compute
class StreamPolicy {
public:
virtual ~StreamPolicy() = default;
virtual ep::Stream* stream() = 0;
virtual vm::Allocator* mut_allocator() = 0;
virtual DeviceType device_type() const = 0;
virtual void InitInstructionStatus(const Stream& stream,
InstructionStatusBuffer* status_buffer) const = 0;
virtual void DeleteInstructionStatus(const Stream& stream,
InstructionStatusBuffer* status_buffer) const = 0;
virtual bool QueryInstructionStatusDone(const Stream& stream,
const InstructionStatusBuffer& status_buffer) const = 0;
virtual void Run(Instruction* instruction) const = 0;
virtual bool OnSchedulerThread(StreamType stream_type) const;
virtual bool SupportingTransportInstructions() const = 0;
protected:
StreamPolicy() = default;
};- stream()方法返回ep::Stream指针,指向的是针对不同平台的ep::stream对象。
- mut_allocator()方法返回一个vm的Allocator指针,用于内存分配/释放。
- InitInstructionStatus/QueryInstructionStatusDone/DeleteInstructionStatus用于创建/查询/销毁指令执行状态
- Run方法则是核心,定义了该Stream具体运行时的逻辑。
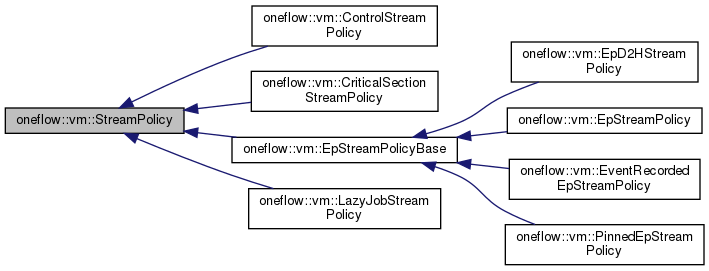
void EpStreamPolicyBase::Run(Instruction* instruction) const {
...
auto* stream = instruction->mut_stream();
EpStreamPolicyBase* ep_stream_policy_base =
dynamic_cast<EpStreamPolicyBase*>(stream->mut_stream_policy());
...
auto* ep_device = ep_stream_policy_base->GetOrCreateEpDevice();
ep_device->SetAsActiveDevice();
instruction->Compute();
...
}2.4 VM执行执行
void OpCallInstructionPolicy::Compute(vm::Instruction* instruction) {
OpCallInstructionUtil::Compute(this, instruction);
}
- TryInitOpKernelStateAndCache——初始化一些kernel计算需要的状态或缓存
- OpKernelCompute——执行该op对应的kernel,kernel内主要是实际的op计算逻辑

2.5 VM指令发送
// Returns true if old scheduler_pending_instruction_list is empty
Maybe<bool> VirtualMachineEngine::Receive(InstructionList* compute_instruction_list) {
OF_PROFILER_RANGE_GUARD("vm:Receive");
#ifdef OF_ENABLE_PROFILER
INTRUSIVE_UNSAFE_FOR_EACH_PTR(compute_instruction, compute_instruction_list) {
OF_PROFILER_RANGE_GUARD(compute_instruction->DebugName());
}
#endif
bool old_list_empty = mut_pending_instruction_list()->MoveFrom(compute_instruction_list);
return old_list_empty;
}3 、小结
3.1 UserOpExpr

3.2 Op执行的宏观脉络
- ReluFunctor
- UserOpExpr
- Interpreter
- PhysicalRun
- VirtualMachine->Receive
- VirtualMachine->ScheduleLoop ...
3.3 虚拟机运行和调度总结
- 从OpExprInterpreter到OpKernel
- 动态调度的“诅咒”| 原有深度学习框架的缺陷③
- 算子在深度学习框架中的执行及interpreter
- OneFlow源码:
- OneFlow v0.8.0正式发布
- 18张图,直观理解神经网络、流形和拓扑
- OneFlow源码解析:Op、Kernel与解释器
- Geoffrey Hinton:深度学习的下一个大事件
- 分布式深度学习编程新范式:Global Tensor
- LLVM之父:为什么我们要重建AI基础设施软件
- 大模型训练难?效率超群、易用的“李白”模型库来了
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢

网络安全笔记5——数字签名

chart.js horizontal column chart plugin

动作捕捉系统用于室内组合定位技术研究

TCP/IP笔记

MySQL executes the query process

ESP8266 Tutorial 2 - Burn AT Firmware

「首席工程师」首席(Principal )工程师修炼之道

Techches Transformer the join wisdom source the author cao, visual basic model study

大连理工&鹏城&UAE提出用于伪装目标检测的混合尺度三重网络ZoomNet,性能SOTA!

「应用架构」六边型架构:三个原则和一个实现示例
随机推荐
高通 msm8953 LCD 休眠/唤醒 流程
"Data Architecture": How can master data management (MDM) help my industry?
ESP8266 教程1 — ESP8266硬件平台介绍
14 high-frequency handwritten JS interview questions and answers to consolidate your JS foundation
Flutter实战-请求封装(五)之Isolate线程改造
ECCV 2022 | 视频理解新框架X-CLIP:仅用微调的成本,达到预训练的全能
「时序数据库」使用cassandra进行时间序列数据扫描
CSDN 21 Days Learning Challenge - Polymorphism (05)
数据库事务
bus事件总线 使用
使用cpolar远程连接群晖NAS(升级固定链接2)
【C语言】头文件#include <conio.h>,conio是Console Input/Output(控制台输入输出)
js guessing game source code
JS高级 之 Promise 详解
【数据架构】概念数据模型和逻辑数据模型有什么区别
数据库中的schema
LiveGBS操作日志页面快速的筛选上级平台的调用记录直播观看录像回看等操作
多租户技术
阻塞队列与线程池原理
C语言题解:倒置字符串