当前位置:网站首页>torch.gather() 用法解读
torch.gather() 用法解读
2022-08-08 05:41:00 【00000cj】
torch.gather(input, dim, index, *, sparse_grad=False, out=None) -> Tensor
沿\(dim\)指定的轴和\(index\)指定的索引从\(input\)中提取对应的值。
对于一个三维张量
\(output[i][j][k]=input[index[i][j][k]][j][k] \quad \#\enspace if \enspace dim==0\)
\(output[i][j][k]=input[i][index[i][j][k]][k] \quad \#\enspace if \enspace dim==1\)
\(output[i][j][k]=input[i][j][index[i][j][k]] \quad \#\enspace if \enspace dim==2\)
\(input\)和\(index\)的\(dimensions\)数目必须相同。 \(out\)和\(index\)的\(shape\)是相同的。(注意\(dimensions\)和\(shape\)的区别)
示例
下面用两个例子来解释一下具体的用法
例1
import torch
dim = 0
_input = torch.tensor([[10, 11, 12],
[13, 14, 15],
[16, 17, 18]])
index = torch.tensor([[0, 1, 2],
[1, 2, 0]])
output = torch.gather(_input, dim, index)
print(output)
# tensor([[10, 14, 18],
# [13, 17, 12]])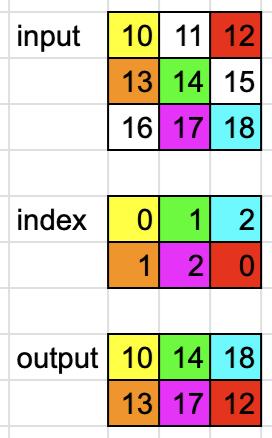
该例中 _input.shape=(3, 3),dimensions=2,其中_input和index的dimensions相同都为2,output和index的shape相同都为(2, 3)。
因为dim=0,index中的每个数其值代表dim=0即"行"这个维度的索引,而每个数本身所在位置的索引指定了其它维度的索引。比如index中第0行的[0, 1, 2]分别表示第0、1、2行,而这三个数本身在dim=1维度的索引为0、1、2即第0、1、2列。因此第一个数0定位到_input中的第0行,而0本身在index中的第0列,因此又定位到_input的第0列,这样就找到了10这个数,同理找到14和18。
index中的第1行[1, 2, 0]分别表示_input中的第1、2、0行和第0、1、2列,因此找到_input中对应的数[13, 17, 12]。
例2
import torch
dim = 1
_input = torch.tensor([[10, 11, 12],
[13, 14, 15],
[16, 17, 18]])
index = torch.tensor([[0, 1],
[1, 2],
[2, 0]])
output = torch.gather(_input, dim, index)
print(output)
# tensor([[10, 11],
# [14, 15],
# [18, 16]])
该例中 _input.shape=(3, 3),dimensions=2,其中_input和index的dimensions相同都为2,output和index的shape相同都为(3, 2)。
因为dim=1,index中的每个数其值代表dim=1即"列"这个维度的索引,而每个数本身所在位置的索引指定了其它维度的索引。比如index中第0行的[0, 1]分别表示第0、1列,而这三个数本身在dim=0维度的索引为0即第0行。因此第一个数0定位到_input中的第0列,而0本身在index中的第0行,因此又定位到_input的第0行,这样就找到了10这个数,同理找到11。
index中的第1行[1, 2]分别表示_input中的第1、2列和第1行,因此找到_input中对应的数[14, 15]。
index中的第2行[2, 0]分别表示_input中的第2、0列和第2行,因此找到_input中对应的数[18, 16]。
总结
上面的示例是二维的情况,同理也可以推广到三维甚至更多维。总结来说,index中每个数其本身的值表示参数dim指定维度的索引,而其它的每个维度都由每个数在index中的对应维度的索引指定。
参考
torch.gather — PyTorch 1.12 documentation
python - What does the gather function do in pytorch in layman terms? - Stack Overflow
边栏推荐
- Day8:面试必考编程题(细心OJ)
- 《动机与人格》笔记(二)——认识和理解的欲望
- Preprocessing Notes
- 值得收藏的几个postman特色功能帮你事半功倍!
- postman---postman parameterization
- Use of Filter
- C language framework FreeSwitch custom event introduction and usage example
- KDD'22 Recommendation System Papers (24 Research & 36 Application Papers)
- 浅学软件逆向笔记(1)
- C语言框架FreeSwitch自定义事件介绍与使用示例
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
Go-Excelize API源码阅读(十)—— SetActiveSheet(index int)
121道分布式面试题和答案
温故知新—Activity的五种启动模式
The big and small end problem caused by union union
字符串题目解析
【js基础】js的垃圾回收机制/内存回收机制
Hard Disk Basics
Week 8 Transformer Language Models and Implications
日常bug小结:
Connect two tables to update the third table (updata) in postgresql
The difference between classification, object detection, semantic segmentation, and instance segmentation
28.异常检测
"Public Administration" exam key points and answers
Unity-CharacterController (Character Controller)
C language - function
C language - score and loop statement
毕设——基于人脸表情的桌面交互精灵设计(分享一下成果,附上人脸表情的数据集和自己训练出来yolov5模型以及基于PYQT5运行yolov5的交互界面)
棋盘染色问题
automation tool
说说Redis分布式锁的原理和实现蚂【蚁金服三面】