当前位置:网站首页>[corner detection]
[corner detection]
2022-04-22 16:45:00 【yangyang_ z】
List of articles
Preface
Corner detection (Corner Detection) It is a method used to obtain image features in computer vision system , It is widely used in motion detection 、 Image matching 、 Video tracking 、 In the fields of 3D modeling and target recognition , The page is called feature point detection .
A corner is usually defined as the intersection of two edges , More strictly speaking , Two local points of a region with different directions should have different neighborhood angles . And in practice , Most of the so-called corner detection methods detect image points with specific features , Not just “ Corner point ”. These feature points have specific coordinates in the image , And has some mathematical characteristics , Such as local maximum or minimum grayscale 、 Some gradient features, etc .
1、Harris Corner detection
In the field of image processing and computer vision , Point of interest (interest points), Also known as key points (key points)、 Characteristic point (feature points). It is widely used to solve object recognition 、 Image recognition 、 Image matching 、 Visual tracking 、 A series of problems such as 3D reconstruction . We don't look at the whole picture anymore , Instead, choose some special points , Then they are analyzed locally and purposefully . If enough of these spots can be detected , At the same time, their discrimination is particularly high , And it can accurately locate stable features , Then this method has use value .
Image feature types can be divided into the following three types :
- edge
- Corner point ( Key points of interest )
- speckle (Blobs)( Region of interest )
Corner detection algorithm
Current image processing neighborhood , Corner detection algorithms can be divided into the following three categories
- Corner detection based on gray image
- Corner detection based on binary image
- Corner detection based on contour curve
void cornerHarris(
InputArray src, // The input image , Source image , fill Mat Class , And must be single channel 8 Bit or floating point image .
OutputArray dst, // The operation result after function call exists here , That is, this parameter is used to store Harris Output result of corner detection , The same size and type as the source image .
int blockSize, // Represents the size of the neighborhood
int ksize, // Express Sobel( The aperture size of the operator .
double k, //Harris Parameters
int borderType = BORDER_DEFAULT // Boundary mode of image pixels
);
C++ Code test example 1
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
using namespace cv;
static int test()
{
// Load the image in grayscale mode and display
Mat srcImage = imread("1.jpg", 0);
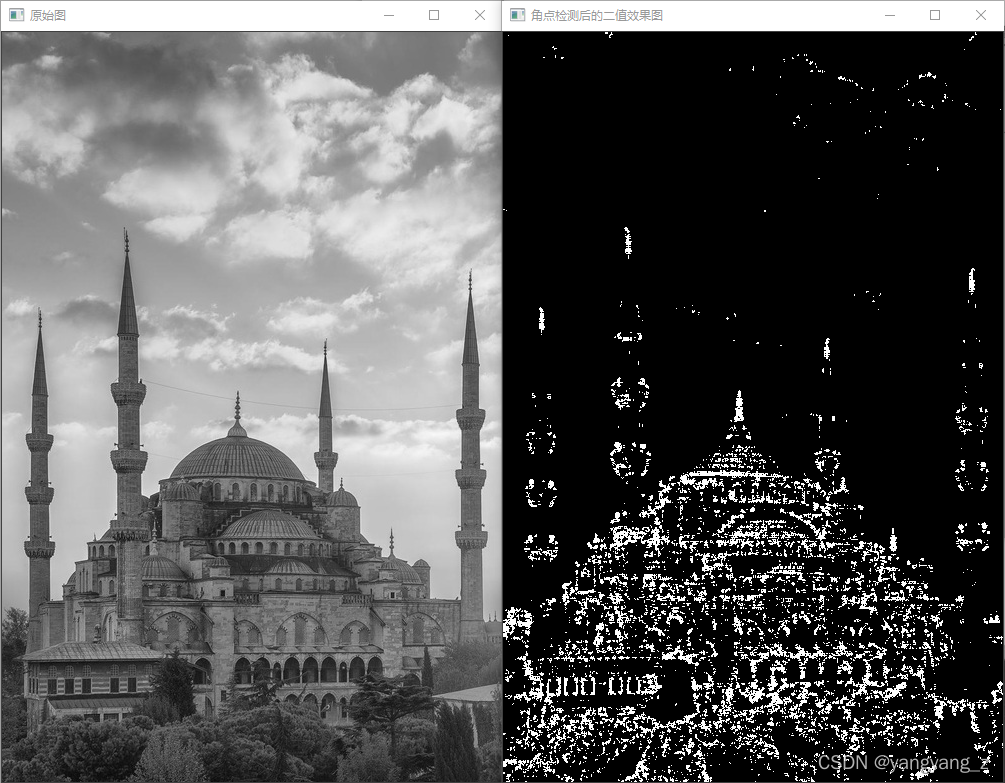
imshow(" The original picture ", srcImage);
// Conduct Harris Corner detection to find out corner points
Mat cornerStrength;
cornerHarris(srcImage, cornerStrength, 2, 3, 0.01);
// Threshold operation on gray image , Get the binary diagram and display
Mat harrisCorner;
threshold(cornerStrength, harrisCorner, 0.00001, 255, THRESH_BINARY);
imshow(" Binary rendering after corner detection ", harrisCorner);
waitKey(0);
return 0;
}
int main()
{
test();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
result
C++ Code test example 2
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
string window_name1 = "【 Program window 1】"; // Window Title Definition
string window_name2 = "【 Program window 2】"; // Window Title Definition
Mat g_srcImage, g_srcImage1, g_grayImage;
int thresh = 30; // Current threshold
int max_thresh = 175; // Maximum threshold
void on_CornerHarris(int, void*);// Callback function
static int test()
{
//【0】 change console The font color
system("color 3F");
//【1】 Load the original drawing and clone it
g_srcImage = imread("1.jpg", 1);
if (!g_srcImage.data) {
cout <<" Error reading picture , Please make sure whether there is... In the directory imread The picture specified by the function does not exist ~! \n"; return false; }
imshow(" The original picture ", g_srcImage);
g_srcImage1 = g_srcImage.clone();
//【2】 Save a grayscale image
cvtColor(g_srcImage1, g_grayImage, COLOR_BGR2GRAY);
//【3】 Create windows and scroll bars
namedWindow(window_name1, WINDOW_AUTOSIZE);
createTrackbar(" threshold : ", window_name1, &thresh, max_thresh, on_CornerHarris);
//【4】 Call the callback function once , To initialize
on_CornerHarris(0, 0);
waitKey(0);
return(0);
}
int main()
{
test();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
void on_CornerHarris(int, void*)
{
//----------------------【1】 Define some local variables ---------------
Mat dstImage;// Goal map
Mat normImage;// Normalized graph
Mat scaledImage;// Graph of 8-bit unsigned integer after linear transformation
//---------------------【2】 initialization ----------------------------
// Set to zero the two pictures currently to be displayed , That is, clear their values the last time this function was called
dstImage = Mat::zeros(g_srcImage.size(), CV_32FC1);
g_srcImage1 = g_srcImage.clone();
//-----------------------【3】 Formal testing ------------------------
// Corner detection
cornerHarris(g_grayImage, dstImage, 2, 3, 0.04, BORDER_DEFAULT);
// Normalization and transformation
normalize(dstImage, normImage, 0, 255, NORM_MINMAX, CV_32FC1, Mat());
convertScaleAbs(normImage, scaledImage);// The normalized graph is linearly transformed into 8 Bit unsigned integer
//-----------------【4】 Drawing ---------------------------
// What will be detected , And the corner points that meet the threshold conditions are drawn
for (int j = 0; j < normImage.rows; j++)
{
for (int i = 0; i < normImage.cols; i++)
{
if ((int)normImage.at<float>(j, i) > thresh + 80)
{
circle(g_srcImage1, Point(i, j), 5, Scalar(10, 10, 255), 2, 8, 0);
circle(scaledImage, Point(i, j), 5, Scalar(0, 10, 255), 2, 8, 0);
}
}
}
//------------------【4】 Show the end result ---------------------
imshow(window_name1, g_srcImage1);
imshow(window_name2, scaledImage);
}
result

2、Shi-Tomasi Corner detection
Besides using Harris Carry out corner detection , We can also usually use Shi-Tomasi Methods corner detection .Shi-Tomasi The algorithm is Harris Algorithm improvement , The original definition of this algorithm is matrix M The determinant value of is the same as M Trace subtraction , Then compare the difference with the preset threshold . later Shi and Tomasi An improved method is proposed , If the smaller of the two eigenvalues is greater than the minimum threshold , You will get strong corners .
C++ Code example
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
string window_name = "【Shi-Tomasi Corner detection 】";
Mat g_srcImage, g_grayImage;
int g_maxCornerNumber = 33;
int g_maxTrackbarNumber = 500;
RNG g_rng(12345);// Initialize random number generator
void on_GoodFeaturesToTrack(int, void*)
{
//【1】 For variables less than or equal to 1 Time processing
if (g_maxCornerNumber <= 1) {
g_maxCornerNumber = 1; }
//【2】Shi-Tomasi Algorithm (goodFeaturesToTrack function ) Parameter preparation for
vector<Point2f> corners;
double qualityLevel = 0.01;// The minimum eigenvalue acceptable for corner detection
double minDistance = 10;// Minimum distance between corners
int blockSize = 3;// The neighborhood range specified when calculating the derivative autocorrelation matrix
double k = 0.04;// Weight factor
Mat copy = g_srcImage.clone(); // Copy the source image to a temporary variable , As a region of interest
//【3】 Conduct Shi-Tomasi Corner detection
goodFeaturesToTrack(g_grayImage,// The input image
corners, // The output vector of the detected corner
g_maxCornerNumber, // The maximum number of corners
qualityLevel, // The minimum eigenvalue acceptable for corner detection
minDistance, // Minimum distance between corners
Mat(), // Region of interest
blockSize, // The neighborhood range specified when calculating the derivative autocorrelation matrix
false, // Don't use Harris Corner detection
k); // Weight factor
//【4】 Output text messages
cout << "\t> The number of corners detected this time is :" << corners.size() << endl;
//【5】 Draw the detected corner
int r = 4;
for (int i = 0; i < corners.size(); i++)
{
// Draw corners in random colors
circle(copy, corners[i], r, Scalar(g_rng.uniform(0, 255), g_rng.uniform(0, 255),
g_rng.uniform(0, 255)), -1, 8, 0);
}
//【6】 Show ( to update ) window
imshow(window_name, copy);
}
static void test()
{
//【0】 change console The font color
system("color 2F");
//【1】 Load the source image and convert it to a grayscale image
g_srcImage = imread("1.jpg", 1);
cvtColor(g_srcImage, g_grayImage, COLOR_BGR2GRAY);
//【2】 Create windows and sliders , And initialize the display and callback functions
namedWindow(window_name, WINDOW_AUTOSIZE);
createTrackbar(" Maximum number of corners ", window_name, &g_maxCornerNumber, g_maxTrackbarNumber, on_GoodFeaturesToTrack);
imshow(window_name, g_srcImage);
on_GoodFeaturesToTrack(0, 0);
waitKey(0);
}
int main()
{
test();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
result

3、 Sub pixel corner detection
Background Overview
If the purpose of image processing is not to extract feature points for recognition, but to carry out geometric measurement , This usually requires higher accuracy , The function goodFeaturesToTrack() Only simple pixel coordinate values can be provided , in other words , Sometimes you need real coordinate values instead of integer coordinate values .
The position of sub-pixel corner detection is in the camera calibration stage 、 Track and reconstruct the trajectory of the camera , Or when reconstructing the three-dimensional structure of the tracking target , Is a basic measurement .
C++ Code test example
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
#include <iostream>
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
string window_name = "【 Sub pixel corner detection 】"; // Window Title Definition
Mat g_srcImage, g_grayImage;
int g_maxCornerNumber = 33;
int g_maxTrackbarNumber = 500;
RNG g_rng(12345);// Initialize random number generator
void on_GoodFeaturesToTrack(int, void*)
{
//【1】 For variables less than or equal to 1 Time processing
if (g_maxCornerNumber <= 1) {
g_maxCornerNumber = 1; }
//【2】Shi-Tomasi Algorithm (goodFeaturesToTrack function ) Parameter preparation for
vector<Point2f> corners;
double qualityLevel = 0.01;// The minimum eigenvalue acceptable for corner detection
double minDistance = 10;// Minimum distance between corners
int blockSize = 3;// The neighborhood range specified when calculating the derivative autocorrelation matrix
double k = 0.04;// Weight factor
Mat copy = g_srcImage.clone(); // Copy the source image to a temporary variable , As a region of interest
//【3】 Conduct Shi-Tomasi Corner detection
goodFeaturesToTrack(g_grayImage,// The input image
corners,// The output vector of the detected corner
g_maxCornerNumber,// The maximum number of corners
qualityLevel,// The minimum eigenvalue acceptable for corner detection
minDistance,// Minimum distance between corners
Mat(),// Region of interest
blockSize,// The neighborhood range specified when calculating the derivative autocorrelation matrix
false,// Don't use Harris Corner detection
k);// Weight factor
//【4】 Output text messages
cout << "\n\t>------------- The number of corners detected this time is :" << corners.size() << endl;
//【5】 Draw the detected corner
int r = 4;
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < corners.size(); i++)
{
// Draw corners in random colors
circle(copy, corners[i], r, Scalar(g_rng.uniform(0, 255), g_rng.uniform(0, 255),
g_rng.uniform(0, 255)), -1, 8, 0);
}
//【6】 Show ( to update ) window
imshow(window_name, copy);
//【7】 Parameter setting of sub-pixel corner detection
Size winSize = Size(5, 5);
Size zeroZone = Size(-1, -1);
TermCriteria criteria = TermCriteria(TermCriteria::EPS + TermCriteria::MAX_ITER, 40, 0.001);
//【8】 Calculate the sub-pixel corner position
cornerSubPix(g_grayImage, corners, winSize, zeroZone, criteria);
//【9】 Output corner information
for (int i = 0; i < corners.size(); i++)
{
cout << " \t>> Exact corner coordinates [" << i << "] (" << corners[i].x << "," << corners[i].y << ")" << endl;
}
}
static void test()
{
//【0】 change console The font color
system("color 2F");
//【1】 Load the source image and convert it to a grayscale image
g_srcImage = imread("1.jpg", 1);
cvtColor(g_srcImage, g_grayImage, COLOR_BGR2GRAY);
//【2】 Create windows and sliders , And initialize the display and callback functions
namedWindow(window_name, WINDOW_AUTOSIZE);
createTrackbar(" Maximum number of corners ", window_name, &g_maxCornerNumber, g_maxTrackbarNumber, on_GoodFeaturesToTrack);
imshow(window_name, g_srcImage);
on_GoodFeaturesToTrack(0, 0);
waitKey(0);
}
int main()
{
test();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
result

版权声明
本文为[yangyang_ z]所创,转载请带上原文链接,感谢
https://yzsam.com/2022/04/202204221639176130.html
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢

Hx711 weight sensor wiring

AQS source code reading

A serial port data receiving mode of stm32

Domain driven model DDD (III) -- using saga to manage transactions

What is the advantage of asemi low voltage drop Schottky diode over ordinary Schottky diode?

DB107-ASEMI整流桥详细数据

JD side: how can a child thread get the value of the parent thread ThreadLocal? I got...

Use of serial port data plot serialplot

8.1 序列模型

matplotlib绘图
随机推荐
国美零售借数字经济东风,打造“船身”的消费体验
MySQL_00_初识MySQL
Code implementation of sequence table
Multithreading uses redis to accumulate. The result is incorrect. Solution
This API hub is powerful. It contains open APIs such as nailing enterprise wechat, and can be debugged directly!
SolidWorks oblique reference plane
AQS源码阅读
Circular linked list application - Joseph Ring
Analysis of JWT permission verification of golang
解决并发问题方案流程及原理总结(表单重复提交问题)
JD side: how can a child thread get the value of the parent thread ThreadLocal? I got...
Scrapy框架进阶学习
SolidWorks insert socket head cap screw
ASEMI低压降肖特基二极管比普通肖特基好在哪?
如何登录MySQL
[Ansys Workbench] Mechanical 界面显示模型树窗口和详细信息窗口
【滤波与卷积(二)】
渗透测试&网络&CTF面试题整理
Web测试需要注意什么?
敏捷实践 | 提高小组可预测性的敏捷指标