最近使用 Android Studio When working on project development,发现对 implementation、api、embed The usage is not very clear,Prepare an article here to summarize its usage scenarios or usage methods.
dependencies {
// Moudle内可见:material对应的api,Only thereMoudleThe corresponding project is called
implementation 'com.google.android.material:material:1.3.0'
// Dependency is conductive:依赖该MoudleEngineering otherModule,仍可使用gson对应的api
api 'com.google.code.gson:gson:2.6.2'
// 合并AAR:将boltspackaged into theMoudle,生成包含bolts的aar
embed 'com.parse.bolts:bolts-tasks:1.4.0'
}
正文开始前,先对implementation、api、embedThe characteristics are summarized as follows:
| 配置 | 行为 |
|---|---|
| implementation | Dependence is not conductive,引入的API仅Moudle可见; 参与Moudle的编译、Not participating in correspondenceAAR打包,But participate in the wholeApk打包; |
| api | Dependency is conductive,依赖该Moudle的其他MoudleImported can also be calledAPI; 参与Moudle的编译、Not participating in correspondenceAAR打包,But participate in the wholeApk打包; |
| embed | 合并AAR,将引入API对应的AARWorks merged into thisMoudle工程,Packed into a brand new oneAAR; Dependence is not conductive,引入的API仅Moudle可见; |
一、implementation、api
implementation、api是Gradle与AGP(Android Gradle Plugin)Supported dependency configuration items:
- AndroidStudio官方文档描述如下:
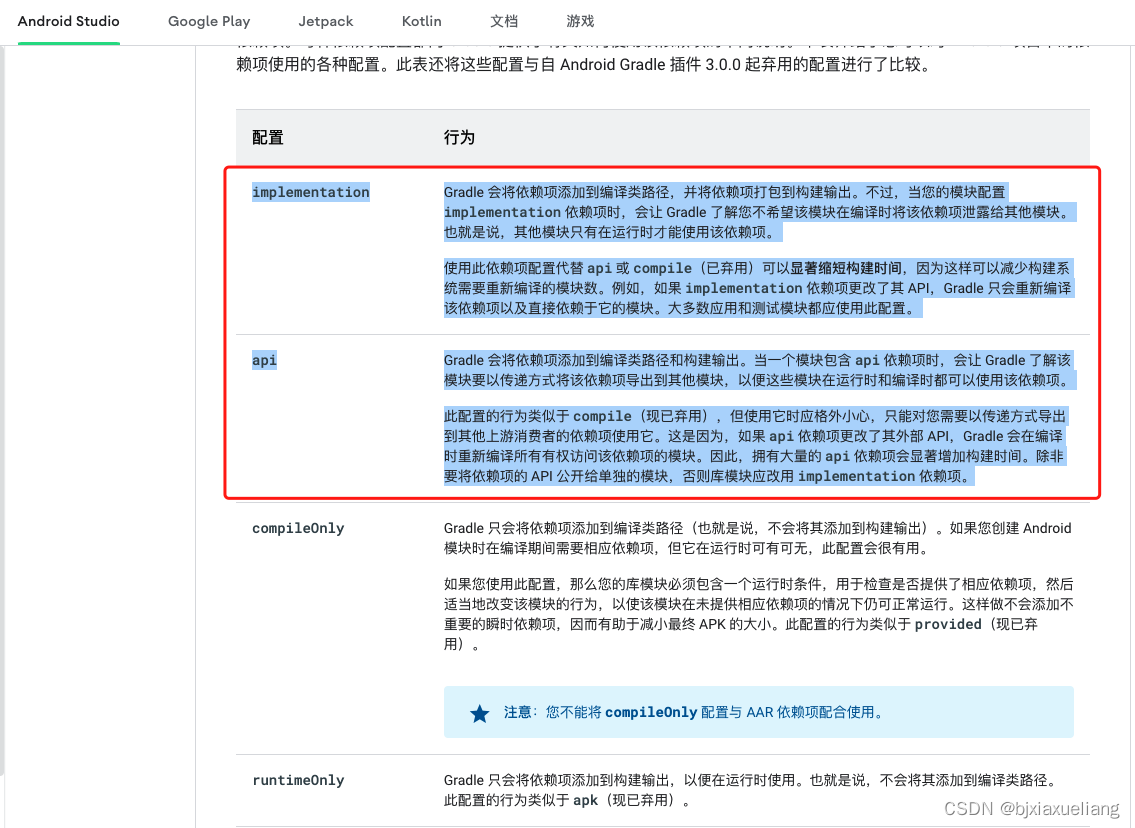
- Gradle官方文档描述如下:
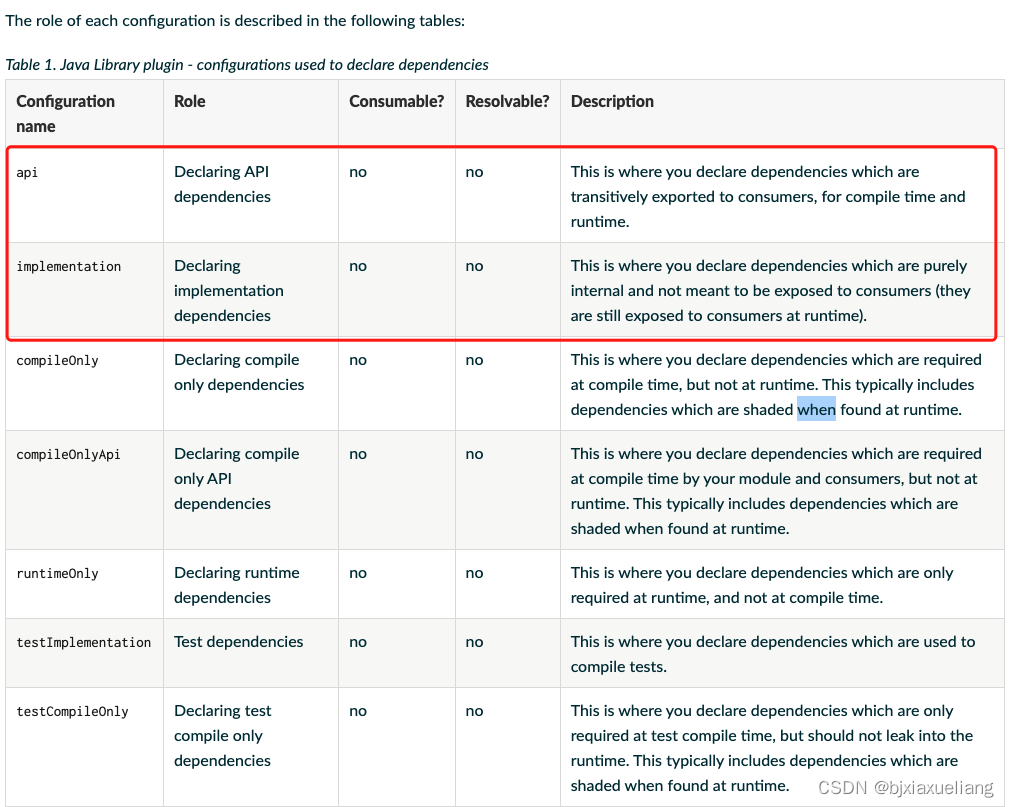
1.1 使用场景
implementation、api的使用场景或者使用方式A summary is given in the table at the beginning of the article:
implementation:
- 依赖
Not conductive,引入的API仅Moudle可见; 参与Moudle的编译、Not participating in correspondenceAAR打包,But participate in the wholeApk打包;
api:
- 依赖
具备传导性,依赖该Moudle的其他MoudleImported can also be calledAPI; 参与Moudle的编译、Not participating in correspondenceAAR打包,But participate in the wholeApk打包;
1.2 验证举例
A summary of the usage scenarios given above,This section provides the basis for the proof of the conclusion:The best way is to write a simple program to verify it.
- implementation Use scenario verification examples;
- api Use scenario verification examples;
implementationUse scenario validation
The verification steps and conclusions are as follows:
- a、新建一个AndroidStudio工程
Android_Test; - b、在
Android_Test工程下,新建Moudle工程Lib_B; - c、使
App依赖Lib_BMoudle工程;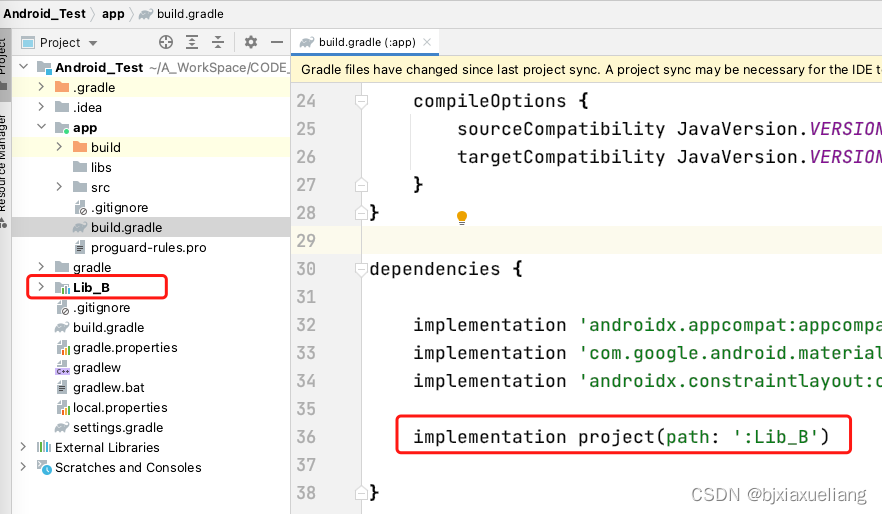
- d、
Lib_B以implementation方式引入gson依赖包: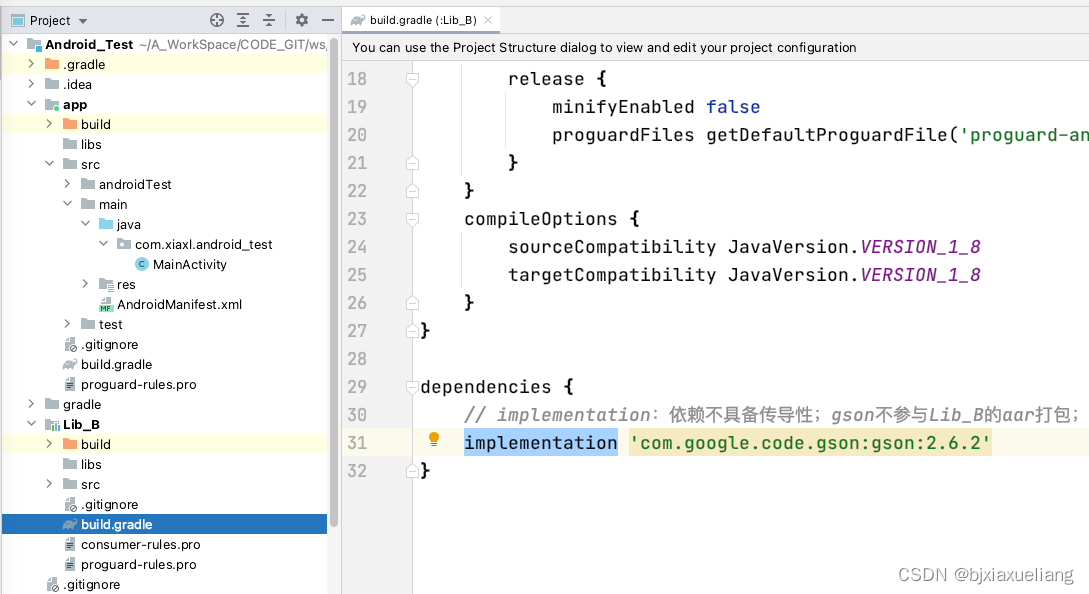
- e、
AppMoudle无法引用gson相关API:
得出第一个结论:Dependence is not conductive,引入的API仅Moudle可见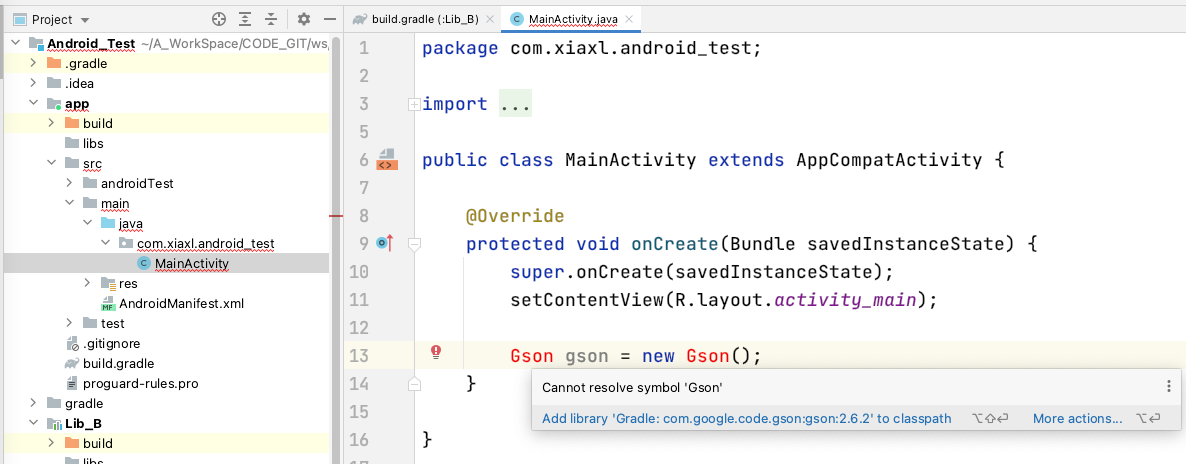
- f、反编译
Lib_B的AAR包,其中不包含gson相关代码;反编译app.apk,其中包含gson相关代码.
得出第二个结论:参与Moudle的编译、Not participating in correspondenceAAR打包,But participate in the wholeApk打包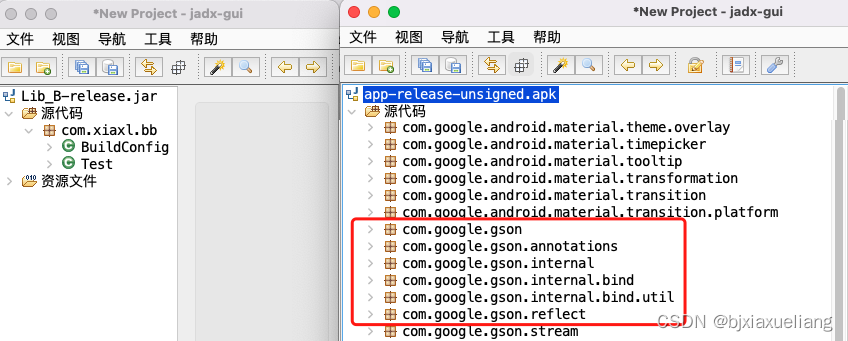
api
The verification steps and conclusions are as follows:
- a、
Lib_B以api方式引入gson依赖包: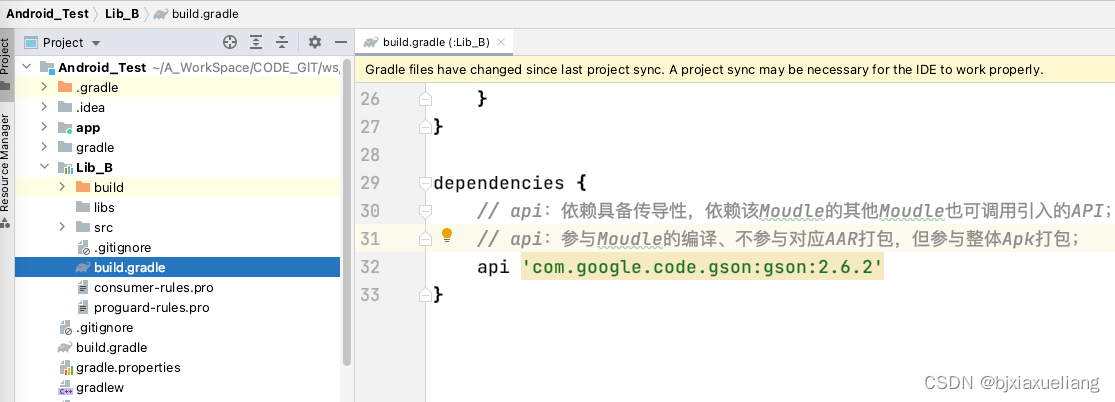
- b、
AppMoudle可引用gson相关API:
得出第一个结论:Dependency is conductive,依赖该Moudle的其他MoudleImported can also be calledAPI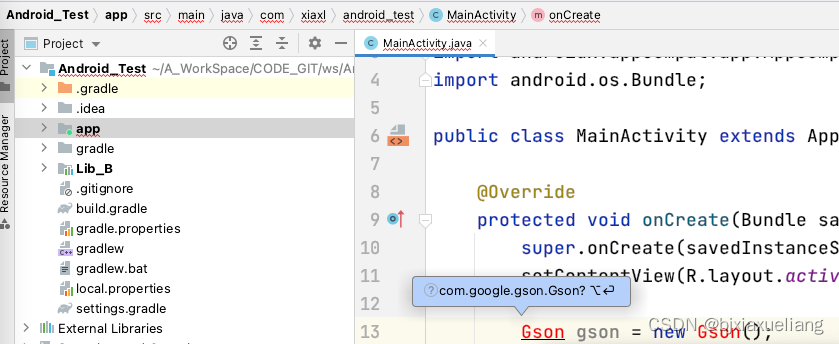
- c、反编译
Lib_B的AAR包,其中不包含gson相关代码;反编译app.apk,其中包含gson相关代码.
得出第二个结论:参与Moudle的编译、Not participating in correspondenceAAR打包,But participate in the wholeApk打包
二、embed
embed 是GitHub开源工程 fat-aar-android Provided third-party dependency configuration,Its main function is将多个AARDependent packages are merged.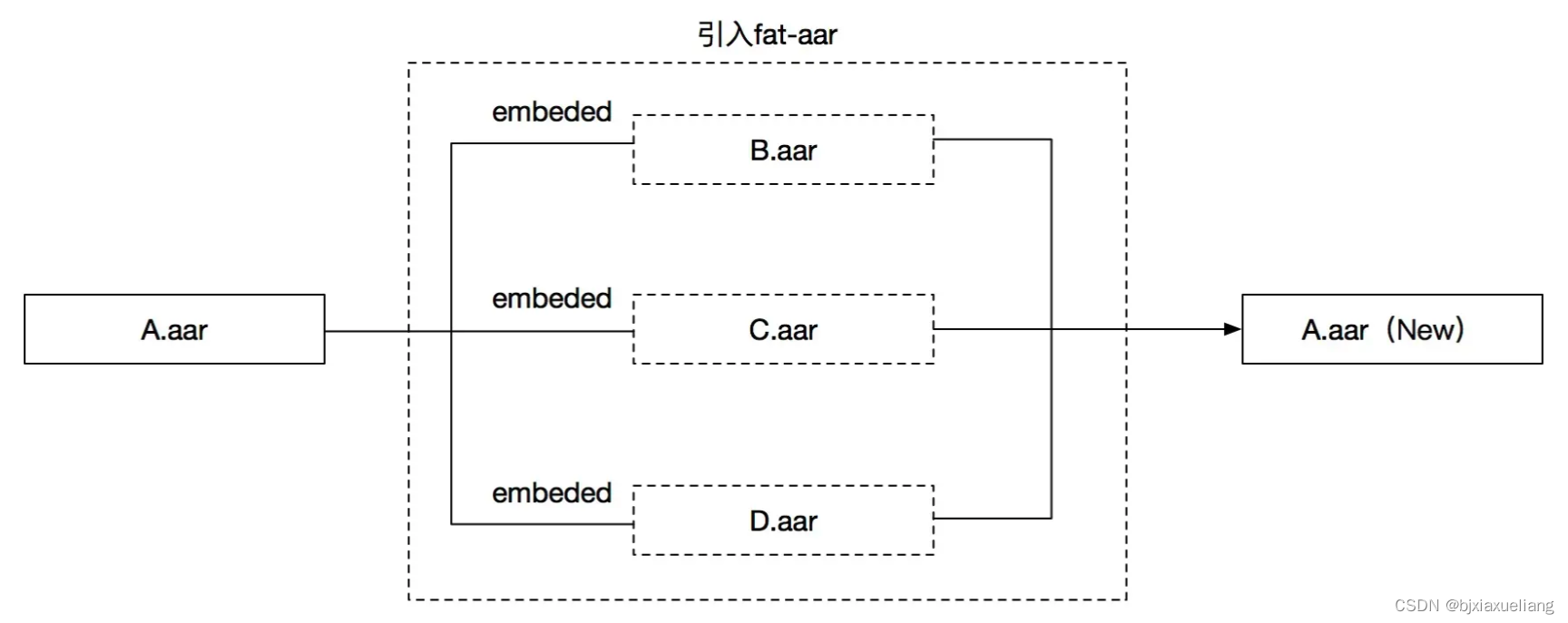
2.1 使用场景
Here's a summary of its use as follows:
合并AAR:将引入API对应的AARWorks merged into thisMoudle工程,Packed into a brand new oneAAR;- 依赖
Not conductive:引入的API仅Moudle可见;
2.2 注意点
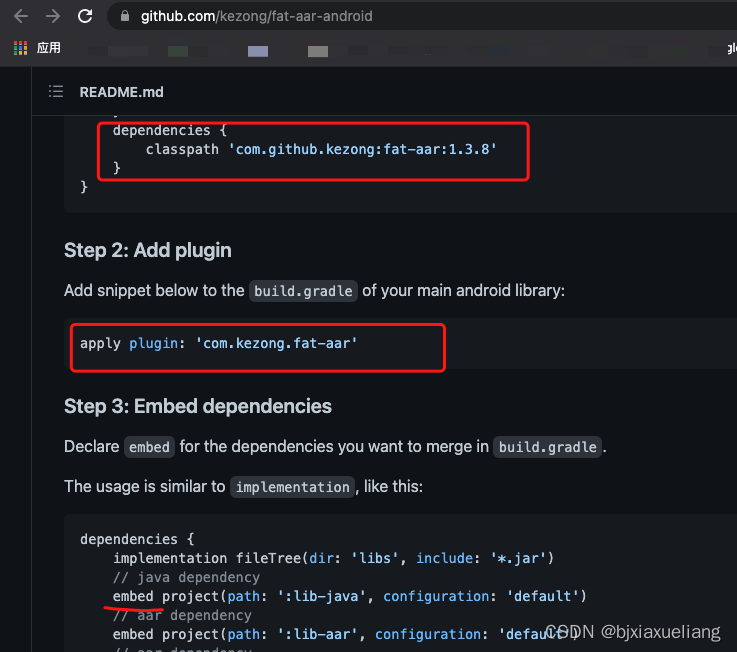
对于embed的使用,No further verification examples are given here,感兴趣的朋友可自行验证.但对于embed的使用,A point to be emphasized here:
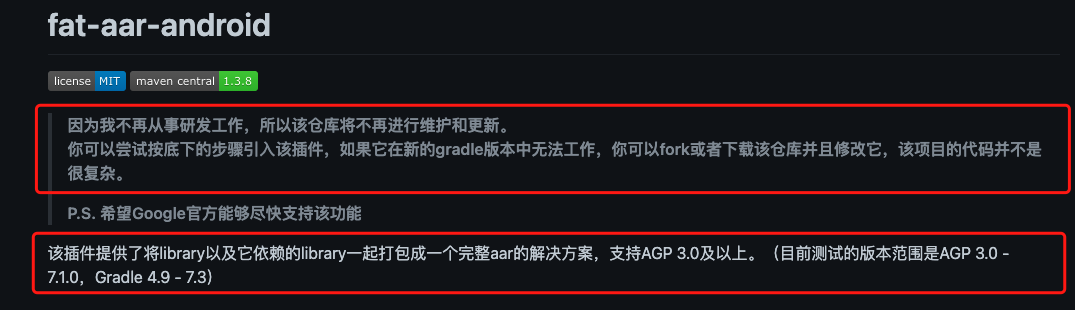
- a、fat-aar-android 将
不再维护更新; - b、
Supported version range:AGP 3.0 - 7.1.0,Gradle 4.9 - 7.3;
三、A scene processing
implementation、api、embed单独使用,It has met most of our usage scenarios,But suppose this is the case:
- 有三个Moudle:
app、Lib_B、Lib_C; app依赖Lib_B,Lib_B依赖Lib_C;
需求是 Lib_C Need to be merged into Lib_B 中,生成一个新的AAR Lib_B ;但 Lib_C 的相关APITo be available again app 调用.
这种情况该如何处理?
// can be used simultaneouslyapi与embed配置依赖
dependencies {
api project(path: ':Lib_C')
embed project(path: ':Lib_C')
}

参考
Android Gradle dependencies:
https://developer.android.google.cn/studio/build/dependencies?hl=zh-cn
fat-aar-android:embed
https://github.com/kezong/fat-aar-android
Gradle官方:
https://gradle.org/releases/
Gradle java_library_plugin:
https://docs.gradle.org/current/userguide/java_library_plugin.html#sec:java_library_separation
= THE END =
文章首发于公众号”CODING技术小馆“,如果文章对您有帮助,欢迎关注我的公众号.









