当前位置:网站首页>Codeforces Round #779 (Div. 2)
Codeforces Round #779 (Div. 2)
2022-04-22 07:27:00 【INGg__】
A - Marin and Photoshoot
The question
Given 01 strand , So that in any interval ,0 No more than 1 The number of
Answer key
Every two 0 There must be at least 2 individual 1
Code
int n;
string s;
void solve(){
cin >> n;
cin >> s;
int cnt = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++){
if (s[i] == '0' && s[i - 1] == '0')
cnt += 2;
if (i >= 2 && s[i] == '0' && s[i - 1] == '1' && s[i - 2] == '0')
cnt += 1;
}
cout << cnt << endl;
}
B - Marin and Anti-coprime Permutation
The question
Give a group 1n Permutation , Ask if you can make each number in the arrangement choose 1n Multiply one of the numbers by yourself (1~n Each can only be used once ) Make the last gcd>1
Ask how many options
Answer key
It's better than a Simple sobbing
If we want to , The essence of multiplication is addition , The addition of odd and even numbers is only the addition of all even numbers and odd numbers , So let's give an odd number a multiplier of an even number , If even numbers are added to odd numbers, it must be even , The remaining odd numbers are given to even numbers , This is all odd , Just gcd That is to say 2 了
So how many methods are there ?
When n When it is odd, there are not enough even numbers to correspond to odd numbers one by one , So the number of schemes is 0
When n When it's even , Yes n 2 \frac{n}{2} 2n An even number , n 2 \frac{n}{2} 2n Odd number , Assigning an even number to an odd number has A n 2 n 2 A_{\frac{n}{2}}^{\frac{n}{2}} A2n2n, Assigning an odd number to an even number has A n 2 n 2 A_{\frac{n}{2}}^{\frac{n}{2}} A2n2n, So the answer is $ (A_{\frac{n}{2}}^{\frac{n}{2}} ) ^2$
Code
void solve(){
cin >> n;
if(n & 1)
cout << 0 << endl;
else{
ll ans = 1;
// ll tmp = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n / 2; i++){
ans = ans * i % mod;
}
cout << ans * ans % mod << endl;
}
}
C - Shinju and the Lost Permutation
The question
We define an array b, For a permutation p, b i = m a x ( p 1 , p 2 , … , p i ) b_i=max(p_1,p_2,\dots,p_i) bi=max(p1,p2,…,pi), The weight of this array is array b Number of types of elements in .
Now give an array c, c i c_i ci To arrange p The first i − 1 i-1 i−1 The weight of the second cycle
Ask according to this array c, Can we be sure that there is an arrangement p With the corresponding
Answer key
According to the above definition , First of all, we can know ,c The length of is n, Then the result of all the rotations of the arrangement will appear , So ,n It must appear at the first position of the array once , And once and only once , therefore c If more than one... Appears in the array 1, Or not 1, Then it must be illegal
secondly , We can judge c The validity of the array ,c The order of the elements in the array doesn't matter , But the relative order cannot become , Because only the initial state of the arrangement is different , And after the arrangement rotates, all States will appear , It doesn't affect c The elements in , The key is the relative order
And because of the way the weight is calculated and the way the element is moved forward, we know , When from 1 At the beginning of the , The next element to appear will be better than n Small , So the weight increases 1, Similarly, the following operations may also increase 1, But it may also appear that the next number to come is more than the current one n All the previous numbers should be large , for example 1 2 3 5 4, This will lead to a sharp drop in the weight , It's legal
But if the next bit is more than the current bit 1, So this is obviously impossible , Because every time, there will only be one more number in front , There can be no one operation ratio n Two more numbers arrived
So to sum up :
- 1 Only in c Must and can only appear once in the array
- from c Array 1 The difference between the number behind the position is less than or equal to 1
What meets the above conditions is YES
Code
// Official solution code , I feel I have learned a lot of new stl
void solve() {
int n; cin >> n;
vector<int> a(n);
for (int &v: a) cin >> v;
if (count(a.begin(), a.end(), 1) != 1) {
cout << "NO\n";
return;
}
int p = find(a.begin(), a.end(), 1) - a.begin();
rotate(a.begin(), a.begin() + p, a.end());
cout << a[0] << ' ';
for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i) {
cout << a[i] << ' ';
if (a[i] - a[i - 1] > 1) {
cout << "NO\n";
return;
}
}
cout << "YES\n";
}
D1 - 388535 (Easy Version)
The question
Given an array a a a、 One l l l And a r r r, Array a Contains a length of r − l + 1 r-l+1 r−l+1 Of l ∼ r l\sim r l∼r Permutation
Change the array element to a i = a i x o r x a_i=a_i \; xor \; x ai=aixorx
Given the last array a, ask x How much is the
ez In the version l l l by 0
Answer key
The problem requires that we only need to XOR the array once , So essentially , For the same bit of each number , If ^1, It means that you have taken the opposite ,
Then we just need to see if there are statistics on each bit of the current given array 1 The number of is the same as that in the original arrangement 0 The number corresponds to , If so, it means x This bit of is 1
Code
int T;
ll l, r;
int a[N];
int b[N];
int cnta[20][2];
int cntb[20][2];
void solve(){
memset(cnta, 0, sizeof(cnta));
memset(cntb, 0, sizeof(cntb));
cin >> l >> r;
for (int i = l; i <= r; i++){
cin >> a[i];
}
for (int i = l; i <= r; i++){
for (int j = 0; j < 20; j++){
cnta[j][(a[i] >> j) & 1]++;
}
}
for (int i = l; i <= r; i++){
for (int j = 0; j < 20; j++){
cntb[j][(i >> j) & 1]++;
}
}
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++){
if(cnta[i][0] == cntb[i][1])
ans += 1ll << i;
}
cout << ans << endl;
// for (int i = l; i <= r; i++){
// cout << (ans ^ a[i]) << ' ';
// }
// cout << endl
// << Endl;
}
D2 - 388535 (Hard Version)
The question
And d1 Agreement , The only difference is l Not necessarily equal to 0 Of
Answer key
ygg tql!https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/488753758
leonard The board of tql
Inspection point : The nature of XOR and 01trie seek
The main points of :
- The nature of XOR
- x^b=a; a^b=x
- $a\neq b \iff a \oplus x \neq b \oplus x $
- a ⊕ a = 0 , a ⊕ 0 = a a \oplus a=0, a\oplus 0=a a⊕a=0,a⊕0=a
- 01trie Ask for the biggest 、 Minimum XOR pair 、
Code
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <cmath>
#include <map>
#include <vector>
#include <set>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <sstream>
#include <unordered_map>
#define ll long long
#define ull unsigned long long
#define re return
#define pb push_back
#define Endl "\n"
#define endl "\n"
#define x first
#define y second
#define all(x) (x).begin(),(x).end()
using namespace std;
using PII = pair<int, int>;
const int N = 1e6 + 10;
const int M = 1e5 + 10;
const int mod = 1000000007;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
int dx[4] = {
-1,0,1,0};
int dy[4] = {
0,1,0,-1};
int T;
int l, r;
int a[N];
int tr[20 * (1 << 18)][2], idx;
// Each number has at most 31 position , One has N Number , Total needs 31 * N Nodes
void insert(int x) {
int p = 0;
for (int i = 20; i >= 0; i--) {
int &s = tr[p][x >> i & 1];
if (!s) s = ++idx;
p = s;
}
}
int query_mx(int x) {
int p = 0, res = 0;
for (int i = 20; i >= 0; i--) {
int s = x >> i & 1;
if (tr[p][!s]) {
res += 1 << i;
p = tr[p][!s];
} else p = tr[p][s];
}
return res;
}
int query_mn(int x) {
int p = 0, res = 0;
for (int i = 20; i >= 0; i--) {
int s = x >> i & 1;
if (tr[p][s]) {
p = tr[p][s];
} else p = tr[p][!s], res += 1 << i;
}
return res;
}
void del(int x) {
int p = 0;
for (int i = 20; i >= 0; i--) {
int s = tr[p][x >> i & 1];
tr[p][x >> i & 1] = 0;
p = s;
}
}
void solve(){
// init();
cin >> l >> r;
for (int i = l; i <= r; i++){
cin >> a[i];
insert(a[i]);
}
for (int i = l; i <= r; i++){
int x = (a[i] ^ l);
int maxx = (query_mx(x));
int minn = (query_mn(x));
//cout << x << " " << maxx << " " << minn << "\n";
if(maxx == r && minn == l){
cout << x << '\n';
break;
}
}
for (int i = l; i <= r; i++)
del(a[i]);
//idx = 0;
}
int main(){
// ios::sync_with_stdio(false), cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
T = 1;
cin >> T;
while(T--){
solve();
}
}
版权声明
本文为[INGg__]所创,转载请带上原文链接,感谢
https://yzsam.com/2022/04/202204220613560366.html
边栏推荐
- JVM中唯一一个不会发生GC和OOM的存储区域
- LeetCode - 6 - (字符串相乘、下一個更大元素<ⅠⅡⅢ>、k個一組翻轉鏈錶)
- Why is the data stored in the leaf node of the non primary key index the primary key value
- 快排与归并排序
- Cannot find interface mapping after updating HDF
- Hand tearing algorithm -- LRU cache elimination strategy, asked so often
- (4) Character set in SQL Server (collation)
- C language | preprocessing
- Vivado generates and invokes EDF netlist files
- Interviewers often ask about the general process and special circumstances of object allocation
猜你喜欢

详解冒泡序列与数组名

顺序表之高速缓存命中率

L2-001 紧急救援 (最短路Dijkstra的扩展 - 最短路径数&路径最大权值)

What is the internal structure of stack frame?

LeetCode - 8 - (三数之和、Z字形变换、两数之和<链表>、盛最多水的容器、电话号码的字母组合)
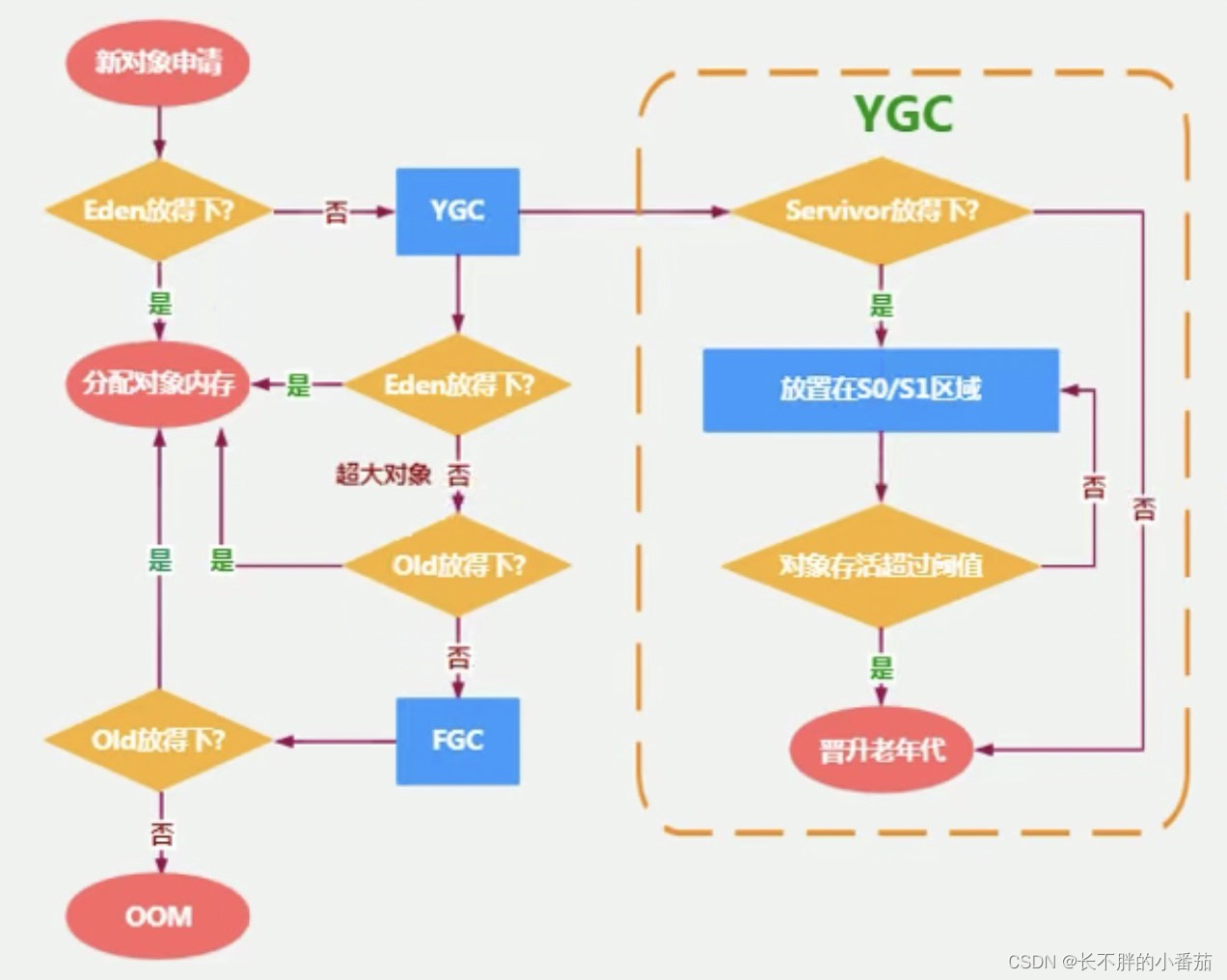
面试官常问的,对象分配的一般过程及特殊情况

Anaconda安装与使用
Cannot find interface mapping after updating HDF

Host cannot Ping virtual machine in bridging mode

带环链表详解
随机推荐
Codeforces Round #610 (Div. 2)
Leetcode - 6 - (chaîne multiplicatrice, prochain élément plus grand < Ⅰ Ⅱ Ⅲ >, K liste de chaînes inversées)
CF1547E Air Conditioners
Detailed tree array template -- Theory and code implementation
[number theory] prime number (V): Mason prime number (lucas_lehmer decision method)
[DRC RTSTAT-1] Unrouted nets: 1 net(s) are unrouted
Relationship between A5 transceiver signal VOD and pre emphasis adjustment
Codeforces Round #634 (Div. 3)
Singleton pool, singleton bean, singleton mode
C language | preprocessing
Some mechanisms of synchronized lock optimization (lock upgrade)
A.Binary Seating (概率) (2021年度训练联盟热身训练赛第五场)
The only storage area in the JVM where GC and oom will not occur
SQL复习语法笔记整理,新鲜出炉
C language | array
LeetCode -3 - (字符串相加、最大连续1的个数<ⅠⅢ>、考试的最大困扰度、删除链表的倒数第N个结点)
[number theory] congruence (V): multivariate linear congruence equation
区间求和的问题——差分
1420 · 最小覆盖子串II
JVM中的逃逸分析,可以实现不在堆上分配内存