当前位置:网站首页>堆的原理与实现以及排序
堆的原理与实现以及排序
2022-08-10 05:32:00 【cbys-1357】
1.堆的构建


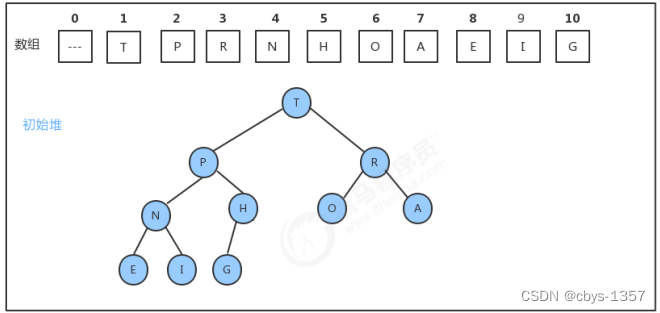









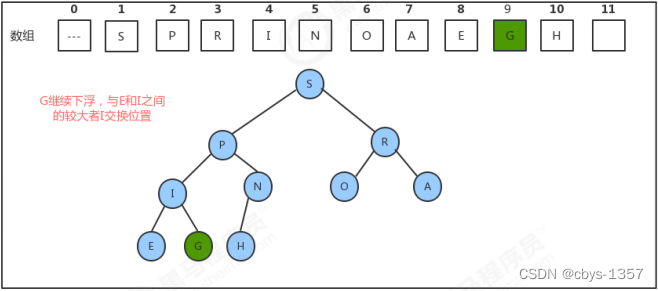
代码实现:
public class Heap<T extends Comparable<T>>{
//存储堆中的元素
private T[] items;
//记录堆中元素的个数
private int N;
// 构造方法
public Heap(int capacity) {
this.N=0;
this.items=(T[]) new Comparable[capacity];
}
// 判断堆中索引i处的元素是否小于索引j处的元素
private boolean less(int i,int j) {
return items[i].compareTo(items[j])<0;
}
// 交换元素
private void exch(int i,int j) {
T tmp=items[i];
items[i]=items[j];
items[j]=tmp;
}
// 往堆中插入一个元素
public void insert(T t) {
items[++N]=t;
swim(N);//让元素t上浮
}
// 使用上浮算法,使索引k处的元素能在堆中处于一个正确的位置
private void swim(int k) {
//如果已经到了根结点,就不需要循环了
while(k>1) {
//比较当前结点和其父结点
if(less(k/2,k)) {
//父结点小于当前结点,需要交换
exch(k/2,k);
}
k=k/2;
}
}
//删除堆中最大的元素,并返回这个最大元素
public T delMax() {
T max=items[1];
//比较当前结点和其父结点
exch(1,N);
//删除最后位置上的元素
items[N]=null;
//个数-1
N--;
sink(1);//让根结点下沉
return max;
}
//使用下沉算法,使索引k处的元素能在堆中处于一个正确的位置
private void sink(int k) {
//如果当前已经是最底层了,就不需要循环了
while(2*k<=N) {
//找到子结点中的较大者
int max;
//若右子结点存在,找到子结点最大值
if(2*k+1<=N) {
if(less(2*k,2*k+1)) {
max=2*k+1;
}else {
max=2*k;
}
}else {//右结点不存在,直接将左结点点赋值给最大值
max=2*k;
}
//比较当前结点和子结点中的较大者,如果当前结点不小,则结束循环
if(!less(k,max)) {
break;
}
//当前结点小,则交换,
exch(k,max);
k=max;
}
}
}
2.堆排序

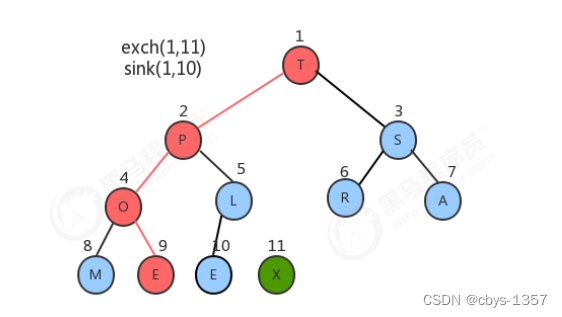




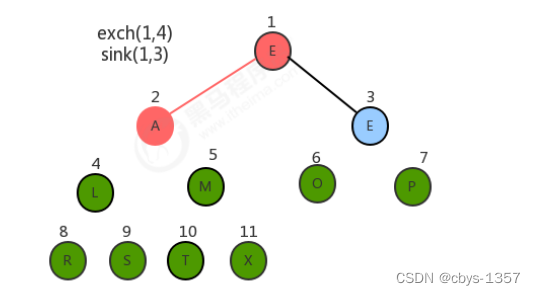

代码实现:
public class HeapSort {
private static boolean less(Comparable[] head,int i,int j) {
return head[i].compareTo(head[j])<0;
}
private static void exch(Comparable[] head,int i,int j) {
Comparable tmp=head[i];
head[i]=head[j];
head[j]=tmp;
}
//根据原数组source,构造出堆heap
private static void createHeap(Comparable[] source,Comparable[] head) {
//1.把source中的数据拷贝到heap中,从heap的1索引处开始填充
System.arraycopy(source, 0, head, 1, source.length);
//2.从heap索引的一半处开始倒叙遍历,对得到的每一个元素做下沉操作
for(int i=head.length/2;i>0;i--) {
sink(head,i,head.length-1);
}
}
//对source数组中的数据从小到大排序
public static void sort(Comparable[] source) {
//1.创建一个比原数组大1的数组
Comparable[] head=new Comparable[source.length+1];
//2.构造堆
createHeap(source,head);
//3.堆排序
//3.1定义一个变量,记录heap中未排序的所有元素中最大的索引
int N=head.length-1;
while(N!=1) {
//3.2交换heap中索引1处的元素和N处的元素
exch(head,1,N);
N--;
//3.3对索引1处的元素在0~N范围内做下沉操作
sink(head,1,N);
}
//4.heap中的数据已经有序,拷贝到source中
System.arraycopy(head, 1, source, 0, source.length);
}
//在heap堆中,对target处的元素做下沉,范围是0~range
private static void sink(Comparable[] head,int target,int range) {
while(2*target<=range) {
int max;
if(2*target+1<=range) {
if(less(head,2*target,2*target+1)) {
max=2*target+1;
}else {
max=2*target;
}
}else {
max=2*target;
}
if(!less(head,target,max)) {
break;
}
exch(head,target,max);
target=max;
}
}
}
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢

链读推荐:从瓷砖到生成式 NFT

Analysis of the investment value of domestic digital collections

最新最全的数字藏品发售日历-07.26

集合 Map

链读好文:热加密存储与冷加密存储有什么区别?
Timer (setInterval) on and off

常用类 BigDecimal

Collection工具类

Chain Reading|The latest and most complete digital collection sales calendar-07.29

Chain Reading | The latest and most complete digital collection calendar-07.28
随机推荐
【el和template区别】
impdp import data
训练集Loss收敛,但是测试集Loss震荡的厉害?
Analysis of the investment value of domestic digital collections
文章复现:超分辨率网络-VDSR
el-dropdown drop-down menu style modification, remove the small triangle
Minio分布式存储系统
安装Robotics-toolbox-matlab, for 点云坐标系转换
链读|最新最全的数字藏品发售日历-08.02
来亲自手搭一个ResNet18网络
定时器(setInterval)的开启与关闭
基本比例尺标准分幅编号流程
AWR1843型号毫米波雷达使用
R绘制图像,图像特征提取
Consensus calculation and incentive mechanism
The latest and most complete digital collection sales calendar-07.27
Bifrost 同步数据库实现微服务跨库数据同步
你不知道的常规流
链读|最新最全的数字藏品发售日历-07.29
网安超基础一周目