notion-py
Unofficial Python 3 client for Notion.so API v3.
- Object-oriented interface (mapping database tables to Python classes/attributes)
- Automatic conversion between internal Notion formats and appropriate Python objects
- Local cache of data in a unified data store (Note: disk cache now disabled by default; to enable, add
enable_caching=Truewhen initializingNotionClient) - Real-time reactive two-way data binding (changing Python object -> live updating of Notion UI, and vice-versa) (Note: Notion->Python automatic updating is currently broken and hence disabled by default; call
my_block.refresh()to update, in the meantime, while monitoring is being fixed) - Callback system for responding to changes in Notion (e.g. for triggering actions, updating another API, etc)
Read more about Notion and Notion-py on Jamie's blog
Usage
Quickstart
Note: the latest version of notion-py requires Python 3.5 or greater.
pip install notion
from notion.client import NotionClient
# Obtain the `token_v2` value by inspecting your browser cookies on a logged-in (non-guest) session on Notion.so
client = NotionClient(token_v2="<token_v2>")
# Replace this URL with the URL of the page you want to edit
page = client.get_block("https://www.notion.so/myorg/Test-c0d20a71c0944985ae96e661ccc99821")
print("The old title is:", page.title)
# Note: You can use Markdown! We convert on-the-fly to Notion's internal formatted text data structure.
page.title = "The title has now changed, and has *live-updated* in the browser!"
Concepts and notes
- We map tables in the Notion database into Python classes (subclassing
Record), with each instance of a class representing a particular record. Some fields from the records (liketitlein the example above) have been mapped to model properties, allowing for easy, instantaneous read/write of the record. Other fields can be read with thegetmethod, and written with thesetmethod, but then you'll need to make sure to match the internal structures exactly. - The tables we currently support are block (via
Blockclass and its subclasses, corresponding to differenttypeof blocks), space (viaSpaceclass), collection (viaCollectionclass), collection_view (viaCollectionViewand subclasses), and notion_user (viaUserclass). - Data for all tables are stored in a central
RecordStore, with theRecordinstances not storing state internally, but always referring to the data in the centralRecordStore. Many API operations return updating versions of a large number of associated records, which we use to update the store, so the data inRecordinstances may sometimes update without being explicitly requested. You can also call therefreshmethod on aRecordto trigger an update, or passforce_updateto methods likeget. - The API doesn't have strong validation of most data, so be careful to maintain the structures Notion is expecting. You can view the full internal structure of a record by calling
myrecord.get()with no arguments. - When you call
client.get_block, you can pass in either an ID, or the URL of a page. Note that pages themselves are justblocks, as are all the chunks of content on the page. You can get the URL for a block within a page by clicking "Copy Link" in the context menu for the block, and pass that URL intoget_blockas well.
Updating records
We keep a local cache of all data that passes through. When you reference an attribute on a Record, we first look to that cache to retrieve the value. If it doesn't find it, it retrieves it from the server. You can also manually refresh the data for a Record by calling the refresh method on it. By default (unless we instantiate NotionClient with monitor=False), we also subscribe to long-polling updates for any instantiated Record, so the local cache data for these Records should be automatically live-updated shortly after any data changes on the server. The long-polling happens in a background daemon thread.
Example: Traversing the block tree
for child in page.children:
print(child.title)
print("Parent of {} is {}".format(page.id, page.parent.id))
Example: Adding a new node
from notion.block import TodoBlock
newchild = page.children.add_new(TodoBlock, title="Something to get done")
newchild.checked = True
Example: Deleting nodes
# soft-delete
page.remove()
# hard-delete
page.remove(permanently=True)
Example: Create an embedded content type (iframe, video, etc)
from notion.block import VideoBlock
video = page.children.add_new(VideoBlock, width=200)
# sets "property.source" to the URL, and "format.display_source" to the embedly-converted URL
video.set_source_url("https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=oHg5SJYRHA0")
Example: Create a new embedded collection view block
collection = client.get_collection(COLLECTION_ID) # get an existing collection
cvb = page.children.add_new(CollectionViewBlock, collection=collection)
view = cvb.views.add_new(view_type="table")
# Before the view can be browsed in Notion,
# the filters and format options on the view should be set as desired.
#
# for example:
# view.set("query", ...)
# view.set("format.board_groups", ...)
# view.set("format.board_properties", ...)
Example: Moving blocks around
# move my block to after the video
my_block.move_to(video, "after")
# move my block to the end of otherblock's children
my_block.move_to(otherblock, "last-child")
# (you can also use "before" and "first-child")
Example: Subscribing to updates
(Note: Notion->Python automatic updating is currently broken and hence disabled by default; call my_block.refresh() to update, in the meantime, while monitoring is being fixed)
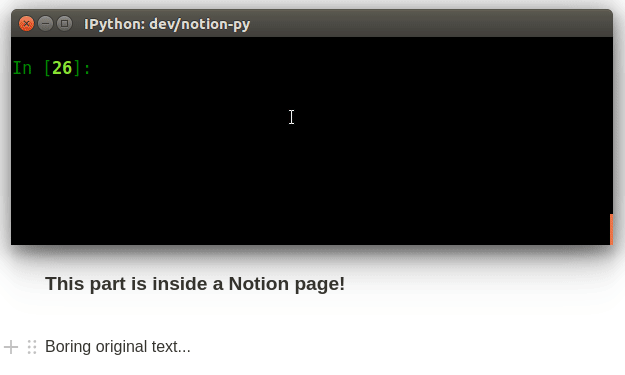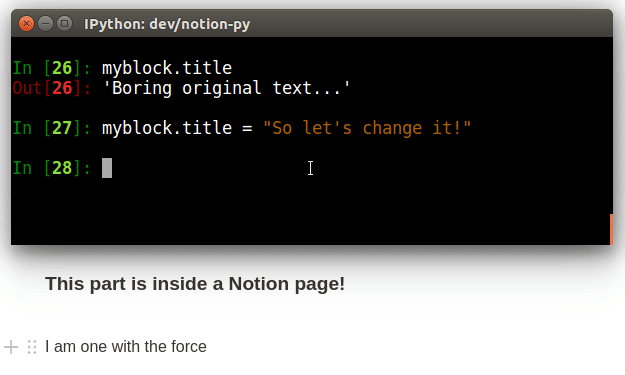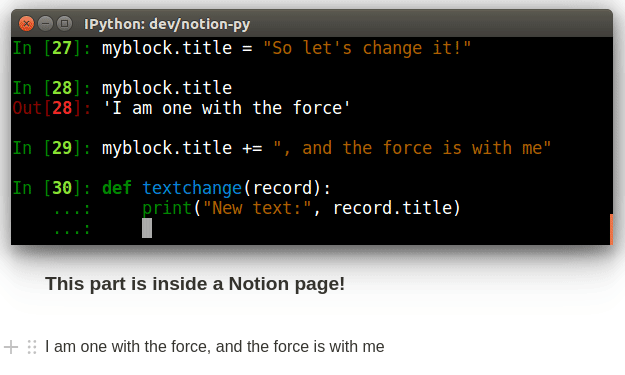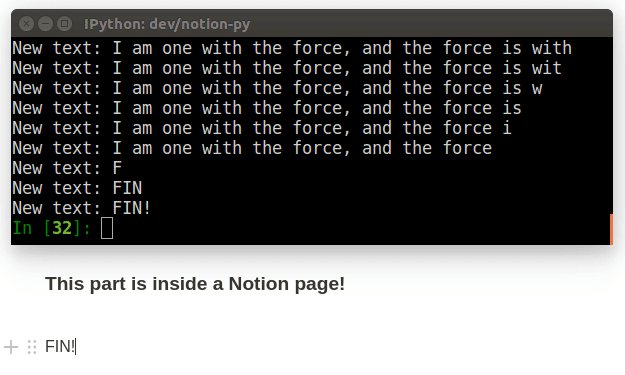
We can "watch" a Record so that we get a callback whenever it changes. Combined with the live-updating of records based on long-polling, this allows for a "reactive" design, where actions in our local application can be triggered in response to interactions with the Notion interface.
# define a callback (note: all arguments are optional, just include the ones you care about)
def my_callback(record, difference):
print("The record's title is now:" record.title)
print("Here's what was changed:")
print(difference)
# move my block to after the video
my_block.add_callback(my_callback)
Example: Working with databases, aka "collections" (tables, boards, etc)
Here's how things fit together:
- Main container block:
CollectionViewBlock(inline) /CollectionViewPageBlock(full-page)Collection(holds the schema, and is parent to the database rows themselves)CollectionRowBlockCollectionRowBlock- ... (more database records)
CollectionView(holds filters/sort/etc about each specific view)
Note: For convenience, we automatically map the database "columns" (aka properties), based on the schema defined in the Collection, into getter/setter attributes on the CollectionRowBlock instances. The attribute name is a "slugified" version of the name of the column. So if you have a column named "Estimated value", you can read and write it via myrowblock.estimated_value. Some basic validation may be conducted, and it will be converted into the appropriate internal format. For columns of type "Person", we expect a User instance, or a list of them, and for a "Relation" we expect a singular/list of instances of a subclass of Block.
# Access a database using the URL of the database page or the inline block
cv = client.get_collection_view("https://www.notion.so/myorg/8511b9fc522249f79b90768b832599cc?v=8dee2a54f6b64cb296c83328adba78e1")
# List all the records with "Bob" in them
for row in cv.collection.get_rows(search="Bob"):
print("We estimate the value of '{}' at {}".format(row.name, row.estimated_value))
# Add a new record
row = cv.collection.add_row()
row.name = "Just some data"
row.is_confirmed = True
row.estimated_value = 399
row.files = ["https://www.birdlife.org/sites/default/files/styles/1600/public/slide.jpg"]
row.person = client.current_user
row.tags = ["A", "C"]
row.where_to = "https://learningequality.org"
# Run a filtered/sorted query using a view's default parameters
result = cv.default_query().execute()
for row in result:
print(row)
# Run an "aggregation" query
aggregations = [{
"property": "estimated_value",
"aggregator": "sum",
"id": "total_value",
}]
result = cv.build_query(aggregate=aggregate_params).execute()
print("Total estimated value:", result.get_aggregate("total_value"))
# Run a "filtered" query (inspect network tab in browser for examples, on queryCollection calls)
filter_params = {
"filters": [{
"filter": {
"value": {
"type": "exact",
"value": {"table": "notion_user", "id": client.current_user.id}
},
"operator": "person_contains"
},
"property": "assigned_to"
}],
"operator": "and"
}
result = cv.build_query(filter=filter_params).execute()
print("Things assigned to me:", result)
# Run a "sorted" query
sort_params = [{
"direction": "descending",
"property": "estimated_value",
}]
result = cv.build_query(sort=sort_params).execute()
print("Sorted results, showing most valuable first:", result)
Note: You can combine filter, aggregate, and sort. See more examples of queries by setting up complex views in Notion, and then inspecting the full query: cv.get("query2").
You can also see more examples in action in the smoke test runner. Run it using:
python run_smoke_test.py --page [YOUR_NOTION_PAGE_URL] --token [YOUR_NOTION_TOKEN_V2]
Example: Lock/Unlock A Page
from notion.client import NotionClient
# Obtain the `token_v2` value by inspecting your browser cookies on a logged-in session on Notion.so
client = NotionClient(token_v2="<token_v2>")
# Replace this URL with the URL of the page or database you want to edit
page = client.get_block("https://www.notion.so/myorg/Test-c0d20a71c0944985ae96e661ccc99821")
# The "locked" property is available on PageBlock and CollectionViewBlock objects
# Set it to True to lock the page/database
page.locked = True
# and False to unlock it again
page.locked = False
Example: Set the current user for multi-account user
from notion.client import NotionClient
client = NotionClient(token_v2="<token_v2>")
# The initial current_user of a multi-account user may be an unwanted user
print(client.current_user.email) # → [email protected]
# Set current_user to the desired user
client.set_user_by_email('[email protected]')
print(client.current_user.email) # → [email protected]
# You can also set the current_user by uid.
client.set_user_by_uid('<uid>')
print(client.current_user.email) # → [email protected]
Quick plug: Learning Equality needs your support!
If you'd like to support notion-py development, please consider donating to my open-source nonprofit, Learning Equality, since when I'm not working on notion-py, it probably means I'm heads-down fundraising for our global education work (bringing resources like Khan Academy to communities with no Internet). COVID has further amplified needs, with over a billion kids stuck at home, and over half of them without the connectivity they need for distance learning. You can now also support our work via GitHub Sponsors!
Related Projects
- md2notion: import Markdown files to Notion
- notion-export-ics: Export Notion Databases to ICS calendar files
- notion-tqdm: Progress Bar displayed in Notion like tqdm
TODO
- Cloning pages hierarchically
- Debounce cache-saving?
- Support inline "user" and "page" links, and reminders, in markdown conversion
- Utilities to support updating/creating collection schemas
- Utilities to support updating/creating collection_view queries
- Support for easily managing page permissions
- Websocket support for live block cache updating
- "Render full page to markdown" mode
- "Import page from html" mode