coloredlogs: Colored terminal output for Python's logging module
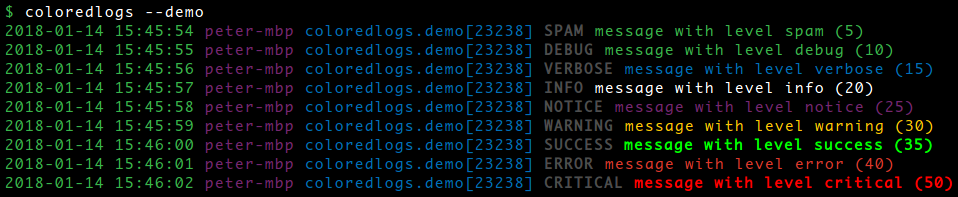
The coloredlogs package enables colored terminal output for Python's logging module. The ColoredFormatter class inherits from logging.Formatter and uses ANSI escape sequences to render your logging messages in color. It uses only standard colors so it should work on any UNIX terminal. It's currently tested on Python 2.7, 3.5+ and PyPy (2 and 3). On Windows coloredlogs automatically tries to enable native ANSI support (on up-to-date Windows 10 installations) and falls back on using colorama (if installed). Here is a screen shot of the demo that is printed when the command coloredlogs --demo is executed:
Note that the screenshot above includes custom logging levels defined by my verboselogs package: if you install both coloredlogs and verboselogs it will Just Work (verboselogs is of course not required to use coloredlogs).
Installation
The coloredlogs package is available on PyPI which means installation should be as simple as:
$ pip install coloredlogs
There's actually a multitude of ways to install Python packages (e.g. the per user site-packages directory, virtual environments or just installing system wide) and I have no intention of getting into that discussion here, so if this intimidates you then read up on your options before returning to these instructions
Optional dependencies
Native ANSI support on Windows requires an up-to-date Windows 10 installation. If this is not working for you then consider installing the colorama package:
$ pip install colorama
Once colorama is installed it will be used automatically.
Usage
Here's an example of how easy it is to get started:
import coloredlogs, logging
# Create a logger object.
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
# By default the install() function installs a handler on the root logger,
# this means that log messages from your code and log messages from the
# libraries that you use will all show up on the terminal.
coloredlogs.install(level='DEBUG')
# If you don't want to see log messages from libraries, you can pass a
# specific logger object to the install() function. In this case only log
# messages originating from that logger will show up on the terminal.
coloredlogs.install(level='DEBUG', logger=logger)
# Some examples.
logger.debug("this is a debugging message")
logger.info("this is an informational message")
logger.warning("this is a warning message")
logger.error("this is an error message")
logger.critical("this is a critical message")
Format of log messages
The ColoredFormatter class supports user defined log formats so you can use any log format you like. The default log format is as follows:
%(asctime)s %(hostname)s %(name)s[%(process)d] %(levelname)s %(message)s
This log format results in the following output:
2015-10-23 03:32:22 peter-macbook coloredlogs.demo[30462] DEBUG message with level 'debug' 2015-10-23 03:32:23 peter-macbook coloredlogs.demo[30462] VERBOSE message with level 'verbose' 2015-10-23 03:32:24 peter-macbook coloredlogs.demo[30462] INFO message with level 'info' ...
You can customize the log format and styling using environment variables as well as programmatically, please refer to the online documentation for details.
Enabling millisecond precision
If you're switching from logging.basicConfig() to coloredlogs.install() you may notice that timestamps no longer include milliseconds. This is because coloredlogs doesn't output milliseconds in timestamps unless you explicitly tell it to. There are three ways to do that:
The easy way is to pass the milliseconds argument to coloredlogs.install():
coloredlogs.install(milliseconds=True)
This became supported in release 7.1 (due to #16).
Alternatively you can change the log format to include 'msecs':
%(asctime)s,%(msecs)03d %(hostname)s %(name)s[%(process)d] %(levelname)s %(message)s
Here's what the call to coloredlogs.install() would then look like:
coloredlogs.install(fmt='%(asctime)s,%(msecs)03d %(hostname)s %(name)s[%(process)d] %(levelname)s %(message)s')
Customizing the log format also enables you to change the delimiter that separates seconds from milliseconds (the comma above). This became possible in release 3.0 which added support for user defined log formats.
If the use of
%(msecs)disn't flexible enough you can instead add%fto the date/time format, it will be replaced by the value of%(msecs)03d. Support for the%fdirective was added to release 9.3 (due to #45).
Custom logging fields
The following custom log format fields are supported:
%(hostname)sprovides the hostname of the local system.%(programname)sprovides the name of the currently running program.%(username)sprovides the username of the currently logged in user.
When coloredlogs.install() detects that any of these fields are used in the format string the applicable logging.Filter subclasses are automatically registered to populate the relevant log record fields.
Changing text styles and colors
The online documentation contains an example of customizing the text styles and colors.
Colored output from cron
When coloredlogs is used in a cron job, the output that's e-mailed to you by cron won't contain any ANSI escape sequences because coloredlogs realizes that it's not attached to an interactive terminal. If you'd like to have colors e-mailed to you by cron there are two ways to make it happen:
Modifying your crontab
Here's an example of a minimal crontab:
MAILTO="[email protected]" CONTENT_TYPE="text/html" * * * * * root coloredlogs --to-html your-command
The coloredlogs program is installed when you install the coloredlogs Python package. When you execute coloredlogs --to-html your-command it runs your-command under the external program script (you need to have this installed). This makes your-command think that it's attached to an interactive terminal which means it will output ANSI escape sequences which will then be converted to HTML by the coloredlogs program. Yes, this is a bit convoluted, but it works great :-)
Modifying your Python code
The ColoredCronMailer class provides a context manager that automatically enables HTML output when the $CONTENT_TYPE variable has been correctly set in the crontab.
This requires my capturer package which you can install using pip install 'coloredlogs[cron]'. The [cron] extra will pull in capturer 2.4 or newer which is required to capture the output while silencing it - otherwise you'd get duplicate output in the emails sent by cron.
The context manager can also be used to retroactively silence output that has already been produced, this can be useful to avoid spammy cron jobs that have nothing useful to do but still email their output to the system administrator every few minutes :-).
Contact
The latest version of coloredlogs is available on PyPI and GitHub. The online documentation is available on Read The Docs and includes a changelog. For bug reports please create an issue on GitHub. If you have questions, suggestions, etc. feel free to send me an e-mail at [email protected].
License
This software is licensed under the MIT license.
© 2020 Peter Odding.