当前位置:网站首页>Kubernetes cluster installation based on Kirin SP10 server version
Kubernetes cluster installation based on Kirin SP10 server version
2022-04-23 02:07:00 【Studio 16】
Kubernetes Cluster installation
1、 planning

2、 System initialization
(1) by master、node1 and node2 Node setting host name .
[root@master ~]# hostnamectl set-hostname master
[root@master ~]# bash
[root@ node1 ~]# hostnamectl set-hostname node1
[root@ node1 ~]# bash
[root@ node2 ~]# hostnamectl set-hostname node2
[root@ node2 ~]# bash
(2) by master、node1 and node2 Node configuration IP Address .
[root@master ~]# nmcli connection modify ens33 ipv4.addresses 192.168.82.10/24 ipv4.gateway 192.168.82.254 ipv4.dns 192.168.82.254,114.114.114.114 ipv4.method manual autoconnect yes
[root@master ~]# nmcli connection up ens33
[root@node1 ~]# nmcli connection modify ens33 ipv4.addresses 192.168.82.20/24 ipv4.gateway 192.168.82.254 ipv4.dns 192.168.82.254,114.114.114.114 ipv4.method manual autoconnect yes
[root@node1 ~]# nmcli connection up ens33
[root@node2 ~]# nmcli connection modify ens33 ipv4.addresses 192.168.82.21/24 ipv4.gateway 192.168.82.254 ipv4.dns 192.168.82.254,114.114.114.114 ipv4.method manual autoconnect yes
[root@node2 ~]# nmcli connection up ens33
(3) Use “vim” command , modify master Node's local domain name resolution file 【/etc/hosts】, Add the domain name resolution of three nodes in the file , After the modification is completed , Use “scp” Command to copy this file to node1 and node2 node .
[root@master ~]# cat /etc/hosts
127.0.0.1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost4 localhost4.localdomain4
::1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost6 localhost6.localdomain6
192.168.82.10 master // Here is what needs to be added
192.168.82.20 node1
192.168.82.21 node2
[root@master ~]# for host in node1 node2;do scp /etc/hosts root@$host:/etc/hosts;done
Authorized users only. All activities may be monitored and reported.
hosts 100% 220 137.1KB/s 00:00
Authorized users only. All activities may be monitored and reported.
hosts 100% 220 200.8KB/s 00:00
(4) Verify the connectivity between the three nodes , Execute within three nodes “ping master” command , The normal return result indicates that the configuration is correct .
[root@master ~]# ping master -c 1
PING master (192.168.82.10) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from master (192.168.82.10): icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=0.048 ms
[root@node1 ~]# ping master -c 1
PING master (192.168.82.10) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from master (192.168.82.10): icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=1.31 ms
[root@node2 ~]# ping master -c 1
PING master (192.168.82.10) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from master (192.168.82.10): icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=1.01 ms
(5) Due to the subsequent need to upload files or mirror to node node , For ease of operation , Need to be for master The node is configured with password free login .
[root@master ~]# ssh-keygen
Generating public/private rsa key pair.
Enter file in which to save the key (/root/.ssh/id_rsa):
Enter passphrase (empty for no passphrase):
Enter same passphrase again:
Your identification has been saved in /root/.ssh/id_rsa.
Your public key has been saved in /root/.ssh/id_rsa.pub.
The key fingerprint is:
SHA256:kYn4oSZXOlbNaEeimOpqYuARrW5JIiQUxRLab0xFO+8 root@ms-student
The key's randomart image is:
+---[RSA 2048]----+
| o=. .+ . |
|.+ + + O o |
|o * + X B |
|.+ = B = . |
|+ + @ . S |
|=+ * . . |
|B.o E |
|oB |
|* |
+----[SHA256]-----+
[root@master ~]# for host in node1 node2;do ssh-copy-id $host;done
/usr/bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: Source of key(s) to be installed: "/root/.ssh/id_rsa.pub"
Authorized users only. All activities may be monitored and reported.
root@node1's password:
Number of key(s) added: 1
Now try logging into the machine, with: "ssh 'node1'"
and check to make sure that only the key(s) you wanted were added.
/usr/bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: Source of key(s) to be installed: "/root/.ssh/id_rsa.pub"
/usr/bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: attempting to log in with the new key(s), to filter out any that are already installed
/usr/bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: 1 key(s) remain to be installed -- if you are prompted now it is to install the new keys
Authorized users only. All activities may be monitored and reported.
root@node2's password:
Number of key(s) added: 1
Now try logging into the machine, with: "ssh 'node2'"
and check to make sure that only the key(s) you wanted were added.
(6) stay master、node1 and node2 node , Use “yum” Command to install Kubernetes Required dependency packages and common tools .( Operate here to master Node as an example )
[root@master ~]# yum install -y conntrack ntpdate ntp ipvsadm ipset iptables curl sysstat libseccomp wget vim net-tools git bash-completion iptables-services lrzsz
[root@master ~]# source /etc/profile
(7) stay master Node configuration clock synchronization (chronyd) service , The address of the synchronized cloud time server is 【ntp1.aliyun.com】 and 【ntp2.aliyun.com】, The network segment that allows time synchronization is 【192.168.82.0/24】, It also stipulates that even if the synchronized network time server is not available , It also allows local time to be synchronized to other clients as standard time .
[root@master ~]# vim /etc/chrony.conf
# Use public servers from the pool.ntp.org project.
# Please consider joining the pool (http://www.pool.ntp.org/join.html).
#pool pool.ntp.org iburst
#server ntp.ntsc.ac.cn iburst
server ntp1.aliyun.com iburst
server ntp2.aliyun.com iburst
#server cn.pool.ntp.org iburst
# Allow NTP client access from local network.
allow 192.168.82.0/24
# Serve time even if not synchronized to a time source.
local stratum 10
(8) When the configuration is complete , restart chronyd service , And set this service to start automatically .
[root@master ~]# systemctl restart chronyd
[root@master ~]# systemctl enable chronyd
(9) stay node1 and node2 Configuration in node chronyd service , Set the synchronization time server address to 【192.168.82.10】, Modification complete, restart chronyd service , And set the service to start automatically .( Here to node1 Node as an example )
[root@node1 ~]# cat /etc/chrony.conf
# Use public servers from the pool.ntp.org project.
# Please consider joining the pool (http://www.pool.ntp.org/join.html).
#pool pool.ntp.org iburst
server 192.168.82.10 iburst
#server cn.pool.ntp.org iburst
[root@node1 ~]# systemctl restart chronyd
[root@node1 ~]# systemctl enable chronyd
(10) Use “chronyc” Relevant command verification ,node Whether the local time of the node is synchronized normally .( Here to node1 Node as an example )
[root@node1 ~]# chronyc sources -v
210 Number of sources = 1
.-- Source mode '^' = server, '=' = peer, '#' = local clock.
/ .- Source state '*' = current synced, '+' = combined , '-' = not combined,
| / '?' = unreachable, 'x' = time may be in error, '~' = time too variable.
|| .- xxxx [ yyyy ] +/- zzzz
|| Reachability register (octal) -. | xxxx = adjusted offset,
|| Log2(Polling interval) --. | | yyyy = measured offset,
|| \ | | zzzz = estimated error.
|| | | \
MS Name/IP address Stratum Poll Reach LastRx Last sample
===============================================================================
^* master 3 6 17 40 +14us[ +139us] +/- 9638us
(11) stay master、node1 and node2 Close in node 【firewalld】 service , And set the service to stop and start automatically .( Here to master Node as an example )
[root@master ~]# systemctl stop firewalld
[root@master ~]# systemctl disable firewalld
(12) stay master、node1 and node2 Enable in node 【iptables】 service , Empty 【iptables】 Service built-in rules , Set the service to start automatically .( Here to master Node as an example )
[root@master ~]# systemctl start iptables
[root@master ~]# systemctl disable iptables
[root@ master ~]# iptables -F
[root@master ~]# service iptables save
iptables: Saving firewall rules to /etc/sysconfig/iptables: [ OK ]
(13) stay master、node1 and node2 Temporary shutdown in node 【selinux】 service , And modify the configuration file corresponding to the service 【/etc/selinux/config】, modify selinux The value of the option is disabled.( Here to master Node as an example )
[root@master ~]# setenforce 0
setenforce: SELinux is disabled
[root@master ~]# getenforce
Disabled
[root@master ~]# sed -i 's/^SELINUX=.*/SELINUX=disabled/' /etc/selinux/config
## Please note , If you use “sed” Command to modify , Cannot modify path to 【/etc/sysconfig/selinux】 The file of , because “sed” The command will break the soft link .
(14) stay master、node1 and node2 Disable swap partition in node , And modify the corresponding global mount configuration file 【/etc/fstab】, Notes the entry of the swap partition .( Here to master Node as an example )
[root@master ~]# swapoff -a
[root@master ~]# sed -i '/ swap / s/^\(.*\)$/#\1/g' /etc/fstab
(15) stay master、node1 and node2 Middle note adjusts kernel parameters . Use “vim” Command in 【~】 Create under directory 【kubernetes.conf】 file , Write corresponding parameters , And copy the file to 【/etc/sysctl.d】 Under the table of contents .( Here to master Node as an example )
[root@master ~]# vim kubernetes.conf
net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-iptables=1 # Forward packets from the kernel bridge to iptables Handle
net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-ip6tables=1
net.ipv4.ip_forward=1 # Turn on route forwarding
net.ipv4.tcp_tw_recycle=0 # close TIME_WAIT Quick recycle of socket
net.netfilter.nf_conntrack_max=2310720 # Change firewall table size , Default 65536
vm.swappiness=0 # Disable swap space
vm.overcommit_memory=1 # The kernel allows all physical memory to be allocated
vm.panic_on_oom=0 # When there is not enough memory , Enable OOM
fs.inotify.max_user_instances=8192 # Modify the maximum value of user created instances
fs.inotify.max_user_watches=1048576 # Modify the maximum value of the directory that users can monitor
fs.file-max=52706963 # Adjust the system file descriptor limit
fs.nr_open=52706963 # Adjust the maximum number of file handles that the process can allocate
[root@master ~]# cp kubernetes.conf /etc/sysctl.d/kubernetes.conf
(16) stay master、node1 and node2 Node Settings 【rsyslodg】 Service and 【systemd-journald】 Combination of services , Realize the function of log persistent storage .( Here to master Node as an example )
[root@master ~]# mkdir /var/log/journal
[root@master ~]# mkdir /etc/systemd/journald.conf.d
[root@master ~]# cd /etc/systemd/journald.conf.d
[root@master journald.conf.d]# vim Jan16.conf
[Journal]
Storage=persistent
Compress=yes
SyncIntervalSec=5m
RateLimitInterval=30s
RateLimitBurst=1000
SystemMaxUse=10G
SystemMaxFileSize=200M
MaxRetentionSec=2week
ForwardToSyslog=no
(17) After configuration , Use “systemctl” Command restart 【systemd-journald】 service , And check the service status .( Here to master Node as an example )
[root@master ~]# systemctl status systemd-journald
[root@master ~]# systemctl status systemd-journald
● systemd-journald.service - Journal Service
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/systemd-journald.service; static; vendor preset: disabled)
Active: active (running) since Sun 2022-04-10 19:13:33 CST; 5h 4min ago
Docs: man:systemd-journald.service(8)
man:journald.conf(5)
Main PID: 692 (systemd-journal)
Status: "Processing requests..."
Tasks: 1
Memory: 19.5M
CGroup: /system.slice/systemd-journald.service
└─692 /usr/lib/systemd/systemd-journald
Apr 10 19:13:33 master systemd-journald[692]: Journal started
Apr 10 19:13:33 master systemd-journald[692]: Runtime Journal (/run/log/journal/8d41f69e06c5446e9b9f5d2c3c5403e0) is 8.0M, max 144.4M, 136.4M free.
Apr 10 19:13:33 master systemd[1]: systemd-journald.service: Succeeded.
Apr 10 19:13:34 master systemd-journald[692]: Time spent on flushing to /var is 143.209ms for 1789 entries.
Apr 10 19:13:34 master systemd-journald[692]: System Journal (/var/log/journal/8d41f69e06c5446e9b9f5d2c3c5403e0) is 32.0M, max 10.0G, 9.9G free.
(18) stay master、node1 and node2 Nodes use “modprobe” Add command to kernel kubernetes(kube-proxy) Modules required , Create and modify the corresponding configuration file 【/etc/sysconfig/modules/ipvs.modules】, After the system is started, the required modules will still be loaded .( Here to master Node as an example )
[root@master ~]# modprobe br_netfilter
[root@master ~]# cat /etc/sysconfig/modules/ipvs.modules
#!/bin/bash
modprobe -- ip_vs
modprobe -- ip_vs_rr
modprobe -- ip_vs_wrr
modprobe -- ip_vs_sh
modprobe -- nf_conntrack
[root@master ~]# chmod 755 /etc/sysconfig/modules/ipvs.modules
[root@master ~]# bash /etc/sysconfig/modules/ipvs.modules
(19) After the configuration file is executed , stay master、node1 and node2 Nodes use “lsmod” Command to view the modules loaded into the system .( Here to master Node as an example )
[root@master ~]# lsmod | grep -e ip_vs -e nf_conntrack
ip_vs_sh 16384 0
ip_vs_wrr 16384 0
ip_vs_rr 16384 0
ip_vs 176128 6 ip_vs_rr,ip_vs_sh,ip_vs_wrr
nf_conntrack_netlink 49152 0
nfnetlink 16384 3 nf_conntrack_netlink,nf_tables
nf_conntrack 163840 7 xt_conntrack,nf_nat,ipt_MASQUERADE,nf_nat_ipv4,xt_nat,nf_conntrack_netlink,ip_vs
nf_defrag_ipv6 20480 2 nf_conntrack,ip_vs
nf_defrag_ipv4 16384 1 nf_conntrack
libcrc32c 16384 4 nf_conntrack,nf_nat,xfs,ip_vs
3、DOCKER install
(1) stay master、node1 and node2 Nodes use “yum” Command to install DOCKER Required dependency packages .( Here to master Node as an example )
[root@master ~]# yum install -y yum-utils device-mapper-persistent-data lvm2
(2) stay master、node1 and node2 Nodes use “vim” Command addition DOCKER Required warehouse source .( Here to master Node as an example )
[root@master ~]# cd /etc/yum.repos.d/
[root@master yum.repos.d]# vim docker.repo
[Kylin-base]
name=Kylin-base
baseurl=https://mirrors.163.com/centos/7/os/$basearch
enabled=1
gpgcheck=0
[Kylin-exteas]
name=Kylin-exteas
baseurl=https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/centos/7/extras/$basearch
enabled=1
gpgcheck=0
[docker]
name=docker
baseurl=https://mirrors.163.com/docker-ce/linux/centos/7Server/x86_64/stable/
enabled=1
gpgcheck=0
(3) After adding warehouse source , stay master、node1 and node2 Nodes use “yum” Command to clear the cache and reload .( Here to master Node as an example )
[root@master ~]# yum clean all
[root@master ~]# yum makecache
Repository Kylin-base is listed more than once in the configuration
Repository Kylin-exteas is listed more than once in the configuration
Repository docker is listed more than once in the configuration
Kylin-base 14 kB/s | 3.6 kB 00:00
Kylin-exteas 570 B/s | 2.9 kB 00:05
docker 13 kB/s | 3.5 kB 00:00
Kylin Linux Advanced Server 10 - Os 21 kB/s | 3.7 kB 00:00
Kylin Linux Advanced Server 10 - Updates 574 B/s | 2.9 kB 00:05
Metadata cache created.
# Please note , If you use “wget” Order or “curl” Command to load the warehouse source , We need to pay attention to 【$releasever】 Variables and 【$basearch】 The value of the variable ,
# The version number or architecture of the domestic operating system may be different from that of other distributions ( Such as Centos、RedHat etc. ) There's a difference . Here you can put 【$releasever】 The value of the variable is forcibly changed to 7,
# stay vim In command mode, type 【:%s/\$releasever/7/g】 Replace .
The query methods of two variables are listed below :
[root@master ~]# rpm -qi kylin-release
Name : kylin-release
Version : 10
Release : 24.6.p41.ky10
Architecture: x86_64
Install Date: Sat 09 Apr 2022 10:02:28 PM CST
Group : Unspecified
Size : 147802
License : Mulan PSL v1
Signature : RSA/SHA1, Mon 24 May 2021 08:22:13 PM CST, Key ID 41f8aebe7a486d9f
Source RPM : kylin-release-10-24.6.p41.ky10.src.rpm
Build Date : Mon 24 May 2021 08:05:28 PM CST
Build Host : kojibuilder3
Packager : Kylin Linux
Vendor : KylinSoft
Summary : kylin release file
Description :
kylin release files
[root@master ~]# arch
x86_64 # Here is $basearch Value
(4) stay master、node1 and node2 Nodes use “yum” Command to install DOCKER, After installation , Use “rpm” Check whether the installation is successful with relevant commands .( Here to master Node as an example )
[root@master ~]# yum -y install docker-ce
[root@master ~]# rpm -qa | grep docker
docker-scan-plugin-0.17.0-3.el7.x86_64
docker-ce-rootless-extras-20.10.14-3.el7.x86_64
docker-ce-cli-20.10.14-3.el7.x86_64
docker-ce-20.10.14-3.el7.x86_64
(5) Apply in Huawei cloud DOCKER Speed up links .
① Access in browser 【https://activity.huaweicloud.com/】 website , Click on the homepage interface 【 Sign in 】 Button , If you don't have an account, you need to click 【 register 】 Button to register . The login interface is shown in the figure 3-1 Shown .
② After login , Enter... In the search bar at the top right 【 Container image service 】 keyword , Click in the check box that pops up 【 Container image service SWR】 Options , Pictured 3-2 Shown .
③ stay 【 Container image service SWR】 Interface , single click 【 Immediate use 】 Button , Get into 【 Container image service 】 Console , Pictured 3-3, chart 3-4 Shown .
④ Click the left navigation bar 【 Mirror resources 】-【 The mirror center 】 Button , In the pop-up 【 The mirror center 】 Interface , single click 【+ Image accelerator 】 Button , Pictured 3-5 Shown .
⑤ appear 【 Operation instructions 】 Popup , This popup describes how to configure the accelerator , The accelerator can significantly improve DOCKER The speed at which the engine downloads images , Copy the accelerator address and save , Pictured 3-6 Shown .
(6) stay master、node1 and node2 Create in node 【daemon.json】 file , adjustment DOCKER Software parameters .( Here to master Node as an example )
[root@master ~]# vim /etc/docker/daemon.json
{
"exec-opts": ["native.cgroupdriver=systemd"],
"log-driver": "json-file",
"log-opts": {
"max-size": "100m"
},
"insecure-registries": ["docker.caijunxian.top"],
"registry-mirrors":["https://27f89b97cdac4473be3d6318dfa25387.mirror.swr.myhuaweicloud.com"]
}
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
## insecure-registries: Specify the address of the private warehouse ( domain name /IP Address )
## exec-opts: Use systemd The service is right DOCKER Limit resources
## mirrors: Specify the mirror accelerator address
(7) stay master、node1 and node2 Node daemon.json When the file configuration is complete , Reload the configuration file , Then restart the DOCKER service , And set the service to start automatically .( Here to master Node as an example )
[root@master ~]# systemctl daemon-reload
[root@master ~]# systemctl restart docker
[root@master ~]# systemctl enable docker
4、 install Kubeadm
(1) stay master、node1 and node2 Nodes use “vim” Command addition Kubernetes Required warehouse source .( Here to master Node as an example )
[root@master ~]# cd /etc/yum.repos.d/
[root@master yum.repos.d]# cat kubernetes.repo
[Kylin-base]
name=Kylin-base
baseurl=https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/centos/7/os/$basearch
enabled=1
gpgcheck=0
[Kylin-exteas]
name=Kylin-exteas
baseurl=https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/centos/7/extras/$basearch
enabled=1
gpgcheck=0
[docker]
name=docker
baseurl=https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/docker-ce/linux/centos/7Server/x86_64/stable/
enabled=1
gpgcheck=0
[kubernetes]
name=kubernetes
baseurl=https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/kubernetes/yum/repos/kubernetes-el7-x86_64/
enabled=1
gpgcheck=0
(2) After adding warehouse source , stay master、node1 and node2 Nodes use “yum” Command to clear the cache and reload .( Here to master Node as an example )
[root@master yum.repos.d]# yum makecache
Repository Kylin-base is listed more than once in the configuration
Repository Kylin-exteas is listed more than once in the configuration
Repository docker is listed more than once in the configuration
Kylin-base 712 B/s | 3.6 kB 00:05
Kylin-exteas 13 kB/s | 2.9 kB 00:00
docker 676 B/s | 3.5 kB 00:05
kubernetes 532 B/s | 2.9 kB 00:05
Kylin Linux Advanced Server 10 - Os 12 kB/s | 3.7 kB 00:00
Kylin Linux Advanced Server 10 - Updates 581 B/s | 2.9 kB 00:05
Metadata cache created.
(3) stay master、node1 and node2 Nodes use “yum” Command to install kubeadm、kubectl、 kubelet service , And specify the version number as 1.20.6, After installation , Use “rpm” Check whether the installation is successful with relevant commands .( Here to master Node as an example )
[root@master ~]# yum -y install kubeadm-1.20.6 kubectl-1.20.6 kubelet-1.20.6
[root@master ~]# rpm -qa | grep kubeadm
kubeadm-1.20.6-0.x86_64
[root@master ~]# rpm -qa | grep kubectl
kubectl-1.20.6-0.x86_64
[root@master ~]# rpm -qa | grep kubelet
kubelet-1.20.6-0.x86_64
(4) stay master、node1 and node2 Nodes use “systemctl” Command settings 【kubelet】 Service starts automatically .
[root@master ~]# systemctl enable kubelet.service
(5) Before cluster installation , Need to use “kubeadm” Command view installation kubernetes Container image required by the cluster , And designate kubernetes The version number of the cluster .( Here to master Node as an example )
[root@master ~]# kubeadm config images list --kubernetes-version v1.20.6
k8s.gcr.io/kube-apiserver:v1.20.6
k8s.gcr.io/kube-controller-manager:v1.20.6
k8s.gcr.io/kube-scheduler:v1.20.6
k8s.gcr.io/kube-proxy:v1.20.6
k8s.gcr.io/pause:3.2
k8s.gcr.io/etcd:3.4.13-0
k8s.gcr.io/coredns:1.7.0
(6) The first chapter describes how to download and modify the image label , Use “rz” Command to upload the packed image compressed package to master node , Pictured x-x, chart x-x Shown .


(7) Upload to master After node , Use “tar” Command to decompress the compressed package .
[root@master ~]# tar -zxvf kubernetes-1.20.6-images.tar.gz
kubernetes-1.20.6-images/
kubernetes-1.20.6-images/coredns.tar
kubernetes-1.20.6-images/flannel.tar
kubernetes-1.20.6-images/kube-apiserver.tar
kubernetes-1.20.6-images/kube-controller-manager.tar
kubernetes-1.20.6-images/kube-proxy.tar
kubernetes-1.20.6-images/kube-scheduler.tar
kubernetes-1.20.6-images/pause.tar
kubernetes-1.20.6-images/etcd.tar
[root@master ~]# ll
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 186 Apr 9 21:30 kubernetes-1.20.6-images
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 243036265 Apr 9 21:31 kubernetes-1.20.6-images.tar.gz
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 484 Apr 9 15:30 kubernetes.conf
(8) stay mater Node usage “vim” Command to write a batch import image script 【load.sh】.
[root@master ~]# vim load.sh
#!/bin/bash
ls /root/kubernetes-1.20.6-images > /root/images.cache
for i in $(cat /root/images.cache)
do
docker load -i /root/kubernetes-1.20.6-images/$i
done
(9) After scripting , Use “chmod” Command gives script execution permission .
[root@master ~]# chmod +x load.sh
(10) stay master Node usage “scp” The command will unzip the directory 【kubernetes-1.20.6-images】 And batch import scripts 【load.sh】 Transferred to the node1 and node2 node .
[root@master ~]# for i in node1 node2;do scp -r load.sh kubernetes-1.20.6-images
root@$i:/root;done
(11) After transmission , Execute at three nodes 【load.sh】 Script .( Here to master Node as an example )
[root@master ~]# bash load.sh
(12) stay master、node1 and node2 Node to view the image upload status .( Here to master Node as an example )
[root@master ~]# docker images
REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE
k8s.gcr.io/kube-proxy v1.20.6 9a1ebfd8124d 12 months ago 118MB
k8s.gcr.io/kube-apiserver v1.20.6 b05d611c1af9 12 months ago 122MB
k8s.gcr.io/kube-scheduler v1.20.6 b93ab2ec4475 12 months ago 47.3MB
k8s.gcr.io/kube-controller-manager v1.20.6 560dd11d4550 12 months ago 116MB
k8s.gcr.io/etcd 3.4.13-0 0369cf4303ff 19 months ago 253MB
k8s.gcr.io/coredns 1.7.0 bfe3a36ebd25 22 months ago 45.2MB
k8s.gcr.io/pause 3.2 80d28bedfe5d 2 years ago 683kB
(13) stay master Node usage “kubeadm” Command to Kubernetes Cluster initialization .
[root@master ~]# kubeadm init --kubernetes-version=1.20.6 --apiserver-advertise-address=192.168.82.10 --image-repository registry.aliyuncs.com/google_containers --pod-network-cidr=10.244.0.0/16
## --kubernetes-version The parameter represents the of the specified installation Kubernetes Cluster version
## --apiserver-advertise-address The parameter represents the specified API Server's IP Address
## --image-repository The parameter represents the specified pull Kubernetes The warehouse of the image required by the cluster
## --pod-network-cidr Parameter specifies the network segment address used within the cluster
(14)Kubernetes After the cluster initialization is successful , It will prompt the operation to be completed in the next step , The code is as follows .
[init] Using Kubernetes version: v1.20.6
[preflight] Running pre-flight checks
[WARNING SystemVerification]: this Docker version is not on the list of validated versions: 20.10.14. Latest validated version: 19.03
[WARNING Service-Kubelet]: kubelet service is not enabled, please run 'systemctl enable kubelet.service'
[preflight] Pulling images required for setting up a Kubernetes cluster
[preflight] This might take a minute or two, depending on the speed of your internet connection
[preflight] You can also perform this action in beforehand using 'kubeadm config images pull'
…… Omitted code
Your Kubernetes control-plane has initialized successfully!
To start using your cluster, you need to run the following as a regular user:
mkdir -p $HOME/.kube
sudo cp -i /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf $HOME/.kube/config
sudo chown $(id -u):$(id -g) $HOME/.kube/config
Alternatively, if you are the root user, you can run:
export KUBECONFIG=/etc/kubernetes/admin.conf
You should now deploy a pod network to the cluster.
Run "kubectl apply -f [podnetwork].yaml" with one of the options listed at:
https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/cluster-administration/addons/
Then you can join any number of worker nodes by running the following on each as root:
kubeadm join 192.168.82.10:6443 --token qavo2e.p75owrp68dydx38d \
--discovery-token-ca-cert-hash sha256:c1c48d451e66f8b3eac766de82216bb3d00c9866758d4c3d258ba38dbb8ab420
(15) stay master Node according to prompt , Create the corresponding directory , And copies 【admin.conf】 File to the specified directory .
[root@master ~]# mkdir -p $HOME/.kube
[root@master ~]# sudo cp -i /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf $HOME/.kube/config
[root@master ~]# sudo chown $(id -u):$(id -g) $HOME/.kube/config
(16) According to the code prompt , stay node1 and node2 Node usage “kubeadm” Relevant command , take node Nodes join the cluster , The code is as follows .( Here to node1 Node as an example )
[root@node1 ~]# kubeadm join 192.168.82.10:6443 --token qavo2e.p75owrp68dydx38d \
> --discovery-token-ca-cert-hash sha256:c1c48d451e66f8b3eac766de82216bb3d00c9866758d4c3d258ba38dbb8ab420
[preflight] Running pre-flight checks
[WARNING SystemVerification]: this Docker version is not on the list of validated versions: 20.10.14. Latest validated version: 19.03
[WARNING Service-Kubelet]: kubelet service is not enabled, please run 'systemctl enable kubelet.service'
[preflight] Reading configuration from the cluster...
[preflight] FYI: You can look at this config file with 'kubectl -n kube-system get cm kubeadm-config -o yaml'
[kubelet-start] Writing kubelet configuration to file "/var/lib/kubelet/config.yaml"
[kubelet-start] Writing kubelet environment file with flags to file "/var/lib/kubelet/kubeadm-flags.env"
[kubelet-start] Starting the kubelet
[kubelet-start] Waiting for the kubelet to perform the TLS Bootstrap...
This node has joined the cluster:
* Certificate signing request was sent to apiserver and a response was received.
* The Kubelet was informed of the new secure connection details.
Run 'kubectl get nodes' on the control-plane to see this node join the cluster.
(17) Return as prompted master node , Use “kubeclt” Use relevant commands to view the startup status of nodes and corresponding containers in the cluster .
[root@master ~]# kubectl get nodes
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
master NotReady control-plane,master 32m v1.20.6
node1 NotReady <none> 23s v1.20.6
node2 NotReady <none> 15s v1.20.6
[root@master ~]# kubectl get pods -A
NAMESPACE NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
kube-system coredns-7f89b7bc75-fsj46 0/1 Pending 0 34m
kube-system coredns-7f89b7bc75-nfrxn 0/1 Pending 0 34m
kube-system etcd-master 1/1 Running 0 34m
kube-system kube-apiserver-master 1/1 Running 0 34m
kube-system kube-controller-manager-master 1/1 Running 0 34m
kube-system kube-proxy-g4fvd 1/1 Running 0 2m34s
kube-system kube-proxy-hj6hq 1/1 Running 0 2m27s
kube-system kube-proxy-vrntc 1/1 Running 0 34m
kube-system kube-scheduler-master 1/1 Running 0 34m
(18) It can be observed that the states of the three nodes are 【NotReady】, And the name is 【coredns】 The container is not ready , Because of installation Kubernetes After cluster , The cluster needs to provide a flat network function , At this time, you need to master、node1 and node2 Node usage “yum” Command to install Kubernetes Network components .
[root@master ~]# yum -y install kubernetes-cni-0.8.7
(19) After the software is installed , Use “rz” Command upload flannel The image compressed package required by the component to master node , And use “tar” Command to decompress . Pictured x-x Shown .

[root@master ~]# tar -zxvf flannel.tar.gz
flannel/
flannel/flannel-cni.tar
flannel/flannel.tar
flannel/kube-flannel.yml
[root@master ~]# ll
total 260056
-rw------- 1 root root 2937 Apr 9 22:08 anaconda-ks.cfg
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 72 Apr 9 22:22 flannel
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 23229933 Apr 9 22:22 flannel.tar.gz
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 112 Apr 9 22:30 images.cache
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 3211 Apr 9 22:13 initial-setup-ks.cfg
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 167 Apr 9 22:27 kubernetes-1.20.6-images
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 243036265 Apr 9 21:31 kubernetes-1.20.6-images.tar.gz
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 484 Apr 9 15:30 kubernetes.conf
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 161 Apr 9 22:30 load.sh
(20) stay master、node1 and node2 node , Use “cd” Command to enter flannel Under the table of contents , And upload the corresponding image to docker In warehouse .( Here to master Node as an example )
[root@master ~]# cd flannel/
[root@master flannel]# ls
flannel-cni.tar flannel.tar kube-flannel.yml
[root@master flannel]# docker load -i flannel-cni.tar
Loaded image: rancher/mirrored-flannelcni-flannel-cni-plugin:v1.0.1
[root@master flannel]# docker load -i flannel.tar
Loaded image: rancher/mirrored-flannelcni-flannel:v0.17.0
(21) After uploading the image , Use “kubectl” Command application directory 【kube-flannel.yml】 file .
[root@master flannel]# kubectl apply -f kube-flannel.yml
podsecuritypolicy.policy/psp.flannel.unprivileged created
clusterrole.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/flannel created
clusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/flannel created
serviceaccount/flannel created
configmap/kube-flannel-cfg created
daemonset.apps/kube-flannel-ds created
(19) When the configuration is complete , stay master The node reexamines the cluster status and container status , At this time, the status of each node of the cluster is 【Ready】, Containers in all namespaces are also in 【Running】 state .
[root@master ~]# kubectl get nodes
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
master Ready control-plane,master 37m v1.20.6
node1 Ready <none> 5m v1.20.6
node2 Ready <none> 5m v1.20.6
[root@master ~]# kubectl get pods -A
NAMESPACE NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
kube-system coredns-7f89b7bc75-6pj65 1/1 Running 1 37m
kube-system coredns-7f89b7bc75-kxfnp 1/1 Running 1 37m
kube-system etcd-master 1/1 Running 1 37m
kube-system kube-apiserver-master 1/1 Running 1 37m
kube-system kube-controller-manager-master 1/1 Running 1 37m
kube-system kube-flannel-ds-mhjf5 1/1 Running 1 37m
kube-system kube-flannel-ds-njsgv 1/1 Running 1 37m
kube-system kube-flannel-ds-r96f5 1/1 Running 1 37m
kube-system kube-proxy-9gwhr 1/1 Running 1 37m
kube-system kube-proxy-hj26k 1/1 Running 1 37m
kube-system kube-proxy-p8bzx 1/1 Running 1 37m
kube-system kube-scheduler-master 1/1 Running 1 37m
author : Cai Junxian
Typesetting : Zheng Weiqin
Preliminary examination : Lapsang souchong
To review : February 2
For more video courses, please visit “CSDN Home page of studio lecturer college on the 16th of the first month ”

版权声明
本文为[Studio 16]所创,转载请带上原文链接,感谢
https://yzsam.com/2022/04/202204220837085933.html
边栏推荐
- What is BGP server and what are its advantages?
- Gray scale range corresponding to colors (red, yellow, green, blue, purple, pink, brick red and magenta) in HSV color space
- Sqlserver data transfer to MySQL
- Quel est le fichier makefile?
- ESP32蓝牙Bluetooth Controller API介绍
- Startup of openstack service
- RuntimeError: The size of tensor a (4) must match the size of tensor b (3) at non-singleton dimensio
- JDBC cannot connect to MySQL, and the error is access denied for user 'root' @ '* * *' (using password: Yes)
- 一些使用代理IP的小技巧。
- 如何对代理IP进行分类?
猜你喜欢
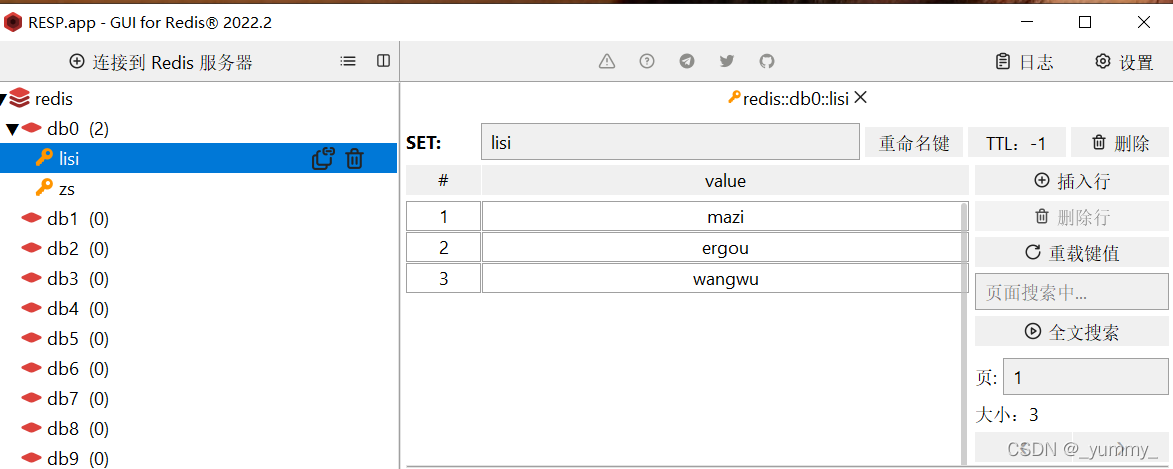
005_redis_set集合

Use Xdebug breakpoint debugging in postman

Esp32 message queue using FreeRTOS
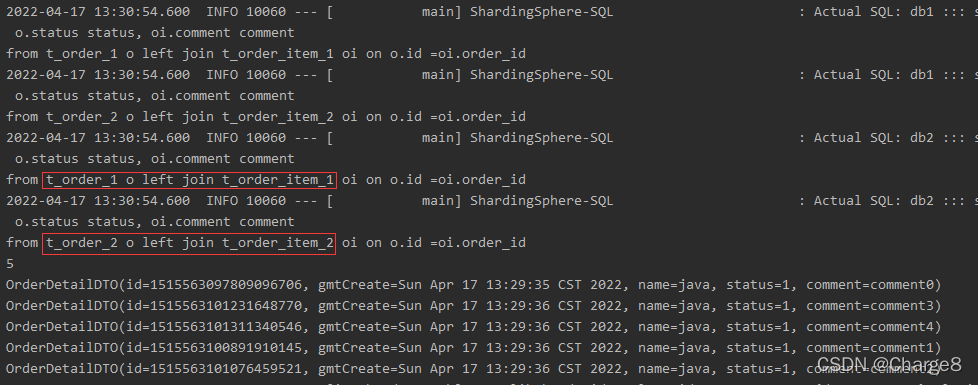
Shardingsphere broadcast table and binding table
Unicorn bio raised $3.2 million to turn prototype equipment used to grow meat into commercial products
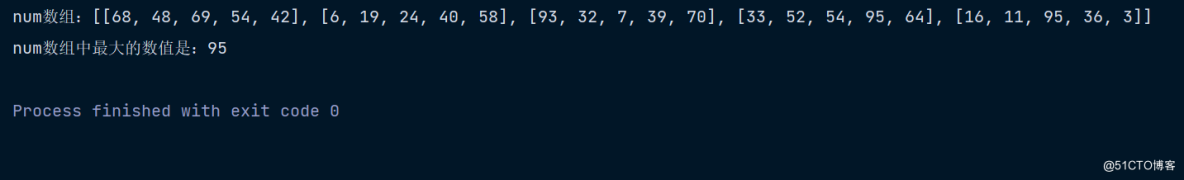
Find the largest number of two-dimensional arrays

001_redis设置存活时间

What problems will you encounter when dialing VPS?

LeetCode 447. Number of boomerangs (permutation and combination problem)

010_StringRedisTemplate
随机推荐
如何设置电脑ip?
2022.4.20-----leetcode.388
How to choose a good dial-up server?
浅析一下隧道代理IP的优缺点。
App optimization and advanced scoreboard Part 2 [Mui + flask + mongodb]
On LAN
Log4j2 configuration
2022.4.20-----leetcode. three hundred and eighty-eight
LeetCode 283. Move zero (simple, array) Day12
我国科学家揭示突破水稻产量瓶颈新机制
2022.4.10-----leetcode. eight hundred and four
Flink real-time data warehouse project - Design and implementation of DWS layer
OJ daily practice - Finish
拨号服务器是什么,有什么用处?
leetcode:27. Remove element [count remove]
NPM yarn startup error [resolved]
2018 China Collegiate Programming Contest - Guilin Site J. stone game
Uncover floating-point operations hidden by the ARM compiler
MySQL active / standby configuration binary log problem
Micro build low code zero foundation introductory course
