当前位置:网站首页>stacks and queues
stacks and queues
2022-08-06 02:41:00 【Science52】
The end of sequential and linked lists,The learning of stacks and queues begins,In fact, stacks and queues are relatively simple to understand,而且实现起来也比较简单
1.栈
1.1栈的概念及结构
栈:一种特殊的线性表,其只允许在固定的一端进行插入和删除元素操作.进行数据插入和删除操作的一端 称为栈顶,另一端称为栈底.栈中的数据元素遵守后进先出LIFO(Last In First Out)的原则.
压栈:栈的插入操作叫做进栈/压栈/入栈,入数据在栈顶.
出栈:栈的删除操作叫做出栈.出数据也在栈顶.

1.2栈的实现
栈的实现一般可以使用数组或者链表实现,相对而言数组的结构实现更优一些.因为数组在尾上插入数据的 代价比较小.

The first is the interface problem:
因为栈的特点是后进先出,So for the insertion and deletion of the stack, one case is the insertion and deletion at the end,The insertion and deletion of sequential tables are very efficient,Now let's implement the stack:
Interfaces and Structures:
typedef int STDatatype;
typedef struct Stack
{
STDatatype* a;
int top ;
int capacity;
}Stack;
void StackInit(Stack* ps);
void StackDestroy(Stack* ps);
void StackPush(Stack* ps,STDatatype x);
void StackPop(Stack* ps);
bool StackEmpty(Stack* ps);
size_t StackSize(Stack* ps);
STDatatype Stacktop(Stack* ps);
The previous sequence table is similar to the implementation of this stack,Even stacks are simpler to implement than sequential lists,这里就不多赘述,直接上代码:
void StackInit(Stack* ps)//初始化
{
ps->a = NULL;
ps->top = ps->capacity = 0;
}
void StackDestroy(Stack* ps)//栈的销毁
{
assert(ps);
free(ps->a);
ps->a = NULL;
ps->top = ps->capacity = 0;
}
void StackPush(Stack* ps,STDatatype x)//插入数据
{
assert(ps);
//判断是否增容
if (ps->top == ps->capacity)
{
int newcapacity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4 : ps->capacity * 2;
STDatatype* tmp = (STDatatype*)realloc(ps->a, newcapacity * sizeof(STDatatype));
if (tmp == NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail");
exit(-1);
}
else
{
ps->a = tmp;
ps->capacity = newcapacity;
}
}
ps->a[ps->top] = x;
ps->top++;
}
void StackPop(Stack* ps)//出栈
{
assert(ps);
assert(!StackEmpty(ps));//判断栈是否为空,为空则不能删除
--ps->top;
}
bool StackEmpty(Stack* ps)//判断栈是否为空
{
assert(ps);
return ps->top == 0;
}
size_t StackSize(Stack* ps)//计算栈的大小
{
assert(ps);
return ps->top;
}
STDatatype Stacktop(Stack* ps)//返回栈顶数据
{
assert(ps);
assert(!StackEmpty(ps));
return ps->a[ps->top-1];
}The last thing I want to talk about is the printing of the stack,Because only the top of the stack data is popped out of the stack,data can be printed,Therefore, the data on the top of the stack must be popped off the stack before each print:
void test1()
{
Stack s;
StackInit(&s);
StackPush(&s, 1);
StackPush(&s, 2);
printf("%d ", Stacktop(&s));
StackPop(&s);
StackPush(&s, 3);
StackPush(&s, 4);
while (!StackEmpty(&s))
{
printf("%d ", Stacktop(&s));
StackPop(&s);
}
printf("\n");
StackDestroy(&s);
}这是最后的结果:It is not difficult to find the last-in-first-out nature of stacks

2.队列
Queue is the opposite of stack,遵守先进先出的原则
2.1队列的概念及结构(Similar to queuing in life)
队列:只允许在一端进行插入数据操作,在另一端进行删除数据操作的特殊线性表,队列具有先进先出 FIFO(First In First Out) 入队列:进行插入操作的一端称为队尾 出队列:进行删除操作的一端称为队头
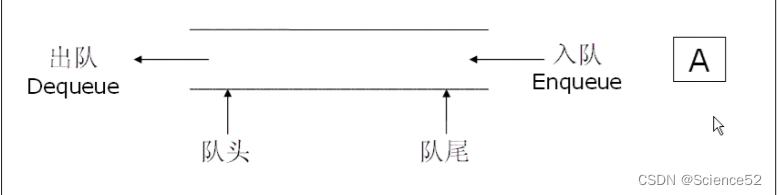
2.2队列的实现
队列也可以数组和链表的结构实现,使用链表的结构实现更优一些,因为如果使用数组的结构,出队列在数 组头上出数据,效率会比较低.
We all know that the head plug deletion of the linked list is very efficient,And if we give another tail pointer, we can implement tail insertion without traversing the linked list once,因此,The structure of the queue should be like this:
typedef int STDatatype;
typedef struct QueueNode//节点
{
STDatatype data;
struct QueueNode* next;
}QNode;
typedef struct Queue//通过结构体的方式,In this way, there is no need to pass secondary pointers to the head and tail
{
QNode* head;
QNode* tail;
int sz;//记录队列的长度
}Qe;
void QueueInit(Qe* pq);
void QueueDestroy(Qe* pq);
void QueuePush(Qe* pq,STDatatype x);
void QueuePop(Qe* pq);
bool QueueEmpty(Qe* pq);
size_t QueueSize(Qe* pq);
STDatatype QueueFront(Qe* pq);
STDatatype QueueBack(Qe* pq);The implementation of these interfaces is relatively simple,Compared with the linked list, there is a difference in the structure storing the head and tail pointers.
Let's implement the interface below:
void QueueInit(Qe* pq)//初始化
{
assert(pq);
pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;
pq->sz = 0;
}
void QueueDestroy(Qe* pq)//队列的销毁
{
assert(pq);
QNode* cur = pq->head;
while (cur)
{
pq->head = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = pq->head;
}
pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;//Not emptying the tail is a wild pointer
}
void QueuePush(Qe* pq, STDatatype x)
{
assert(pq);
QNode* newnode = (QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode));//创建节点
if (newnode == NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail");
exit(-1);
}
else
{
newnode->data = x;
newnode->next = NULL;
}
//A situation where it is plugged into its other plugs
if (pq->head == NULL)//Regardless of the situation here, the head pointer is a null pointer
{
pq->head = pq->tail = newnode;
}
else
{
pq->tail->next = newnode;
pq->tail = newnode;
}
pq->sz++;
}
void QueuePop(Qe* pq)//删除数据
{
assert(pq);
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
if (pq->head->next == NULL)//处理最后一个,Not dealing with it separately will resulttail指针是野指针
{
free(pq->head);
pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;
}
else
{
QNode* cur = pq->head;
pq->head = pq->head->next;
free(cur);
}
pq->sz--;
}
bool QueueEmpty(Qe* pq)//判断队列是否为空
{
assert(pq);
return pq->sz == 0;
}
size_t QueueSize(Qe* pq)//计算队列的大小
{
assert(pq);
return pq->sz;
}
STDatatype QueueFront(Qe* pq)//The data at the top of the queue
{
assert(pq);
return pq->head->data;
}
STDatatype QueueBack(Qe* pq)//The last data in the queue
{
assert(pq);
return pq->tail->data;
}The last test is to observe the FIFO nature of the queue by printing:
void test()
{
Qe q;
QueueInit(&q);
QueuePush(&q, 1);
QueuePush(&q, 2);
printf("%d ", QueueFront(&q));
QueuePop(&q);
QueuePush(&q, 3);
printf("%d ", QueueFront(&q));
QueuePop(&q);
QueuePush(&q, 4);
while (!QueueEmpty(&q))
{
printf("%d ", QueueFront(&q));
QueuePop(&q);
}
printf("\n");
QueueDestroy(&q);
}最后打印出来的结果:

Believe in the implementation of the stack and queue above and the printed results,You can clearly recognize the essential difference between stack and queue:栈是后进先出的,队列是先进先出的;
边栏推荐
- 软件工程-大学体育馆管理系统用例图
- CAD一键添加审图批注、AUTOCAD——图形界线怎么设置
- Use MySQL to intercept JSON string, the result is null
- 纳科星融资逾2亿美元用于电池材料生产
- ansible script 模块
- 小程序的对象监听事件
- Two implementations of vtk patch hole
- Compose Advanced Challenge is here!Live Preview|August 7th at 19:30 pm face to face with GDE instructor
- 2022/08/05 学习笔记 (day24)集合
- Harbor offline synchronization
猜你喜欢

How to make a pictogram in PPT

LeetCode Daily 2 Questions 02: Number of Palindromes (1200 each)

Wasabi Technologies adds Japanese and Australian executives to leadership team to support demand for hot cloud storage across Asia Pacific

软件工程-大学体育馆管理系统交互图

Software Engineering - University Gymnasium Management System Class Diagram

FTX交易平台收购合规加密交易所 Bitvo,打开加拿大市场
Use MySQL to intercept JSON string, the result is null

Transformer pytorch实现逐行详解
向港交所递交招股书的Soul,如何以社交元宇宙俘获万千Z世代的心?

ansible fetch 模块
随机推荐
从采集到存储:时序数据库到底怎么处理时间?
Case|Industrial Internet of Things Solutions•Industrial Internet Cloud Platform
harbor 离线同步
NRF52840-QIAA-R Nordic BLE5.0蓝牙无线收发芯片
二次开发入门须知
2022/08/05 学习笔记 (day24)集合
CAD一键添加审图批注、AUTOCAD——图形界线怎么设置
Freemodbus 移植过程记录
TS (TypeScript) variable type
基于Flask框架实现Mock Server
用低代码如何搭建一套进销存管理系统(采购、销售、库存一体化管理)?
【HCIP】BGP实验
方法区、永久代、元空间
LeetCode Daily 2 Questions 01: Flip word prefixes (both 1200 questions)
TS (TypeScript) Binary Operators + , - , * , / , % , << , >> , >>> , & , | , ^ Analysis
GET和POST的区别
vtk 补洞 两种实现
Harbor offline synchronization
相机标定 >> 坐标系转换@内参、外参
实现Redis主从复制