当前位置:网站首页>Glide监听Activity生命周期源码分析
Glide监听Activity生命周期源码分析
2022-08-10 22:13:00 【AD钙奶-lalala】
为了分析Glide源码,我们需要先引入Glide。新建一个项目,在app.build里面引入:
dependencies {
implementation 'androidx.appcompat:appcompat:1.3.0'
implementation 'com.google.android.material:material:1.4.0'
implementation 'androidx.constraintlayout:constraintlayout:2.0.4'
testImplementation 'junit:junit:4.13.2'
androidTestImplementation 'androidx.test.ext:junit:1.1.3'
androidTestImplementation 'androidx.test.espresso:espresso-core:3.4.0'
implementation 'com.github.bumptech.glide:glide:3.7.0' //Glide
}Glide基本用法:
Glide.with(this).load(url).into(imageView);
Glide的基本用法就不讲了,我们先来看Glide.with方法:
public static RequestManager with(Activity activity) {
RequestManagerRetriever retriever = RequestManagerRetriever.get();
return retriever.get(activity);
}RequestManager可以理解为Glide的管理类,而RequestManagerRetriever可以理解为管理RequestManager的类。我们来看下retriever的英文意思:

我们进上面的方法第一个get看下:
public static RequestManagerRetriever get() {
return INSTANCE;
}再来看下这个INSTANCE是什么东西?
private static final RequestManagerRetriever
INSTANCE = new RequestManagerRetriever();很明显,这是一个单例。
我们再进第二个get里面看下实现:
@TargetApi(Build.VERSION_CODES.HONEYCOMB)
public RequestManager get(Activity activity) {
if (Util.isOnBackgroundThread() ||
Build.VERSION.SDK_INT < Build.VERSION_CODES.HONEYCOMB) {
return get(activity.getApplicationContext());
} else {
assertNotDestroyed(activity);
android.app.FragmentManager fm = activity.getFragmentManager();
return fragmentGet(activity, fm);
}
}if语句里面的判断条件意思是后台线程或者SDK版本号小于11,所以我们关注else里面代码。
断言activity没有被销毁,获取activity的FragmentManager,将activity和fm作为参数传到fragmentGet方法中:
@TargetApi(Build.VERSION_CODES.HONEYCOMB)
RequestManager fragmentGet(Context context,
android.app.FragmentManager fm) {
RequestManagerFragment current = getRequestManagerFragment(fm);//1
RequestManager requestManager = current.getRequestManager();
if (requestManager == null) {
requestManager = new RequestManager(context,
current.getLifecycle(), current.getRequestManagerTreeNode());
current.setRequestManager(requestManager);
}
return requestManager;
}先来看注释1:
@TargetApi(Build.VERSION_CODES.JELLY_BEAN_MR1)
RequestManagerFragment getRequestManagerFragment(
final android.app.FragmentManager fm) {
RequestManagerFragment current =
(RequestManagerFragment) fm.findFragmentByTag(FRAGMENT_TAG);
if (current == null) {
current = pendingRequestManagerFragments.get(fm);
if (current == null) {
current = new RequestManagerFragment();
pendingRequestManagerFragments.put(fm, current);
fm.beginTransaction()
.add(current, FRAGMENT_TAG).commitAllowingStateLoss();
handler
.obtainMessage(ID_REMOVE_FRAGMENT_MANAGER, fm).sendToTarget();
}
}
return current;
}先来通过Tag找这个Fragment,如果没找到,再去pending~里面找(HashMap),如果还没有找到,就创建一个对象,然后加到activity里面。
来看RequestManagerFragment:
@TargetApi(Build.VERSION_CODES.HONEYCOMB)
public class RequestManagerFragment extends Fragment {
private final ActivityFragmentLifecycle lifecycle;
private RequestManager requestManager;
···
public RequestManagerFragment() {
this(new ActivityFragmentLifecycle());
}
// For testing only.
@SuppressLint("ValidFragment")
RequestManagerFragment(ActivityFragmentLifecycle lifecycle) {
this.lifecycle = lifecycle;
}
/**
* Sets the current {@link com.bumptech.glide.RequestManager}.
*
* @param requestManager The request manager to use.
*/
public void setRequestManager(RequestManager requestManager) {
this.requestManager = requestManager;
}
ActivityFragmentLifecycle getLifecycle() {
return lifecycle;
}
/**
* Returns the current {@link com.bumptech.glide.RequestManager} or null if none exists.
*/
public RequestManager getRequestManager() {
return requestManager;
}
@Override
public void onStart() {
super.onStart();
lifecycle.onStart();
}
@Override
public void onStop() {
super.onStop();
lifecycle.onStop();
}
@Override
public void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
lifecycle.onDestroy();
}
···
}只保留了一些核心代码,一起来看下这些核心代码解释。
我们再来重点看RequestManager的构造方法:
new RequestManager(context,
current.getLifecycle(), current.getRequestManagerTreeNode());
public RequestManager(Context context, Lifecycle lifecycle,
RequestManagerTreeNode treeNode) {
this(context, lifecycle, treeNode,
new RequestTracker(), new ConnectivityMonitorFactory());
}
RequestManager(Context context,
final Lifecycle lifecycle,
RequestManagerTreeNode treeNode,
RequestTracker requestTracker,
ConnectivityMonitorFactory factory) {
this.context = context.getApplicationContext();
this.lifecycle = lifecycle;
this.treeNode = treeNode;
this.requestTracker = requestTracker;
this.glide = Glide.get(context);
this.optionsApplier = new OptionsApplier();
ConnectivityMonitor connectivityMonitor = factory.build(context,
new RequestManagerConnectivityListener(requestTracker));
// If we're the application level request manager, we may be created on a background thread. In that case we
// cannot risk synchronously pausing or resuming requests, so we hack around the issue by delaying adding
// ourselves as a lifecycle listener by posting to the main thread. This should be entirely safe.
if (Util.isOnBackgroundThread()) {
new Handler(Looper.getMainLooper()).post(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
lifecycle.addListener(RequestManager.this);
}
});
} else {
lifecycle.addListener(this);//1
}
lifecycle.addListener(connectivityMonitor);
}传入了此Fragment的lifecycle,很明显这个lifecycle就是ActivityFragmentLifecycle。
我们再来看下这个类的源码:
class ActivityFragmentLifecycle implements Lifecycle {
private final Set<LifecycleListener> lifecycleListeners =
Collections
.newSetFromMap(new WeakHashMap<LifecycleListener, Boolean>());
private boolean isStarted;
private boolean isDestroyed;
@Override
public void addListener(LifecycleListener listener) {
lifecycleListeners.add(listener);
if (isDestroyed) {
listener.onDestroy();
} else if (isStarted) {
listener.onStart();
} else {
listener.onStop();
}
}
void onStart() {
isStarted = true;
for (LifecycleListener
lifecycleListener : Util.getSnapshot(lifecycleListeners)) {
lifecycleListener.onStart();
}
}
void onStop() {
isStarted = false;
for (LifecycleListener
lifecycleListener : Util.getSnapshot(lifecycleListeners)) {
lifecycleListener.onStop();
}
}
void onDestroy() {
isDestroyed = true;
for (LifecycleListener
lifecycleListener : Util.getSnapshot(lifecycleListeners)) {
lifecycleListener.onDestroy();
}
}
}我们来理一理:Glide.with()里面传入一个activity,with方法里面先通过单例获取一个RequestManagerRetriever对象,然后通过这个对象的get方法获取一个RequestManager对象。
而RequestManager初始化的时候传入的Lifecycle对象会调用addListener将RequestManager传入。我们来看RequestManagerFragment的生命周期里面调用:
@Override
public void onStart() {
super.onStart();
lifecycle.onStart();
}
@Override
public void onStop() {
super.onStop();
lifecycle.onStop();
}
@Override
public void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
lifecycle.onDestroy();
}每当fragment这几个生命周期触发的时候,就会调用ActivityFragmentLifecycle的对应方法。
void onStart() {
isStarted = true;
for (LifecycleListener lifecycleListener : Util.getSnapshot(lifecycleListeners)) {
lifecycleListener.onStart();
}
}
void onStop() {
isStarted = false;
for (LifecycleListener lifecycleListener : Util.getSnapshot(lifecycleListeners)) {
lifecycleListener.onStop();
}
}
void onDestroy() {
isDestroyed = true;
for (LifecycleListener lifecycleListener : Util.getSnapshot(lifecycleListeners)) {
lifecycleListener.onDestroy();
}
}这里面有调用了LifecycleListener的对应方法,典型的接口回调。Util.getSnapshot代码:
public static <T> List<T> getSnapshot(Collection<T> other) {
List<T> result = new ArrayList<T>(other.size());
for (T item : other) {
result.add(item);
}
return result;
}将Set转化成集合,其实目前的使用来看这个集合就一个对象,就是RequestManager对象。我们才想RequestManager肯定实现了LifecycleListener接口:
RequestManager implements LifecycleListener
@Override
public void onStart() {
resumeRequests();
}
@Override
public void onStop() {
pauseRequests();
}
@Override
public void onDestroy() {
requestTracker.clearRequests();
}来做一个总结吧:通过Glide.with(Activity activity)会获取一个RequestManager对象,具体with方法是这样的:先通过单例获取一个RequestManagerRetriever,然后调用这个对象的get方法返回一个RequestManager对象,这个get方法里面又获取了activity的FragmentManager,然后又将activity和这个fm传入fragmentGet方法中,这个fragmentGet里面创建了一个无界面的fragment,然后这个fargment里面持有ActivityFragmentLifecycle,这个lifecycle就监听了无界面fragment的生命周期。fragmentGet里面还做了一件事,就是将这个获取到的fragment再拿到这个fragment的lifecycle,传入RequestManager构造并返回RequestManager对象。RequestManager构造里面有一个lifecycle.addListener方法很重要,将RequestManager对象本身传入。这样fragment生命周期变化->lifecyle对应方法触发->lifecycleListener接口回调->lifecycleListener接口实现类RequestManager对应方法触发。
边栏推荐
- 服务——DNS正向反向域名解析服务
- OneNote 教程,如何在 OneNote 中整理笔记本?
- mmpose关键点(一):评价指标(PCK,OKS,mAP)
- This visual tool artifact is more intuitive and easy to use!love so much
- 文件IO-缓冲区
- What are the concepts, purposes, processes, and testing methods of interface testing?
- 带着昇腾去旅行:一日看尽金陵城里的AI胜景
- CFdiv2-Common Number-(奇偶数二分+规律)
- unusual understanding
- 过滤器
猜你喜欢
Shell 编程--Sed
2021IDEA创建web工程
![Research on multi-element N-k fault model of power system based on AC power flow (implemented by Matlab code) [Power System Fault]](/img/d0/13ae2b9987a4fff6f28607a0c01b58.gif)
Research on multi-element N-k fault model of power system based on AC power flow (implemented by Matlab code) [Power System Fault]
使用 Cloudreve 搭建私有云盘
LeetCode Daily 2 Questions 02: Reverse the words in a string (1200 each)
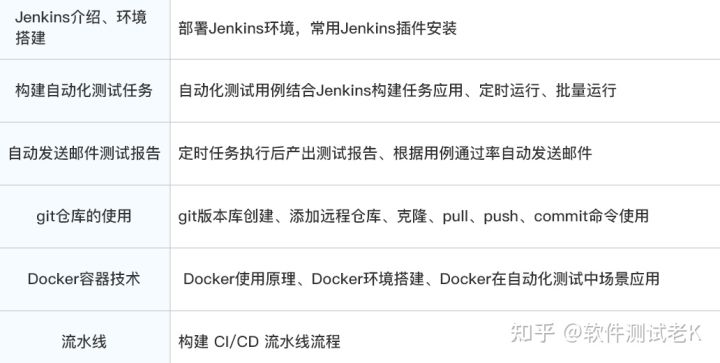
测试4年感觉和1、2年时没什么不同?这和应届生有什么区别?

Thread State 详解
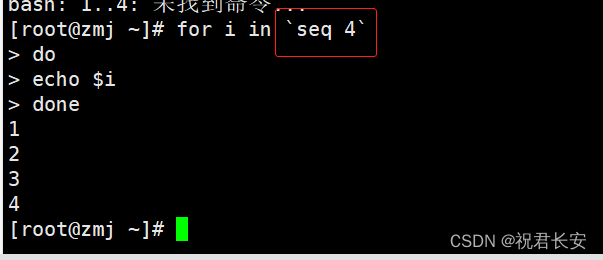
A shell script the for loop statements, while statement
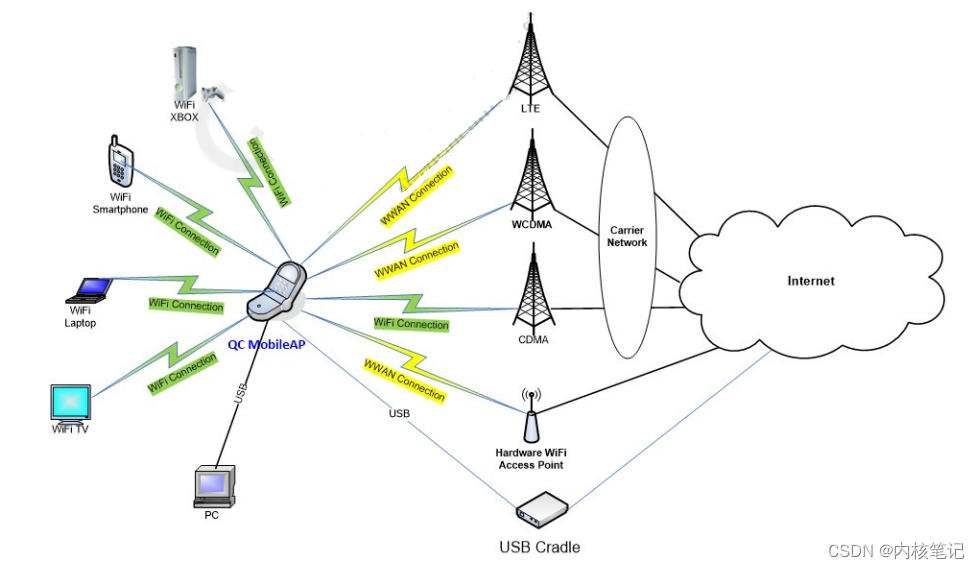
高通平台开发系列讲解(应用篇)QCMAP应用框架介绍
String类的常用方法
随机推荐
“数据引擎”开启前装规模量产新赛道,「智协慧同」崭露头角
TCP连接过程中如果拔掉网线会发生什么?
服务——DNS正向反向域名解析服务
谁是边缘计算服务的采购者?是这六个关键角色
Use Cloudreve to build a private cloud disk
Common interview questions for APP UI automation testing, maybe useful~
华为HCIE云计算之Fusion Access桌面云
BM13 determines whether a linked list is a palindrome
OneNote 教程,如何在 OneNote 中整理笔记本?
uni-app微信小程序——下拉多选框
学会开会|成为有连接感组织的重要技能
基于交流潮流的电力系统多元件N-k故障模型研究(Matlab代码实现)【电力系统故障】
What would happen if disconnecting during the process of TCP connection?
How to translate financial annual report, why choose a professional translation company?
Conditional Statements of Shell Programming (2)
camera预览流程 --- 从HAL到OEM
Translating scientific and technological papers, how to translate from Russian to Chinese
MySQL Advanced Commands
shell编程之正则表达式与文本处理器
企业云存储日常运行维护实践经验分享