当前位置:网站首页>Chapter 7 of C language programming (fifth edition of Tan Haoqiang) analysis and answer of modular programming exercises with functions
Chapter 7 of C language programming (fifth edition of Tan Haoqiang) analysis and answer of modular programming exercises with functions
2022-04-23 03:14:00 【RubyHan1314】
You can also go to the program coffee (https://meta.chengxuka.com), Open the college screen question section , There are not only answers , Explain , You can also answer questions online .
subject 1: Write two functions , Find the maximum common divisor and the minimum common multiple of two integers respectively , Call these two functions with the main function , And output the result . Two integers are entered by the keyboard .
Explain : Let two integers be u and v, The algorithm for finding the maximum common divisor by rolling division is as follows ∶
ifv>u
Put the variable u And v The value of the swap ( Make the big one u For divisor )
while(u/v The remainder of r≠0)
{
u=v ( Divisor v Become a divisor u)
v=r ( Make the remainder r Become a divisor v)
}
Output the greatest common divisor r
Minimum common multiple 1= u* v/ greatest common divisor r
You can use the following two methods ∶
Method 1 : Use two functions hcf and lcd Find the greatest common divisor and the least common multiple respectively . Enter two integers in the main function u and v, And pass it to the function hcf, The maximum common divisor is returned to the integer variable assigned by the main function h, Then take it. h And two integers u ,v Pass it to the function as an argument lcd, Find the least common multiple , Return to the main function and assign it to the integer variable l. Output the maximum common divisor and the minimum common multiple .
Write the program accordingly :
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int hef(int, int); // Function declaration
int lcd(int, int, int); // Function declaration
int u, v, h, l;
scanf("%d,%d", &u, &v);
h = hef(u, v);
printf("H.C.F=%d\n", h);
l = lcd(u, v, h);
printf("L.C.D=%d\n", l);
return 0;
}
int hef(int u, int v)
{
int t, r;
if (v > u)
{
t = u;
u = v;
v = t;
}
while ((r = u % v) != 0)
{
u = v;
v = r;
}
return (v);
}
int lcd(int u, int v, int h)
{
return (u * v / h);
}
Running results :

Input 24 and 16 Two Numbers , The maximum common divisor of program output is 8, The least common multiple is 48.
Method 2 : Using global variables . Global variables Hcf and Lcd Represent the greatest common divisor and the least common multiple respectively . Use two functions to find the maximum common divisor and the minimum common multiple , The value is not brought back by the function , It's assigned to global variables Hcf and Lcd. Output their values in the main function .
The procedure is as follows :
#include <stdio.h>
int Hcf, Lcd; // Hcf and Lcd Global variable
int main()
{
void hcf(int, int);
void lcd(int, int);
int u, v;
scanf("%d,%d", &u, &v);
hcf(u, v); // call hcf function
lcd(u, v); // call lcd function
printf("H.C.F=%d\n", Hcf);
printf("L.C.D=%d\n", Lcd);
return 0;
}
void hcf(int u, int v)
{
int t, r;
if (v > u)
{
t = u;
u = v;
v = t;
}
while ((r = u % v) != 0)
{
u = v;
v = r;
}
Hcf = v; // Assign the maximum common divisor to the global variable Hcf
}
void lcd(int u, int v)
{
Lcd = u * v / Hcf; // Assign the least common multiple to the global variable Lcd
}
The running result is the same as method 1 .
Hcf Global variable ,hcf Is the function name , The case of the two names is different , There is no confusion . stay hcf Find the maximum common divisor in the function and assign it to the global variable Hcf, stay lcd The global variable... Is referenced in the function Hcf Value , The least common multiple obtained is assigned to the global variable Lcd. Output... In the main function Hcf and Lcd Value .
subject 2: Find the equation $ ax^2+bx+c=0 $ The root of the , use 3 When two functions are solved separately :$ b^2-4ac $ Greater than 0、 be equal to 0 And less than 0 And output the result . Enter... From the main function a,b,c Value .
Explain :
Answer code :
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
float x1, x2, disc, p, q;
int main()
{
void greater_than_zero(float, float);
void equal_to_zero(float, float);
void smaller_than_zero(float, float);
float a, b, c;
printf("input a,b,c:");
scanf("%f,%f,%f", &a, &b, &c);
printf("equation:%5.2f*x*x+%5.2f*x+%5.2f=0\n", a, b, c);
disc = b * b - 4 * a * c;
printf("root:\n");
if (disc > 0)
{
greater_than_zero(a, b);
printf("x1=%f\t\tx2=%f\n", x1, x2);
}
else if (disc == 0)
{
equal_to_zero(a, b);
printf("xl=%f\t\tx2=%f\n", x1, x2);
}
else
{
smaller_than_zero(a, b);
printf("x1=%f+%fi\tx2=%f-%fi\n", p, q, p, q);
}
return 0;
}
void greater_than_zero(float a, float b)
{
x1 = (-b + sqrt(disc)) / (2 * a);
x2 = (-b - sqrt(disc)) / (2 * a);
}
void equal_to_zero(float a, float b)
{
x1 = x2 = (-b) / (2 * a);
}
void smaller_than_zero(float a, float b)
{
p = -b / (2 * a);
q = sqrt(-disc) / (2 * a);
}
Running results :
① Two unequal real roots .

② Two equal real roots .

③ The complex roots of two conjugates .

subject 3: Write a function that judges prime numbers , Enter an integer in the main function , Output information about whether it is a prime number .
Explain :
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int prime(int);
int n;
printf("input an integer:");
scanf("%d", &n);
if (prime(n))
printf("%d is a prime.\n", n);
else
printf("%d is not a prime.\n", n);
return 0;
}
int prime(int n)
{
int flag = 1, i;
for (i = 2; i < n / 2 && flag == 1; i++)
if (n % i == 0)
flag = 0;
return (flag);
}
Running results :
①

②

subject 4: Write a function , Make a given 3×3 Transpose a two-dimensional integer array , That's row and column interchange .
Explain :
Answer code :
#include <stdio.h>
#define N 3
int array[N][N];
int main()
{
void convert(int array[][3]);
int i, j;
printf("input array:\n");
for (i = 0; i < N; i++)
for (j = 0; j < N; j++)
scanf("%d", &array[i][j]);
printf("\noriginal array:\n");
for (i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < N; j++)
printf("%5d", array[i][j]);
printf("\n");
}
convert(array);
printf("convert array:\n");
for (i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < N; j++)
printf("%5d", array[i][j]);
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}
void convert(int array[][3]) // Functions that define transpose arrays
{
int i, j, t;
for (i = 0; i < N; i++)
for (j = i + 1; j < N; j++)
{
t = array[i][j];
array[i][j] = array[j][i];
array[j][i] = t;
}
}
Running results :

subject 5: Write a function , Causes an input string to be stored in reverse order , Enter and output strings in the main function .
Explain :
Answer code :
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
{
void inverse(char str[]);
char str[100];
printf("input string:");
scanf("%s", str);
inverse(str);
printf("inverse string:%s\n", str);
return 0;
}
void inverse(char str[])
{
char t;
int i, j;
for (i = 0, j = strlen(str); i < (strlen(str) / 2); i++, j--)
{
t = str[i];
str[i] = str[j - 1];
str[j - 1] = t;
}
}
Running results :

Input string ∶abcdefg, Output ∶gfedcba.
subject 6: Write a function , Connect two strings .
Explain :
Answer code :
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
{
void concatenate(char stringl[], char string2[], char string[]);
char s1[100], s2[100], s[100];
printf("input string1:");
scanf("%s", s1);
printf("input string2:");
scanf("%s", s2);
concatenate(s1, s2, s);
printf("\nThe new string is %s\n", s);
return 0;
}
void concatenate(char string1[], char string2[], char string[])
{
int i, j;
for (i = 0; string1[i] != '\0'; i++)
string[i] = string1[i];
for (j = 0; string2[j] != '\0'; j++)
string[i + j] = string2[j];
string[i + j] = '\0';
}
Running results :

Enter two strings ∶country and side, The program connects two strings into a string and outputs ;countryside.
subject 7: Write a function , Copy vowels from one string to another , Then the output .
Explain :
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
void cpy(char[], char[]);
char str[80], c[80];
printf("input string:");
gets(str);
cpy(str, c);
printf("The vowel letters are:%s\n", c);
return 0;
}
void cpy(char s[], char c[])
{
int i, j;
for (i = 0, j = 0; s[i] != '\0'; i++)
if (s[i] == 'a' || s[i] == 'A' || s[i] == 'e' || s[i] == 'E' || s[i] == 'i' || s[i] == 'I' || s[i] == 'o' || s[i] == 'O' || s[i] == 'u' || s[i] == 'U')
{
c[j] = s[i];
j++;
}
c[j] = '\0';
}
Running results :

take abcdefghijklm Vowel output in .
subject 8: Write a function , Enter a 4 Digit number , This is required to be output 4 Number characters , But there is a space between every two numbers . Such as the input 1990, The output should be "1 9 9 0".
Explain :
Answer code :
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
{
void insert(char[]);
char str[80];
printf("input four digits:");
scanf("%s", str);
insert(str);
return 0;
}
void insert(char str[])
{
int i;
for (i = strlen(str); i > 0; i--)
{
str[2 * i] = str[i];
str[2 * i - 1] = ' ';
}
printf("output:\n%s\n", str);
}
Running results :
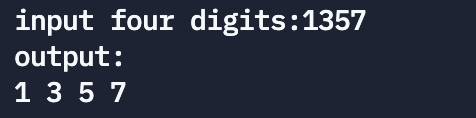
subject 9: Write a function , Pass a string from the argument , Count the letters in this string 、 Numbers 、 Number of spaces and other characters , Enter the string in the main function and output the above results .
Explain :
Answer code :
#include <stdio.h>
int letter, digit, space, others;
int main()
{
void count(char[]);
char text[80];
printf("input string:\n");
gets(text);
printf("string:");
puts(text);
letter = 0;
digit = 0;
space = 0;
others = 0;
count(text);
printf("\nletter:%d\ndigit:%d\nspace:%d\nothers:%d\n", letter, digit, space, others);
return 0;
}
void count(char str[])
{
int i;
for (i = 0; str[i] != '\0'; i++)
if ((str[i] >= 'a' && str[i] <= 'z') || (str[i] >= 'A' && str[i] <= 'Z'))
letter++;
else if (str[i] >= '0' && str[i] <= '9')
digit++;
else if (str[i] == 32)
space++;
else
others++;
}
Running results :

subject 10: Write a function , Enter a line of characters , Output the longest word in this string .
Explain : Think of a word as a string of all letters , Program setting longest The function is to find the position of the longest word . The return value of this function is the starting position of the longest word in the line of characters .longest Functional N-S Pictured graph 7.1 Shown .

chart 7.1 of use flag Indicates whether the word has started ,flag=0 Indicates that... Has not started ,flag=1 Indicates the beginning of the word ; len Represents the accumulated number of letters of the current word ; length Represents the length of the longest word in the previous word ; point Represents the starting position of the current word ( Use subscripts to indicate ); place Represents the starting position of the longest word . function alphabetic The function of is to judge whether the current character is a letter , If so, return to 1 , Otherwise return to 0 .
Answer code :
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
{
int alphabetic(char);
int longest(char[]);
int i;
char line[100];
printf("input one line:\n");
gets(line);
printf("The longest word is :");
for (i = longest(line); alphabetic(line[i]); i++)
printf("%c", line[i]);
printf("\n");
return 0;
}
int alphabetic(char c)
{
if ((c >= 'a' && c <= 'z') || (c >= 'A' && c <= 'z'))
return (1);
else
return (0);
}
int longest(char string[])
{
int len = 0, i, length = 0, flag = 1, place = 0, point;
for (i = 0; i <= strlen(string); i++)
if (alphabetic(string[i]))
if (flag)
{
point = i;
flag = 0;
}
else
len++;
else
{
flag = 1;
if (len >= length)
{
length = len;
place = point;
len = 0;
}
}
return (place);
}
Running results :

subject 11: Write a function , use " Foaming method " For the input 10 The characters are arranged in descending order .
Explain : Of the main function N-S Pictured graph 7.2 Shown .sort The function is used to sort , Its N-S Pictured graph 7.3 Shown .

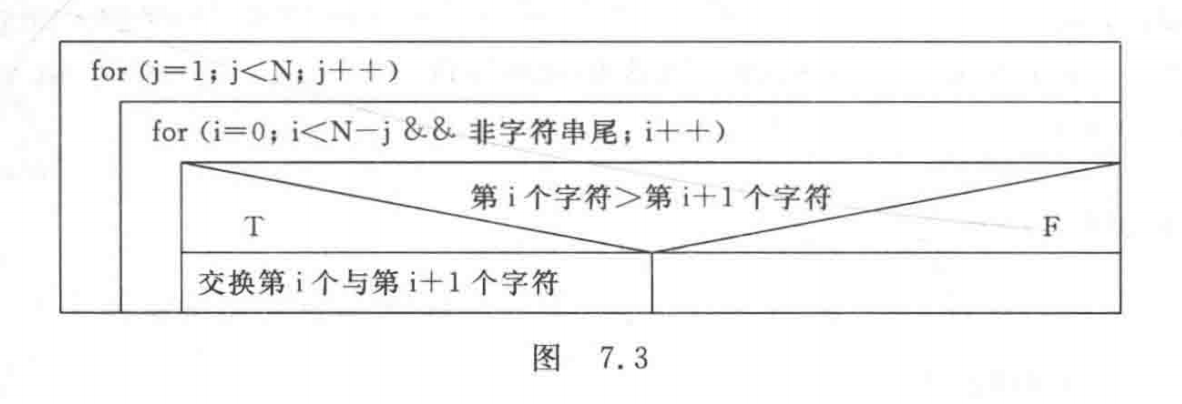
Answer code :
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#define N 10
char str[N];
int main()
{
void sort(char[]);
int i, flag;
for (flag = 1; flag == 1;)
{
printf("input string:\n");
scanf("%s", &str);
if (strlen(str) > N)
printf("string too long,input again!");
else
flag = 0;
}
sort(str);
printf("string sorted:\n");
for (i = 0; i < N; i++)
printf("%c", str[i]);
printf("\n");
return 0;
}
void sort(char str[])
{
int i, j;
char t;
for (j = 1; j < N; j++)
for (i = 0; (i < N - j) && (str[i] != '0'); i++)
if (str[i] > str[i + 1])
{
t = str[i];
str[i] = str[i + 1];
str[i + 1] = t;
}
}
Running results :

subject 12: Find the root by Newton iterative method . The equation is $ ax3+bx2+cx+d=0 $ , coefficient a,b,c,d The values of are 1,2,3,4, Input by the main function . seek x stay 1 A real root nearby . After finding the root, the main function outputs .
Explain :
Newton's iterative formula is $ x=x_0-\frac{f(x_0)}{f’(x_0)} $
among ,$ x_0 $ Is the approximate root obtained last time , At the beginning, according to the questions $ x_0=1 $( I hope to ask x stay 1 A real root nearby , So the first 1 The approximate value of times can be set to 1 ). today $ f(x)=ax3+bx2+cx+d $ , Plug in a,b,c,d Value , obtain $ f(x) =x3+2x2+3x+4 $ . $ f’(x) $ yes $ f(x) $ The derivative of , today $ f’(x)=3x^2+6x+3 . The first 1 Time Overlapping generation , . The first 1 Sub iteration , . The first 1 Time Overlapping generation , x=1-\frac{f(1)}{f’(1)}=1-\frac{1+2+3+4}{3+6+3}=1-\frac{10}{12}=0.1666666 $ . The first 2 Iterations are performed with 0.1666666 As $ x_0 $ Substitute into the iterative formula , Find out x The next approximation of . And so on , Every iteration starts with x Find the next one closer to the true value x. Iterate until $ |x-x_0|\le10^{-3} $ End of time .
Find the function of the root of the equation by Newton iterative method solut Of N-S chart , Pictured 7.4 Shown .
The procedure is as follows :
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
int main()
{
float solut(float a, float b, float c, float d);
float a, b, c, d;
printf("input a,b,c,d:");
scanf("%f,%f,%f,%f", &a, &b, &c, &d);
printf("x=%10.7f\n", solut(a, b, c, d));
return 0;
}
float solut(float a, float b, float c, float d)
{
float x = 1, x0, f, f1;
do
{
x0 = x;
f = ((a * x0 + b) * x0 + c) * x0 + d;
f1 = (3 * a * x0 + 2 * b) * x0 + c;
x = x0 - f / f1;
} while (fabs(x - x0) >= 1e-3);
return (x);
}
Running results

Input coefficient 1,2,3,4, Find the approximate root is -1.6506292.
subject 13: Find... Recursively n The value of Legendre polynomials of order , The recursive formula is
p n ( x ) = { 1 ( n = 0 ) x ( n = 1 ) ( ( 2 n − 1 ) × x − p n − 1 ( x ) − ( n − 1 ) × p n − 2 ( x ) ) / n ( n ≥ 1 ) p_n(x)= \begin{cases} 1 &(n=0)\\ x &(n=1)\\ ((2n-1)\times x-p_{n-1}(x)-(n-1)\times p_{n-2}(x))/n &(n\ge1) \end{cases} pn(x)=⎩⎪⎨⎪⎧1x((2n−1)×x−pn−1(x)−(n−1)×pn−2(x))/n(n=0)(n=1)(n≥1)
Explain : Find a recursive function p Of N-S chart , Pictured 7.5 Shown .
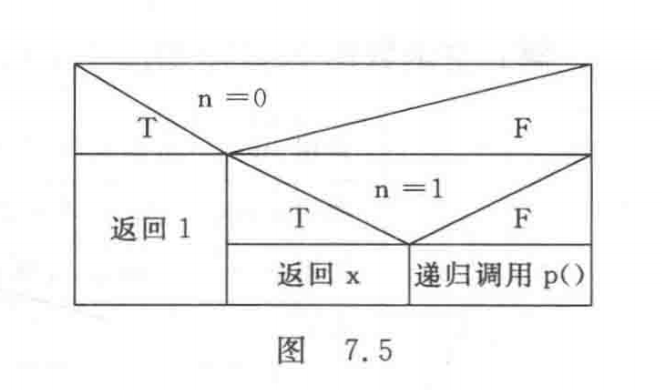
Answer code :
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int x, n;
float p(int, int);
printf("\ninput n & x:");
scanf("%d,%d", &n, &x);
printf("n=%d,x=%d\n", n, x);
printf("P%d(%d)=%6.2f\n", n, x, p(n, x));
return 0;
}
float p(int n, int x)
{
if (n == 0)
return (1);
else if (n == 1)
return (x);
else
return (2 * n - 1) * x * p((n - 1), x) - (n - 1) * p((n - 2), x) / n;
}
Running results :
①:

②:

③:

subject 14: Input 10 A student 5 Results of courses , Use functions to realize the following functions :
① Calculate the average score of each student ;
② Calculate the average score of each course ;
③ Find out all 50 The student and course with the highest score among the scores ;
④ Calculate the mean score variance ∶
σ = 1 n ∑ x i 2 − ( ∑ x i n ) 2 \sigma = \frac{1}{n} \sum x^2_i - (\frac{\sum x_i}{n})^2 σ=n1∑xi2−(n∑xi)2
among ,x; Is the average score of a student .
Explain : Of the main function N-S Pictured graph 7.6 Shown .

function input_stu The execution result is to give the whole process variable student score array score Input the initial value of each element .
function aver_stu The function of is to calculate the average score of each student , And assign the result to the whole variable array a_stu Elements in . function aver cour The function of is to calculate the average score of each course , The calculation results are stored in the whole variable array a_Cur.
function highest The return value of is the highest score ,r,c It's two global variables , Each represents the row with the highest score 、 Column number . Of this function N-S See Figure 7.7.
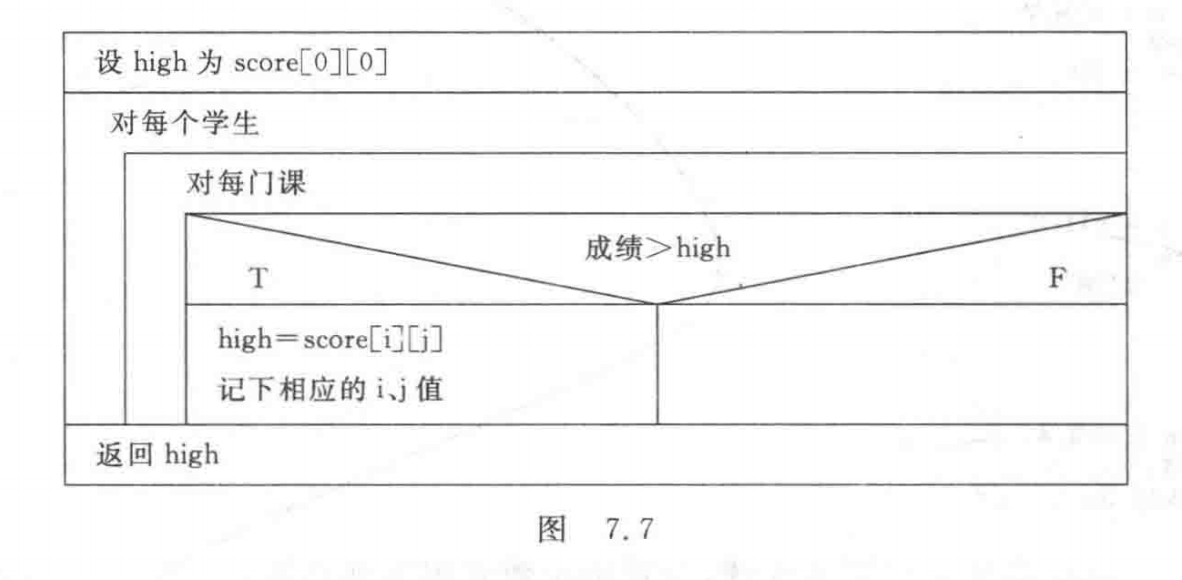
function s_var The return value of is the variance of the average score .
Answer code :
#include <stdio.h>
#define N 10
#define M 5
float score[N][M]; // Global array
float a_stu[N], a_cour[M]; // Global array
int r, c; // Global variables
int main()
{
int i, j;
float h; // Function declaration
float s_var(void); // Function declaration
float highest(); // Function declaration
void input_stu(void); // Function declaration
void aver_stu(void); // Function declaration
void aver_cour(void);
input_stu(); // Function call , Input 10 Students' grades
aver_stu(); // Function call , Calculation 10 Student GPA
aver_cour();
printf("\n NO. cour1 cour2 cour3 cour4 cour5 aver\n");
for (i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
printf("\n NO %2d", i + 1); // Output a student number
for (j = 0; j < M; j++)
printf("%8.2f", score[i][j]); // Output a student's grades in each course
printf("%8.2f\n", a_stu[i]); // Output the average score of a student
}
printf("\naverage:"); // Output 5 Average grade of each course
for (j = 0; j < M; j++)
printf("%8.2f", a_cour[j]);
printf("\n");
h = highest(); // Call function , Get the highest score and which student it belongs to 、 Which course
printf("highest:%7.2f NO. %2d course %2d\n", h, r, c); // Output the highest score and student number 、 Course no.
printf("variance %8.2f\n", s_var()); // Call function , Calculate and output variance
return 0;
}
void input_stu(void) // Input 10 A function of student achievement
{
int i, j;
for (i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
printf("\ninput score of student%2d:\n", i + 1); // Student number from 1 Start
for (j = 0; j < M; j++)
scanf("%f", &score[i][j]);
}
}
void aver_stu(void) // Calculation 10 A function of a student's average grade
{
int i, j;
float s;
for (i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
for (j = 0, s = 0; j < M; j++)
s += score[i][j];
a_stu[i] = s / 5.0;
}
}
void aver_cour(void) // Calculation 5 A function of the average grade of a course
{
int i, j;
float s;
for (j = 0; j < M; j++)
{
s = 0;
for (i = 0; i < N; i++)
s += score[i][j];
a_cour[j] = s / (float)N;
}
}
float highest() // Get the highest score and which student it belongs to 、 Which course's function
{
float high;
int i, j;
high = score[0][0];
for (i = 0; i < N; i++)
for (j = 0; j < M; j++)
if (score[i][j] > high)
{
high = score[i][j];
r = i + 1; // Array line number i from 0 Start , Student number r from 1 Start , so r=i+1
c = j + 1; // Array column number j from 0 Start , Course no. c from 1 Start , so c=j+1
}
return (high);
}
float s_var(void) // Find the function of variance
{
int i;
float sumx, sumxn;
sumx = 0.0;
sumxn = 0.0;
for (i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
sumx += a_stu[i] * a_stu[i];
sumxn += a_stu[i];
}
return (sumx / N - (sumxn / N) * (sumxn / N));
}
Running results
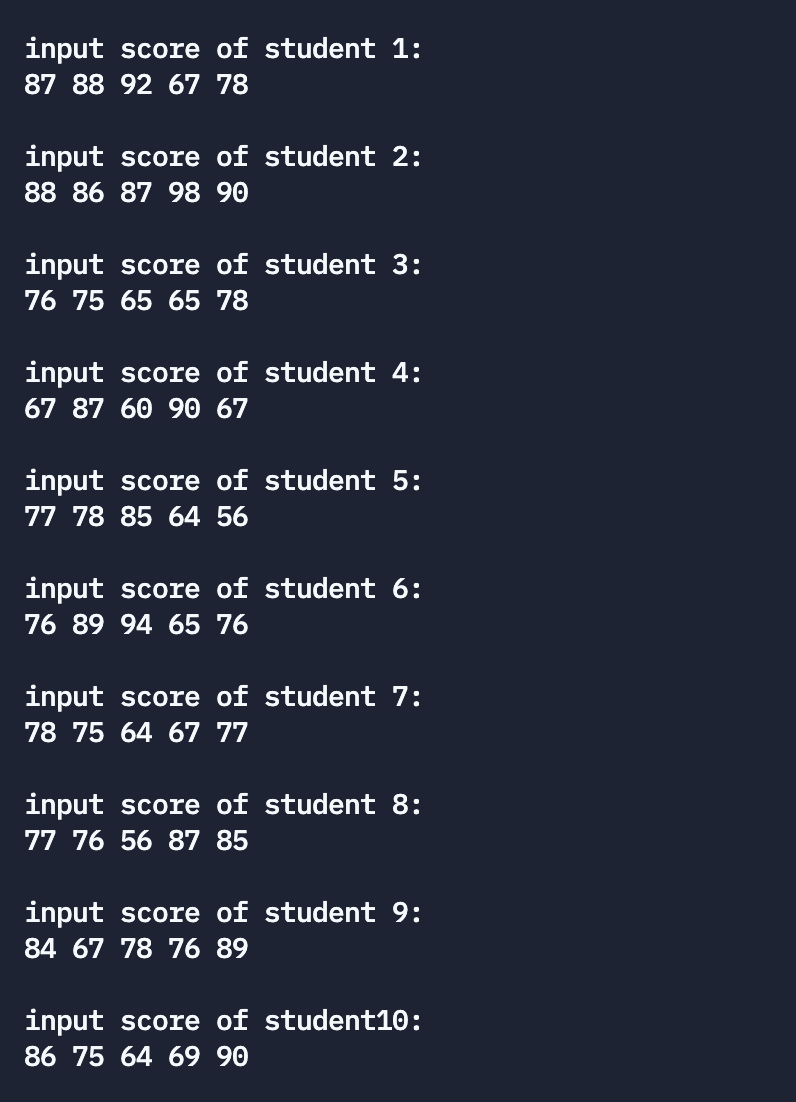
The above is the input 10 Of a student 5 Results of courses , Here is the output :

subject 15: Write several functions ∶
① Input 10 The name and number of an employee ;
② Sort by employee number from small to large , The order of names is also adjusted ;
③ An employee number is required , Find out the name of the employee by half search method ; Enter the employee number to be searched from the main function , Output the employee's name .
Explain :
input The function is to complete 10 Data entry of employees .sort The function is to sort by selection , The process is similar to the problem solving section in this book 6 Chapter one 2 topic .
search The employee name() function is used to find the employee name of the specified employee number by half searching , The search algorithm is shown in the problem solving section of this book 6 Chapter one 9 topic .
Answer code :
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#define N 10
int main()
{
void input(int[], char name[][8]);
void sort(int[], char name[][8]);
void search(int, int[], char name[][8]);
int num[N], number, flag = 1, c;
char name[N][8];
input(num, name);
sort(num, name);
while (flag == 1)
{
printf("\ninput number to look for:");
scanf("%d", &number);
search(number, num, name);
printf("continue ot not(Y/N)?");
getchar();
c = getchar();
if (c == 'N' || c == 'n')
flag = 0;
}
return 0;
}
void input(int num[], char name[N][8]) // Function of input data
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
printf("input NO.:");
scanf("%d", &num[i]);
printf("input name:");
getchar();
gets(name[i]);
}
}
void sort(int num[], char name[N][8]) // Sort function
{
int i, j, min, temp1;
char temp2[8];
for (i = 0; i < N - 1; i++)
{
min = i;
for (j = i; j < N; j++)
if (num[min] > num[j])
min = j;
temp1 = num[i];
strcpy(temp2, name[i]);
num[i] = num[min];
strcpy(name[i], name[min]);
num[min] = temp1;
strcpy(name[min], temp2);
}
printf("\n result:\n");
for (i = 0; i < N; i++)
printf("\n %5d%10s", num[i], name[i]);
}
void search(int n, int num[], char name[N][8]) // Half search function
{
int top, bott, mid, loca, sign;
top = 0;
bott = N - 1;
loca = 0;
sign = 1;
if ((n < num[0]) || (n > num[N - 1]))
loca = -1;
while ((sign == 1) && (top <= bott))
{
mid = (bott + top) / 2;
if (n == num[mid])
{
loca = mid;
printf("NO.%d,his name is %s.\n", n, name[loca]);
sign = -1;
}
else if (n < num[mid])
bott = mid - 1;
else
top = mid + 1;
}
if (sign == 1 || loca == -1)
printf("%d not been found.\n", n);
}
Running results :


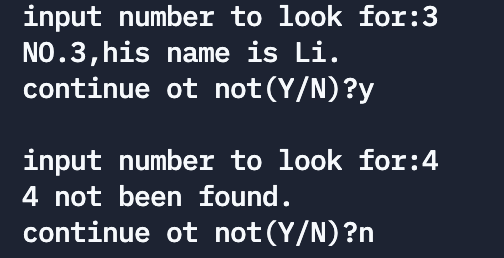
First enter 10 The number and name of an employee , Then sort according to the employee number from small to large . The inquiry employee number is 3 and 4 The name of .
subject 16: Write a function , Enter a hexadecimal number , Output the corresponding decimal number .
Explain :
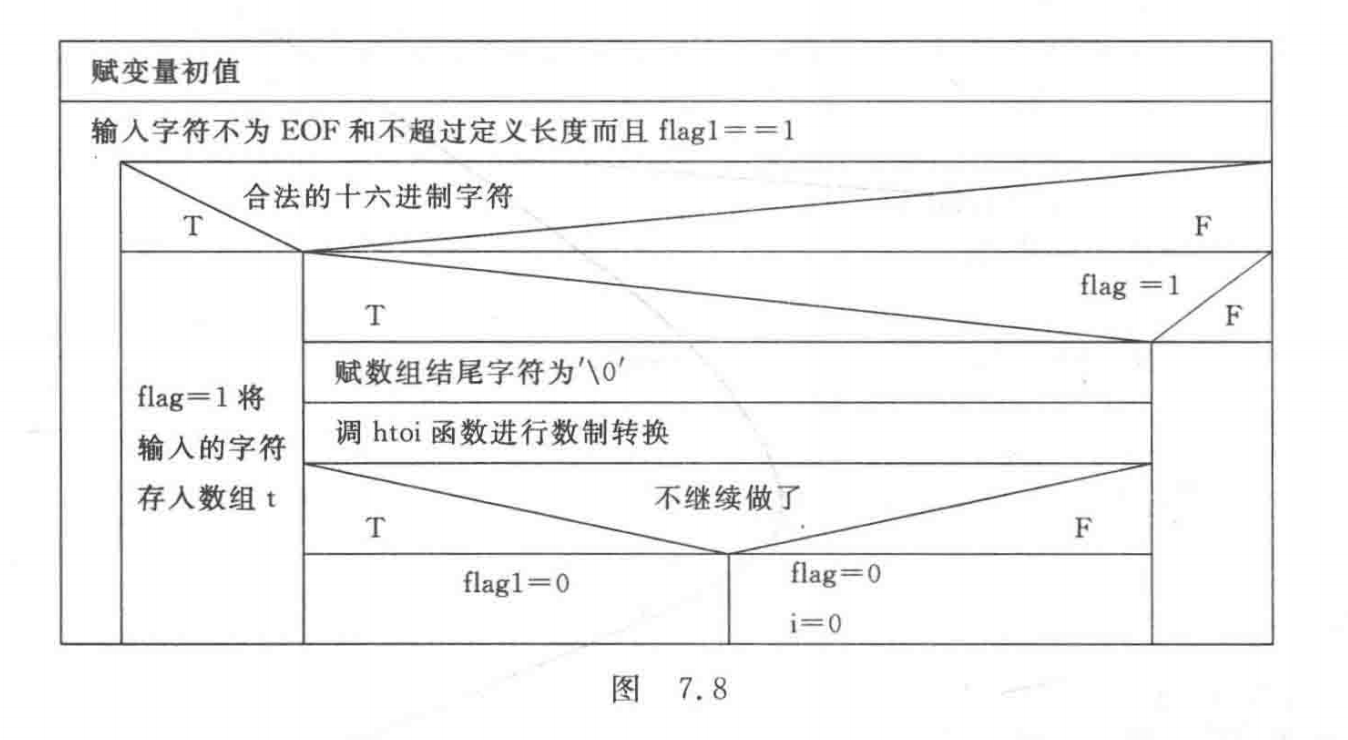
The main function main Of N-S Pictured graph 7.8 Shown .
A function for finding decimal numbers htoi Of N-S chart , Pictured 7.9 Shown .

Answer code :
#include <stdio.h>
#define MAX 1000
int main()
{
int htoi(char s[]);
int c, i, flag, flag1;
char t[MAX];
i = 0;
flag = 0;
flag1 = 1;
printf("input a HEX number:");
while ((c = getchar()) != '\0' && i < MAX && flag1)
{
if (c >= '0' && c <= '9' || c >= 'a' && c <= 'f' || c >= 'A' && c <= 'F')
{
flag = 1;
t[i++] = c;
}
else if (flag)
{
t[i] = '\0';
printf("decimal number %d\n", htoi(t));
printf("continue or not?");
c = getchar();
if (c == 'N' || c == 'n')
flag1 = 0;
else
{
flag = 0;
i = -0;
printf("\ninput a HEX number:");
}
}
}
return 0;
}
int htoi(char s[])
{
int i, n;
n = 0;
for (i = 0; s[i] != '\0'; i++)
{
if (s[i] >= '0' && s[i] <= '9')
n = n * 16 + s[i] - '0';
if (s[i] >= 'a' && s[i] <= 'f')
n = n * 16 + s[i] - 'a' + 10;
if (s[i] >= 'A' && s[i] <= 'F')
n = n * 16 + s[i] - 'A' + 10;
}
return (n);
}
Running results :
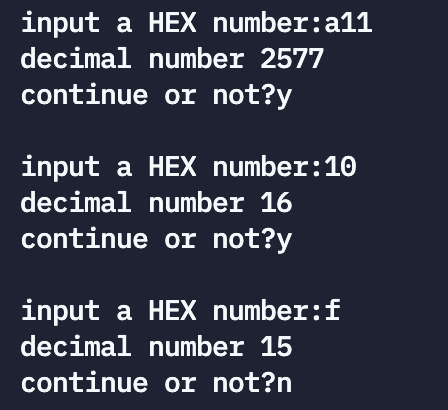
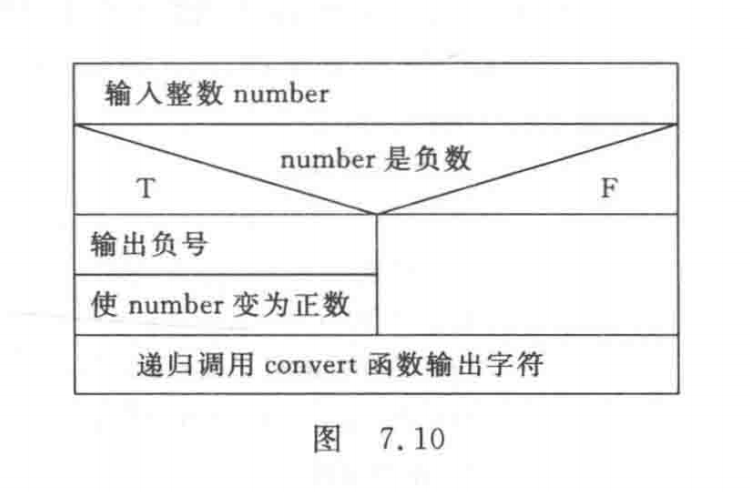
subject 17: Recursively convert an integer n Convert to string . for example , Input 483, Expected output string "483".n The number of digits is uncertain , It can be an integer with any number of digits .
Explain : Of the main function N-S Pictured graph 7.10 Shown .
Answer code :
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
void convert(int n);
int number;
printf("input an integer;");
scanf("%d", &number);
printf("output:");
if (number < 0)
{
putchar('-'); // Output one first " One " Sign and space
putchar(' ');
number = -number;
}
convert(number);
printf("\n");
return 0;
}
void convert(int n) // Recursive function
{
int i;
if ((i = n / 10) != 0)
convert(i);
putchar(n % 10 + '0');
putchar(32);
}
Running results :
①:

②:
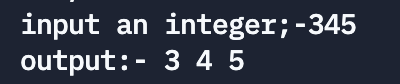
explain : If it's a negative number , To convert it to a positive number , At the same time, manually output a "-" Number .convert The function only deals with positive numbers . If number The value of is 345, call convert Function, put 345 Pass to n. Execute function body , n/10 Value ( It's also i Value ) by 34, It's not equal to 0. Call again convert function , At this time parameter n The value of is 34. Then execute the function body ,n/10 Value ( It's also i Value ) by 3, It's not equal to 0. Call again convert function , At this time parameter n The value of is 3. Then execute the function body ,n/10 Value ( It's also i Value ) be equal to 0. No more calls convert function , And perform putchar (n%10+‘0’), here n The value of is 3, so n%10 The value of is 3(% Is the complement operator ), character ‘0’ Of ASCII The code is 48,3 Add 4 be equal to 51,51 Is the character ’3’ Of ASCII Code , therefore putchar(n%10+’0’) The output characters ‘3’. next putchar(32) Output a space , So that two characters are separated by spaces .
then , The process returns to the last call convert At function , It should be followed by putchar(n%10+’0’), Pay attention to the n It's the last call convert Function n, Its value is 34, therefore n%10 The value of is 4, add ‘0’ be equal to 52,52 Is the character ‘4’ Of ASCII Code , therefore putchar(n%10+’0’) The output characters ‘4’ , next putchar(32) Output a space .
The process returns to the last call convert At function , It should be followed by putchar(n%10+’0’), Pay attention to the n It's No 1 Secondary call convert Function n , Its value is 345 , therefore n%10 The value of is 5, add ‘0’ be equal to 53,53 Is the character ‘5’ Of ASCII Code , therefore putchar(n%10+’0’) The output characters ‘5’ , next putchar(32) Output a space .
thus , Yes convert The recursive call to the function ends , Return the main function , Output a newline , Program end .
putchar(n%10+’0’) It can also be rewritten as putchar(n%10+48), because 48 Is the character ‘0’ Of ASCII Code .
subject 18: Given year 、 month 、 Japan , Calculate the day of the year .
Explain : The main function receives the date entered from the keyboard , And call sum_day and leap The function calculates the number of days . Its N-S See Figure 7.11.sum_day Number of days to calculate the input date .leap Function returns whether it is a leap year .

Answer code :
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int sum_day(int month, int day);
int leap(int year);
int year, month, day, days;
printf("input date(year,month,day):");
scanf("%d,%d,%d", &year, &month, &day);
printf("%d/%d/%d ", year, month, day); // Call function sum_day
days = sum_day(month, day); // Call function leap
if (leap(year) && month >= 3)
days = days + 1;
printf("is the %dth day in this year.\n", days);
return 0;
}
int sum_day(int month, int day) // function sum_day∶ Calculate the date
{
int day_tab[13] = {
0, 31, 28, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31};
int i;
for (i = 1; i < month; i++)
day += day_tab[i]; // Accumulate the number of days before the current month
return (day);
}
int leap(int year) // function leap∶ Determine if it's a leap year
{
int leap;
leap = year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0 || year % 400 == 0;
return (leap);
}
Running results :

版权声明
本文为[RubyHan1314]所创,转载请带上原文链接,感谢
https://yzsam.com/2022/04/202204230309237111.html
边栏推荐
- What kind of experience is it to prepare for a month to participate in ACM?
- Drawing polygons with < polygon / > circular array in SVG tag
- 2022T电梯修理考试模拟100题及在线模拟考试
- Establishing and traversing binary tree
- Recommend reading | share the trader's book list and ask famous experts for trading advice. The trading is wonderful
- Blazor University (12) - component lifecycle
- TP5 email (2020-05-27)
- Source Generator实战
- Huawei mobile ADB devices connection device is empty
- 手机连接电脑后,QT的QDIR怎么读取手机文件路径
猜你喜欢

12.<tag-链表和常考点综合>-lt.234-回文链表

Tencent video VIP member, weekly card special price of 9 yuan! Tencent official direct charging, members take effect immediately!

C语言实现通讯录----(静态版本)

2022T电梯修理考试模拟100题及在线模拟考试

A set of combination boxing to create an idea eye protection scheme
C WPF UI framework mahapps switching theme

IOTOS物联中台对接海康安防平台(iSecure Center)门禁系统

Mise en service PID du moteur de codage (anneau de vitesse | anneau de position | suivant)

Configuration table and page information automatically generate curd operation page
Course design of Database Principle -- material distribution management system
随机推荐
2022年P气瓶充装培训试题及模拟考试
Creating wechat voucher process with PHP
Mise en service PID du moteur de codage (anneau de vitesse | anneau de position | suivant)
A set of combination boxing to create an idea eye protection scheme
Charles uses three ways to modify requests and responses
Xamarin effect Chapter 22 recording effect
全网讲的最细,软件测试度量,怎样优化软件测试成本提高效率---火爆
Tencent video price rise: earn more than 7.4 billion a year! Pay attention to me to receive Tencent VIP members, and the weekly card is as low as 7 yuan
[MySQL] left Function | Right Function
Load view Caton
2022g2 boiler stoker examination question bank and online simulation examination
Use DFS to solve the problem of "number of dictionary rows"
Xutils3 corrected a bug I reported. Happy
全网最全,接口自动化测试怎么做的?精通接口自动化测试详解
Miniapi of. Net7 (special section): NET7 Preview3
Experiment 5 components and event handling
Use of ADB command [1]
Laravel8- use JWT
[authentication / authorization] customize an authentication handler
A set of C interview questions about memory alignment. Many people make mistakes!