当前位置:网站首页>Multithreaded copy set (New 4)
Multithreaded copy set (New 4)
2022-04-21 09:15:00 【Zhu Xiaosi】
ConcurrentHashMap
ConcurrentHashMap It's thread safe HashMap, No key value can be null.
JDK7 The implementation of the : Section lock is used internally to realize , The default initial capacity is 16( So in theory, this time can support at most 16 Two threads write concurrently , As long as their operations are distributed separately Segment On . This value can be set to other values at initialization time , But once it's initialized , It cannot be expanded ), The loading factor is 0.75f, piecewise 16, Each segment of the HashEntry<K,V>[] The size is 2. Each expansion is... Of the original capacity 2 times ,ConcurrentHashMap No expansion of the entire container , And only for one segment super-popular . In obtaining size During operation , Try first 2(RETRIES_BEFORE_LOCK) The second pass is not locked Segment Statistics of various Segment size , If in the process of Statistics , Container of count There is a change , Then use the way of locking to count all Segment Size .

JDK8 The implementation of the :ConcurrentHashMap The middle structure is : Array 、 Chain list and red black tree . When the number of elements in a slot increases to 8 Geqi table The capacity is greater than or equal to 64 when , From linked list to red black tree ; When the number of elements in a slot is reduced to 6 Time , From the red black tree back to the linked list . The process of transferring a linked list to a red black tree , It is the process of constructing elements in a given order into a red black tree . It should be noted that , When table Capacity is less than 64 when , It's just capacity expansion , It will not turn the linked list into a red black tree . In the process of transformation , Use the sync block to lock the first element of the current slot , Prevent other processes from adding, deleting or modifying the current slot , After the conversion, use CAS Replace the original linked list .

Whether it's JDK7 still JDK8,ConcurrentHashMap Of size Methods can only return an approximate number , Can't do 100% Accuracy of , Because the slots that have been counted are size There may be another change before returning to the final result , This results in a slight difference between the returned size and the actual size .
JDK8 in size The implementation of the method is better than JDK7 It's a lot easier :
public int size() {
long n = sumCount();
return ((n < 0L) ? 0 :
(n > (long)Integer.MAX_VALUE) ? Integer.MAX_VALUE : (int)n);
}
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
The maximum is Integer Maximum of type , however Map Of size May exceed MAX_VALUE, So there's another way mappingCount(),JDK It is recommended to use mappingCount() instead of size().mappingCount() The code for is as follows :
public long mappingCount() {
long n = sumCount();
return (n < 0L) ? 0L : n; // ignore transient negative values
}
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
As can be seen above , Whether it's size() still mappingCount(), The core method of calculating size is sumCount().sumCount() The code for is as follows :
final long sumCount() {
CounterCell[] as = counterCells; CounterCell a;
long sum = baseCount;
if (as != null) {
for (int i = 0; i < as.length; ++i) {
if ((a = as[i]) != null)
sum += a.value;
}
}
return sum;
}
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
CounterCell What is this class ? We'll find that it uses @sun.misc.Contended Marked class , Inside contains a volatile Variable [email protected] This annotation indicates that the class needs to prevent “ False sharing ”.
JDK1.8 size Is based on baseCount and counterCell Conduct CAS Calculation , Finally through baseCount and Traverse CounterCell Array yields size.
JDK8 ConcurrentHashMap CPU 100%
Recursively call computeIfAbsent Method
Thread safe non blocking queue
Non blocking queues have ConcurrentLinkedQueue, ConcurrentLinkedDeque. The element cannot be null. With ConcurrentLinkedQueue For example , Have a head head And tail tail Two pointers , follow FIFO The principle of entering and leaving the team , There are methods add(E e), peek() Remove without deleting , poll() Remove delete , remove(Object o),size(), contains(Object o), addAll(Collection c), isEmpty().ConcurrentLinkedDeque It's a two-way queue , The corresponding operation can be carried out in the head and tail directions .
Blocking queues
Blocking queues (BlockingQueue) Is a queue that supports two additional operations . These two additional operations support blocking insert and remove methods . Supports blocking insertion methods : It means when the queue is full , The queue blocks the thread that inserts the element , Until the line is not satisfied . Support blocking removal methods : When the queue is empty , The thread that gets the element will wait for the queue to become non empty . No element in any blocking queue can be null.
The insertion and removal of the blocking queue are handled in the following way :
Method - processing method |
Throw an exception |
Return special value |
May block waiting |
Waiting time can be set |
The team |
add(e) |
offer(e) |
put(e) |
offer(e,timeout,unit) |
Out of the team |
remove() |
poll() |
take() |
poll(timeout,unit) |
see |
element() |
peek() |
nothing |
nothing |
If it's an unbounded queue , The queue can't be full , So use put or offer Methods will never be blocked , And use offer When the method is used , The method always returns true.
Java The blocking line in :ArrayBlockingQueue: A bounded blocking queue composed of array structure . LinkedeBlockingQueue: A with a linked list structure ( bounded / unbounded ) Blocking queues . PriorityBlockingQueue: An unbounded blocking queue supporting priority sorting .DelayQueue: An unbounded blocking queue using priority queue . SynchronousQueue: A blocked queue that does not store elements . LinkedTransferQueue: An unbounded blocking queue composed of linked list structure . LinkedBlockingDeque: A bidirectional blocking queue composed of linked list structure .
ArrayBlockingQueue
This queue is based on FIFO The principle of sorting elements , Support fair and unfair strategies , The default is unfair . The capacity size must be set during initialization .
public ArrayBlockingQueue(int capacity)
public ArrayBlockingQueue(int capacity, boolean fair)
public ArrayBlockingQueue(int capacity, boolean fair,
Collection<? extends E> c)
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
LinkedBlockingQueue
And ArrayBlockingQueue equally , according to FIFO Order by principle , The internal use of linked list structure , And cannot be set to fair . The default queue length is Integer.MAX_VALUE.
public LinkedBlockingQueue() {
this(Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}
public LinkedBlockingQueue(int capacity)
public LinkedBlockingQueue(Collection<? extends E> c)
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
PriorityBlockingQueue
It is an unbounded blocking queue that supports priority , The default initial capacity is 11, By default, it is arranged in natural ascending order , There is no guarantee of the order of elements of the same priority . The bottom layer is realized by binary heap . Internal elements either implement Comparable Interface , Or specify the constructor during initialization Comparator To sort the elements .
public PriorityBlockingQueue()
public PriorityBlockingQueue(int initialCapacity)
public PriorityBlockingQueue(int initialCapacity,
Comparator<? super E> comparator)
public PriorityBlockingQueue(Collection<? extends E> c)
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
DelayQueue
Support the infinite blocking queue of delay getting elements . Inside contains a PriorityQueue To achieve , Elements in the queue must implement Delayed Interface , When you create an element, you can specify how long it takes to get the current element from the queue . Elements can only be extracted from the queue when the delay expires . DelayQueue Very useful , Can be DelayQueue Use it in the following application scenarios .
- The design of cache system : It can be used DelayQueue Save the validity of the cache elements , Use a thread loop to query DelayQueue, Once you can get from DelayQueue When getting elements in , Indicates that the cache expiration date is .
- Scheduled task scheduling : Use DelayQueue Save the tasks and execution time that will be performed on that day , Once from DelayQueue Get the task and start executing .
public interface Delayed extends Comparable<Delayed> {
long getDelay(TimeUnit unit);
}
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
SynchronousQueue
Blocking queues that do not store elements , Support fair and unfair strategies . every last put The operation must wait for a take operation , Otherwise, you can't continue to add elements . Perfect for transitive scenarios .
CopyOnWriteArrayList
At each revision , Will create and republish a new copy of the container , To achieve variability .CopyOnWriteArrayList The iterator retains a reference to the underlying underlying array , This array is currently at the beginning of the iterator , Because it won't be modified , Therefore, when synchronizing it, you only need to ensure the visibility of the contents of the array . therefore , Multiple threads can iterate over the container at the same time , Without interfering with each other or with the threads that modify the container .“ When writing copy ” An iterator that does not return an iterator ConcurrentModificationException And the returned element is exactly the same as the element when the iterator was created , Without considering the impact of subsequent modification operations . obviously , Whenever the container is modified, the underlying array is copied , It's going to cost something , Especially when the container is large , Only if there are far more iterations than modifications , Should use “ Assignment on write ” Containers .
Atomic classes
Java in Atomic There's a total of 12 Classes , Belong to 4 There are kinds of ways to update atoms , These are the basic types of atomic renewal 、 Atomic update array 、 Atomic update references 、 Atom update properties ( Field ).Atomic The classes in the package basically use Unsafe Implemented wrapper class .
1) Basic types of atomic renewal :AtomicBoolean,AtomicInteger, AtomicLong.
2) Atomic update array :AtomicIntegerArray,AtomicLongArray, AtomicReferenceArray.
3) Atomic update reference types :AtomicReference, AtomicStampedReference, AtomicMarkableReference.
4 ) Atomic update field type :AtomicReferenceFieldUpdater, AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater, AtomicLongFieldUpdater.
Basic types of atomic renewal
AtomicBoolean,AtomicInteger, AtomicLong The methods provided by the three classes are similar , With AtomicInteger For example : Yes int addAndGet(int delta), boolean compareAndSet(int expect, int update), int getAndIncrement(), void lazySet(int newValue),int getAndSet(int newValue).
// setup to use Unsafe.compareAndSwapInt for updates
private static final Unsafe unsafe = Unsafe.getUnsafe();
private static final long valueOffset;
static {
try {
valueOffset = unsafe.objectFieldOffset
(AtomicInteger.class.getDeclaredField("value"));
} catch (Exception ex) { throw new Error(ex); }
}
private volatile int value;
public final boolean compareAndSet(int expect, int update) {
return unsafe.compareAndSwapInt(this, valueOffset, expect, update);
}
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
sun.misc.Unsafe Only three kinds of CAS Method :compareAndSwapObject, compareAndSwapInt and compareAndSwapLong. about AtomicBoolean, It is to put Boolean Convert to plastic , Reuse compareAndSwapInt Conduct CAS, Atomic updates char,float,double Variables can be implemented in a similar way .
Atomic update array
With AtomicIntegerArray For example , This class mainly provides an atomic way to update the shape in the array , Common methods are as follows :
- int addAndGet(int i, int delta): Atomically match the input value with the index in the array i Sum of the elements of .
- boolean compareAndSet(int i, int expect, int update): If the current value is equal to the expected value , Then, the array positions are arranged in the atomic way i Is set to update value .
- AtomicIntegerArray Two construction methods of :
- AtomicIntegerArray(int length): Specify the size of the array , And initialize to 0
- AtomicIntegerArray(int [] array): Copy the given array .
Case study :
int value[] = new int[]{1,2,3};
AtomicIntegerArray aia = new AtomicIntegerArray(value);
System.out.println(aia.getAndSet(1, 9));
System.out.println(aia.get(1));
System.out.println(value[1]);
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
Running results :2 9 2
Atomic update reference example
public class AtomicReferenceDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
User user = new User("conan", 15);
AtomicReference<User> userRef = new AtomicReference<>(user);
User userChg = new User("Shinichi", 17);
userRef.compareAndSet(user, userChg);
User newUser = userRef.get();
System.out.println(user);
System.out.println(userChg);
System.out.println(userRef.get());
AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater<User> fieldUpdater = AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater.newUpdater(User.class, "age");
fieldUpdater.getAndIncrement(newUser);
System.out.println(newUser);
System.out.println(fieldUpdater.get(newUser));
}
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
static class User{
private String name;
volatile int age;
}
}
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
- 19.
- 20.
- 21.
- 22.
- 23.
- 24.
Output :
AtomicReferenceDemo.User(name=conan, age=15)
AtomicReferenceDemo.User(name=Shinichi, age=17)
AtomicReferenceDemo.User(name=Shinichi, age=17)
AtomicReferenceDemo.User(name=Shinichi, age=18)
18
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
CAS
Full name CompareAndSwap. Suppose there are three operands : Memory value V, Old expectations A, Value to modify B, If and only if expected A And memory values V Phase at the same time , Will change the memory value to B And back to true, Otherwise do nothing and return false. Of course CAS We must cooperate with volatile Variable , In this way, we can ensure that the traversal we get every time is the latest value in the main memory , Otherwise the old expectations A For a thread , It's always a constant value A, Just one time CAS operation failed , You can never succeed .cmpxchg Instructions
AQS
Full name AbstractQueuedSynchronizer. if JUC(java.util.concurrent) The foundation is CAS Words , that AQS It 's the whole thing JAVA And the core of the contract ,ReentrantLock, ReentrantReadWriteLock, CountDownLatch, Semaphore And so on, we all use it .
CAS The problem of
- ABA The problem occurs in a scenario like this : Threads 1 Change use CAS Put the variable A Replace the value of with C, At this point, the thread 2 Change the value of the variable from A Replace with C, Again by C Replace with A, Then the thread 1 perform CAS It is found that the value of the variable is still A, therefore CAS success . But in fact, the scene at this time is different from the original . Most of the time ABA The problem will have no impact . If there are special circumstances due to ABA Contribute to the , We can use AtomicStampedReference To solve , principle : Optimism lock +version.
AtomicStampedReference
public boolean compareAndSet(V expectedReference,
V newReference,
int expectedStamp,
int newStamp)
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
The cycle time is long and the cost is high
The spin CAS If it doesn't work for a long time , Will give CPU It's very expensive to execute .Only one atomic operation of shared variables can be guaranteed
When operating on a shared variable , We can use cycles CAS The way to guarantee atomic operation , But when operating on multiple shared variables , loop CAS There is no guarantee of atomicity of operation .AtomicReference Class to ensure atomicity between reference objects , You can put multiple variables in one object to execute CAS operation .
How to avoid deadlock
Deadlock refers to the execution of two or more processes , A phenomenon of waiting for each other caused by competing for resources , If there is no external force , They will not be able to move on . This is a serious problem , Because the deadlock will cause your program to hang up and cannot complete the task , The occurrence of deadlock must meet the following 4 Conditions :
- mutual exclusion : A resource can only be used by one process at a time .
- Request and hold conditions : When a process is blocked by a request for resources , Keep the acquired resources .
- Conditions of non deprivation : Resources obtained by the process , Before use , Can't be forcibly deprived .
- Loop wait condition : A circular waiting resource relationship is formed between several processes .
The easiest way to avoid deadlocks is to prevent circular wait conditions , Set all resources in the system to flag bits 、 Sort , It is stipulated that all process application resources must be operated in a certain order to avoid deadlock .
Support timing lock boolean tryLock(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
adopt ThreadDump To analyze and find out the deadlock
How to detect whether a thread has a lock
java.lang.Thread There is a method in :public static native boolean holdsLock(Object obj). Returns if and only if the current thread has a lock on a specific object true
JAVA Thread scheduling algorithm in
Preemptive . One thread runs out CPU after , The operating system will be based on the site priority 、 Data such as thread starvation calculates a total priority and assigns the next time slice to a thread for execution .
unlocked
Make sure the scene is safe , It doesn't have to be synced , There is no causal relationship between the two . Synchronization is just a way to ensure the correctness of data sharing when competing , If a method doesn't involve sharing data , Then it naturally does not need any synchronization measures to ensure the correctness , So some code is inherently thread safe .
- Stateless programming . Stateless code has some common characteristics : Independent of the data stored on the pair and the common system resources 、 The state variables used are all passed in by parameters 、 Do not call non stateless methods, etc . You can refer to Servlet.
- Thread local storage . You can refer to ThreadLocal
- volatile
- CAS
- coroutines : Multitask scheduling in a single thread , And maintain the switch between multiple tasks in a single thread .
版权声明
本文为[Zhu Xiaosi]所创,转载请带上原文链接,感谢
https://yzsam.com/2022/04/202204210732096177.html
边栏推荐
- Postman test excel file import and export function
- 编程如何提高自己的水平能力?学编程最重要的是什么?请看凡人浅谈如何学C
- Add log4j log function
- 1155: multiple instances of string
- A value is trying to be set on a copy of a slice from a DataFrame.
- PageRank case Airport
- 1161: string length (pointer)
- YApi基本使用(2022-04-15)
- 1148: combine one of three digits
- OpenCV——分离颜色通道,图像对比度,亮度调整,离散傅里叶变换(10)
猜你喜欢
C language counting and sorting
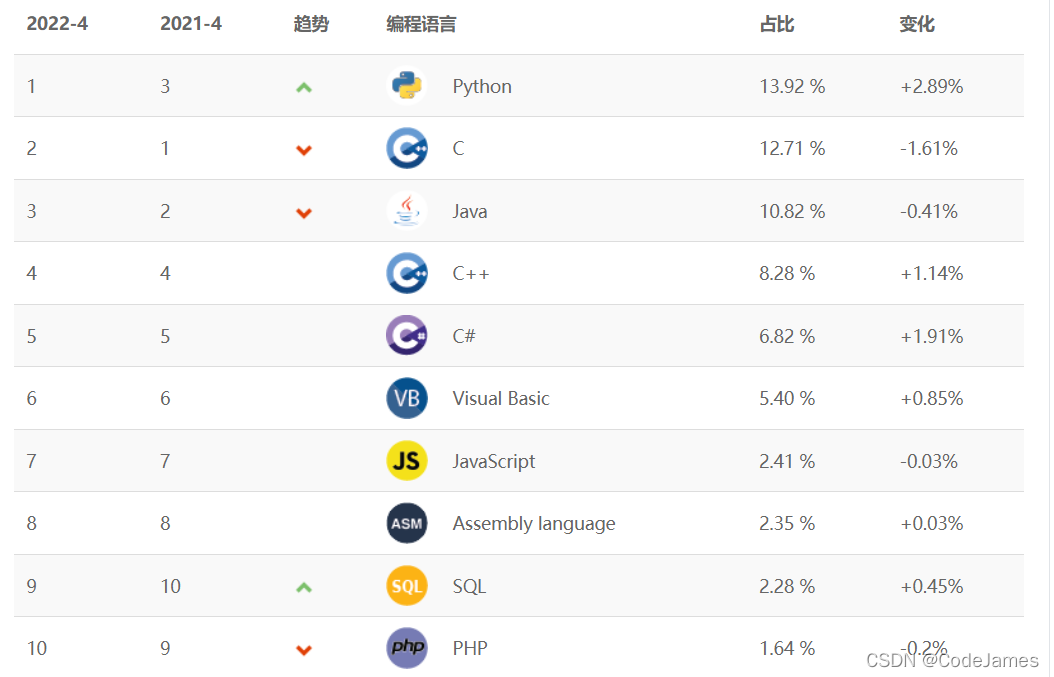
Major programming languages and applications in 2022
Penetration test - get the system fofa keyword to brush the hole

【CVPR 2020】PointASNL :Robust Point Clouds Processing using Nonlocal Neural Networks

YApi基本使用(2022-04-15)

笔记0104. MySQL 高级 - 索引 - 概述

How to improve the ability of programming? What is the most important thing about learning programming? Please see how mortals learn C

Convolution operation and cross correlation operation

CC10000.CloudJenkins—————————————

【ACM】131. 分割回文串
随机推荐
PageRank case Airport
1167: 逆转数(指针专题)
Simulation implementation vector
[CTF. Show. Reverse] moon cake cup RE1_ Northwest Wangxiang, re2_ Homing, RE3_ If there is no month
年金险安全靠谱吗?收益是多少啊?
【ACM】131. Split palindrome string
PyS1:概述
2022 mobile crane driver examination exercises simulated examination platform operation
深蓝-视觉slam-第六节习题
Intranet penetration - proxy penetration - rights lifting - injection - MSF Middleware - domain penetration - log clearing - learning resources
Drafting and Revision: Laplacian Pyramid Network for Fast High-Quality Artistic Style Transfer--T Li
L2-031 deep into the tiger's den (25 points)
Surfaceview high performance rendering (V) code practice - let the drawn picture move
Buuctf [actf2020 freshman competition] include
模拟实现vector
Selection of WiFi module for data transmission through industrial control serial port of intelligent gateway of Internet of things
1152: binary search
全网最全谷粒商城笔记_02、简介项目整体效果展示(2022-04-02)
1153: 简易版最长序列
批量处理数据对比(<foreach>标签和sqlsession)