当前位置:网站首页>C language counting and sorting
C language counting and sorting
2022-04-21 08:42:00 【I only know printf】
Analysis of examples and ideas
If you sort a byte array ( Each element is unsigned char), The contents of the array are :
| Indexes |
0 |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
| ASCII |
a |
b |
b |
a |
a |
a |
b |
a |
\n |
| Decimal system | 97 | 98 | 98 | 97 | 97 | 97 | 98 | 97 | 10 |
We require the above arrays to be sorted from small to large , Elements of the same size are sorted by index in the array . The sequence number of the final result is from 1 Start , That is, for example, the final sorted array is res, The first element is placed in res[1] in , instead of res[0] in .
The idea of counting and sorting is :
First determine the sequence to be sorted , There are several numbers in each size from small to large , Take the sequence above , Yes 3 A number of different sizes , Namely 10、97、98, They each have 1 individual 、5 individual 、3 individual . This step is to prepare for accumulation in the next step .
Then why do you need to add up ?
Let's see how to accumulate first , We put each different number Number Add up , Get... Separately 1、6、9, They stand for :
All values are 10 In bytes of , In the final sorting result , The last serial number is 1!
All values are 97 In bytes of , In the final sorting result , The last serial number is 6!
All values are 98 In bytes of , In the final sorting result , The last serial number is 9!
This is the meaning of accumulation .
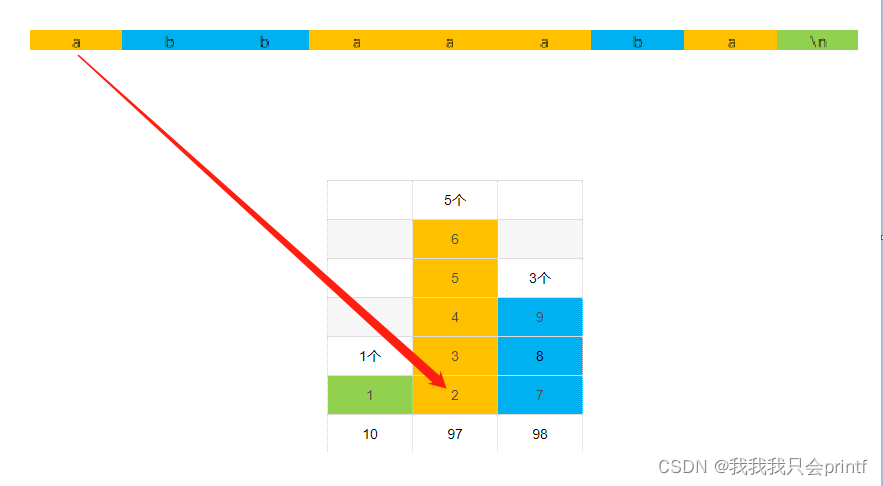
Because this step is determined , We can get... In the above sequence , In the first 1 Yes. 10, In the first 2~6 Yes. 97, In the first 7~9 Yes. 98. That's us First determine the order of different numbers of each size Range ! Then we put it all 97 Of the 2 To the first 6 According to their index in the array ( That is, the order of occurrence ) Sort , The resulting sequence is the final result of sorting .
Represented by an image is :
| 5 individual | ||
| 6 | ||
| 5 | 3 individual | |
| 4 | 9 | |
| 1 individual | 3 | 8 |
| 1 | 2 | 7 |
| 10 | 97 | 98 |
When you see the picture above, you should understand , The number of the final sequence is the size. We have determined , But we don't know its position in the original sequence . For example, in the figure above, it is ranked No 4 It must be 97, But in the original sequence 5 individual 97, Their indexes are 0、3、4、5、7, That's second 4 Of 97 Our index needs further sorting .
So next, sort according to the original sequence , There are two sorting methods , But it doesn't make any difference , One is to start from the first of each number ( That is, in order ), One is to start from the last of each number ( That is, in reverse order ).
The idea of reverse order is the red description of why to accumulate , such as :
All values are 97 In bytes of , In the final sorting result , The last serial number is 6!
Sort ideas in order , This passage can be reinterpreted as :
All values are 98 In bytes of , In the final sorting result , The first serial number is 7!
It should be noted that , Because the value is 10 The numbers add up to only one , Prove that there is no smaller number , So all values are 10 In bytes of , In the final sorting result , The first serial number is 1.
Order
The so-called sequential sorting , That is, go through the original sequence in order , Assign each number to the range of each number in order . It sounds a bit awkward , Follow the example above , Let's start with the first element 'a' Start , It's in the final sorting result , The starting sequence number is 2, This has been calculated from the previous accumulation , Then we'll assign its serial number to 2, This is its final sequence number .
If we cycle to the second 3 A byte is also 'a', Because of its scope 2~6 in ,2 This serial number has been assigned , So assign its serial number to 3. Others in the same way .



The following sorting pictures will not be repeated , Is it simple ? The second step is to sort and sum up 4 A word : first come , first served ! Put all the numbers of the original sequence in order and then put them into their corresponding Range Inside you can .
Reverse order
Reverse the idea above , Let's allocate... From the back to the front , Assign each number to the last serial number in its range .




C The language code
According to our thinking , The first step is to calculate the number of each number , Be careful , Here the author stipulates that this is a Byte array Sort , So we think each element is unsigned char type , The value is 0~255 Between .
Let's first calculate how many of each number :
void CountingSort(unsigned char *ary,int size)
{
int count[256] = {0};
int i;
for(i=0;i<size;i++)
++count[ary[i]];
}count Save the number of each number in , such as count[0] be equal to ary The median is equal to 0 The number of ,count[97] be equal to ary Median, etc 97 Number of, etc .
here count The internal data is :
| count[10] |
1 |
| count[97] |
5 |
| count[98] |
3 |
| count For the other 0 |
|
Then we add up all the values in the array :
void CountingSort(unsigned char *ary,unsigned char *sary,int size)
{
int count[256] = {0};
int i;
for(i=0;i<size;++i)
++count[ary[i]];
for(i=1;i<256;++i)
count[i] += count[i-1];
}here count The internal data is :
| Indexes |
value |
| count[0]~count[9] |
0 |
| count[10]~count[96] |
1 |
| count[97] |
6 |
| count[98]~count[255] |
9 |
Then allocate in order or reverse order :
void CountingSort(unsigned char *ary,unsigned char *sary,int size)
{
int count[256] = {0};
int i;
for(i=0;i<size;++i)
++count[ary[i]];
for(i=1;i<256;++i)
count[i] += count[i-1];
// The reverse
for(i=size-1;i>=0;--i)
sary[count[ary[i]]--] = ary[i];
// The order
// for(i=0;i<size;i++)
// sary[1+count[ary[i]-1]++] = ary[i];
}stay main Test code in :
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
unsigned char ary[] = "abbaaaba\n";// Pay attention to the end '\0' Don't count in
unsigned char sary[sizeof(ary)] = {0};
CountingSort(ary,sary,sizeof(ary)-1);
for(int i=1;i<sizeof(ary);++i)
printf("sary[%d] = %d\n",i,sary[i]);
return 0;
}
The final run result :

If you put the above code , The assignment of the last step is changed to i, Then output the result :

sary[1] = 8 Express , Sort from small to large , The number at the top , The subscript of the original array is 8.
版权声明
本文为[I only know printf]所创,转载请带上原文链接,感谢
https://yzsam.com/2022/04/202204210841147216.html
边栏推荐
- 将pyx文件编译成pyd文件(很多坑,已解决)
- Theme model of image
- Kotlin's extended function knowledge points
- Experiment 1: basic operation of database
- knn预测最小案例总结
- Convert file to multipartfile
- JVM——》G1垃圾收集器
- 某系统拥有N个进程,总共7个资源,每个进程需要3个资源,问N数量最多为多少不会死锁?(附解析)
- Count the number of linked lists and look up linked lists
- 51 单片机学习_1.3 LED流水灯
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
分类中解决类别不平衡问题
【Appium】使用模拟器实现有道云App的业务功能-新增、搜索、修改、删除
2022年上海市安全员C证考试模拟100题及模拟考试
[GYCTF2020]Blacklist
一种带开关量的开口式电流互感器的应用
Zabbix 5.4 Server安装
regular expression
2022年流动式起重机司机考试练习题模拟考试平台操作
The problem of reading configuration file in feign request interceptor
[arm assembly judgment] how to use assembly to judge the number of positive and negative numbers in an array?
方格分割【dfs】
数据集划分小探
Kotlin project cannot run after IntelliJ update
Enter four integers in descending order
渗透测试-从公有云到内网漫游RCE-反序列化-frp
51 single chip microcomputer learning_ 1.1 turn on an LED
机器学习笔记 - SVD奇异值分解(2)
51 单片机学习_2.1 独立按键控制LED亮灭
神经网络学习之Opencv使用记录
ssm+double 用redis实现三次登录,三次登录失败锁定五分钟









