当前位置:网站首页>JWT source code analysis (four layer package with schematic diagram)
JWT source code analysis (four layer package with schematic diagram)
2022-04-22 10:12:00 【Juntong】
JWT Source analyses
Write it at the front
In this year 2-3 In June, I wrote a project of campus community , I was in charge of Koa Back end construction of , Mainly responsible for user related and attention related interfaces , We used token As a solution for us to stay logged in , It's here jsonwebtoken(JWT) This plugin
This plug-in haunts me , Today I will share with you the process of reading the source code and understanding it !
You will learn :
JWTWhere did you usedefineProperty, Why use ?jwt.signThere arecallbackfunction , When will it be called ?JWTWhat is the default encryption algorithm for ?jwt.verifyHow to validateoptionMediumjwtidandpayload.jtiWhether it is equal or not ?( It's convenientsessionidComparison of )optionSome other unusual parameters in , such ascomplete.- Why?
jws.createSignYou can use callback functions ? jwaHow to use regular to extract the required parameters .
wait … deng dua Lang
Share the wrong place , Everybody put forward , Give front end Mengxin a little help !
Let's start with Kangkang. Let me see the flow chart of the source code summary
- I want to go in and have a look jwt How to complete the generation token Of the process , It turns out that layers of packaging , See the 4 Layer to see the encryption source code
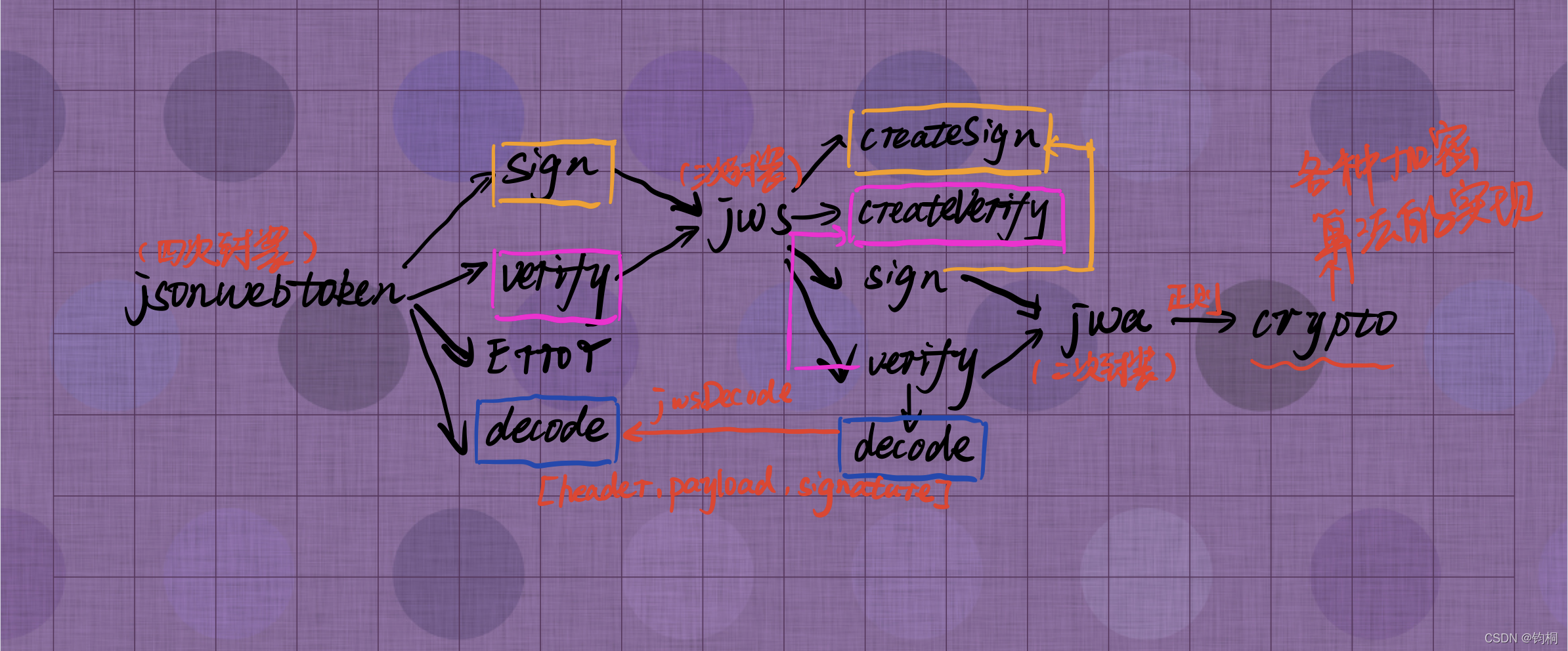
Briefly explain the flow chart
- From the first floor ,
jsonwebtokenIt is mainly divided intosign,verify,decodeThe implementation of the , alsoErrorWrong throw- among
sign,verify,decodeIt's all usedjwsplug-in unit , So let's move on to the next floor signUsedjws.createSign, Why notjws.signWell ?verifyUsedjws.createVerify, Why notjws.verifyWell ?- Let's move on
- among
jwsIt mainly encapsulatescreateSign,sign,createVerify,verify,decode- among
createSignIs to return aSignStreamobject , This object is mountedsignMethod - among
createVerifyIs to return aVerifyStreamobject , This object is mountedverifyMethod decodeIt's mount toVerifyStreamUpper , Alone becausejwtUsing the- The main reason is that the integration has returned
[header,payload,signature]Head , Load and signature
- The main reason is that the integration has returned
Errorstay lib Inside the directory , UsedJsonWebTokenError.jsUnified error handling , There are other mistakesrequireThis file 【 We have also made unified handling of errors in the project 】jws.signandjws.verifyAgain jwa plug-in unit- So let's keep looking down
- among
jwaThe base note is to segment the parameters by regular division and then call them.cryptoplug-in unitcryptoThe plug-in is the bottom implementation of various encryption algorithms- I won't introduce them here
More details may be shared with you at the place where the source code is posted below !
- I won't introduce them here
- Look at the source code ideas , Personally, I think it's also used
Component encapsulationSimilar ideas , There is still some training for thinking ! - After reading it, I just feel closer to the essence of things , Better understanding
JWTWhat has been done - Can have a good understanding of things , It should be the self-cultivation of most programmers !
jsonwebtoken
index.js
- We can see it very clearly
jsonwebtokenPlug in deconstruction - What is particularly interesting is ,
definePropertyEveryone knows that he isvue2The foundation of data monitoring (getandsetTo intercept data ), But it is essentially used to define attributes , This attribute is made enumerable here , Just to prevent direct access !
module.exports = {
verify: require('./verify'),
sign: require('./sign'),
JsonWebTokenError: require('./lib/JsonWebTokenError'),
NotBeforeError: require('./lib/NotBeforeError'),
TokenExpiredError: require('./lib/TokenExpiredError'),
};
Object.defineProperty(module.exports, 'decode', {
enumerable: false,
value: require('./decode'),
});
sign.js
- In this document, we only focus on the key points !( Avoid being too long , Only part of the source code is put here )
- We can see
signIn the function , Yespayload,secretOrPrivateKey,options,callbackFour parameters- However, we actually use the first three parameters in the project , And the third parameter only uses the parameter of expiration time
optionsThere are 7 Parameters can use , We only used itexpiresIn, I'm too superficial !
- options Is the function , Is directly identified as callback, Guarantee options At least for {}
- Called when it fails
callbackTo deal with iterror
- However, we actually use the first three parameters in the project , And the third parameter only uses the parameter of expiration time
- We can see , If there is callback, We are calling
jws.createSign - without callback Callback function parameters , We are calling
jws.sign - We're down there
jwsSee the difference in this detail in the plug-in- At present, it seems that the former can call callback functions
var options_for_objects = [
'expiresIn',
'notBefore',
'noTimestamp',
'audience',
'issuer',
'subject',
'jwtid',
];
module.exports = function (payload, secretOrPrivateKey, options, callback) {
if (typeof options === 'function') {
// It's also done here options Is the function , Is directly identified as callback
callback = options;
options = {
};
} else {
options = options || {
};
}
function failure(err) {
// call callback function
if (callback) {
return callback(err);
}
throw err;
}
if (typeof callback === 'function') {
callback = callback && once(callback);
jws.createSign({
header: header,
privateKey: secretOrPrivateKey,
payload: payload,
encoding: encoding
}).once('error', callback)
.once('done', function (signature) {
callback(null, signature);
});
} else {
return jws.sign({
header: header, payload: payload, secret: secretOrPrivateKey, encoding: encoding});
}
};
- about
verifyalike , It also has callback functions - Don't repeat the above , Look at some interesting points
optionsThere are encryption algorithms that can be passed in ( I didn't think backnone)- there
noneWhat algorithm is it , We don't know until we see the last
- there
- Then there is the extraction of a private key and public key , Yes
ES6Ofincludes, It's silky - jwtid It can be done by option Incoming , There will be an automatic comparison
- So in the project sessionid( It's best to specify it as the code in the source code
jti) Put in load , Then it's stupid to compare manually !, We areoptionGive it to me , There will be an automatic comparison !
- So in the project sessionid( It's best to specify it as the code in the source code
- Last called
doneIt's essentially importedcallback- We can see
option.completeCan control the last call base notedoneParameters of
- We can see
- At last we know
header.algHow to control the algorithm , So I knowjwtThe default algorithm isHS256
var header = Object.assign({
alg: options.algorithm || 'HS256',
typ: isObjectPayload ? 'JWT' : undefined,
kid: options.keyid
}, options.header);
verify.js
module.exports = function (jwtString, secretOrPublicKey, options, callback) {
var done;
if (callback) {
done = callback;
} else {
done = function(err, data) {
if (err) throw err;
return data;
};
}
if (!hasSignature && !options.algorithms) {
options.algorithms = ['none'];
}
if (!options.algorithms) {
options.algorithms = secretOrPublicKey.toString().includes('BEGIN CERTIFICATE') ||
secretOrPublicKey.toString().includes('BEGIN PUBLIC KEY') ? PUB_KEY_ALGS :
secretOrPublicKey.toString().includes('BEGIN RSA PUBLIC KEY') ? RSA_KEY_ALGS : HS_ALGS;
}
if (options.jwtid) {
if (payload.jti !== options.jwtid) {
return done(new JsonWebTokenError('jwt jwtid invalid. expected: ' + options.jwtid));
}
}
if (options.complete === true) {
var signature = decodedToken.signature;
return done(null, {
header: header,
payload: payload,
signature: signature
});
}
return done(null, payload);
});
};
decode.js
- The main function is to return to our
payloadload - How to get it depends
jwsplug-in unit
var jws = require('jws');
module.exports = function (jwt, options) {
options = options || {
};
var decoded = jws.decode(jwt, options);
if (!decoded) {
return null; }
var payload = decoded.payload;
if (options.complete === true) {
return {
header: decoded.header,
payload: payload,
signature: decoded.signature
};
}
return payload;
};
jws
- We came to the next floor
jwsPlug in !
index.js
- We can see that the focus is
SignStreamandVerifyStreamThe implementation of the - What's more interesting is that :
createSignyes new A newSignStreamsignyesSignStream.sign
- You should know why right away
createSignYou can call back
/*global exports*/
var SignStream = require('./lib/sign-stream');
var VerifyStream = require('./lib/verify-stream');
var ALGORITHMS = [
'HS256', 'HS384', 'HS512',
'RS256', 'RS384', 'RS512',
'PS256', 'PS384', 'PS512',
'ES256', 'ES384', 'ES512'
];
exports.ALGORITHMS = ALGORITHMS;
exports.sign = SignStream.sign;
exports.verify = VerifyStream.verify;
exports.decode = VerifyStream.decode;
exports.isValid = VerifyStream.isValid;
exports.createSign = function createSign(opts) {
return new SignStream(opts);
};
exports.createVerify = function createVerify(opts) {
return new VerifyStream(opts);
};
lib
sign-stream.js
jwsSignforjwaUse of plug-ins , It is a pity that , Still no real source codecreatSignOfonceThat's why callbacks can be usedonceIt's fromDataStreamTo the , We won't look at this anymore !
- It's mounting
signFunction , YesemitThe throw of- Where to deal with it
emitI haven't figured it out yet
- Where to deal with it
function jwsSign(opts) {
var header = opts.header;
var payload = opts.payload;
var secretOrKey = opts.secret || opts.privateKey;
var encoding = opts.encoding;
var algo = jwa(header.alg);
var securedInput = jwsSecuredInput(header, payload, encoding);
var signature = algo.sign(securedInput, secretOrKey);
return util.format('%s.%s', securedInput, signature);
}
function SignStream(opts) {
var secret = opts.secret||opts.privateKey||opts.key;
var secretStream = new DataStream(secret);
this.readable = true;
this.header = opts.header;
this.encoding = opts.encoding;
this.secret = this.privateKey = this.key = secretStream;
this.payload = new DataStream(opts.payload);
this.secret.once('close', function () {
if (!this.payload.writable && this.readable)
this.sign();
}.bind(this));
this.payload.once('close', function () {
if (!this.secret.writable && this.readable)
this.sign();
}.bind(this));
}
util.inherits(SignStream, Stream);
SignStream.prototype.sign = function sign() {
try {
var signature = jwsSign({
header: this.header,
payload: this.payload.buffer,
secret: this.secret.buffer,
encoding: this.encoding
});
this.emit('done', signature);
this.emit('data', signature);
this.emit('end');
this.readable = false;
return signature;
} catch (e) {
this.readable = false;
this.emit('error', e);
this.emit('close');
}
};
SignStream.sign = jwsSign;
module.exports = SignStream;
verify-stream.js
decode
- You can see
decodeJust put your head , load , Visa combinedheaderusesplitSplit up , Should bectx.request.such , Get the following parameters
function signatureFromJWS(jwsSig) {
return jwsSig.split('.')[2];
}
function jwsDecode(jwsSig, opts) {
opts = opts || {
};
jwsSig = toString(jwsSig);
if (!isValidJws(jwsSig))
return null;
var header = headerFromJWS(jwsSig);
if (!header)
return null;
var payload = payloadFromJWS(jwsSig);
if (header.typ === 'JWT' || opts.json)
payload = JSON.parse(payload, opts.encoding);
return {
header: header,
payload: payload,
signature: signatureFromJWS(jwsSig)
};
}
VerifyStream.decode = jwsDecode;
verify
- The core implementation is still in
algo, andalgocome fromjwaplug-in unit
function securedInputFromJWS(jwsSig) {
return jwsSig.split('.', 2).join('.');
}
function signatureFromJWS(jwsSig) {
return jwsSig.split('.')[2];
}
function jwsVerify(jwsSig, algorithm, secretOrKey) {
if (!algorithm) {
var err = new Error("Missing algorithm parameter for jws.verify");
err.code = "MISSING_ALGORITHM";
throw err;
}
jwsSig = toString(jwsSig);
var signature = signatureFromJWS(jwsSig);
var securedInput = securedInputFromJWS(jwsSig);
var algo = jwa(algorithm);
return algo.verify(securedInput, signature, secretOrKey);
}
jwa
- We used base note for incoming parameters and then called different functions.
- For ease of invocation , We wrote different functions
signerFactories,verifierFactoriesInside
module.exports = function jwa(algorithm) {
var signerFactories = {
hs: createHmacSigner,
rs: createKeySigner,
ps: createPSSKeySigner,
es: createECDSASigner,
none: createNoneSigner,
}
var verifierFactories = {
hs: createHmacVerifier,
rs: createKeyVerifier,
ps: createPSSKeyVerifier,
es: createECDSAVerifer,
none: createNoneVerifier,
}
var match = algorithm.match(/^(RS|PS|ES|HS)(256|384|512)$|^(none)$/);
if (!match)
throw typeError(MSG_INVALID_ALGORITHM, algorithm);
var algo = (match[1] || match[3]).toLowerCase();
var bits = match[2];
return {
sign: signerFactories[algo](bits),
verify: verifierFactories[algo](bits),
}
};
With createHmacSigner For example
- The whole core code is still in
crypto-jsPlug in - But it feels close !
function createHmacSigner(bits) {
return function sign(thing, secret) {
checkIsSecretKey(secret); // A function to check the key , No more details
thing = normalizeInput(thing); // There is one stringify The operation of
var hmac = crypto.createHmac('sha' + bits, secret);
var sig = (hmac.update(thing), hmac.digest('base64'))
return fromBase64(sig);
}
}
crypto-js
- This is the end
- The bottom implementation is the specific implementation of various encryption algorithms , I'm exhausted
- If you like it a hundred times , Let's show the specific implementation of Kangkang encryption algorithm
Let's go to Kangkang documentcrypto-jsSpecific use of - Encrypted content + Generated hash value
- Then call the loaded algorithm for encryption , Private key encryption is used here
- What's more interesting is that :
- The document says client You can also use , Therefore, it is possible to know that the private key can be decrypted in the browser
<script type="text/javascript" src="path-to/bower_components/crypto-js/crypto-js.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript">
var encrypted = CryptoJS.AES(...);
var encrypted = CryptoJS.SHA256(...);
</script>
import sha256 from 'crypto-js/sha256';
import hmacSHA512 from 'crypto-js/hmac-sha512';
import Base64 from 'crypto-js/enc-base64';
const message, nonce, path, privateKey; // ...
const hashDigest = sha256(nonce + message);
const hmacDigest = Base64.stringify(hmacSHA512(path + hashDigest, privateKey));
*** Or the second method of use
var CryptoJS = require("crypto-js");
console.log(CryptoJS.HmacSHA1("Message", "Key"));
版权声明
本文为[Juntong]所创,转载请带上原文链接,感谢
https://yzsam.com/2022/04/202204220958320703.html
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
idea写sparksql程序local[*]模式可以运行,提交到spark yarn运行出现ClassNotFoundException
Glide设置圆角图片(支持自定义圆角位置)
5.嵌入式控制器(Embedded Controller,EC)学习 PS/2协议
分享几个 Sklearn 模块中不为人知又超级好用的 API 函数
Matplotlib tutorial 04 --- drawing commonly used graphics
cobbler补鞋匠
关于tpshop开源商城6.0版本图片库不显示图片问题
[age appropriate friends of interesting programming questions] (detailed explanation of the original title of leetcode)
SQL 关系型数据库管理系统
Zhezheng nail scanning code login
西门子PLC能否通过以太网数据模块实现无线通讯?
OGG-00663 OCI Error ORA-02396: exceeded maximum idle time
中商惠⺠交易中台架构演进:对 Apache ShardingSphere 的应⽤
天梯22模拟 L3-2 拼题A打卡奖励 (30 分)
Multi target tracking extended Kalman filter (EKF)
Text justify, orientation, combine text attributes
The root cause of Android's security vulnerability is Apple's lossless audio codec
Simple operation of QT axobject Library
Can Siemens PLC realize wireless communication through Ethernet data module?
Tensorflow Experiment 4 -- Boston house price forecast








