当前位置:网站首页>The use of Promise and the use of async/await
The use of Promise and the use of async/await
2022-08-08 06:23:00 【wendyTan10】
jsAsynchronous programming
jsThe runner is single threaded,All queues are done in one thread.一旦遇到大量任务或者遇到一个耗时的任务,比如加载一个高清图片,网页就会出现"假死",因为JavaScript停不下来,也就无法响应用户的行为. 那么js是如何执行的呢?
- 从前到后,一行一行执行
- 如果某一行执行报错,则停止下面代码的执行
- Execute the synchronized code first,再执行异步
为了防止主线程的阻塞,JavaScript 有了 同步和 异步的概念:
- 同步:Expected results are immediately available;
- 异步:To return the result based on the callback;而
event loopThis is the principle of asynchronous callback implementation;
event loop(事件循环/事件轮询)
循环的机制: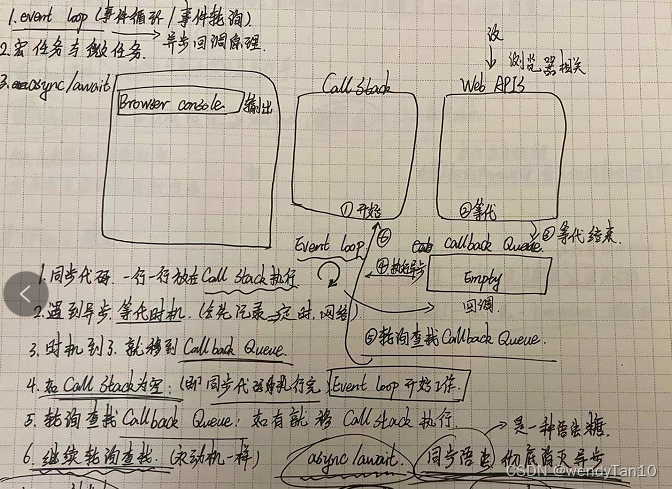
执行的步骤:
- 同步代码,一行一行放在
Call stack执行 - 遇到异步 -
等待时机(会先记录 - 定时/网络) - 时机到了,就移动到
Callback Queue - 如
Callback Queue的为空;(即同步代码执行完) - 轮询查找
Callback Queue,Move it if there isCallback stack执行; - Continue polling for lookups(永动机一样);
异步(setTimeout ,ajax等)使用回调,基于event loop;
promise
先回顾一下 Promise 的基本使用:
// 加载图片
function loadImg(src) {
const p = new Promise(
(resolve, reject) => {
const img = document.createElement('img')
img.onload = () => {
resolve(img)
}
img.onerror = () => {
const err = new Error(`图片加载失败 ${
src}`)
reject(err)
}
img.src = src
}
)
return p
}
const url = 'https://img.mukewang.com/5a9fc8070001a82402060220-140-140.jpg'
loadImg(url).then(img => {
console.log(img.width)
return img
}).then(img => {
console.log(img.height)
}).catch(ex => console.error(ex))
promise的三种状态
pending(继续) ,resolved(成功)和rejected(失败);
pending状态:不会触发then和catch;resolved状态: 触发then回调;rejected状态:触发catch回调;
// when just defined,状态默认为 pending
const p1 = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
})
// 执行 resolve() 后,状态变成 resolved
const p2 = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve()
})
})
// 执行 reject() 后,状态变成 rejected
const p3 = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
reject()
})
})
// 直接返回一个 resolved 状态
Promise.resolve(100)
// 直接返回一个 rejected 状态
Promise.reject('some error')
promise的执行;并且不可逆
- pending --> resolved;成功
- pending --> rejected;失败
then和catch改变状态
then正常返回resolved,里面有报错则返回rejected;catch正常返回resolved,里面有报错则返回rejected;
then catch 会继续返回 Promise ,此时可能会发生状态变化!!!
// then() Usually returns normally resolved 状态的 promise
Promise.resolve().then(() => {
return 100
})
// then() throws an error,会返回 rejected 状态的 promise
Promise.resolve().then(() => {
throw new Error('err')
})
// catch() 不抛出错误,会返回 resolved 状态的 promise
Promise.reject().catch(() => {
console.error('catch some error')
})
// catch() 抛出错误,会返回 rejected 状态的 promise
Promise.reject().catch(() => {
console.error('catch some error')
throw new Error('err')
})
promise的then/catch题目
// 第一题
Promise.resolve().then(() => {
console.log(1); // 返回的是resolved,All that is executed is the latterthen
}).catch(() => {
console.log(2);
}).then(() => {
console.log(3);
})
// 1 3
// 第二题
Promise.resolve().then(() => {
// 返回 rejected 状态的 promise
console.log(1)
throw new Error('erro1'); // 错误Error,执行catch
}).catch(() => {
console.log(2)
}).then(() => {
console.log(3)
})
// 1 2 3
// 第三题
Promise.resolve().then(() => {
// 返回 rejected 状态的 promise
console.log(1)
throw new Error('erro1')
}).catch(() => {
console.log(2); // 正常的执行resolved的事件
}).catch(() => {
// 注意这里是 catch
console.log(3)
})
// 1 2
async/await
It is a synchronous syntax that completely eliminates asynchrony,is a form of syntactic sugar;Write asynchronous in a synchronous way:
- 执行
async函数,返回的是promise对象; await相当于promise的then;try...catchAsync can be captured,代替了promise的catch;
For example, synchronous writing of loading pictures:
function loadImg(src) {
const promise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
const img = document.createElement('img')
img.onload = () => {
resolve(img)
}
img.onerror = () => {
reject(new Error(`图片加载失败 ${
src}`))
}
img.src = src
})
return promise
}
async function loadImg1() {
const src1 = 'http://www.imooc.com/static/img/index/logo_new.png'
const img1 = await loadImg(src1)
return img1
}
async function loadImg2() {
const src2 = 'https://avatars3.githubusercontent.com/u/9583120'
const img2 = await loadImg(src2)
return img2
}
(async function () {
// 注意:await 必须放在 async 函数中,否则会报错
try {
// 加载第一张图片
const img1 = await loadImg1()
console.log(img1)
// 加载第二张图片
const img2 = await loadImg2()
console.log(img2)
} catch (ex) {
console.error(ex)
}
})()
async function fn() {
return 100
}
(async function () {
const a = fn() // ?? // promise
const b = await fn() // ?? // 100
})()
和 Promise 的关系
async函数返回结果都是Promise对象(如果函数内没返回Promise,则自动封装一下)
async function fn2() {
return new Promise(() => {
})
}
console.log( fn2() )
async function fn1() {
return 100
}
console.log( fn1() ) // 相当于 Promise.resolve(100)
await后面跟Promise对象:会阻断后续代码,等待状态变为resolved,才获取结果并继续执行await后续跟非Promise对象:会直接返回
(async function () {
const p1 = new Promise(() => {
})
await p1
console.log('p1') // 不会执行
})()
(async function () {
const p2 = Promise.resolve(100)
const res = await p2
console.log(res) // 100
})()
(async function () {
const res = await 100
console.log(res) // 100
})()
(async function () {
const p3 = Promise.reject('some err')
const res = await p3; // 前面是reject
console.log(res) // 不会执行
})()
try...catch捕获rejected状态
(async function () {
const p4 = Promise.reject('some err')
try {
const res = await p4
console.log(res)
} catch (ex) {
console.error(ex)
}
})()
总结来看:
- async 封装 Promise
- await 处理 Promise 成功
- try…catch 处理 Promise 失败
异步本质
await 是同步写法,但本质还是异步调用.
async function async1 () {
console.log('async1 start'); // 2
await async2()
console.log('async1 end'); // 5 关键在这一步,它相当于放在 callback 中,最后执行
}
async function async2 () {
console.log('async2'); // 3
}
console.log('script start'); // 1
async1();
console.log('script end'); // 4
即,只要遇到了 await ,后面的代码都相当于放在 callback 里.
for…of
// 定时算乘法
function multi(num) {
return new Promise((resolve) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve(num * num)
}, 1000)
})
}
// // 使用 forEach ,是 1s 之后打印出所有结果,即 3 个值是一起被计算出来的
// function test1 () {
// const nums = [1, 2, 3];
// nums.forEach(async x => {
// const res = await multi(x);
// console.log(res);
// })
// }
// test1();
// 使用 for...of ,可以让计算挨个串行执行
async function test2 () {
const nums = [1, 2, 3];
for (let x of nums) {
// 在 for...of 循环体的内部,遇到 await 会挨个串行计算
const res = await multi(x)
console.log(res)
}
}
test2()
微任务/宏任务
- 宏任务:setTimeout setInterval DOM 事件
- 微任务:Promise(对于前端来说)
- Microtasks are executed earlier than macrotasks
console.log(100)
setTimeout(() => {
console.log(200)
})
Promise.resolve().then(() => {
console.log(300)
})
console.log(400)
// 100 400 300 200
event loop 和 DOM 渲染
再次回顾 event loop 的过程
- 每一次 call stack 结束,都会触发 DOM 渲染(It doesn't have to be rendered,Just give it once DOM Rendering opportunity!!!)
- 然后再进行 event loop
const $p1 = $('<p>一段文字</p>')
const $p2 = $('<p>一段文字</p>')
const $p3 = $('<p>一段文字</p>')
$('#container')
.append($p1)
.append($p2)
.append($p3)
console.log('length', $('#container').children().length )
alert('本次 call stack 结束,DOM 结构已更新,但尚未触发渲染')
// (alert 会阻断 js 执行,也会阻断 DOM 渲染,便于查看效果)
// 到此,即本次 call stack 结束后(同步任务都执行完了),The browser will automatically trigger the rendering,No code intervention
// 另外,按照 event loop 触发 DOM 渲染时机,setTimeout 时 alert ,就能看到 DOM Rendered result
setTimeout(function () {
alert('setTimeout 是在下一次 Call Stack ,就能看到 DOM Rendered result')
})
宏任务和微任务的区别
- 宏任务:DOM Triggered after rendering
- 微任务:DOM Fired before rendering
// 修改 DOM
const $p1 = $('<p>一段文字</p>')
const $p2 = $('<p>一段文字</p>')
const $p3 = $('<p>一段文字</p>')
$('#container')
.append($p1)
.append($p2)
.append($p3)
// // 微任务:渲染之前执行(DOM 结构已更新)
// Promise.resolve().then(() => {
// const length = $('#container').children().length
// alert(`micro task ${length}`)
// })
// 宏任务:渲染之后执行(DOM 结构已更新)
setTimeout(() => {
const length = $('#container').children().length
alert(`macro task ${
length}`)
})
再深入思考一下:Why are there differences between the two,One before rendering,One after rendering?
微任务:ES within the grammatical standards,JS engine for unified processing.即,No browser has anything to do with it,can be processed at one time,Faster and more timely.宏任务:ES grammar no,JS The engine doesn't handle it,浏览器(或nodejs)intervention treatment.
边栏推荐
- Query and track multiple express tracking numbers, and filter the tracking numbers shipped at a certain time
- How to batch import files and rename them all to the same file name
- 日常bug小结:
- File Operations - IO
- Postman显示验证码图片(base64字符串)
- 2-SAT
- Synchronization and Asynchrony of Clocks
- torch.gather() usage interpretation
- 机器学习之R语言caret包trainControl函数详解
- 主脑提示( Master-Mind Hints )
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
Assertion failure in -[UITableView _configureCellForDisplay:forIndexPath:]
Shorthand for flex layout properties
Basic tools - NETCAT (Telnet - banner, transfer text message)
LLVM系列第二十九章:写一个简单的常量加法“消除”工具(Pass)
flex布局属性简约速记
独立成分分析ICA/FastICA
【u-boot】u-boot的驱动模型分析
selenium模拟登录某宝
分页组件的使用
State Compression Review
神经网络解决哪些问题,神经网络结果不稳定
Rust学习:5_所有权与借用
tkinter-TinUI-xml combat (7) PDF paging and merging
apifox使用文档之环境变量 / 全局变量 / 临时变量附apifox学习路线图
人体神经元细胞分布图片,神经元人体分布大图
C人脸识别
cnn卷积神经网络反向传播,卷积神经网络维度变化
代码自动初始化
The CAP theorem instance analysis
神经网络一般训练多少次,神经网络训练时间过长