当前位置:网站首页>STL function library
STL function library
2022-04-23 05:32:00 【Mikawa】
STL
vector
| Members of the function | The functionality |
|---|---|
| begin() | Returns the iterator that points to the first element in the container . |
| end() | Returns an iterator pointing to the position after the last element of the container , Usually and begin() Use a combination of . |
| rbegin() | Returns the iterator that points to the last element . |
| rend() | Returns the iterator pointing to the position before the position of the first element . |
| cbegin() | and begin() Function the same , It's just based on it , Added const attribute , Cannot be used to modify elements . |
| cend() | and end() Function the same , It's just based on it , Added const attribute , Cannot be used to modify elements . |
| crbegin() | and rbegin() Function the same , It's just based on it , Added const attribute , Cannot be used to modify elements . |
| crend() | and rend() Function the same , It's just based on it , Added const attribute , Cannot be used to modify elements . |
| size() | Returns the actual number of elements . |
| max_size() | Returns the maximum number of elements . This is usually a great value , It's usually 232-1, So we rarely use this function . |
| resize() | Change the number of actual elements . |
| capacity() | Return to current capacity . |
| empty() | Determine if there are elements in the container , If there is no element , Then return to true; conversely , return false. |
| reserve() | Increase the capacity of the container . |
| shrink _to_fit() | Reduce memory to the size that the current element is actually using . |
| operator[ ] | Reload the [ ] Operator , You can access the elements in the array as , You can access or even modify... Through subscript vector Elements in the container . |
| at() | Access elements using a boundary checked index . |
| front() | Returns the reference to the first element . |
| back() | Returns the reference to the last element . |
| data() | Returns a pointer to the first element in the container . |
| assign() | Replace the original with new elements . |
| push_back() | Add an element at the end of the sequence . |
| pop_back() | Remove the element at the end of the sequence . |
| insert() | Insert one or more elements at the specified location . |
| erase() | Remove an element or a segment of elements . |
| clear() | Remove all elements , The container size becomes 0. |
| swap() | Exchange all elements of two containers . |
| emplace() | Generate an element directly at the specified location . |
| emplace_back() | Generate an element at the end of the sequence . |
deque
| Members of the function | The functionality |
|---|---|
| begin() | Returns the iterator that points to the first element in the container . |
| end() | Returns an iterator pointing to the position after the last element of the container , Usually and begin() Use a combination of . |
| rbegin() | Returns the iterator that points to the last element . |
| rend() | Returns the iterator pointing to the position before the position of the first element . |
| cbegin() | and begin() Function the same , It's just based on it , Added const attribute , Cannot be used to modify elements . |
| cend() | and end() Function the same , It's just based on it , Added const attribute , Cannot be used to modify elements . |
| crbegin() | and rbegin() Function the same , It's just based on it , Added const attribute , Cannot be used to modify elements . |
| crend() | and rend() Function the same , It's just based on it , Added const attribute , Cannot be used to modify elements . |
| size() | Returns the actual number of elements . |
| max_size() | Returns the maximum number of elements that the container can hold . This is usually a great value , It's usually 232-1, We rarely use this function . |
| resize() | Change the number of actual elements . |
| empty() | Determine if there are elements in the container , If there is no element , Then return to true; conversely , return false. |
| shrink _to_fit() | Reduce memory to the size that the current element is actually using . |
| at() | Access elements using a boundary checked index . |
| front() | Returns the reference to the first element . |
| back() | Returns the reference to the last element . |
| assign() | Replace the original with new elements . |
| push_back() | Add an element at the end of the sequence . |
| push_front() | Add an element to the head of the sequence . |
| pop_back() | Remove the element at the end of the container . |
| pop_front() | Remove the element from the head of the container . |
| insert() | Insert one or more elements at the specified location . |
| erase() | Remove an element or a piece of element . |
| clear() | Remove all elements , The container size becomes 0. |
| swap() | Exchange all elements of two containers . |
| emplace() | Generate an element directly at the specified location . |
| emplace_front() | Generate an element at the head of the container . and push_front() Is the difference between the , This function constructs elements directly at the head of the container , Saves the process of copying moving elements . |
| emplace_back() | Generate an element at the end of the container . and push_back() Is the difference between the , This function constructs elements directly at the end of the container , Saves the process of copying moving elements . |
list
| Member functions | function |
|---|---|
| begin() | Returns a bidirectional iterator that points to the first element in the container . |
| end() | Returns a bidirectional iterator that points to the last element in the container . |
| rbegin() | Returns the reverse bidirectional iterator pointing to the last element . |
| rend() | Returns a reverse bidirectional iterator that points to the previous position of the first element . |
| cbegin() | and begin() Function the same , It's just based on it , Added const attribute , Cannot be used to modify elements . |
| cend() | and end() Function the same , It's just based on it , Added const attribute , Cannot be used to modify elements . |
| crbegin() | and rbegin() Function the same , It's just based on it , Added const attribute , Cannot be used to modify elements . |
| crend() | and rend() Function the same , It's just based on it , Added const attribute , Cannot be used to modify elements . |
| empty() | Determine if there are elements in the container , If there is no element , Then return to true; conversely , return false. |
| size() | Returns the number of elements actually contained in the current container . |
| max_size() | Returns the maximum number of elements a container can contain . This is usually a great value , It's usually 232-1, So we rarely use this function . |
| front() | Returns the reference to the first element . |
| back() | Returns the reference to the last element . |
| assign() | Replace the original contents of the container with new elements . |
| emplace_front() | Generate an element at the head of the container . This function and push_front() The same function , But it's more efficient . |
| push_front() | Insert an element in the head of the container . |
| pop_front() | Delete an element in the container header . |
| emplace_back() | Generate an element directly at the end of the container . This function and push_back() The same function , But it's more efficient . |
| push_back() | Insert an element at the end of the container . |
| pop_back() | Delete an element at the end of the container . |
| emplace() | Insert the element at the specified position in the container . This function and insert() Function the same , But it's more efficient . |
| insert() | Insert the element at the specified position in the container . |
| erase() | Delete an element in one or a region of the container . |
| swap() | Exchange elements in two containers , You must ensure that the element types stored in the two containers are the same . |
| resize() | Size the container . |
| clear() | Delete all elements stored in the container . |
| splice() | Will a list The element in the container is inserted into the specified location of another container . |
| remove(val) | Delete all containers equal to val The elements of . |
| remove_if() | Delete the elements that meet the conditions in the container . |
| unique() | Delete adjacent duplicate elements in the container , Keep only one . |
| merge() | Merge two pre ordered list Containers , And after the merger list The container is still in order . |
| sort() | By changing the position of elements in the container , Sort them . |
| reverse() | Reverse the order of elements in the container . |
map
| Member method | function |
|---|---|
| begin() | Return points to the first... In the container ( Be careful , It's the first one in order ) Bidirectional iterators for key value pairs . If map For containers const limit , The method returns const Two way iterator of type . |
| end() | Returns the last element pointing to the container ( Be careful , It's the last one in order ) The two-way iterator next to the location , Usually and begin() Use a combination of . If map For containers const limit , The method returns const Two way iterator of type . |
| rbegin() | Return to last ( Be careful , It's the last one in order ) The inverse bidirectional iterator of the element . If map For containers const limit , The method returns const Reverse bidirectional iterator of type . |
| rend() | Return to the first ( Be careful , It's the first one in order ) The inverse bidirectional iterator of the previous position of the element . If map For containers const limit , The method returns const Reverse bidirectional iterator of type . |
| cbegin() | and begin() Function the same , It's just based on it , Added const attribute , Cannot be used to modify key value pairs stored in containers . |
| cend() | and end() Function the same , It's just based on it , Added const attribute , Cannot be used to modify key value pairs stored in containers . |
| crbegin() | and rbegin() Function the same , It's just based on it , Added const attribute , Cannot be used to modify key value pairs stored in containers . |
| crend() | and rend() Function the same , It's just based on it , Added const attribute , Cannot be used to modify key value pairs stored in containers . |
| find(key) | stay map The search key in the container is key The key/value pair , If you succeed in finding , Returns the bidirectional iterator pointing to the key value pair ; conversely , Then go back and end() Iterators with the same method . in addition , If map For containers const limit , The method returns const Two way iterator of type . |
| lower_bound(key) | Returns a pointer to the current map The first in the container is greater than or equal to key A two-way iterator of key value pairs . If map For containers const limit , The method returns const Two way iterator of type . |
| upper_bound(key) | Returns a pointer to the current map The first in the container is greater than key The iterator of the key value pair of . If map For containers const limit , The method returns const Two way iterator of type . |
| equal_range(key) | This method returns a pair object ( contain 2 Two way iterators ), among pair.first and lower_bound() The return value of the method is equivalent ,pair.second and upper_bound() The return value of the method is equivalent . in other words , This method will return a range , The keys in this range are key The key/value pair (map The container key value pair is unique , So the range contains at most one key value pair ). |
| empty() | If the container is empty , Then return to true; otherwise false. |
| size() | Returns the current map The number of key value pairs in the container . |
| max_size() | return map The maximum number of key value pairs a container can hold , Different operating systems , The return values are also different . |
| operator[] | map The container is overloaded [] Operator , As long as you know map The value of the key of a key value pair in the container , It's like getting elements in an array , Get the corresponding value directly through the key . |
| at(key) | find map In the container key The value of the key , If you can't find it , This function raises out_of_range abnormal . |
| insert() | towards map Insert key value pairs into the container . |
| erase() | Delete map Container designated location 、 Specify key (key) Value or key value pairs in the specified region . The following chapters will focus on this method . |
| swap() | In exchange for 2 individual map Key value pairs stored in the container , It means , Operation of the 2 Key value pairs must be of the same type . |
| clear() | Empty map All key value pairs in the container , Even if map Container of size() by 0. |
| emplace() | At present map Construct a new key value pair at the specified position in the container . The effect is the same as inserting key value pairs , But it's more efficient . |
| emplace_hint() | In essence and emplace() stay map The way to construct new key value pairs in a container is the same , The difference is , The user must provide the method with an iterator that indicates where the key value pair is generated , As the first parameter of the method . |
| count(key) | At present map In the container , The search key is key The number of key value pairs and returns . Be careful , because map The key value of each key value pair in the container is unique , Therefore, the maximum return value of this function is 1. |
set
| Member method | function |
|---|---|
| begin() | Return points to the first... In the container ( Be careful , It's the first one in order ) Bidirectional iterator of element . If set For containers const limit , The method returns const Two way iterator of type . |
| end() | Returns the last element pointing to the container ( Be careful , It's the last one in order ) The two-way iterator next to the location , Usually and begin() Use a combination of . If set For containers const limit , The method returns const Two way iterator of type . |
| rbegin() | Return to last ( Be careful , It's the last one in order ) The inverse bidirectional iterator of the element . If set For containers const limit , The method returns const Reverse bidirectional iterator of type . |
| rend() | Return to the first ( Be careful , It's the first one in order ) The inverse bidirectional iterator of the previous position of the element . If set For containers const limit , The method returns const Reverse bidirectional iterator of type . |
| cbegin() | and begin() Function the same , It's just based on it , Added const attribute , Cannot be used to modify element values stored in containers . |
| cend() | and end() Function the same , It's just based on it , Added const attribute , Cannot be used to modify element values stored in containers . |
| crbegin() | and rbegin() Function the same , It's just based on it , Added const attribute , Cannot be used to modify element values stored in containers . |
| crend() | and rend() Function the same , It's just based on it , Added const attribute , Cannot be used to modify element values stored in containers . |
| find(val) | stay set The lookup value in the container is val The elements of , If you succeed in finding , Returns a bidirectional iterator that points to the element ; conversely , Then go back and end() Iterators with the same method . in addition , If set For containers const limit , The method returns const Two way iterator of type . |
| lower_bound(val) | Returns a pointer to the current set The first in the container is greater than or equal to val A bidirectional iterator of the elements of . If set For containers const limit , The method returns const Two way iterator of type . |
| upper_bound(val) | Returns a pointer to the current set The first in the container is greater than val The iterator of the elements of . If set For containers const limit , The method returns const Two way iterator of type . |
| equal_range(val) | This method returns a pair object ( contain 2 Two way iterators ), among pair.first and lower_bound() The return value of the method is equivalent ,pair.second and upper_bound() The return value of the method is equivalent . in other words , This method will return a range , The values contained in this range are val The elements of (set Each element in the container is unique , Therefore, the range contains at most one element ). |
| empty() | If the container is empty , Then return to true; otherwise false. |
| size() | Returns the current set The number of elements in the container . |
| max_size() | return set The maximum number of elements that a container can hold , Different operating systems , The return values are also different . |
| insert() | towards set Insert element into container . |
| erase() | Delete set Elements stored in containers . |
| swap() | In exchange for 2 individual set All elements stored in the container . It means , Operation of the 2 individual set Containers must be of the same type . |
| clear() | Empty set All elements in the container , But even set Container of size() by 0. |
| emplace() | At present set Construct the new element directly at the specified location in the container . Its effect and insert() equally , But it's more efficient . |
| emplace_hint() | In essence and emplace() stay set The way new elements are constructed in containers is the same , The difference is , The consumer must provide the method with an iterator that indicates where the new element is generated , As the first parameter of the method . |
| count(val) | At present set In the container , The lookup value is val The number of elements of , And back to . Be careful , because set The value of each element in the container is unique , Therefore, the maximum return value of this function is 1. |
unordered_map
| Member method | function |
|---|---|
| begin() | Returns a forward iterator pointing to the first key value pair in the container . |
| end() | Returns a forward iterator pointing to the position after the last key value pair in the container . |
| cbegin() | and begin() Function the same , It just adds const attribute , That is, the iterator returned by this method cannot be used to modify the key value pairs stored in the container . |
| cend() | and end() Function the same , It's just based on it , Added const attribute , That is, the iterator returned by this method cannot be used to modify the key value pairs stored in the container . |
| empty() | If the container is empty , Then return to true; otherwise false. |
| size() | Returns the number of key value pairs stored in the current container . |
| max_size() | Returns the maximum number of key value pairs that the container can hold , Different operating systems , The return values are also different . |
| operator[key] | The template class is overloaded with [] Operator , Its function is to access the elements in the array , Just give the key of a key value pair key, You can get the value corresponding to the key . Be careful , If there is no in the current container with key Is the key value pair of the key , Then it will use this key to insert a new key value pair into the current container . |
| at(key) | Returns the key stored in the container key Corresponding value , If key non-existent , It will be thrown out. out_of_range abnormal . |
| find(key) | Looking to key Is the key value pair of the key , If you find , Returns a forward iterator pointing to the key value pair ; conversely , Returns an iterator that points to the position after the last key value pair in the container ( If end() Method return iterator ). |
| count(key) | Look in the container to key The number of key value pairs of a key . |
| equal_range(key) | Return to one pair object , It contains 2 An iterator , Used to indicate that the key in the current container is key The range of key value pairs . |
| emplace() | Add a new key value pair to the container , Efficient than insert() The method is high . |
| emplace_hint() | Add a new key value pair to the container , Efficient than insert() The method is high . |
| insert() | Add a new key value pair to the container . |
| erase() | Delete the specified key value pair . |
| clear() | Empty the container , That is, delete all key value pairs stored in the container . |
| swap() | In exchange for 2 individual unordered_map Key value pairs stored in the container , The premise is that this 2 The types of containers are exactly the same . |
| bucket_count() | Returns the key value pair stored at the bottom of the current container , Use the bucket ( A linear linked list represents a bucket ) The number of . |
| max_bucket_count() | Return to the current system ,unordered_map How many barrels can be used at the bottom of the container . |
| bucket_size(n) | Back to page n The number of key value pairs stored in buckets . |
| bucket(key) | Return to key Is the key value of the key to the bucket number . |
| load_factor() | return unordered_map The current load factor in the container . Load factor , It refers to the number of key value pairs stored in the current container (size()) And the number of barrels used (bucket_count()) The ratio of the , namely load_factor() = size() / bucket_count(). |
| max_load_factor() | Returns or sets the current unordered_map The load factor of the container . |
| rehash(n) | Set the number of buckets used at the bottom of the current container to n. |
| reserve() | The number of buckets ( That is to say bucket_count() Return value of method ) Set to accommodate at least count Yuan ( Do not exceed the maximum load factor ) The amount needed , And rearrange the container . |
| hash_function() | Returns the hash function object used by the current container . |
stack
| Member functions | function |
|---|---|
| empty() | When stack When there are no elements in the stack , The member function returns true; conversely , return false. |
| size() | return stack The number of elements stored in the stack . |
| top() | Returns a reference to a stack top element , The type is T&. If the stack is empty , The program will report an error . |
| push(const T& val) | Copy first val, then val The copy is pushed to the top of the stack . This is done by calling the underlying container push_back() Function completed . |
| push(T&& obj) | Push the element into the top of the stack by moving it . This is done by calling the right value reference parameter of the underlying container push_back() Function completed . |
| pop() | Pop up top element . |
| emplace(arg…) | arg… It can be a parameter , It can also be multiple parameters , But they are only used to construct an object , And directly generate the object at the top of the stack , As a new stack top element . |
| swap(stack & other_stack) | Put two stack The elements in the adapter are interchanged , It should be noted that , For exchange 2 individual stack The element types stored in the adapter and the underlying container types , All have to be the same . |
queue
| Member functions | function |
|---|---|
| empty() | If queue If there is no element in , return true. |
| size() | return queue The number of elements in . |
| front() | return queue Reference to the first element in . If queue Is a constant , Just return a frequent quote ; If queue It's empty , The return value is undefined . |
| back() | return queue Reference to the last element in . If queue Is a constant , Just return a frequent quote ; If queue It's empty , The return value is undefined . |
| push(const T& obj) | stay queue Add a copy of the element at the end of . This is by calling the member functions of the underlying container push_back() To complete . |
| emplace() | stay queue Add an element directly to the tail of the . |
| push(T&& obj) | In a mobile way queue Add elements to the tail of . This is by calling the member function of the underlying container with the right value reference parameter push_back() To complete . |
| pop() | Delete queue The first element in . |
| swap(queue &other_queue) | Put two queue Elements in the container adapter are interchanged , It should be noted that , For exchange 2 individual queue The element types stored in the container adapter and the underlying container types , All have to be the same . |
sort
#include <iostream> // std::cout
#include <algorithm> // std::sort
#include <vector> // std::vector
// Implement custom sorting rules in the way of ordinary functions
bool mycomp(int i, int j) {
return (i < j);
}
// Implement custom collation as a function object
class mycomp2 {
public:
bool operator() (int i, int j) {
return (i < j);
}
};
int main() {
std::vector<int> myvector{ 32, 71, 12, 45, 26, 80, 53, 33 };
// Call the first syntax format , Yes 32、71、12、45 Sort
std::sort(myvector.begin(), myvector.begin() + 4); //(12 32 45 71) 26 80 53 33
// Call the second syntax format , utilize STL Other comparison rules provided by the standard library ( such as greater<T>) Sort
std::sort(myvector.begin(), myvector.begin() + 4, std::greater<int>()); //(71 45 32 12) 26 80 53 33
// Call the second syntax format , Sorting by custom comparison rules
std::sort(myvector.begin(), myvector.end(), mycomp2());//12 26 32 33 45 53 71 80
// Output myvector Elements in the container
for (std::vector<int>::iterator it = myvector.begin(); it != myvector.end(); ++it) {
std::cout << *it << ' ';
}
return 0;
}
版权声明
本文为[Mikawa]所创,转载请带上原文链接,感谢
https://yzsam.com/2022/04/202204220543093697.html
边栏推荐
- Interview Basics
- [the background color changes after clicking a line]
- Data bus realizes the communication between brother components
- Watch depth monitoring mode
- String class understanding - final is immutable
- IPI interrupt
- 可执行程序执行流程
- 使用宝塔+xdebug+vscode远程调试代码
- Create process memory management copy_ Mm - processes and threads (IX)
- Hongji | how does HR carry out self change and organizational change in the digital era?
猜你喜欢

what is wifi6?
![[no title] Click the classification jump page to display the details](/img/a6/fb302129c06e07b8d1eddeaabc9d2d.png)
[no title] Click the classification jump page to display the details

(十一)vscode代码格式化配置

Various situations of data / component binding
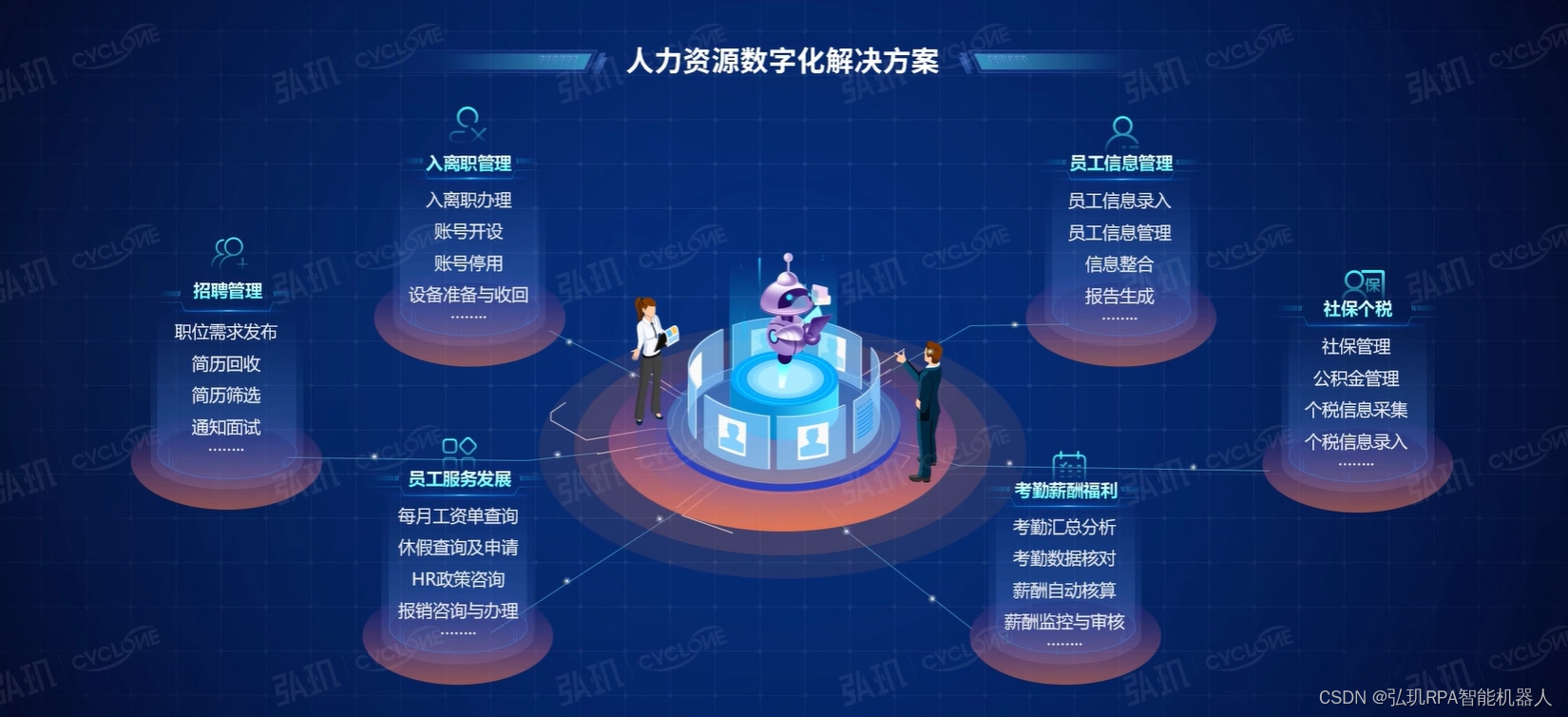
Hongji | how does HR carry out self change and organizational change in the digital era?
es6数组的使用

Cross platform packaging of QT packaging program

selenium預先加載cookie的必要性
Laravel routing job

Intel SGX preliminary learning and understanding notes (continuously updated)
随机推荐
what is wifi6?
Escape characters \ splicing of data formats
创建进程内存管理copy_mm - 进程与线程(九)
shell指令学习1
catkin_ What did package do
egg中的多进程模型--egg文档搬运工
Pavlov and hobbies
Call the interface to get the time
Vscode settings JSON configuration
Some pits used by uni
JS time format conversion
2021-09-27
Redis的基本知识
STD:: String implements split
Quick app bottom navigation bar
Create cells through JS (while loop)
X86 assembly syntax: at & T and Intel
Cmake basic tutorial (39) pkgconfig
[untitled]
Watch depth monitoring mode