当前位置:网站首页>Insect merging count
Insect merging count
2022-04-21 14:21:00 【Hua Weiyun】
Sort
Common sorting algorithms
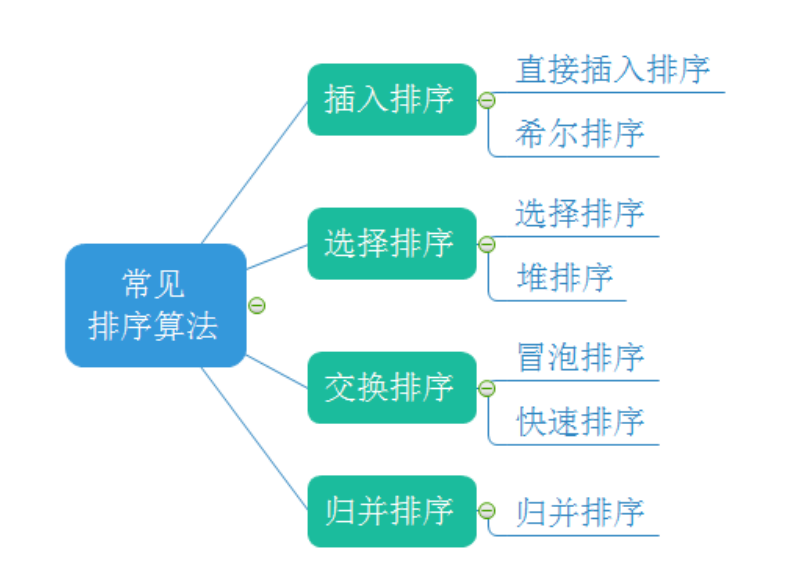
Implementation of common sorting algorithms
Merge sort
The basic idea
Merge sort (MERGE-SORT) It is an effective sorting algorithm based on merge operation , The algorithm is a divide-and-conquer method (Divide and Conquer) A very typical application . Merges ordered subsequences , You get a perfectly ordered sequence ; So let's make each subsequence in order , Then make the subsequence segments in order . If two ordered tables are merged into one ordered table , It's called a two-way merge . The core steps of merging and sorting :
In fact, merging is not our first contact , We've been in contact before , such as Merge two ordered arrays This is the idea of merging

But our topic above is left interval order , The right interval is also ordered . Our normal questions will certainly not be given to you directly . This time a little deeper , Don't you have no order , Then let's divide , To the point that you can't share any more ,== That is, there is only one , Can you say that there is no order , Definitely not ==, So we continue to divide and conquer .

Recursive writing
Look at the above. GIF Also know that the first reaction is recursion
Check the phenomenon through debugging
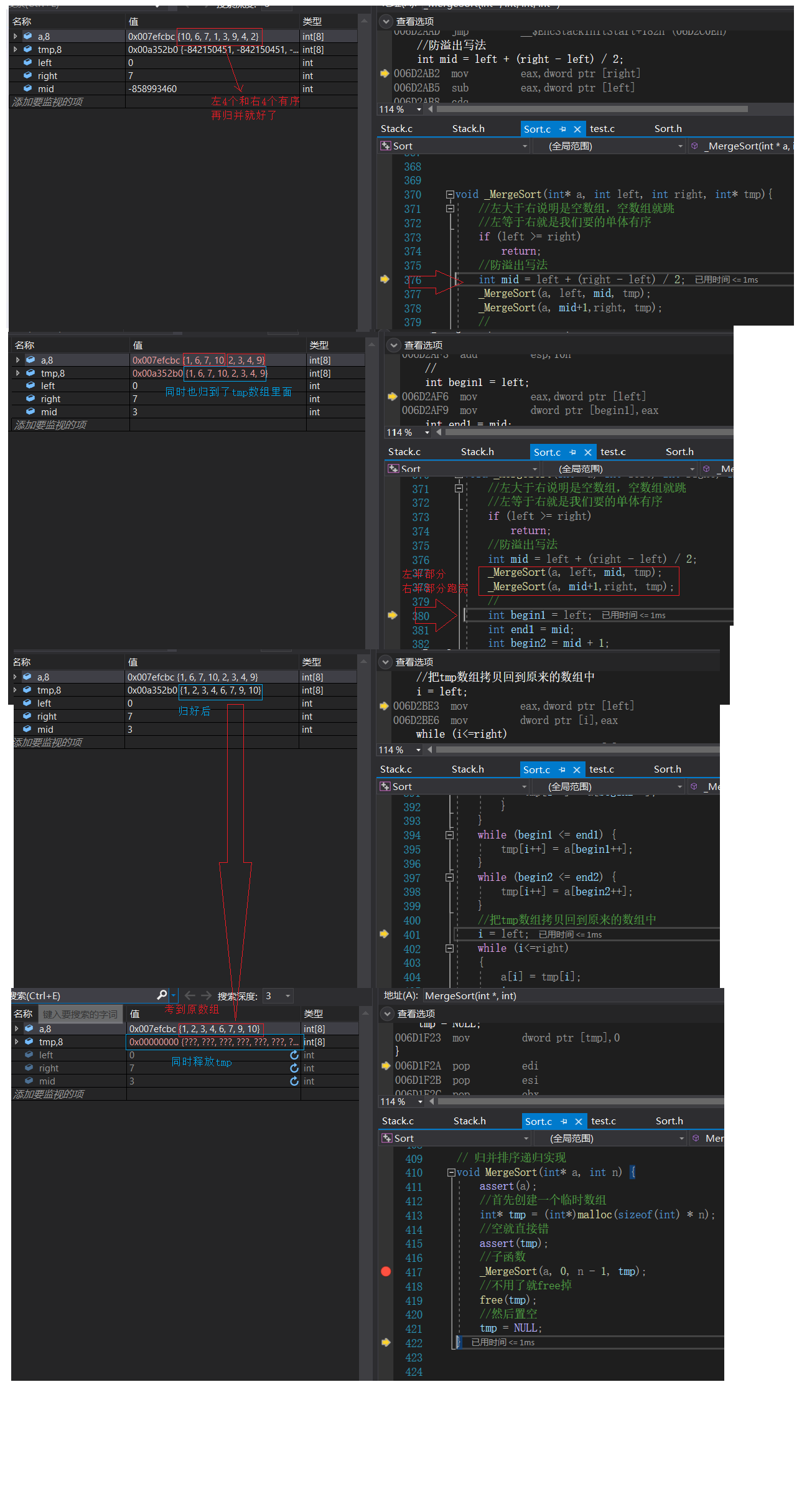
Merging order
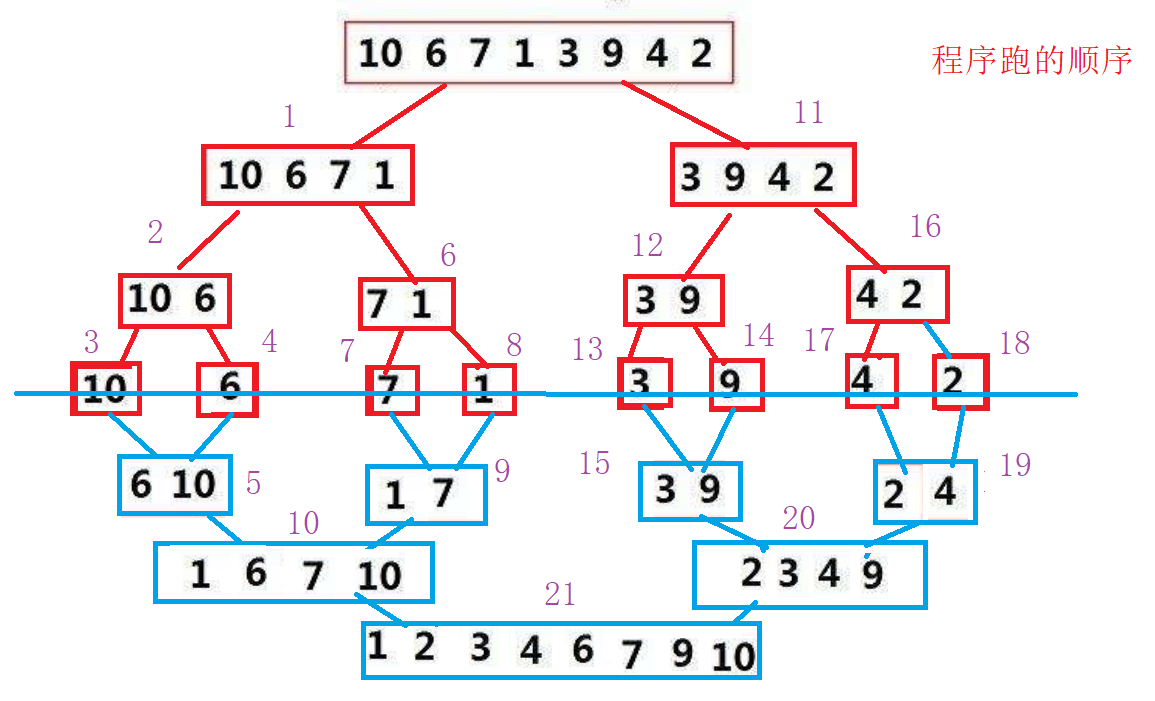
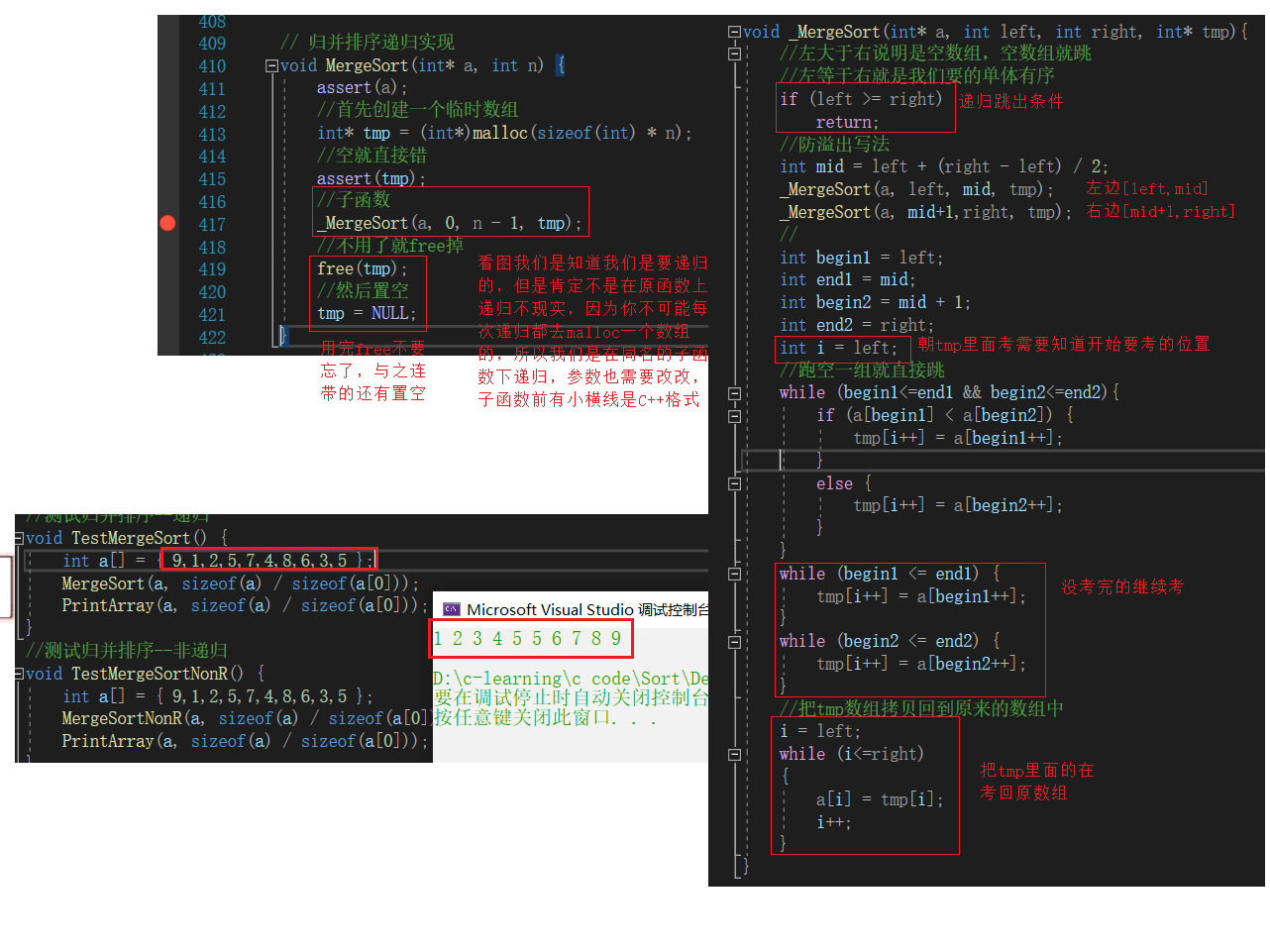
Merge sort recursive sub functions
// Merge sort recursive sub functions void _MergeSort(int* a, int left, int right, int* tmp){ // If the left is greater than the right, it means that it is an empty array , Empty arrays jump // Left equals right, which is the monomer order we want if (left >= right) return; // Anti overflow writing int mid = left + (right - left) / 2; _MergeSort(a, left, mid, tmp); _MergeSort(a, mid+1,right, tmp); // int begin1 = left; int end1 = mid; int begin2 = mid + 1; int end2 = right; int i = left; // Run empty group and jump directly while (begin1<=end1 && begin2<=end2){ if (a[begin1] < a[begin2]) { tmp[i++] = a[begin1++]; } else { tmp[i++] = a[begin2++]; } } while (begin1 <= end1) { tmp[i++] = a[begin1++]; } while (begin2 <= end2) { tmp[i++] = a[begin2++]; } // hold tmp Copy the array back to the original array i = left; while (i<=right) { a[i] = tmp[i]; i++; }}Merge sort recursive implementation
// Merge sort recursive implementation void MergeSort(int* a, int n) { assert(a); // First create a temporary array int* tmp = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * n); // Empty is directly wrong assert(tmp); // Subfunctions _MergeSort(a, 0, n - 1, tmp); // No, it's fine free fall free(tmp); // Then leave it empty tmp = NULL;}Non recursive writing
2^n^ Array of elements

We see there seems to be nothing wrong with it , That's used as the number of array elements. It's really good , There has been no single element , Well, it's not true
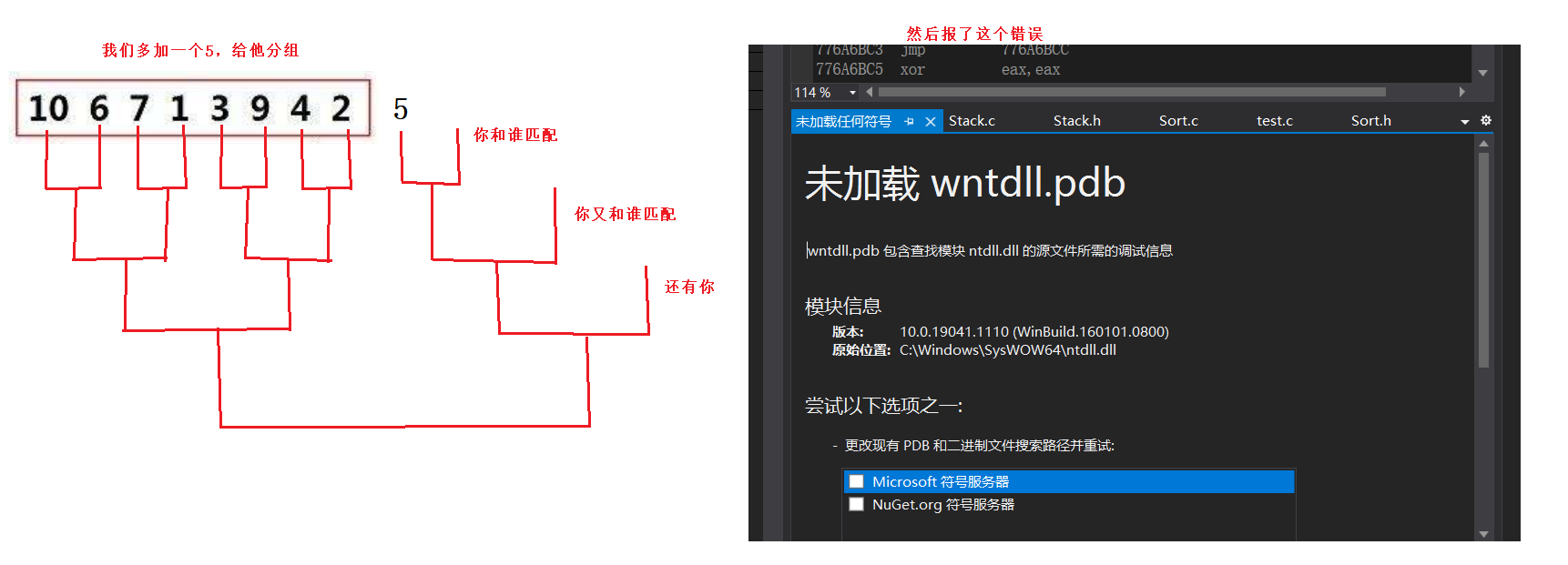
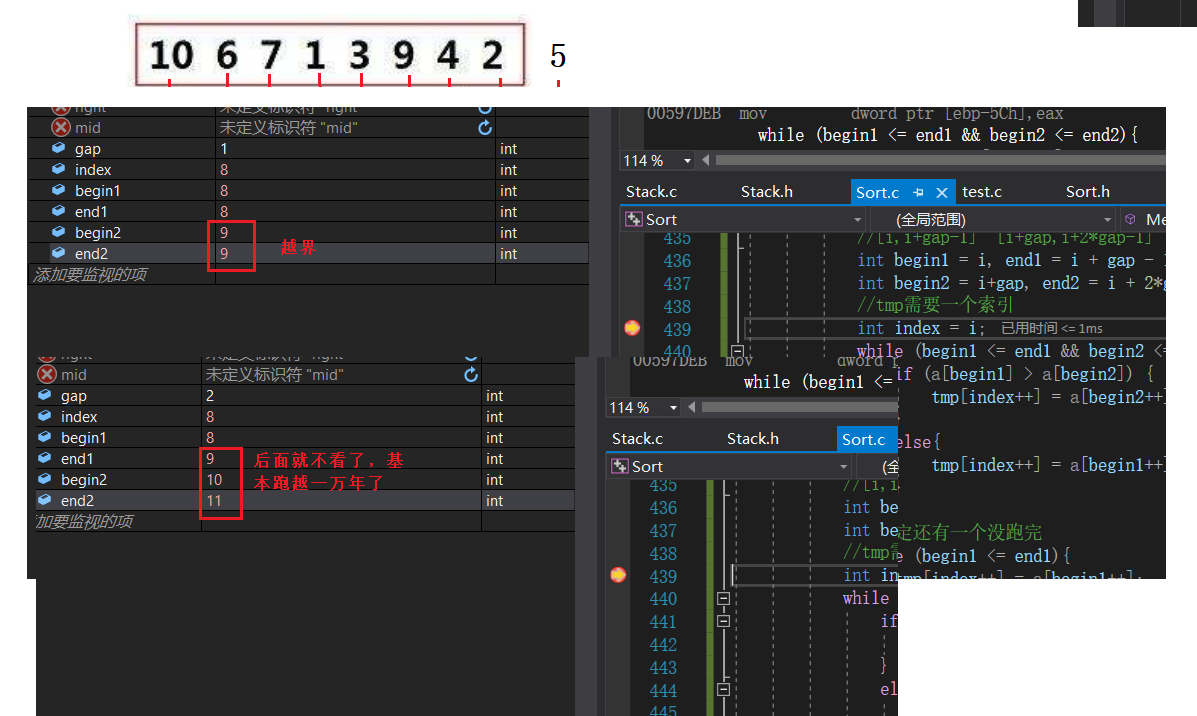
An array of any number of elements
Fixed subscript
Cross border discussions

But there's another kind of nausea == Duplicate copy ==

So next we need to solve index problem

We revised it to n-1, You can also modify the array to be nonexistent , Let him not enter the following cycle, so he can not merge


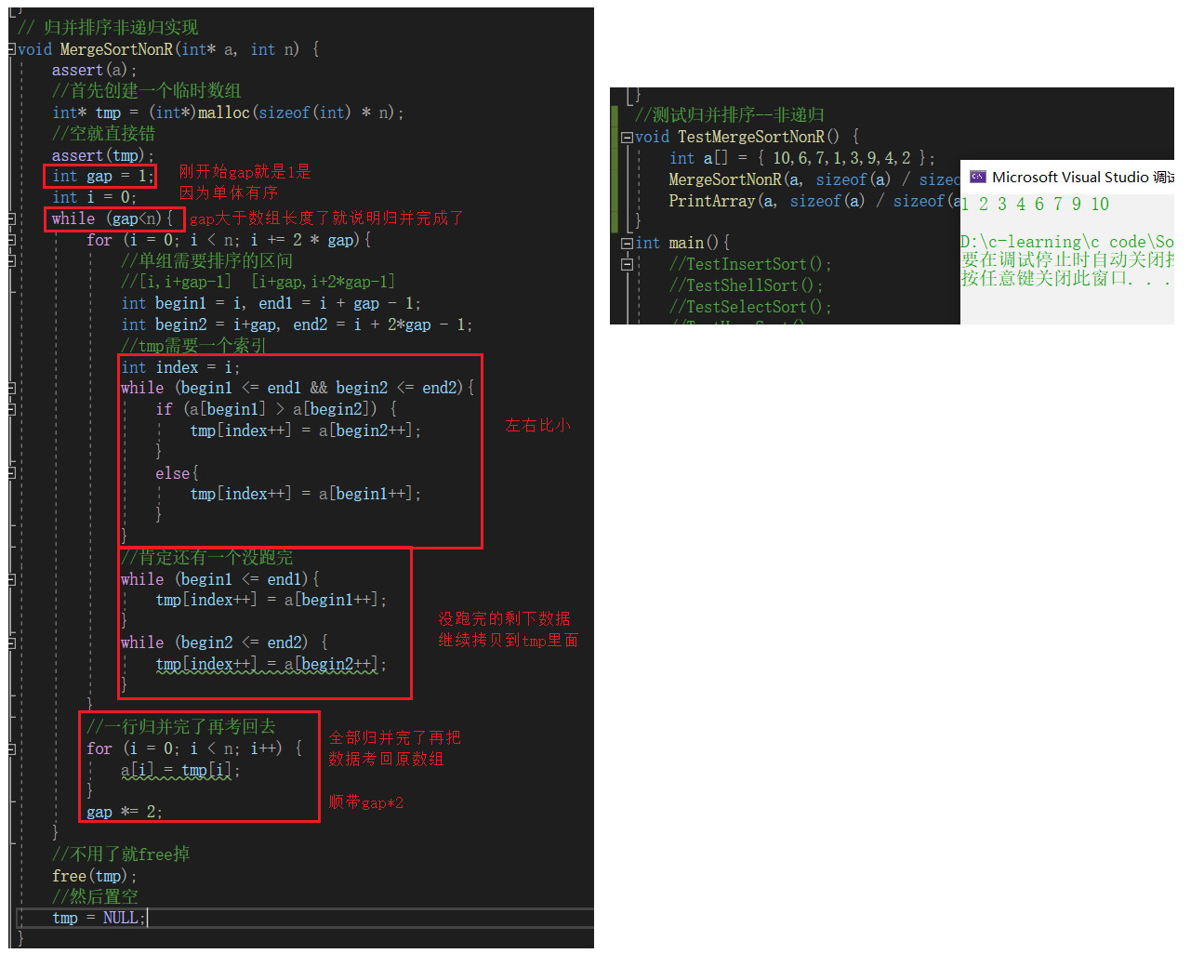
Merge sort non recursive implementation Fixed subscript
// Merge sort non recursive implementation void MergeSortNonR(int* a, int n) { assert(a); // First create a temporary array int* tmp = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * n); // Empty is directly wrong assert(tmp); int gap = 1; int i = 0; while (gap<n){ for (i = 0; i < n; i += 2 * gap){ // A single group of intervals to be sorted //[i,i+gap-1] [i+gap,i+2*gap-1] int begin1 = i, end1 = i + gap - 1; int begin2 = i+gap, end2 = i + 2*gap - 1; // Applicable to the core part of any number of elements //end1 out ,[begin2,end2] non-existent if (end1 >= n) { end1 = n - 1; } //[begin2,end2] non-existent if (begin2 >= n) { begin2 = n ; end2 = n - 1; } //end2 out if (end2 >= n) { end2 = n - 1; } //printf("[%d,%d],[%d,%d]",begin1,end1,begin2,end2); //// Duplicate copies are basically why we fix to the same location //// Let's talk about //if (begin1 == end1 && end1 == begin2 && begin2 == end2 && end2 == n-1) //{ // // Any code to accept breakpoints , A fee code // int a = 0; //} //tmp Need an index int index = i; while (begin1 <= end1 && begin2 <= end2){ if (a[begin1] > a[begin2]) { tmp[index++] = a[begin2++]; } else{ tmp[index++] = a[begin1++]; } } // There must be another one who hasn't finished while (begin1 <= end1){ tmp[index++] = a[begin1++]; } while (begin2 <= end2) { tmp[index++] = a[begin2++]; } //printf(" %d", index); } //printf("\n"); // After a line is merged, go back to the exam for (i = 0; i < n; i++) { a[i] = tmp[i]; } gap *= 2; } // No, it's fine free fall free(tmp); // Then leave it empty tmp = NULL;}Part by part, part by part
We can also divide the copy into half and part like recursion , There's no need to fix it , Because many boundary conditions have to be considered in the correction , It's a bit tedious.

Merge sort non recursive implementation Part by part, part by part
// Merge sort non recursive implementation void MergeSortNonR(int* a, int n) { assert(a); // First create a temporary array int* tmp = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * n); // Empty is directly wrong assert(tmp); int gap = 1; int i = 0; while (gap<n){ for (i = 0; i < n; i += 2 * gap){ // A single group of intervals to be sorted //[i,i+gap-1] [i+gap,i+2*gap-1] int begin1 = i, end1 = i + gap - 1; int begin2 = i+gap, end2 = i + 2*gap - 1; //// Applicable to the core part of any number of elements ////end1 out ,[begin2,end2] non-existent //if (end1 >= n) { // end1 = n - 1; //} ////[begin2,end2] non-existent //if (begin2 >= n) { // begin2 = n ; // end2 = n - 1; //} ////end2 out //if (end2 >= n) { // end2 = n - 1; //} // Applicable to the core part of any number of elements //end1 out ,[begin2,end2] non-existent There is no need to merge if (end1 >= n || begin2 >= n) { // Jump directly , Because it is operated in the original array, there is no need to worry about the last one not being taken into account break; } //end2 out Need to merge On correction if (end2 >= n) { end2 = n - 1; } //printf("[%d,%d],[%d,%d]",begin1,end1,begin2,end2); //// Duplicate copies are basically why we fix to the same location //// Let's talk about //if (begin1 == end1 && end1 == begin2 && begin2 == end2 && end2 == n-1) //{ // // Any code to accept breakpoints , A fee code // int a = 0; //} //tmp Need an index int index = i; while (begin1 <= end1 && begin2 <= end2){ if (a[begin1] > a[begin2]) { tmp[index++] = a[begin2++]; } else{ tmp[index++] = a[begin1++]; } } // There must be another one who hasn't finished while (begin1 <= end1){ tmp[index++] = a[begin1++]; } while (begin2 <= end2) { tmp[index++] = a[begin2++]; } // Copy one part of the file int j = 0; for (j = i; j <= end2; j++) { a[j] = tmp[j]; } //printf(" %d", index); } //printf("\n"); //// After a line is merged, go back to the exam //for (i = 0; i < n; i++) { // a[i] = tmp[i]; //} gap *= 2; } // No, it's fine free fall free(tmp); // Then leave it empty tmp = NULL;}Summary of the characteristics of merge sorting
- The disadvantage of merging is that it requires O(N) Spatial complexity of , The thinking of merge sort is more about solving the problem of external sort in disk .
- Time complexity :O(N*logN)
- Spatial complexity :O(N)
- stability : Stable
Time complexity
Time complexity :O(N*logN)
The method of merging and sorting is to put a group of n Sequence of Numbers , Split into two sequences , Then divide the two sequences , Keep dividing , Until divided into n A length of 1 Sequence . Then merge two by two . So again and again , Until the final form contains n An array of numbers .
== Total merge sort time = Decomposition time + The time when the subsequence is arranged + Merger time ==
No matter how many numbers each sequence has, it is a compromise decomposition , So the decomposition time is a constant , Negligible .
== be : Total merge sort time = The time when the subsequence is arranged + Merger time ==
Test performance
1000 A thousand

10000 Ten thousand == Abandon choice and bubbling first ==

100000 One hundred thousand == Then discard the direct insertion ==

1000000 One million

10000000 Ten million

Code
Sort.h
#pragma once#include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h>#include <assert.h>#include <time.h>#define HEAP 1// Interface for sorting implementation // Print array extern void PrintArray(int* a, int n);// Insertion sort extern void InsertSort(int* a, int n);// Shell Sort extern void ShellSort(int* a, int n);// Data exchange extern void Swap(int* pa, int* pb);// Selection sort extern void SelectSort(int* a, int n);// Downward adjustments extern void AdjustDwon(int* a, int n, int parent);// Heap sort extern void HeapSort(int* a, int n);// Bubble sort extern void BubbleSort(int* a, int n);// Quick sort recursive implementation // Quick sort hoare edition extern int PartSort1(int* a, int left, int right);// Quick sort digging extern int PartSort2(int* a, int left, int right);// Pointer before and after quick sort extern int PartSort3(int* a, int left, int right);extern void QuickSort(int* a, int left, int right);// Quick sort Non recursive implementation extern void QuickSortNonR(int* a, int left, int right);// Merge sort recursive implementation extern void MergeSort(int* a, int n);// Merge sort non recursive implementation extern void MergeSortNonR(int* a, int n);// Count sorting extern void CountSort(int* a, int n);Sort.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1#include "Sort.h"#include"Stack.h"// Print array void PrintArray(int* a, int n) { assert(a); int i = 0; for (i = 0; i < n; i++) { printf("%d ", a[i]); } printf("\n");}// Insertion sort void InsertSort(int* a, int n) { assert(a); int i = 0; for (i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) { int end = i; int x = a[end+1]; while (end >= 0) { // If the number to be inserted is smaller than the number in the sequence, prepare to move the position if (a[end] > x) { a[end + 1] = a[end]; end--; } else { // If the number inserted is larger than that in the order, jump out break; } } // Jump out of two situations //1.end == -1 When //2.break When // hold x to end Front one a[end + 1] = x; }}// Shell Sort void ShellSort(int* a, int n) { // grouping int gap = n; // Multiple pre sort (gap>1)+ Directly inserted into the (gap == 1) while (gap>1){ //gap /= 2; // Divided by three, we know we don't have to pass 1, So we +1 Let him have a must 1 Conditions gap = gap / 3 + 1; // Single group lie more int i = 0; for (i = 0; i < n - gap; i++) { int end = i; int x = a[end + gap]; while (end >= 0) { if (a[end] > x) { a[end + gap] = a[end]; // Step length is gap end -= gap; } else { break; } } a[end + gap] = x; } } }// Data exchange void Swap(int* pa, int* pb) { int tmp = *pa; *pa = *pb; *pb = tmp;}// Selection sort void SelectSort(int* a, int n) { int begin = 0; int end = n - 1; while (begin < end){ // Single trip // The maximum number , The subscript of the lowest decimal int mini = begin;// Let's say the initial subscript int maxi = end; // Let's assume that this is the subscript at the end int i = 0; for (i = begin; i <= end; i++) { if (a[i] < a[mini]) mini = i; if (a[i] > a[maxi]) maxi = i; } // The smallest one is in the front Swap(&a[begin], &a[mini]); if (begin == maxi) // If the maximum number is begin Positional , Then when exchanging, the maximum number moves with the subscript maxi = mini; // Put the biggest one in the back Swap(&a[end], &a[maxi]); begin++; end--; }}// Adjust the function down void AdjustDown(int* a, int n, int parent){ assert(a); // Create a child variable , Two children add... To this 1 Just go int child = parent * 2 + 1;#if HEAP while (child < n) { // Choose older children if (child + 1 < n && a[child] < a[child + 1]) { child++; } // Older children exchange when they are older than their father if (a[child] > a[parent]) { Swap(&a[child], &a[parent]); parent = child; child = parent * 2 + 1; } else { break; } }#elif !HEAP while (child < n) { // Choose children if (child + 1 < n && a[child] > a[child + 1]) { child++; } // Young children exchange when they are younger than their father if (a[child] < a[parent]) { Swap(&a[child], &a[parent]); parent = child; child = parent * 2 + 1; } else { break; } }#endif // HEAP }// Heap sort We talked about building a lot in ascending order before void HeapSort(int* a, int n) { // Reactor building time complexity O(N) // Build a pile int i = 0; for (i = (n - 1 - 1) / 2; i >= 0; i--) { AdjustDown(a, n, i); } int end = n - 1; // Heap sort time complexity O(N*logN) while (end>0){ // In exchange for Put the biggest back Swap(&a[0], &a[end]); // Adjust down AdjustDown(a,end,0); end--; }}// Bubble sort void BubbleSort(int* a, int n) { // Lie more int j = 0; for (j = 0; j < n - 1; j++) { // Swap tag variables int flag = 0; // Single trip int i = 0; for (i = 0; i < n - 1-j; i++) { if (a[i] > a[i + 1]) { // Exchange mark change flag = 1; Swap(&a[i], &a[i + 1]); } } // Mark or 0 Just jump out if (!flag) break; }}// Take the three Numbers int GetMinIndex(int* a, int left, int right) { // This will prevent int overflow int mid = left + (right - left) / 2; if (a[left] < a[mid]) { if (a[mid] < a[right]) return mid; else if (a[left] > a[right]) return left; else return right; } else //a[left] >= a[mid] { if (a[mid] > a[right]) return mid; else if (a[left] < a[right]) return left; else return right; }}// Quick sort hoare edition Single pass sorting // Leftmost do key [left,right] Let's give you an interval here int PartSort1(int* a, int left, int right) { // Take the three Numbers int mini = GetMinIndex(a, left, right); // Put the middle number to the far left , In exchange Swap(&a[mini], &a[left]); // Or on the far left keyi int keyi = left; // Stop when you meet left and right while (left < right) { // On the far left is key, Then move first on the far right // Find less than key Of while (left < right && a[right] >= a[keyi]) { right--; } // Then move the right // Find more than key Of while (left < right && a[left] <= a[keyi]) { left++; } Swap(&a[left], &a[right]); } Swap(&a[keyi], &a[right]); // After returning to the correct position keyi return left;}// Quick sort digging int PartSort2(int* a, int left, int right) { assert(a); // Take the three Numbers int mini = GetMinIndex(a, left, right); // Put the middle number to the far left , In exchange Swap(&a[mini], &a[left]); // The first Key Save it int Key = a[left]; // Dig a hole int pit = left; while (left<right){ // Look for a small on the right while (left < right && a[right] >= Key) { right--; } // Throw the data into the pit when you find it Swap(&a[right],&a[pit]); // You become a new pit pit = right; // Look big on the left while (left < right && a[left] <= Key) { left++; } // Throw the data into the pit when you find it Swap(&a[left], &a[pit]); // You become a new pit pit = left; } // When you come out, put Key Put it in the pit a[pit] = Key; return pit;}// Pointer before and after quick sort int PartSort3(int* a, int left, int right) { assert(a); // Take the three Numbers int mini = GetMinIndex(a, left, right); // Put the middle number to the far left , In exchange Swap(&a[mini], &a[left]); // hold keyi write down int keyi = left; int prev = left; int cur = prev + 1; while (cur <= right){ //// Than Key Jump out when you're young //while (cur <= right && a[cur] >= a[keyi]) { // cur++; //} //if (cur <= right) { // // Jump out prev++ // prev++; // // In exchange for // Swap(&a[prev], &a[cur]); // // After the exchange cur also ++ // cur++; //} if(a[cur] < a[keyi]) Swap(&a[prev++], &a[cur]); cur++; } // Jump out to explain the exchange a[prev] and Key Swap(&a[prev],&a[keyi]); return prev;}// Quick sort Inter cell optimization void QuickSort(int* a, int left, int right) { if (left >= right) return; if (right - left + 1 < 10)//10 Insert a number within { InsertSort(a + left, right - left + 1); } else { int keyi = PartSort3(a, left, right); //[left,keyi-1] keyi [keyi+1,right] QuickSort(a, left, keyi - 1); QuickSort(a, keyi + 1, right); } }// Quick sort Non recursive implementation void QuickSortNonR(int* a, int left, int right) { // Build a stack ST st; // Initialization stack StackInit(&st); //left Into the stack StackPush(&st, left); //right Into the stack StackPush(&st, right); // Empty stack jumps out while (!StackEmpty(&st)) { // Take the tail first int end = StackTop(&st); //pop fall StackPop(&st); // Then take the head int start = StackTop(&st); // Again pop fall StackPop(&st); // Then, sort in a single pass to find keyi int keyi = PartSort3(a,start,end); //[start,keyi-1] keyi [keyi+1,end] if (keyi + 1 < end)// Indicates that the separated interval is greater than 1 { // Because we take the tail first , So ask first StackPush(&st, keyi + 1); // Reentry tail StackPush(&st, end); } if (keyi - 1 > start)// Indicates that the separated interval is greater than 1 { // Because we take the tail first , So ask first StackPush(&st, start); // Reentry tail StackPush(&st, keyi - 1); } } // Stack destruction linked with initialization StackDestroy(&st);}// Merge sort recursive sub functions void _MergeSort(int* a, int left, int right, int* tmp){ // If the left is greater than the right, it means that it is an empty array , Empty arrays jump // Left equals right, which is the monomer order we want if (left >= right) return; // Anti overflow writing int mid = left + (right - left) / 2; _MergeSort(a, left, mid, tmp); _MergeSort(a, mid+1,right, tmp); // int begin1 = left; int end1 = mid; int begin2 = mid + 1; int end2 = right; int i = left; // Run empty group and jump directly while (begin1<=end1 && begin2<=end2){ if (a[begin1] < a[begin2]) { tmp[i++] = a[begin1++]; } else { tmp[i++] = a[begin2++]; } } while (begin1 <= end1) { tmp[i++] = a[begin1++]; } while (begin2 <= end2) { tmp[i++] = a[begin2++]; } // hold tmp Copy the array back to the original array i = left; while (i<=right) { a[i] = tmp[i]; i++; }}// Merge sort recursive implementation void MergeSort(int* a, int n) { assert(a); // First create a temporary array int* tmp = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * n); // Empty is directly wrong assert(tmp); // Subfunctions _MergeSort(a, 0, n - 1, tmp); // No, it's fine free fall free(tmp); // Then leave it empty tmp = NULL;}// Merge sort non recursive implementation void MergeSortNonR(int* a, int n) { assert(a); // First create a temporary array int* tmp = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * n); // Empty is directly wrong assert(tmp); int gap = 1; int i = 0; while (gap<n){ for (i = 0; i < n; i += 2 * gap){ // A single group of intervals to be sorted //[i,i+gap-1] [i+gap,i+2*gap-1] int begin1 = i, end1 = i + gap - 1; int begin2 = i+gap, end2 = i + 2*gap - 1; //// Applicable to the core part of any number of elements ////end1 out ,[begin2,end2] non-existent //if (end1 >= n) { // end1 = n - 1; //} ////[begin2,end2] non-existent //if (begin2 >= n) { // begin2 = n ; // end2 = n - 1; //} ////end2 out //if (end2 >= n) { // end2 = n - 1; //} // Applicable to the core part of any number of elements //end1 out ,[begin2,end2] non-existent There is no need to merge if (end1 >= n || begin2 >= n) { // Jump directly , Because it is operated in the original array, there is no need to worry about the last one not being taken into account break; } //end2 out Need to merge On correction if (end2 >= n) { end2 = n - 1; } //printf("[%d,%d],[%d,%d]",begin1,end1,begin2,end2); //// Duplicate copies are basically why we fix to the same location //// Let's talk about //if (begin1 == end1 && end1 == begin2 && begin2 == end2 && end2 == n-1) //{ // // Any code to accept breakpoints , A fee code // int a = 0; //} //tmp Need an index int index = i; while (begin1 <= end1 && begin2 <= end2){ if (a[begin1] > a[begin2]) { tmp[index++] = a[begin2++]; } else{ tmp[index++] = a[begin1++]; } } // There must be another one who hasn't finished while (begin1 <= end1){ tmp[index++] = a[begin1++]; } while (begin2 <= end2) { tmp[index++] = a[begin2++]; } // Copy one part of the file int j = 0; for (j = i; j <= end2; j++) { a[j] = tmp[j]; } //printf(" %d", index); } //printf("\n"); //// After a line is merged, go back to the exam //for (i = 0; i < n; i++) { // a[i] = tmp[i]; //} gap *= 2; } // No, it's fine free fall free(tmp); // Then leave it empty tmp = NULL;}test.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1#include "Sort.h"// Test the performance comparison of sorting void TestOP(){ // Set a random starting point srand(time(NULL)); // The size of the array to be created const int N = 10000000; int* a1 = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * N); int* a2 = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * N); int* a3 = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * N); int* a4 = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * N); int* a5 = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * N); int* a6 = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * N); int* a7 = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * N); int* a8 = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * N); int* a9 = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * N); for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i) { // Ensure that the two arrays are the same a1[i] = rand(); a2[i] = a1[i]; a3[i] = a1[i]; a4[i] = a1[i]; a5[i] = a1[i]; a6[i] = a1[i]; a7[i] = a1[i]; a8[i] = a1[i]; a9[i] = a1[i]; } int begin1 = clock();// Starting time //InsertSort(a1, N); int end1 = clock(); // End time int begin2 = clock(); ShellSort(a2, N); int end2 = clock(); int begin3 = clock(); //SelectSort(a3, N); int end3 = clock(); int begin4 = clock(); HeapSort(a4, N); int end4 = clock(); int begin5 = clock(); //BubbleSort(a5, N); int end5 = clock(); int begin6 = clock(); QuickSort(a6, 0, N - 1); int end6 = clock(); int begin7 = clock(); QuickSortNonR(a7, 0, N - 1); int end7 = clock(); int begin8 = clock(); MergeSort(a8, N); int end8 = clock(); int begin9 = clock(); MergeSort(a9, N); int end9 = clock(); printf("InsertSort:%d\n", end1 - begin1);// End time minus start time printf("ShellSort:%d\n", end2 - begin2); printf("SelectSort:%d\n", end3 - begin3); printf("HeapSort:%d\n", end4 - begin4); printf("BubbleSort:%d\n", end5 - begin5); printf("QuickSort:%d\n", end6 - begin6); printf("QuickSortNonR:%d\n", end7 - begin7); printf("MergeSort:%d\n", end8 - begin8); printf("MergeSortNonR:%d\n", end9 - begin9); free(a1); free(a2); free(a3); free(a4); free(a5); free(a6); free(a7); free(a8); free(a9);}// Test insert sort void TestInsertSort() { int a[] = { 1,5,3,7,0,9 }; InsertSort(a, sizeof(a) / sizeof(a[0])); PrintArray(a, sizeof(a) / sizeof(a[0]));}// Test Hill sort void TestShellSort() { int a[] = { 9,1,2,5,7,4,8,6,3,5 }; ShellSort(a, sizeof(a) / sizeof(a[0])); PrintArray(a, sizeof(a) / sizeof(a[0]));}// Test selection sort void TestSelectSort() { int a[] = { 9,1,2,5,7,4,8,6,3,5 }; SelectSort(a, sizeof(a) / sizeof(a[0])); PrintArray(a, sizeof(a) / sizeof(a[0]));}// Test heap sorting void TestHeapSort() { int a[] = { 9,1,2,5,7,4,8,6,3,5 }; HeapSort(a, sizeof(a) / sizeof(a[0])); PrintArray(a, sizeof(a) / sizeof(a[0]));}// Test bubble sort void TestBubbleSort() { int a[] = { 9,1,2,5,7,4,8,6,3,5 }; BubbleSort(a, sizeof(a) / sizeof(a[0])); PrintArray(a, sizeof(a) / sizeof(a[0]));}// Test single pass sorting void TestPartSort1() { int a[] = { 5,5,5,5,5,5,5,5,5,5 }; PartSort1(a,0 ,sizeof(a) / sizeof(a[0])-1); PrintArray(a, sizeof(a) / sizeof(a[0]));}// Test quick sort void TestQuickSort() { int a[] = { 9,1,2,5,7,4,8,6,3,5 }; QuickSort(a, 0, sizeof(a) / sizeof(a[0]) - 1); PrintArray(a, sizeof(a) / sizeof(a[0]));}// Test quick sort -- Non recursive void TestQuickSortNonR() { int a[] = { 9,1,2,5,7,4,8,6,3,5 }; QuickSortNonR(a, 0, sizeof(a) / sizeof(a[0]) - 1); PrintArray(a, sizeof(a) / sizeof(a[0]));}// Test merge sort -- recursive void TestMergeSort() { int a[] = { 10,6,7,1,3,9,4,2 }; MergeSort(a, sizeof(a) / sizeof(a[0])); PrintArray(a, sizeof(a) / sizeof(a[0]));}// Test merge sort -- Non recursive void TestMergeSortNonR() { int a[] = { 10,6,7,1,3,9,4,2,5 }; MergeSortNonR(a, sizeof(a) / sizeof(a[0])); PrintArray(a, sizeof(a) / sizeof(a[0]));}int main(){ //TestInsertSort(); //TestShellSort(); //TestSelectSort(); //TestHeapSort(); //TestBubbleSort(); //TestPartSort1(); //TestQuickSort(); //TestQuickSortNonR(); //TestMergeSort(); //TestMergeSortNonR(); TestOP(); return 0;}版权声明
本文为[Hua Weiyun]所创,转载请带上原文链接,感谢
https://yzsam.com/2022/04/202204211406369483.html
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢

ROS2学习笔记(八)-- ROS2参数应用实现道路识别调试

Web Course Design - photo recording website (flask)

In depth analysis of TCP three handshakes, the interviewer applauded

English word memory method based on anki + vocabulary

Brutally crack the latest JVM interview question of meituan: unlimited execution

Crawler example: crawl Taobao commodity information

Crawler example: climb the ranking of Chinese Universities

数据仓库架构演变和建设思路

利用 pytest 玩转数据驱动测试框架

原来升职加薪的测试工程师都擅长做接口测试
随机推荐
53.最大子数组和
2500字,手把手带你初步了解static关键字和指针,结构体
一篇文章带你玩转c语言变量和数据类型
Redisjson: a redis that can store JSON
代码重构之内联临时变量以查询取代临时变量
基本功:SQL 多表联合查询的几种方式
Detect and open WhatsApp
There are two important limits of the limit existence criterion
ROS2学习笔记(八)-- ROS2参数应用实现道路识别调试
堆排序--TOP-K问题解决及复杂度分析
Dynamic creation of array
两天两夜,1M图片优化到100kb
Ros2 learning notes (VII) -- customized actions to realize intersection turning
带你轻松玩转C语言scanf和getchar
虫子 栈
A quietly rising domestic software
Crawler example: crawl Taobao commodity information
How to turn off vs Code eslint verification? Let's have a look
无人驾驶虚拟仿真(十四)--图像处理之交通标志牌识别2
带你轻松玩转C语言函数