当前位置:网站首页>Elementary Structure
Elementary Structure
2022-08-10 06:32:00 【learning process】
文章目录
1.结构体的声明
1.1 结构的基础知识
结构是一些值的集合,这些值称为成员变量.For example an array is a collection of elements of the same type,但是结构的每个成员可以是不同类型的变量.
CSome built-in types are built into the language,例如int,char,short,int,long long,double等;Be able to describe some simple things,But there are many complex things in our daily life,例如人,一本书,人:名字+电话+性别+身高,书:书名+作者+定价+书号.At this time, a single type cannot be described,We can use structs.
1.2 结构的声明
//声明的结构体类型struct tag
struct tag//tag是结构体标签
{
member-list;//成员变量
}variable-list;//变量列表,可有可无
例如描述一个学生:
struct Stu
{
char name[20];//名字
int age;//年龄
char sex[5];//性别
char id[20];//学号
};//分号不能丢
例如描述一本书:
struct Book
{
char name[20];//名字
int price;//价格
char writer[10];//性别
char id[20];//书号
}b1,b2;//b1,b2是使用struct BookStructure type created2个全局的结构体变量
int main()
{
struct Book b3 = {
0};//结构体变量的创建,b3是局部变量
return 0;
}
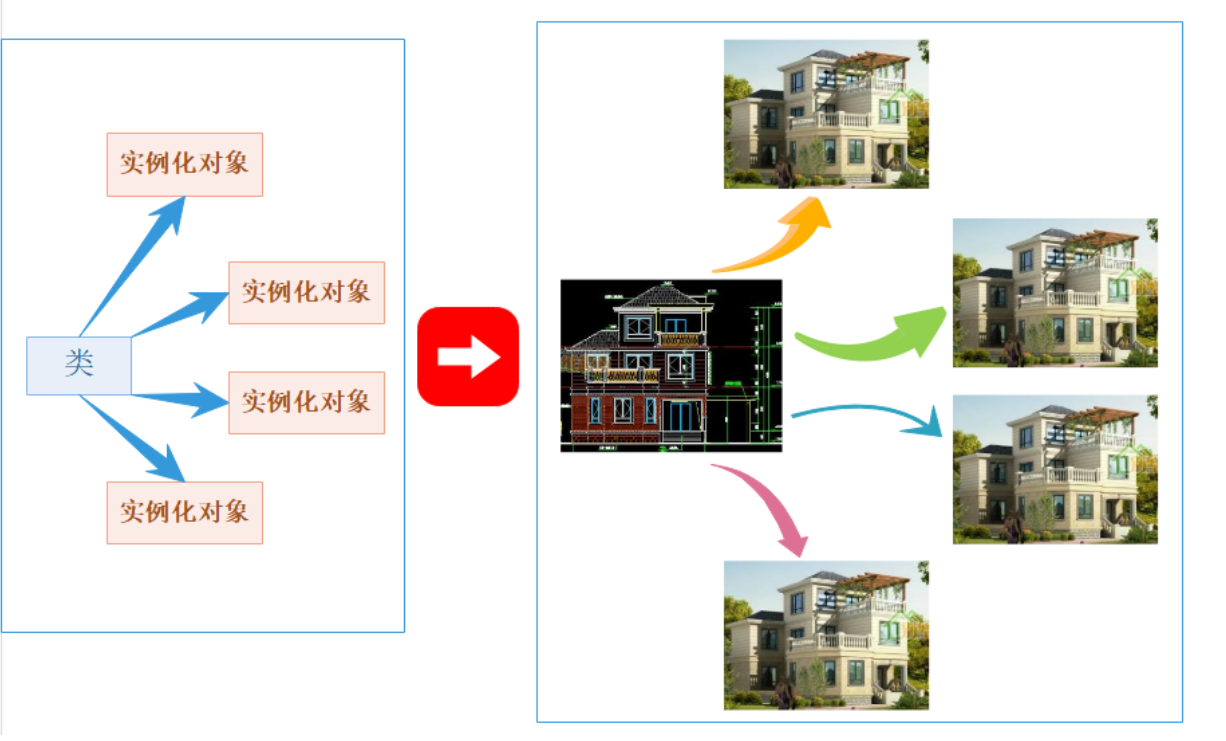
Structure types are equivalent to drawings,Structure variables are equivalent to houses,类比javaClass and Object Ideas in ,It's like the drawings don't take up space,And the house is taking up space;A struct type is just a template,Does not occupy memory space,Only the created structure variables occupy a certain amount of memory space.
1.3 结构成员的类型
结构的成员可以是标量、数组、指针,甚至是其他结构体.
sturct At
{
int arr[20];
int* pa;
};
struct St
{
struct Peo p;
int num;
float f;
};
struct Node
{
int data;
struct Point p;
struct Node* next;
}n1;
1.4 结构体变量的定义和初始化
有了结构体类型,We can create struct variables directly,And initialize the structure variable.
struct Peo
{
char name[20];
char tele[12];
char sex[5];
int height;
}p3,p4;
struct Peo p5,p6;
struct St
{
struct Peo p;
int num;
float f;
};
struct Node
{
int data;
struct Point p;
struct Node* next;
}n1 = {
10, {
4,5}, NULL}; //结构体嵌套初始化
int main()
{
//The order of initialization is in one-to-one correspondence with the member variables of the structure type
struct Peo p1 = {
"zhangsan", "13503532463", "男", 190};
struct St s = {
{
"lisi","15235335492","女",168}, 100, 3.14f};
return 0;
}
2.结构体成员的访问
2.1 结构体变量访问成员
结构变量的成员是通过点操作符(.)访问的.点操作符接受两个操作数. 例如:
struct Peo
{
char name[20];
char tele[12];
char sex[5];
int height;
};
struct St
{
struct Peo p;
int num;
float f;
};
int main()
{
struct Peo p1 = {
"zhangsan", "13503532463", "男", 190};
struct St s = {
{
"lisi","15235335492","女",168}, 100, 3.14f};
printf("%s %s %s %d\n",p1.name, p1.tele, p1.sex, p1.height);//结构体.成员变量
printf("%s %s %s %d %d %f\n",s.p.name, s.p.tele, s.p.sex, s.p.height, s.num, s.f);
return 0;
}
运行结果:
2.2 结构体指针访问指向变量的成员
有时候我们得到的不是一个结构体变量,而是指向一个结构体的指针.那该如何访问成员. 如下:
struct Peo
{
char name[20];
char tele[12];
char sex[5];
int height;
};
struct St
{
struct Peo p;
int num;
float f;
};
void print1(struct Peo* p)
{
printf("%s %s %s %d\n", p->name, p->tele, p->sex, p->height);// 结构体指针->成员变量
printf("%s %s %s %d\n", (*p).name, (*p).tele, (*p).sex, (*p).height);// *(结构体指针).成员变量
}
void print2(struct St* s)
{
printf("%s %s %s %d %d %f\n", (*s).p.name, (*s).p.tele, (*s).p.sex, (*s).p.height, (*s).num, (*s).f);
printf("%s %s %s %d %d %f\n", s->p.name, s->p.tele, s->p.sex, s->p.height, s->num, s->f);
}
int main()
{
struct Peo p1 = {
"zhangsan", "13503532463", "男", 190 };
struct St s1 = {
{
"lisi","15235335492","女",168}, 100, 3.14f };
print1(&p1);
print2(&s1);
return 0;
}
运行结果: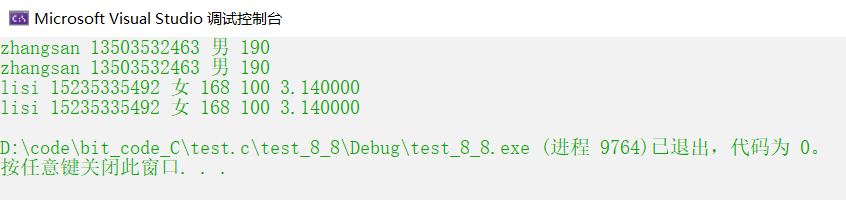
3.结构体传参
直接上代码:
struct S
{
int data[1000];
int num;
};
struct S s = {
{
1,2,3,4}, 1000};
//结构体传参
void print1(struct S s)
{
printf("%d\n", s.num);
}
//结构体地址传参
void print2(struct S* ps)
{
printf("%d\n", ps->num);
printf("%d\n", *(ps).num);
}
int main()
{
print1(s); //传结构体
print2(&s); //传地址
return 0;
}
上面的 print1和 print2函数哪个好些?
答案是:首选print2函数.
原因:
函数传参的时候,参数是需要压栈的. You pass structs as parameters,What is passed is a temporary copy of the struct,如果传递一个结构体对象的时候,结构体过大,The system space overhead of parameter stacking is relatively large,And it is time consuming,所以会导致性能的下降.And we pass the struct address(指针)作为参数,What is passed is actually the address of the space occupied by the structure,The size of the address is nothing more than that4/8字节,空间较小,The pointer will point to the space where the address is located for access,And you can also change the structure.
结论:结构体传参的时候,尽量传结构体的地址.
边栏推荐
- Teach you to change the kernel source code--sysfs virtual file system 2
- 3.事务篇【mysql高级】
- 2022河南萌新联赛第(五)场:信息工程大学 C - 丢手绢
- 进制的前缀表示和后缀表示
- Kernel Image File Format
- OSPF的dr和bdr
- 如何在AdsPower中设置YiLu代理?
- Talking about the realization idea of "frame" of "frame synchronization online game"
- 驱动的参数传入:module_param,module_param_array,module_param_cb
- 第12章 数据库其它调优策略【2.索引及调优篇】【MySQL高级】
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
【强化学习】《Easy RL》- Q-learning - CliffWalking(悬崖行走)代码解读
什么是代理ip?市面上好用的代理软件有哪些
进制的前缀表示和后缀表示
2022河南萌新联赛第(五)场:信息工程大学 H - 小明喝奶茶
NetKeeper(创翼)开WIFI方法——2018.5
2022河南萌新联赛第(五)场:信息工程大学 B - 交通改造
Qt绘制椭圆曲线的角度问题(离心角和旋转角)
全网可达,交换机和路由器的配置,vlan
如何在VMlogin中设置YiLu代理?
【备份】《Unity Shader入门精要》配图
UnityShader入门精要--Unity中的基础光照
Qt列表下方增加弹出加载数据提示效果
MySQL笔记
动态规划——从0-1背包问题到leetcode正则匹配
ArgumentException: GetComponent requires that the requested component ‘GameObject‘ derives from Mono
如何在AdsPower中设置YiLu代理?
语法基础(判断语句)
Screen post-processing: Sobel operator to achieve edge detection
DRM Memory Management
驱动的参数传入:module_param,module_param_array,module_param_cb