当前位置:网站首页>QML advanced (V) - realize all kinds of cool special effects through particle simulation system
QML advanced (V) - realize all kinds of cool special effects through particle simulation system
2022-04-23 04:34:00 【Manon Feifei】
Particle simulation is the visual effect of computer graphics technology . The typical effect is : The fallen leaves , flame , The explosion , A shooting star , Clouds and so on . It's different from other graphics rendering , Particles are rendered based on blur . Its results are unpredictable based on pixels . The parameters of particle system describe the boundary of stochastic simulation . Traditional rendering technology is difficult to achieve particle rendering effect .
The core of particle simulation is particle system (ParticleSystem), It controls the shared timeline . There can be multiple particle systems in a scene , Each has its own unique timeline . A particle uses emitter elements (Emitter) launch , Using particle brushes (ParticlePainter) Visualization , It can be a picture , One QML Item or a colored item . An emitter element also provides vectors to control the direction of particles . After a particle is sent, it can no longer be controlled . Particle models provide particle simulators , It can control the parameters of emitted particles . In a system , Particles can use particle swarm parameters (ParticleGroup) To share mobile time .
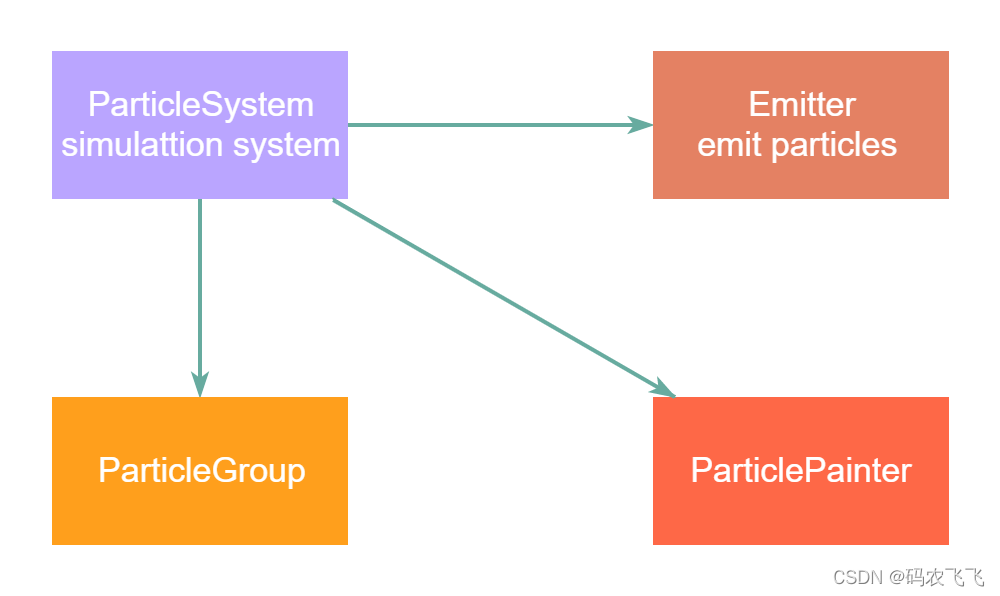
particle system (ParticleSystem)
Responsible for managing the shared timeline between emitters
The emitter (Emitter)
Responsible for launching logical particles into the system
Particle brush (ParticlePainter)
Responsible for particle visualization
Direction (Drection)
Responsible for the vector space of emitted particles
Particle group (ParticleGroup)
Each particle is a member of a particle group
Particle controller (Affector)
Control the emitted particles
Simple particle system simulation effect
import QtQuick 2.8
import QtQuick.Window 2.2
import QtQuick.Particles 2.0
Window {
visible: true
width: 640
height: 480
title: qsTr("ParticleSystem")
// Background image
Rectangle {
id: root
width: 640; height: 480
color: "#EEEEEE"
// Particle emission system
ParticleSystem {
id: particleSystem
}
Emitter {
id: emitter
anchors.centerIn: parent
// Launch range
width: 640; height: 480
system: particleSystem
// The emission frequency of particles , The period of existence of particles
emitRate: 60
lifeSpan: 1000
// The speed of life cycle change
lifeSpanVariation: 500
// The size of the particle and the size of the end
size: 16
endSize: 64
}
// The type of particle
ImageParticle {
source: "qrc:/images/flower.png"
system: particleSystem
}
}
}
Modify the animation effects and corresponding attributes of particles
import QtQuick 2.8
import QtQuick.Window 2.2
import QtQuick.Particles 2.0
Window {
visible: true
width: 640
height: 480
title: qsTr("ParticleSystem")
// Background image
Rectangle {
id: root
width: 640; height: 480
color: "#EEEEEE"
// Particle emission system
ParticleSystem {
id: particleSystem
}
Emitter {
id: emitter
anchors.centerIn: parent
// Launch range
width: 640; height: 480
system: particleSystem
// The emission frequency of particles , The period of existence of particles
emitRate: 60
lifeSpan: 2000
// The speed of life cycle change
lifeSpanVariation: 200
// The size of the particle and the size of the end
size: 16
endSize: 64
}
// The type of particle
ImageParticle {
source: "qrc:/images/heart.png"
system: particleSystem
// Initial color and color variation range
color: '#FFD700'
colorVariation: 0.2
// First rotate clockwise 15 degree
rotation: 15
// Different particles in +/-5 Change between degrees
rotationVariation: 5
// Each particle will be represented by 45 Degree of rotation
rotationVelocity: 45
// The rotation speed of each particle is +/-15 Change between degrees
rotationVelocityVariation: 15
// The entrance effect
entryEffect: ImageParticle.scale
}
}
}
Specify the particle emission direction
Particles can already rotate , But how to make particles have a trajectory . The trajectory is specified by the velocity or the acceleration in the random direction of the particle , It can also be called vector space .
There are many vector spaces available to define the velocity or acceleration of particles :
1. Angle direction (AngleDirection)- Use the direction change of angle
2. Point direction (PointDirection)- Use x,y The direction of component composition changes
3. Target direction (TargetDirection)- Change towards the target point
import QtQuick 2.8
import QtQuick.Window 2.2
import QtQuick.Particles 2.0
Window {
visible: true
width: 640
height: 480
title: qsTr("ParticleSystem")
// Background image
Rectangle {
id: root
width: 640; height: 480
color: "#EEEEEE"
// Particle emission system
ParticleSystem {
id: particleSystem
}
Emitter {
id: emitter
// From the same location
width: 1; height: 1
x:0; y:240
system: particleSystem
lifeSpan: 6400
// The speed of life cycle change
lifeSpanVariation: 500
// The size of the particle and the size of the end
size: 64
velocity: AngleDirection{
// The angle of Launch
angle: 0
angleVariation: 15
// The gradient value of emission changes
magnitude: 100
magnitudeVariation: 50
}
}
// The type of particle
ImageParticle {
source: "qrc:/images/heart.png"
system: particleSystem
// Initial color and color variation range
color: '#FFD700'
colorVariation: 0.2
// First rotate clockwise 15 degree
rotation: 15
// Different particles in +/-5 Change between degrees
rotationVariation: 5
// Each particle will be represented by 45 Degree of rotation
rotationVelocity: 45
// The rotation speed of each particle is +/-15 Change between degrees
rotationVelocityVariation: 15
// The entrance effect
entryEffect: ImageParticle.scale
}
}
}The display effect is as shown in the following figure :

Particle emission system with emission angle
import QtQuick 2.8
import QtQuick.Window 2.2
import QtQuick.Particles 2.0
Window {
visible: true
width: 640
height: 480
title: qsTr("ParticleSystem")
// Background image
Rectangle {
id: root
width: 640; height: 480
color: "#EEEEEE"
// Particle emission system
ParticleSystem {
id: particleSystem
}
Emitter {
id: emitter
// Launch range
width: 1; height: 1
x:0; y:240
system: particleSystem
emitRate: 3
lifeSpan: 6400
// The speed of life cycle change
lifeSpanVariation: 500
size: 32
velocity: AngleDirection{
// The angle of Launch
angle: -45
angleVariation: 0
magnitude: 120
}
// The change in acceleration
acceleration: AngleDirection{
angle: 90
magnitude: 25
}
}
// The type of particle
ImageParticle {
source: "qrc:/images/bomb.png"
system: particleSystem
rotation: 15
// Different particles in +/-5 Change between degrees
rotationVariation: 5
// Each particle will be represented by 45 Degree of rotation
rotationVelocity: 10
// The rotation speed of each particle is +/-15 Change between degrees
rotationVelocityVariation: 15
entryEffect: ImageParticle.scale
}
}
}
The direction of particle emission can be a point , By specifying an emission point , And in x and y The speed of change in direction , We can control the direction of the particles .
velocity: PointDirection{
x: 100
y: 0
xVariation: 0
yVariation: 100/6
}We can also put a QML Medium Item Object is set as the emission target of particles , This allows particles to be sent to a UI Control .
velocity: TargetDirection{
targetItem:rootItem
}Specify the particle type by customizing the brush
stay QML We can also draw our own UI Elements are emitted as particles , We need to use
ItemParticle and CustomParticle Element .
ItemParticle: Based on granular ⼦ Brush agent
CustomParticle: Shader based on particle brush
import QtQuick 2.8
import QtQuick.Window 2.2
import QtQuick.Particles 2.0
Window {
visible: true
width: 640
height: 480
title: qsTr("ParticleSystem")
// Background image
Rectangle {
id: root
width: 640; height: 480
color: "#EEEEEE"
// Particle emission system
ParticleSystem {
id: particleSystem
}
Emitter {
id: emitter
// Launch range
width: 1; height: 1
x:0; y:100
system: particleSystem
emitRate: 3
lifeSpan: 6400
// The speed of life cycle change
lifeSpanVariation: 500
size: 32
velocity: PointDirection{
x: 100
y: 0
xVariation: 5
yVariation: 0
}
// The change in acceleration
acceleration: AngleDirection{
angle: 90
magnitude: 25
}
}
ItemParticle{
id: particle
system: particleSystem
delegate: itemDelegate
}
Component{
id: itemDelegate
Rectangle{
id: container
width: 20*Math.ceil(Math.random()*3);height: width
color: 'white'
Image {
anchors.fill:parent
anchors.margins: 4
source: "qrc:/images/heart.png"
}
}
}
}
}The operation effect is shown in the figure below :

Particle control parameters
Particles are emitted by particle emitters . After the particles are emitted , The emitter can no longer change the particles . But the particle controller allows you to control the parameters of the emitted particles , By modifying the corresponding parameters, we can control the state of particles .
The parameters of the controller affecting particles include the following :
1. Life cycle (Age)- Life cycle modification of particles
2. attract (Attrator)- Attract particles towards the specified point
3. friction (Friction)- Slow down in proportion to the particle speed
4. gravity (Gravity)- Set the acceleration of an angle
5. Turbulence (Turbulence)- Force the flow based on the direction of the noisy image
7. drift (Wander)- Randomly varying trajectories
8. Group target (GroupGoal)- Change the state of a particle group
9. Sub particles (SpriteGoal)- Change the state of a sub particle
Particle combination emission
We can add multiple particle emitters to a system , Emit multiple particles at the same time , In this way, all kinds of cool special effects can be realized . Here is an example to illustrate :
import QtQuick 2.8
import QtQuick.Window 2.2
import QtQuick.Particles 2.0
Window {
visible: true
width: 640
height: 480
title: qsTr("Particles")
Rectangle {
id: root
width: 480; height: 240
color: "#000000"
property bool tracer: false
ParticleSystem {
id: particleSystem
}
ImageParticle {
id: smokePainter
system: particleSystem
groups: ['smoke']
source: "qrc:/images/bomb.png"
alpha: 0.3
}
ImageParticle {
id: rocketPainter
system: particleSystem
groups: ['rocket']
source: "qrc:/images/heart.png"
entryEffect: ImageParticle.Fade
}
Emitter {
id: rocketEmitter
anchors.bottom: parent.bottom
width: parent.width; height: 40
system: particleSystem
group: 'rocket'
emitRate: 2
maximumEmitted: 8
lifeSpan: 4800
lifeSpanVariation: 400
size: 128
velocity: AngleDirection { angle: 270; magnitude: 150; magnitudeVariation: 10 }
acceleration: AngleDirection { angle: 90; magnitude: 50 }
}
TrailEmitter {
id: smokeEmitter
system: particleSystem
group: 'smoke'
follow: 'rocket'
size: 16
sizeVariation: 8
emitRatePerParticle: 16
velocity: AngleDirection { angle: 90; magnitude: 100; angleVariation: 15 }
lifeSpan: 200
}
Friction {
groups: ['rocket']
anchors.top: parent.top
width: parent.width; height: 80
system: particleSystem
threshold: 5
factor: 0.9
}
Turbulence {
groups: ['rocket']
anchors.bottom: parent.bottom
width: parent.width; height: 160
system: particleSystem
strength:25
}
ImageParticle {
id: sparklePainter
system: particleSystem
groups: ['sparkle']
color: 'red'
colorVariation: 0.6
source: "qrc:/images/flower.png"
alpha: 0.3
}
GroupGoal {
id: rocketChanger
anchors.top: parent.top
width: parent.width; height: 80
system: particleSystem
groups: ['rocket']
goalState: 'explosion'
jump: true
}
ParticleGroup {
name: 'explosion'
system: particleSystem
TrailEmitter {
id: explosionEmitter
anchors.fill: parent
group: 'sparkle'
follow: 'rocket'
lifeSpan: 750
emitRatePerParticle: 200
size: 32
velocity: AngleDirection { angle: -90; angleVariation: 180; magnitude: 50 }
}
TrailEmitter {
id: explosion2Emitter
anchors.fill: parent
group: 'sparkle'
follow: 'rocket'
lifeSpan: 250
emitRatePerParticle: 100
size: 32
velocity: AngleDirection { angle: 90; angleVariation: 15; magnitude: 400 }
}
}
}
}The operation effect is shown in the figure below :

版权声明
本文为[Manon Feifei]所创,转载请带上原文链接,感谢
https://yzsam.com/2022/04/202204230432049885.html
边栏推荐
- KVM error: Failed to connect socket to ‘/var/run/libvirt/libvirt-sock‘
- 520. Detect capital letters
- Effects of antibiotics on microbiome and human health
- 协程与多进程的完美结合
- Stm32f4 MCU ADC sampling and FFT of ARM-DSP Library
- IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics(TII)投稿须知
- 顺序表的基本操作
- Set经典小题目
- AWS EKS添加集群用户或IAM角色
- Alibaba cloud IOT transfer to PostgreSQL database scheme
猜你喜欢

HMS Core Discovery第14期回顾长文|纵享丝滑剪辑,释放视频创作力

补充番外14:cmake实践项目笔记(未完待续4/22)

Difference between LabVIEW small end sequence and large end sequence
Express middleware ② (classification of Middleware)

Qtspim manual - Chinese Translation

上海航芯技术分享 | ACM32 MCU安全特性概述

Chapter 4 - understanding standard equipment documents, filters and pipelines

Matlab reads multiple fig graphs and then combines them into one graph (in the form of sub graph)
![[echart] Introduction to echart](/img/40/e057f4ac07754fe6f3500f3dc72293.jpg)
[echart] Introduction to echart

Fusobacterium -- symbiotic bacteria, opportunistic bacteria, oncobacterium
随机推荐
[AI vision · quick review of NLP natural language processing papers today, issue 31] Fri, 15 APR 2022
Opencv -- yoact case segmentation model reasoning
[AI vision · quick review of NLP natural language processing papers today, No. 32] wed, 20 APR 2022
Interaction of diet gut microbiota on cardiovascular disease
Leetcode->1 两数之和
Common string processing functions in C language
STM32单片机ADC规则组多通道转换-DMA模式
Set classic topics
用D435i录制自己的数据集运行ORBslam2并构建稠密点云
单片机串口数据处理(1)——串口中断发送数据
Iron and intestinal flora
HMS Core Discovery第14期回顾长文|纵享丝滑剪辑,释放视频创作力
Matlab minimalist configuration of vscode configuration
Jetpack 之 LifeCycle 组件使用详解
Mysql---数据读写分离、多实例
[AI vision · quick review of robot papers today, issue 32] wed, 20 APR 2022
C language character constant
【论文阅读】【3d目标检测】Improving 3D Object Detection with Channel-wise Transformer
Why recommend you to study embedded
Huawei machine test -- high precision integer addition