当前位置:网站首页>Qiskit 学习笔记2
Qiskit 学习笔记2
2022-08-10 05:29:00 【溴锑锑跃迁】
进阶电路
Gate类 (qiskit.circuit)
官方文档介绍(包括源码)Gate — Qiskit 0.37.1 documentation
初始化:
from qiskit.circuit import Gate
gt1 = Gate(name="my_gate", num_qubits=2, params=[])此处name将会在后面绘制出的电路图里显示,num_qubits就是该门需要作为参数的量子比特数
如果要把门添加到某一电路中去,使用append方法:
from qiskit import QuantumRegister, QuantumCircuit
qr1 = QuantumRegister(2)
circ1 = QuantumCircuit(qr1)
circ1.append(gt1, [qr1[0], qr1[1]])
print(circ1.draw())
# ┌──────────┐
# q0_0: ┤0 ├
# │ my_gate │
# q0_1: ┤1 ├
# └──────────┘
子电路 (Subcircuit)
让我们新建一个电路:
qr2 = QuantumRegister(2)
circ2 = QuantumCircuit(qr2)
circ2.h(qr2[1])
circ2.cx(qr2[1],qr2[0])
circ2.name = 'subcircuit_1'同样地,如果我们想要把一个子电路嵌入另一个电路里,也要使用append方法:
circ1.append(circ2.to_instruction(), [qr1[0], qr1[1]])
print(circ1.draw())
print(circ1.decompose().draw())
# ┌──────────┐┌───────────────┐
# q0_0: ┤0 ├┤0 ├
# │ my_gate ││ subcircuit_1 │
# q0_1: ┤1 ├┤1 ├
# └──────────┘└───────────────┘
# ┌──────────┐ ┌───┐
# q0_0: ┤0 ├─────┤ X ├
# │ my_gate │┌───┐└─┬─┘
# q0_1: ┤1 ├┤ H ├──■──
# └──────────┘└───┘在绘制电路图时,Qiskit会自动包装电路,如果想要完全展开,需要decompose方法(注意,是函数式编程,不会改变对象本身,展开的电路会被直接返回)
参数化
Parameter类(qiskit.circuit)
初始化及传入参数(传入参数依旧不会改变原电路):
from qiskit.circuit import Parameter
phi = Parameter('φ')
# phi就像正常角度一样传入即可
circ1.rx(phi, qr1[0])
circ1.cry(phi,qr1[0], qr1[1])
# 绑定参数用 bind_parameters()
print(circ1.bind_parameters({phi: pi/3}).draw())
print(circ1.draw())
# 效果:
# ┌──────────┐┌───────────────┐┌─────────┐
# q0_0: ┤0 ├┤0 ├┤ RX(π/3) ├─────■─────
# │ my_gate ││ subcircuit_1 │└─────────┘┌────┴────┐
# q0_1: ┤1 ├┤1 ├───────────┤ RY(π/3) ├
# └──────────┘└───────────────┘ └─────────┘
# ┌──────────┐┌───────────────┐┌───────┐
# q0_0: ┤0 ├┤0 ├┤ RX(φ) ├────■────
# │ my_gate ││ subcircuit_1 │└───────┘┌───┴───┐
# q0_1: ┤1 ├┤1 ├─────────┤ RY(φ) ├
# └──────────┘└───────────────┘ └───────┘
关于参数化电路有两点需要注意:
- 参数化电路会减少编译损耗(详情: Reducing-compilation-cost)
- 参数化可以像普通电路那样被组合
下面看一个综合性的例子:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from qiskit.circuit import QuantumCircuit, Parameter
from qiskit import BasicAer, execute
backend = BasicAer.get_backend('qasm_simulator')
circuit1 = QuantumCircuit(1, 1)
theta = Parameter('θ')
theta_range = np.linspace(0, 2 * np.pi, 128)
circuit1.h(0) # 相当于添加了一个初相位 pi/4
circuit1.ry(theta, 0)
circuit1.measure(0, 0)
job = backend.run([circuit1.bind_parameters(theta_val) for theta_val in theta_range])
print(circuit1.draw())
counts = job.result().get_counts()
# 绘图部分
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(8, 6))
ax = fig.add_subplot(111)
ax.plot(theta_range, list(map(lambda c: c.get('0', 0), counts)), '.-', label='0')
ax.plot(theta_range, list(map(lambda c: c.get('1', 0), counts)), '.-', label='1')
ax.set_xticks([i * np.pi / 2 for i in range(5)])
ax.set_xticklabels(['0', r'$\frac{\pi}{2}$', r'$\pi$', r'$\frac{3\pi}{2}$', r'$2\pi$'], fontsize=14)
ax.set_xlabel('θ', fontsize=14)
ax.set_ylabel('Counts', fontsize=14)
ax.legend(fontsize=14)
fig.savefig(r'D:\1.png')
可以这样想象,因为之前在第一篇中提到过,我们选择用 来表示
来表示 态,当对于1个量子态,等价于
态,当对于1个量子态,等价于 维空间时,我们可以用一个模长始终为1矢量表示一个量子态。在比较Rx、Ry、Rz三个门后,不难发现Ry正好对应着二维空间中的旋转群,由是便有了上面的例子,我们给定初态为一个夹角为
维空间时,我们可以用一个模长始终为1矢量表示一个量子态。在比较Rx、Ry、Rz三个门后,不难发现Ry正好对应着二维空间中的旋转群,由是便有了上面的例子,我们给定初态为一个夹角为 的量子态,之后旋转它(可以从theta_range看出)一步步从0到
的量子态,之后旋转它(可以从theta_range看出)一步步从0到 .结果如下图:
.结果如下图:
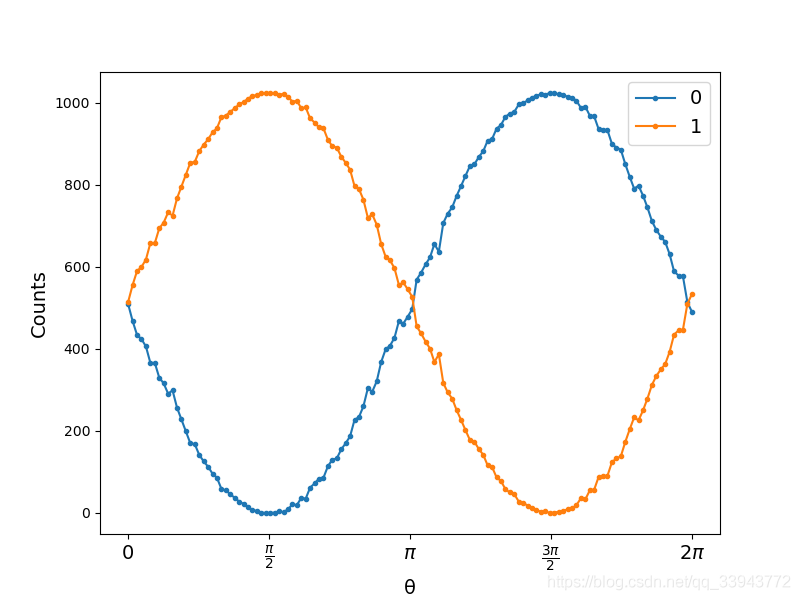
官网有一个略微复杂的实例:Binding parameters to values
操作子
Operator类(qiskit.quantum_info.operaters)
创建和基本属性
每一个Operator实例都包含两个基本属性(继承自BasicOperator) :
- data:numpy array, 储存操作子的矩阵表示
- dim:操作子的维数信息,不一定和data中的矩阵相同
创建操作子时,只需要提供一个矩阵即可(实际上就是二维列表),无论是不是numpy array都可
操作子维数分为input_dims和output_dims,分别对应的是操作子要施加的量子态数和生成的量子态数,对此官网有如下表述:
For
by
operators, the input and output dimension will be automatically assumed to be M-qubit and N-qubit
谨记,每一个量子比特对应着一个“2”,它们之间用张量积 连结
连结
from qiskit.quantum_info.operators import Operator
import numpy as np
op = Operator(np.random.rand(2 ** 1, 2 ** 2))
print(op.data) # 会输出随机生成的矩阵
print(op.dim) # 输出(4, 2)
print(op.input_dims()) # 输出(2, 2)
print(op.output_dims()) # 输出(2,)那么对于无法表示成2的幂的维数,qiskit通常不会再处理,例如对于维数为(6, 6)的操作子,其输入维和输出维都是(6,),但也可以根据张量积将其分解:
op2 = Operator(np.random.rand(4, 6), input_dims=[2, 3], output_dims=[4])
# 2 × 3 = 6
print(op2.output_dims) # 是(4,)而不是(2, 2)通过实例可见,当指定输出输入维时,不仅原矩阵非2的幂的维数可以被人工分解,还可以避免2的幂的维数被自动分解
相关类型转换
Operator也可以通过Pauli、Gate、Instruction甚至是QuantumCircuit来创建:
from qiskit.circuit.library import HGate
op = Operator(HGate())
print(op)
# Operator([[ 0.70710678+0.j, 0.70710678+0.j],
# [ 0.70710678+0.j, -0.70710678+0.j]],
# input_dims=(2,), output_dims=(2,))需要在电路中使用操作子时,和其他操作一样,调用电路的append()方法并附量子态即可
操作子的组合
张量积对应的两个函数(这里先假设Op1和Op2都是单量子门):
- op1.tensor(op2) 等价于
 ,其结果还可以表示成一个矩阵,但是在实际作用时,则是Op2对应qubit_0, Op1对应qubit_1
,其结果还可以表示成一个矩阵,但是在实际作用时,则是Op2对应qubit_0, Op1对应qubit_1 - op1.expand(op2) 等价于

普通的矩阵乘法,调用compose()方法,但和张量积相同,它也在顺序上存在两种形式(矩阵乘法对两矩阵有一定的维数要求):
- op1.compose(op2)等价于op2·op1
- op1.compose(op2, front=True)等价于op1.op2
子系统乘法
刚才说过普通矩阵乘法会对两矩阵的维数作一定要求,而子系统乘法会将大的矩阵作张量分解,将其拆成若干小矩阵,而我们的目的则是选出那些我们想要作用的小矩阵,结果会自然作张量积变回大矩阵:
op = Operator(np.eye(2 ** 3))
XZ = Operator(Pauli(label='XZ'))
op.compose(XZ, qargs=[0, 2])(在front参数为False的情况,即默认情况下,调用方应是那个较大的矩阵)
这里可以将op拆成 ,这三个实际上都是2维单位矩阵,下标用来表示编号,此时我们就可以拿
,这三个实际上都是2维单位矩阵,下标用来表示编号,此时我们就可以拿 和
和 去和XZ门做普通矩阵乘法(实际上是XZ · I,因为默认front=False)
去和XZ门做普通矩阵乘法(实际上是XZ · I,因为默认front=False)
另外,维数相同的操作子还可以作线性组合
欢迎加入Qiskit交流群: 1064371332
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢

canvas canvas drawing clock
西门子Step7和TIA软件“交叉引用”的使用

MySQL使用简单教程

An article to master the entire JVM, JVM ultra-detailed analysis!!!

MySql之json_extract函数处理json字段

Depth of carding: prevent model fitting method

MongoDB 基础了解(一)
暑期学前作业

awk of the Three Musketeers of Shell Programming

大咖说·对话生态|当Confluent遇见云:实时流动的数据更有价值
随机推荐
Guys, the test in the idea uses FlinkCDC SQL to read Mysql data and write it into Kafka. The code creates
聊聊 API 管理-开源版 到 SaaS 版
conda创建虚拟环境方法和pqi使用国内镜像源安装第三方库的方法教程
最强大脑(1)
Guys, is it normal that the oracle archive log grows by 3G in 20 minutes after running cdc?
顺序表的删除,插入和查找操作
Error when installing oracle rac 11g and executing root.sh
strongest brain (1)
FPGA engineer interview questions collection 11~20
软考考生注意!2022年下半年报名详细流程来了!
如何从代码层提高产品质量
西门子Step7和TIA软件“交叉引用”的使用
`id` bigint(20) unsigned NOT NULL COMMENT '数据库主键',
MySql之json_extract函数处理json字段
aliases node analysis
【Static proxy】
FPGA engineer interview questions collection 31~40
从GET切换为POST提交数据的方法
FPGA工程师面试试题集锦41~50
Stacks and Queues | Valid parentheses, delete all adjacent elements in a string, reverse Polish expression evaluation, maximum sliding window, top K high frequency elements | leecode brush questions
 by
by  operators, the input and output dimension will be automatically assumed to be M-qubit and N-qubit
operators, the input and output dimension will be automatically assumed to be M-qubit and N-qubit ,其结果还可以表示成一个矩阵,但是在实际作用时,则是Op2对应qubit_0, Op1对应qubit_1
,其结果还可以表示成一个矩阵,但是在实际作用时,则是Op2对应qubit_0, Op1对应qubit_1