当前位置:网站首页>C language simple [stack and queue] (bracket matching problem)
C language simple [stack and queue] (bracket matching problem)
2022-04-22 04:42:00 【Lang Shiyi】
C The data structure is simple
The whole series presents C The language is simple to realize the data structure
An ugly catalogue
Preface
College students who have been rotten for a month come back to write stacks and queues
The whole code is very simple , And each line has a comment , There are also icons ~
One 、 Stack
Stack : A special linear table , It only allows the insertion and deletion of elements at the fixed end . The end at which data is inserted and deleted is called the top of the stack , The other end is called the bottom of the stack . Data elements in the stack comply with last in, first out LIFO(Last In First Out) Principles .
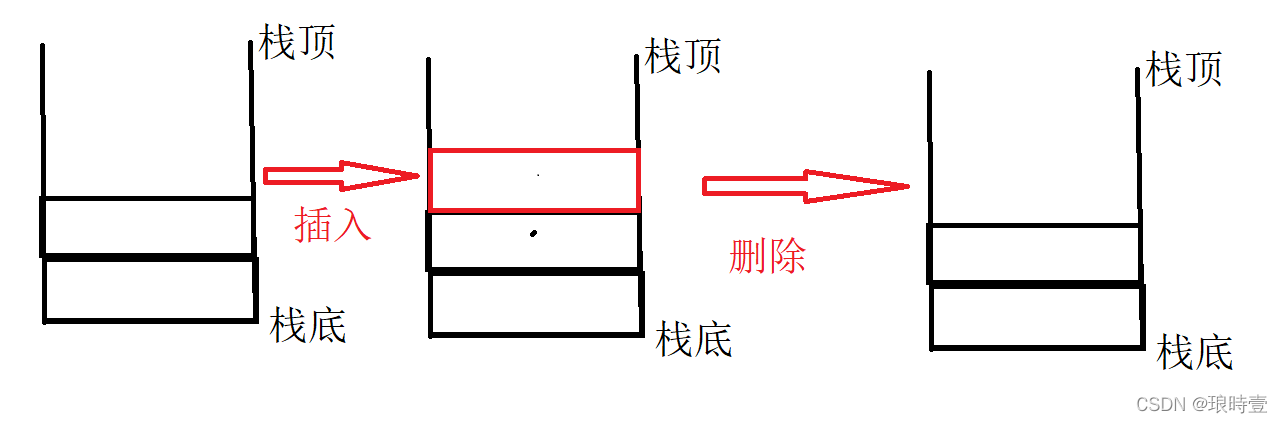
C Language simple implementation stack
Understand the characteristics of stack , We found that the implementation of stack is particularly simple , Whether it's an array or a linked list, it's especially easy , From the perspective of operation and understanding , as well as The stack only needs to operate on the tail , Array manipulation is easier
Why not use linked list , Every time we find the tail node, we need to traverse the linked list , Waste of time .

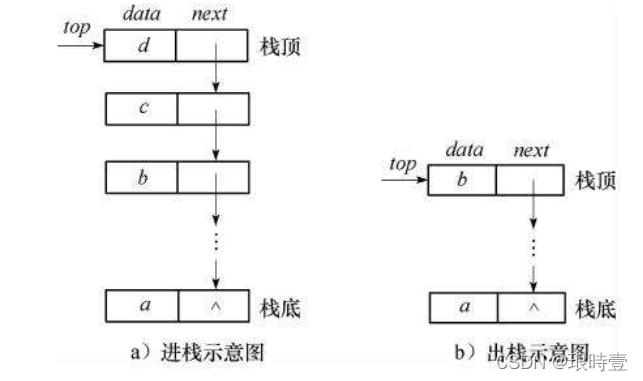
First, understand the general framework and structural principle
typedef struct Stack
{
STDataType* a;
int top; // The top of the stack
int capacity; // Capacity
}ST;
Stack.h
#pragma once// Prevent duplicate header files
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <assert.h>
typedef int STDataType;// The data type stored in the stack
typedef struct Stack
{
STDataType* a;
int top; // The top of the stack
int capacity; // Capacity
}ST;
void StackInit(ST* ps);// Stack initialization
void StackDestory(ST* ps);// Destruction of the stack
void StackPush(ST* ps, STDataType x);// Pressing stack
void StackPop(ST* ps);// Out of the stack
bool StackEmpty(ST* ps);// Judge whether the stack is empty
int StackSize(ST* ps);// Number of elements in the stack
STDataType StackTop(ST* ps);// Top element of stack
- void StackInit(ST* ps);// Stack initialization
void StackInit(ST* ps) { assert(ps); ps->a = NULL; ps->top = ps->capacity = 0; }Destroy the stack , The first address of the array is empty , The stack top position and stack capacity are reset to 0( You don't need to draw pictures to talk about it )
- void StackDestory(ST* ps);// Destruction of the stack
void StackDestory(ST* ps) { assert(ps); free(ps->a); ps->a = NULL; ps->top = ps->capacity = 0; }assert Assertion stack ps Is it empty , If it is empty, it is not necessary to perform the following operations , And then it's normal free operation , Different from initialization Namely free Will return this space to the system , The operator cannot use it again .
- void StackPush(ST* ps, STDataType x);// Pressing stack
void StackPush(ST* ps, STDataType x) { assert(ps); if (ps->top == ps->capacity)// Full... Full { int newCapacity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4 : ps->capacity * 2;// Is the stack empty or full , Double the capacity, no more, no less ps->a = (STDataType*)realloc(ps->a, newCapacity * sizeof(STDataType));// To the stack newnode Size space . if (ps->a == NULL)//realloc Failure returns a null pointer { printf("realloc fail\n"); exit(-1); } ps->capacity = newCapacity; } ps->a[ps->top] = x;// Pay attention to the distinction here top and capacity The location of ps->top++; } The code has line by line comments , Think like this

Popular speaking ,top And capacity Are the array subscript positions of the corresponding elements +1, Or the number of elements
- void StackPop(ST* ps);// Out of the stack
void StackPop(ST* ps) { assert(ps); assert(ps->top > 0);// Is the stack empty ps->top--;// You don't even have to reset the data , Because we won't use the deleted data later , Using structural characteristics top-- that will do . } 0~~~ Relatively simple
- bool StackEmpty(ST* ps);// Judge whether the stack is empty
bool StackEmpty(ST* ps) { assert(ps); return ps->top == 0; } ps->top by 0 It's empty , Go back to 1, Because it can't be negative , Greater than 0 If it is false and not empty, return 0
- int StackSize(ST* ps);// Number of elements in the stack
int StackSize(ST* ps) { assert(ps); return ps->top;// See the picture }
The stack can be understood as a beverage bottle ,top That's the bottle cap
- STDataType StackTop(ST* ps);// Top element of stack
STDataType StackTop(ST* ps) { assert(ps); assert(ps->top > 0); return ps->a[ps->top - 1]; }It describes top It's a bottle cap , So if we want to find the top piece of water, we have to find a place under the bottle cap to access the last element .
Two 、 queue
queue : Data insertion is only allowed at one end , A special linear table that deletes data at the other end , Queue has first in first out
FIFO(First In First Out) Queue entry : The end of the insertion is called the end of the queue Outgoing queue : The end of the delete operation is called the queue head
C Language simple implementation of queue
Like a stack , Understand from concept , Queues can also be implemented with arrays or linked lists , However, considering that the queue needs to operate on the head and tail, it only needs to operate on the head and tail , Using the linked list for head and tail operation is quite convenient .
Why not use arrays
When inserting and deleting headers, you need to move the whole array .
General framework and structural principle
typedef int QDataType; typedef struct QListNode { struct QListNode* next;// Pointing to the next node QDataType data;// The data in this node }QNode;// A data node // The structure of the queue typedef struct Queue { QNode* front;// Right QNode* rear;// Opposite tail }Queue;
Only two nodes are placed in the queue structure .
In the end , No, it is. Single chain list Head and tail operation .
Queue.h
#pragma once
// The chain structure : Represents a queue
#include <stdio.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef int QDataType;
typedef struct QListNode
{
struct QListNode* next;
QDataType data;
}QNode;
// The structure of the queue
typedef struct Queue
{
QNode* front;
QNode* rear;
}Queue;
// Initialize queue
void QueueInit(Queue* q);
// Tail in queue
void QueuePush(Queue* q, QDataType data);
// Team leader out of line
void QueuePop(Queue* q);
// Get queue header elements
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* q);
// Get queue tail element
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* q);
// Get the number of valid elements in the queue
int QueueSize(Queue* q);
// Check if the queue is empty , If NULL, return non-zero result , If not null, return 0
int QueueEmpty(Queue* q);
// Destroy queue
void QueueDestroy(Queue* q);
- Initialize queue
void QueueInit(Queue* q);
void QueueInit(Queue* q) { assert(q); q->front = NULL; q->rear = NULL; }Too simple
- Tail in queue
void QueuePush(Queue* q, QDataType data);
void QueuePush(Queue* q, QDataType data) { assert(q); QNode* newnode = (QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode));// Open up a node that needs to be inserted assert(newnode);// Do not rule out malloc The possibility of failure newnode->data = data;// Node assignment newnode->next = NULL;// The of the tail node in a single linked list next by NULL if (q->rear == NULL)// Judge whether there is data in the queue { assert(q->front == NULL); q->front = q->rear = newnode;// It is equivalent to inserting a node into an empty queue , After insertion, it is the head node and the tail node } else// Normal condition , There is data in the queue , Normal single chain table tail insertion { q->rear->next = newnode; q->rear = newnode; } }Every line of code has comments , And the code itself is easy to understand
- Team leader out of line
void QueuePop(Queue* q);
Quite common single column header deletionvoid QueuePop(Queue* q) { assert(q); assert(q->front && q->rear);// There must be something to delete when deleting the head if (q->front->next == NULL)// There is only one data { q->front = q->rear == NULL; } else { QNode* next = q->front->next;// Save the next node of the header node in advance , Otherwise free I can't find it after free(q->front);// Normal operation , Delete node , No more use, need to free up space q->front = next;//front substitutions ( The second ) 了 } }
- Get queue header elements
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* q);
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* q) { assert(q); if (q->front == NULL && q->rear == NULL)// Empty queue { return NULL; } return q->front->data;// Is it very simple }Need a diagram , I don't need it .
- Get queue tail element
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* q);
// Get queue tail element QDataType QueueBack(Queue* q) { assert(q); if (q->front == NULL && q->rear == NULL)// It's empty { return NULL; } return q->rear->data;//《???》 }Very simple. , The queue is simple , The understanding of stack and queue is very simple
- Get the number of valid elements in the queue
int QueueSize(Queue* q);
// Get the number of valid elements in the queue int QueueSize(Queue* q) { assert(q); QNode* cur = q->front;// A programming habit , Don't use formal parameters directly int size = 0; while (cur)// Traverse { size++;// The method of counting cur = cur->next; } return size; }
- Check if the queue is empty , If NULL, return non-zero result , If not null, return 0
int QueueEmpty(Queue* q);
int QueueEmpty(Queue* q) { assert(q); return q->front == NULL;// The expression returns 1 The queue is empty }The head is empty ~~~
- Destroy queue
void QueueDestroy(Queue* q);
void QueueDestroy(Queue* q) { assert(q); QNode* cur = q->front;// Establishing a connection while (cur)// One by one free node { QNode* next = cur->next; free(cur); cur = next; } q->front = q->rear = NULL; }Not directly free Head node , Nor can we directly free The address of the queue , The nodes inside are still there , Will cause memory leaks .
Bracket matching problem
- Parentheses matching Topic link
Given one only includes ‘(’,‘)’,‘{’,‘}’,‘[’,‘]’ String s , Determines whether the string is valid .
Valid string needs to meet :
Opening parentheses must be closed with closing parentheses of the same type .
The left parenthesis must be closed in the correct order .
- Ideas
Matching problems , If you want the brackets to match correctly, you must have the corresponding left and right brackets , Considering the matching operation , You can take advantage of stack features , Put the left bracket on the stack , Once the right bracket is encountered, it matches the nearest left bracket in the stack , If it matches, continue to judge backward , Mismatch returned FALSE.
Considering the need to use stack , We can use the stack we implemented ( Here is C Language channel ,STL Temporary does not involve )
The rest is to implement the idea in code
The title only gives the function name and the passed parameters .
// This part can be put at the beginning
typedef int STDataType;
typedef struct Stack
{
STDataType* a;
int top; // The top of the stack
int capacity; // Capacity
}ST;
void StackInit(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
ps->a = NULL;
ps->top = ps->capacity = 0;
}
void StackDestory(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
free(ps->a);
ps->a = NULL;
ps->top = ps->capacity = 0;
}
void StackPush(ST* ps, STDataType x)
{
assert(ps);
if (ps->top == ps->capacity)
{
int newCapacity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4 : ps->capacity * 2;
ps->a = (STDataType*)realloc(ps->a, newCapacity * sizeof(STDataType));
if (ps->a == NULL)
{
printf("realloc fail\n");
exit(-1);
}
ps->capacity = newCapacity;
}
ps->a[ps->top] = x;
ps->top++;
}
void StackPop(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(ps->top > 0);
ps->top--;
}
bool StackEmpty(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->top == 0;
}
int StackSize(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->top;
}
STDataType StackTop(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(ps->top > 0);
return ps->a[ps->top - 1];
}
bool isValid(char * s){
ST st;// Create a stack
StackInit(&st);
while(*s)// The title passed in an array of parentheses
{
if(*s == '(' || *s == '{' || *s == '[')// Left bracket in stack
{
// Push
StackPush(&st, *s);
s++;
}
else
{
// matching
if(StackEmpty(&st))// Until the first right bracket is encountered, there is no left bracket , Bracket mismatch
{
return false;
}
// There are left parentheses in the stack , You can match
char top = StackTop(&st);// Get the data at the top of the stack and record , Because the next step will delete
StackPop(&st);// After matching, you need to continue to match with the bracket on the left of it until the matching is finished
if(*s == ']' && top != '['
|| *s == '}' && top != '{'
|| *s == ')' && top != '(')// Mismatch
{
StackDestory(&st); Prevent memory leaks , Because we started the stack ourselves
return false;
}
else// Single parentheses match
{
// Continue than
++s;// find s The next bracket in the , Again, judge whether you need to enter the stack or match the remaining brackets at the top of the stack
}
}
}
bool ret = StackEmpty(&st);// The stack is empty. , It means that all matches
StackDestory(&st);// The stack was developed by ourselves
return ret;
}
Every time only s When the closing bracket appears, match it with the bracket at the top of the stack , Then delete the stack top array .
summary
Stacks and queues are simple , They are subsets of sequential tables and single linked tables
Next time there will be Using queue to implement stack 、 Using stack to realize queue 、 Circular queue And other classic topics .
版权声明
本文为[Lang Shiyi]所创,转载请带上原文链接,感谢
https://yzsam.com/2022/04/202204210921141888.html
边栏推荐
- Statistics of authoritative institutions: the best data center network company in 2021, China Huawei and H3C, were listed
- 排序一
- Pycharm + Anaconda installation package
- 2021-08-14
- How much do you know about the testing methods of software testing?
- 2022 a special equipment related management (elevator) retraining question bank and answers
- 将矩阵转换为稀疏矩阵,再将稀疏矩阵转换为矩阵(第一篇)
- Solve the problem of Chinese garbled code in idea (garbled code in configuration file)
- crypto-js加密算法库【安装教程、缓存加密】
- 链表第四篇
猜你喜欢

不同品牌设备如何兼容实现互联?一文教你看懂
Matlab曲线的颜色、线型等参数设置方法

Peer interview sharing Lenovo WinForm direction 20220420

论文阅读 (47):DTFD-MIL: Double-Tier Feature Distillation Multiple Instance Learning for Histopathology..

2022年山东省安全员C证考试题及在线模拟考试

DS18B20 temperature sensor based on 51 single chip microcomputer

Mui pop up menu

Solve the problem of Chinese garbled code in idea (garbled code in configuration file)

同行面试分享 联想 winform方向 20220420

2022T电梯修理考试练习题及在线模拟考试
随机推荐
How to combine acrobat Pro DC with other files to create a single PDF file?
Shell variables $, $@, $0, $1, $2, ${},%% use explanation and easy-to-use shell formatting tools
11. Libevent tests horizontal trigger and edge trigger
Paper reading (49): big data security and privacy protection (Kopp)
Article 1 of linked list
安装opencv时遇到的报错
2022a special equipment related management (elevator) test question simulation test question bank simulation test platform operation
Leetcode refers to offer 68 - I. the nearest common ancestor of the binary search tree
如何在 Bash 中将字符串计算为数字?
Leetcode sword finger offer 51 Reverse order pair in array***
2022年A特种设备相关管理(电梯)复训题库及答案
将矩阵转换为稀疏矩阵,再将稀疏矩阵转换为矩阵(第一篇)
10. Libevent receives and processes server messages
requires XXX>=YYY, but you‘ll have XXXX=ZZZ which is incompatible
AT32 MCU F435/437 DFU DEMO
论文阅读 (47):DTFD-MIL: Double-Tier Feature Distillation Multiple Instance Learning for Histopathology..
ES next相关
kaggle实战4.1--时间序列预测问题
The simulation generates random numbers and calculates the birthday of each student
Peer interview sharing Lenovo WinForm direction 20220420













