当前位置:网站首页>C language | quick sorting
C language | quick sorting
2022-04-22 07:25:00 【ZXXL】
Algorithm principle
Quick sort by C. A. R. Hoare stay 1962 in . its The basic idea is : Divide the data to be sorted into two independent parts by one sorting , All the data in one part is smaller than all the data in the other part , Then according to this method, the two parts of data are sorted quickly , The whole sort process can be done recursively , So that the whole data becomes an ordered sequence .
When sorted from small to large , Take the first of the array every time / The last element is used as the comparison standard ( Sentinel element ), Anything larger than this sentinel element is placed on its right , Anything smaller than this sentinel element is placed on its left ;
About the steps :
- Judge the parameter condition , This is actually the exit of recursion ;
- Take the first element of the array as the sentinel element , Let the other elements compare to it in size ;( Remember that the position of the first element is mouth , Because the values are saved as sentinel elements )
- Start looping forward from the end of the array to get a smaller than the sentinel element Elements A , Take this Elements A Put it in the first element position ( That is, the sentinel element position , Because the sentinel element position is empty );( Remember this time Elements A The position is empty )
- Start looping back from the head of the array to get a larger... Than the sentinel element Elements B , Take this Elements B Put the... Removed in the previous step Elements A Location ;
- Cycle through the top 3、4 Step , Until the last element , So the last element is the sentinel element .
- The part smaller than the sentinel element and the part larger than the sentinel element recursively call this function , Sort all the elements recursively in turn ;

Code implementation
Based on the first element
#include<stdio.h>
void quick_sort(int *a, int left, int right)
{
if (left >= right) // Return condition
{
return ;
}
int i = left;
int j = right;
int key = a[i];// First mark a key( This key It's not fixed , It's just a relative benchmark )
while(i < j) // Ahead i Less than the following j Explain that we haven't finished a random inspection yet .(i And j Meeting is the condition of ending )
{
while(i < j && a[j] >key) // This time it is sorted from small to large , And key On the left , therefore j First move
// First find key The latter part , And ratio key Small first value
j--;
a[i] = a[j]; // take key Put the back in the front
while(i < j && a[i]<key) // ditto
i++;
a[j] = a[i];
}
a[i] = key; // Will record key Reassign to i And j Meeting point , Here, the parameter is written j It's the same
quick_sort(a,left,i-1); // Because it's recursion , So start over , here key Is the relative middle dividing line of this array
// for example :5 9 4 key 10 15 12 ;( The left is smaller than the right ); Equivalent to row 5 9 4
quick_sort(a,i+1,right); //key The right part 10 15 12 Recurse until it returns .
}
int main()
{
int i ;
int a[] = {
23,45,0,12,9,80,1};// Subscript 1~7, address-of 0~6
quick_sort(a,0,sizeof(a)/sizeof(int)-1);
//printf("sizeof(a)/sizeof(int)-1 = %d\n", sizeof(a)/sizeof(int)-1);
for(i=0; i < sizeof(a)/sizeof(int); i++)
{
printf("%-3d",a[i]);
}
printf("\n");
return 0;
}
Based on the last element
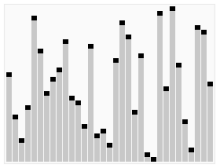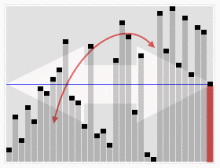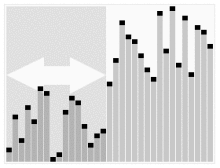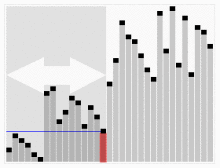
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<time.h>
int Partsort(int *a , int left , int right)
{
int key = a[right];// Take the benchmark value and save it
while(left < right)
{
while(left < right && a[left] <= key)
left++;
a[right] = a[left];
while(left < right && a[right]>=key)
right--;
a[left] = a[right];
}
a[right] = key; // Assign the reference value back
return left;
}
void QuicSort(int *a , int left , int right)
{
int part;
if(left >= right)
return ;
part = Partsort(a,left,right);// Divide left and right
QuicSort(a, left , part-1);// Recursion on the left
QuicSort(a , part+1, right);// Recursion on the right side
return;
}
int main()
{
int i;
int a[10] = {
5,3,6,9,8,2,1,7,4,0};
QuicSort(a, 0, 9);
for(i 0; i < 10; i++)
printf("%d", a[i]);
return 0;
}
Complexity calculation
Time complexity
Quick sort involves recursive calls , Therefore, the time complexity of the algorithm also needs to start with the complexity of recursive algorithm ;
Time complexity formula of recursive algorithm :T[n] = aT[n/b] + f(n) ; The time complexity of recursive algorithm is not expanded here ;
Time complexity in the optimal case
The best case of quick sorting is that the elements obtained each time are just divided into the whole array ( Obviously, it's not );
At this time, the time complexity formula is :T[n] = 2T[n/2] + f(n);T[n/2] Is the time complexity of the sub array after bisection ,f[n] The time it takes to divide the array equally ;
Let's calculate , In the optimal case, the calculation of time complexity of quick sorting ( With iteration ):
T[n] = 2T[n/2] + n ---------------- The first recursion
Make :n = n/2 = 2 { 2 T[n/4] + (n/2) } + n ---------------- Second recursion
= 2^2 T[ n/ (2^2) ] + 2n
Make :n = n/(2^2) = 2^2 { 2 T[n/ (2^3) ] + n/(2^2)} + 2n ---------------- The third recursion
= 2^3 T[ n/ (2^3) ] + 3n
......................................................................................
Make :n = n/( 2^(m-1) ) = 2^m T[1] + mn ---------------- The first m Sub recursion (m After that )
When the last one can't be divided equally , That is to say, keep the formula down , Finally get T[1] when , It shows that the formula has been iterated (T[1] It's a constant ).
obtain :T[n/ (2^m) ] = T[1] ===>> n = 2^m ====>> m = logn;
T[n] = 2^m T[1] + mn ; among m = logn;
T[n] = 2^(logn) T[1] + nlogn = n T[1] + nlogn = n + nlogn ; among n Is the number of elements
And because of dang n >= 2 when :nlogn >= n ( That is to say logn > 1), So take the back nlogn;
in summary : In the case of the best fast sorting, the time complexity is :O( nlogn )
Worst case time complexity
The worst case is that every time we get the smallest element in the array / maximal , In fact, this situation is bubble sorting ( Order one element at a time )
In this case, the time complexity is easy to calculate , Is the time complexity of bubble sorting :T[n] = n * (n-1) = n^2 + n;
in summary : The time complexity of quicksort in the worst case is :O( n^2 )
Average time complexity
The average time complexity of quick sorting is also :O(nlogn)
Spatial complexity
In fact, the complexity of this space is not easy to calculate , Because some people use non in place sorting , That's not easy to calculate ( Because some people use auxiliary arrays , So that's how you count your elements ); Let me analyze the spatial complexity of in place quick sorting ;
First, the space used for in place quick sorting is O(1) Of , It's a constant ; And what really consumes space is recursive calls , Because every time you recurs, you have to keep some data ;
In the optimal case, the space complexity is :O(logn) ; Every time we divide the array equally
In the worst case, the spatial complexity is :O( n ) ; Degenerated to bubbling sort
Advantages and disadvantages of quick sorting
Fast
Quicksort is faster , Because compared to bubble sort , Every exchange is leaping . Set a benchmark for each sorting , Put the number less than or equal to the datum point to the left of the datum point , Put the number greater than or equal to the reference point to the right of the reference point . In this way, each exchange will not be the same as bubble sort, and can only exchange between adjacent numbers at a time , The exchange distance is much larger . So the total number of comparisons and exchanges is less , The speed naturally increases .
unstable
In the worst case , It's still possible that two adjacent numbers have exchanged , At this time, the worst time complexity of quick sort is the same as bubble sort O(n^2)
版权声明
本文为[ZXXL]所创,转载请带上原文链接,感谢
https://yzsam.com/2022/04/202204220610405304.html
边栏推荐
- Find a notepad file by yourself, find the data material by yourself, and count the times of three keywords or sentence entries in the whole text.
- Redis進階
- sql server快速入门
- 树+二叉树 详解 详解 +Top-k问题
- Beyond compare solution to "authorization key has been revoked"
- Complete a student information management system and systematically practice object-oriented, function, string and other knowledge. Realize the comprehensive application of knowledge. Use classes, fun
- (五) 使用Navicat创建数据库数据表并设置id自增
- LaTex用模板的时候图片的caption标题无法左对齐
- [number theory] prime number (I): basic concepts, properties, conjectures and theorems
- (六) Sql Server的DCL丶DML语法
猜你喜欢

JVM中唯一一个不会发生GC和OOM的存储区域

在类加载的过程中,类变量的分配区域和实例变量的分配区域不一样
![Error: [HSI 55-1545], unable to generate fsbl normally, unable to read in MSS file, failed to close system mss](/img/4e/34e2820ff8579007b20b33b27d8f1d.png)
Error: [HSI 55-1545], unable to generate fsbl normally, unable to read in MSS file, failed to close system mss

LaTex中插入图片报错Unknown graphics extension: .1.jpg. }

Win10 modify command line default font

. net learning notes (2) -- ubiquitous reflection (including the method of reading JSON)
队列(详解)——手撕队列习题

快排与归并排序

Virtual machine disk space shrinks

带环链表详解
随机推荐
Complete a student information management system and systematically practice object-oriented, function, string and other knowledge. Realize the comprehensive application of knowledge. Use classes, fun
ROS installation and foundation and introduction
快排与归并排序
modelsim仿真加速注意点
最强数组学习之路
[DRC RTSTAT-1] Unrouted nets: 1 net(s) are unrouted
双向循环链表(详)
C语言 | i++ 与 ++i
win10修改命令行默认字体
Jenkins deployment PM2
MySQL learning notes
[number theory] prime number (2): prime number sieve method (Egyptian sieve, Euler sieve, interval sieve)
Quartus II防止信号被综合
Mongodb install self start service
Robomaster Dajiang flying hand assessment
Beyond Compare“授权密钥已被吊销”的解决办法
synchronized锁优化的一些机制(锁升级)
Write a method Sanjiao (a, B, c) to judge whether the three parameters can form a triangle. If not, throw an exception illegalargumentexception and display the exception information a, B, C "cannot fo
C语言 | 快速排序
Virtual machine disk space shrinks