当前位置:网站首页>【Pytorch】学习笔记(一)
【Pytorch】学习笔记(一)
2022-08-08 22:58:00 【摇曳的树】
引言
课程视频链接:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1Y7411d7Ys?from=search&seid=17942018663670881374
笔者认为讲得十分通俗易懂
1 线性模型
1.1 线性模型
y ^ = x ∗ w + b \hat y=x*w+b y^=x∗w+b
1.2 损失(针对单个样本)
l o s s = ( y ^ − y ) 2 = ( x ∗ w − y ) 2 loss = (\hat y-y)^2=(x*w-y)^2 loss=(y^−y)2=(x∗w−y)2
1.3 均方误差 MSE(针对整个训练样本)
c o s t = 1 N ∑ n = 1 N ( y ^ n − y n ) 2 cost = \frac {1} {N}\sum_{n=1}^{N} {(\hat y_n-y_n)^2} cost=N1n=1∑N(y^n−yn)2
1.4 代码实现(用numpy)
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 数据集准备
x_data = [1.0,2.0,3.0]
y_data = [2.0,4.0,6.0]
def forward(x): # 定义线性模型
return x*w
def loss(x,y): # 定义损失函数(单个样本计算损失)
y_pred = forward(x)
return (y_pred - y)*(y_pred - y)
w_list = []
mse_list = []
for w in np.arange(0.0,4.1,0.1): # 穷举法列举权重
print('w = ',w)
l_sum = 0
for x_val,y_val in zip(x_data,y_data):
y_pred_val = forward(x_val)
loss_val = loss(x_val,y_val)
l_sum+=loss_val
print('\t',x_val,y_val,y_pred_val,loss_val)
print('MSE=',l_sum/3)
w_list.append(w)
mse_list.append(l_sum/3)
# 绘图
plt.plot(w_list,mse_list)
plt.ylabel('loss')
plt.xlabel('w')
plt.show()
运行结果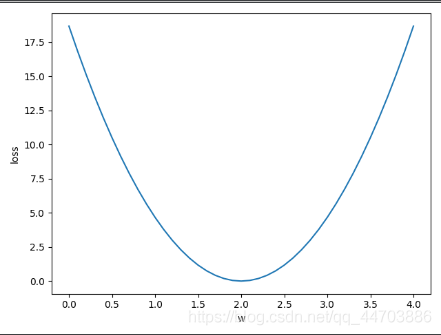
可视化训练过程(Visdom工具)
http://github.com/facebookresearch/visdom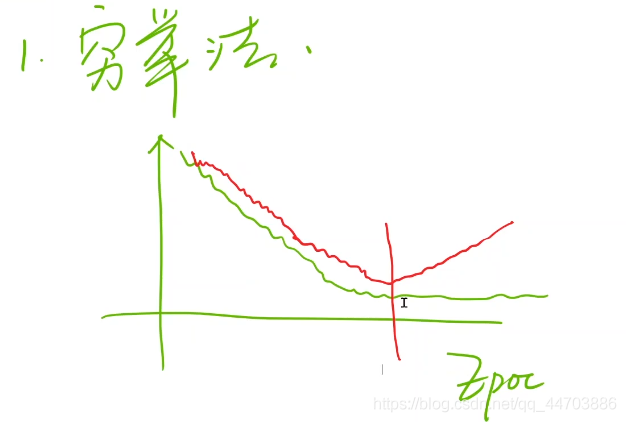
matlab 3d图绘制
2 梯度下降
搜索最佳权重的方法(优化问题):
- 穷举法
- 分治法(只针对凸函数,否则只能找到局部最优)
- 梯度下降法(贪心)

梯度定义:
∂ c o s t ( w ) ∂ w = ∂ ∂ w 1 N ∑ n = 1 N ( y ^ n − y n ) 2 = 1 N ∑ n = 1 N ∂ ∂ w ( x n ⋅ w − y n ) 2 = 1 N ∑ n = 1 N 2 ⋅ ( x n ⋅ w − y n ) ∂ ( x n ⋅ w − y n ) ∂ w = 1 N ∑ n = 1 N 2 ⋅ x n ⋅ ( x n ⋅ w − y n ) \frac {\partial cost(w)} {\partial w} = \frac {\partial} {\partial w} \frac {1} {N} \sum_{n=1}^{N} {(\hat y_n-y_n)^2} \\= \frac {1} {N} \sum_{n=1}^{N}\frac {\partial} {\partial w} {(x_n\cdot w-y_n)^2} \\= \frac {1} {N} \sum_{n=1}^{N} 2\cdot{(x_n\cdot w-y_n)} \frac {\partial (x_n\cdot w-y_n)} {\partial w}\\= \frac {1} {N} \sum_{n=1}^{N} {2 \cdot x_n\cdot(x_n\cdot w-y_n)} ∂w∂cost(w)=∂w∂N1n=1∑N(y^n−yn)2=N1n=1∑N∂w∂(xn⋅w−yn)2=N1n=1∑N2⋅(xn⋅w−yn)∂w∂(xn⋅w−yn)=N1n=1∑N2⋅xn⋅(xn⋅w−yn)
2.1 梯度下降算法
w = w − ∂ c o s t ∂ w w=w- \frac {\partial cost} {\partial w} w=w−∂w∂cost
其中
∂ c o s t ∂ w = 1 N ∑ n = 1 N 2 ⋅ x n ⋅ ( x n ⋅ w − y n ) \frac {\partial cost} {\partial w} = \frac {1} {N} \sum_{n=1}^{N} {2 \cdot x_n\cdot(x_n\cdot w-y_n)} ∂w∂cost=N1n=1∑N2⋅xn⋅(xn⋅w−yn)
w = 1.0
def forward(x): # 线性模型
return x*w
def cost(xs,ys):
cost = 0
for x,y in zip(xs,ys):
y_pred = forward(x)
cost += (y_pred-y)**2
return cost/len(xs)
def gradient(xs,ys):
grad = 0
for x,y in zip(xs,ys):
grad += 2*x*(x*w-y)
return grad/len(xs)
print('Predict (before training)', 4, forward(4))
for epoch in range(100):
cost_val = cost(x_data,y_data)
grad_val = gradient(x_data,y_data)
w-=0.01*grad_val
print('Epoch:',epoch,'w=',w,'loss=',cost_val)
print('Predict (after training)',4,forward(4))
2.2 随机梯度下降
意义:大样本学习时,采用所有样本的损失,计算量太大,训练太慢
w = w − ∂ l o s s ∂ w w=w- \frac {\partial loss} {\partial w} w=w−∂w∂loss
其中
∂ l o s s n ∂ w = 2 ⋅ x n ⋅ ( x n ⋅ w − y n ) \frac {\partial loss_n} {\partial w} =2 \cdot x_n\cdot(x_n\cdot w-y_n) ∂w∂lossn=2⋅xn⋅(xn⋅w−yn)

# 2.2 随机梯度下降
w = 1.0
def forward(x): # 线性模型
return x*w
def loss(x,y):
y_pred = forward(x)
return (y_pred-y)**2
def gradient(x,y):
return 2*x*(x*w-y)
print('Predict (before training)', 4, forward(4))
for epoch in range(100):
for x,y in zip(x_data,y_data):
grad = gradient(x_data,y_data)
w = w-0.01*grad
print('\tgrad:',x,y,grad)
l = loss(x,y)
print('progress:',epoch,'w=',w,'loss',l)
print('Predict (after training)',4,forward(4))
综合上述的两种梯度下降算法,目前最常用的批量随机梯度下降(Mini_Batch)
3 反向传播算法
3.1 权重的更新计算
w = w − ∂ c o s t ∂ w w=w- \frac {\partial cost} {\partial w} w=w−∂w∂cost
权重的维度:输出维度*输入维度
非线性激活的意义
线性变换,不管增加多少层,最终还是线性模式,增加层数变得毫无意义。
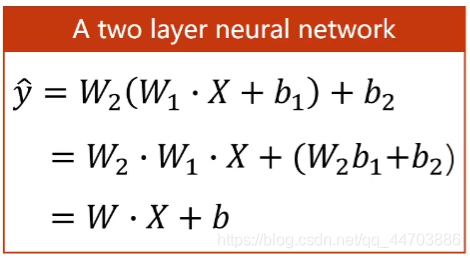
为了提高模型的复杂程度,在每一个线性层的最终输出增加一个非线性变换函数(激活函数)。
3.2 链式求导法则

反向传播示例: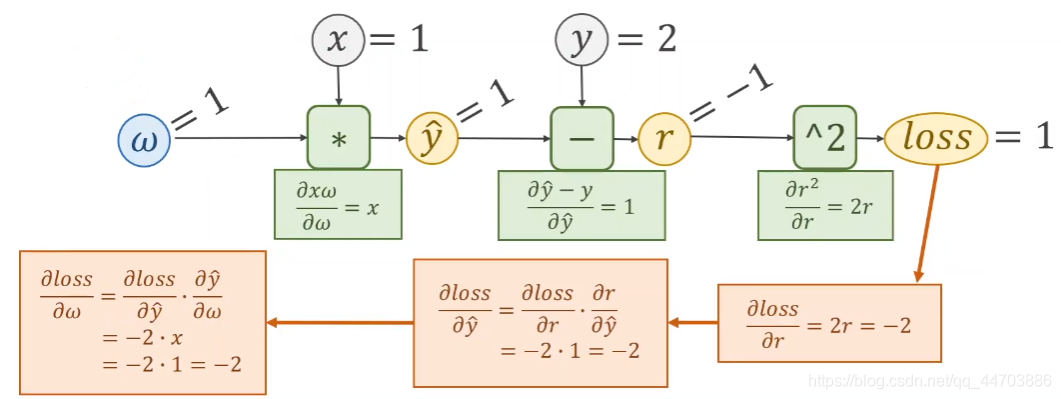
3.3 pytorch实现反向传播
在pytorch中张量包含权重的值和损失对权重的导数
import torch
x_data = [1.0,2.0,3.0]
y_data = [2.0,4.0,6.0]
w = torch.Tensor([1.0]) # 张量
w.requires_grad = True # 需要计算梯度
# 只要含有张量,定义的函数不再是简单的计算,而是构建计算图
def forward(x):
return x*w
def loss(x,y):
y_pred = forward(x)
return (y_pred-y)**2
# 训练
print('predict(before training)',4,forward(4).item())
for epoch in range(100):
for x,y in zip(x_data,y_data):
l = loss(x,y) # 张量
l.backward() # 反向传播,自动存到w,同时计算图释放
print('\tgrad:',x,y,w.grad.item())
w.data = w.data - 0.01*w.grad.data # 权重更新
w.grad.data.zero_() # 梯度清零
print('progress:',epoch,l.item())
print('predict(after training)',4,forward(4).item())
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
如何搭建一套自己公司的知识共享平台
在chrome中呈现RTSP
免费ARP
GIL和池的概念
详解JS中for...of、in关键字
You know you every day in the use of NAT?
Button Wizard Delete File Command
Virtual router redundancy protocol VRRP - double-machine hot backup
Unity Text自定义多重渐变色且渐变色位置可调
meta learning
Excuse me: is it safe to pay treasure to buy fund on
thinkphp5 if else的表达式怎么写?
iptables防火墙内容全解
Kubernetes 1.25 中的删除和主要变化
浅析WLAN——无线局域网
嵌入式驱动开发整体调试
ABP中的数据过滤器
腾讯技术支持实习二面——腾讯爸爸的临幸就是这么突然(offer到手)
ArcPy要素批量转dwg
防火墙初接触