Semantic Image Synthesis with SPADE
New implementation available at imaginaire repository
We have a reimplementation of the SPADE method that is more performant. It is avaiable at Imaginaire
Project page | Paper | Online Interactive Demo of GauGAN | GTC 2019 demo | Youtube Demo of GauGAN
Semantic Image Synthesis with Spatially-Adaptive Normalization.
Taesung Park, Ming-Yu Liu, Ting-Chun Wang, and Jun-Yan Zhu.
In CVPR 2019 (Oral).
License
Copyright (C) 2019 NVIDIA Corporation.
All rights reserved. Licensed under the CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 (Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International)
The code is released for academic research use only. For commercial use or business inquiries, please contact [email protected].
For press and other inquiries, please contact Hector Marinez
Installation
Clone this repo.
git clone https://github.com/NVlabs/SPADE.git
cd SPADE/
This code requires PyTorch 1.0 and python 3+. Please install dependencies by
pip install -r requirements.txt
This code also requires the Synchronized-BatchNorm-PyTorch rep.
cd models/networks/
git clone https://github.com/vacancy/Synchronized-BatchNorm-PyTorch
cp -rf Synchronized-BatchNorm-PyTorch/sync_batchnorm .
cd ../../
To reproduce the results reported in the paper, you would need an NVIDIA DGX1 machine with 8 V100 GPUs.
Dataset Preparation
For COCO-Stuff, Cityscapes or ADE20K, the datasets must be downloaded beforehand. Please download them on the respective webpages. In the case of COCO-stuff, we put a few sample images in this code repo.
Preparing COCO-Stuff Dataset. The dataset can be downloaded here. In particular, you will need to download train2017.zip, val2017.zip, stuffthingmaps_trainval2017.zip, and annotations_trainval2017.zip. The images, labels, and instance maps should be arranged in the same directory structure as in datasets/coco_stuff/. In particular, we used an instance map that combines both the boundaries of "things instance map" and "stuff label map". To do this, we used a simple script datasets/coco_generate_instance_map.py. Please install pycocotools using pip install pycocotools and refer to the script to generate instance maps.
Preparing ADE20K Dataset. The dataset can be downloaded here, which is from MIT Scene Parsing BenchMark. After unzipping the datgaset, put the jpg image files ADEChallengeData2016/images/ and png label files ADEChallengeData2016/annotatoins/ in the same directory.
There are different modes to load images by specifying --preprocess_mode along with --load_size. --crop_size. There are options such as resize_and_crop, which resizes the images into square images of side length load_size and randomly crops to crop_size. scale_shortside_and_crop scales the image to have a short side of length load_size and crops to crop_size x crop_size square. To see all modes, please use python train.py --help and take a look at data/base_dataset.py. By default at the training phase, the images are randomly flipped horizontally. To prevent this use --no_flip.
Generating Images Using Pretrained Model
Once the dataset is ready, the result images can be generated using pretrained models.
-
Download the tar of the pretrained models from the Google Drive Folder, save it in 'checkpoints/', and run
cd checkpoints tar xvf checkpoints.tar.gz cd ../ -
Generate images using the pretrained model.
python test.py --name [type]_pretrained --dataset_mode [dataset] --dataroot [path_to_dataset]
[type]_pretrainedis the directory name of the checkpoint file downloaded in Step 1, which should be one ofcoco_pretrained,ade20k_pretrained, andcityscapes_pretrained.[dataset]can be one ofcoco,ade20k, andcityscapes, and[path_to_dataset], is the path to the dataset. If you are running on CPU mode, append--gpu_ids -1. -
The outputs images are stored at
./results/[type]_pretrained/by default. You can view them using the autogenerated HTML file in the directory.
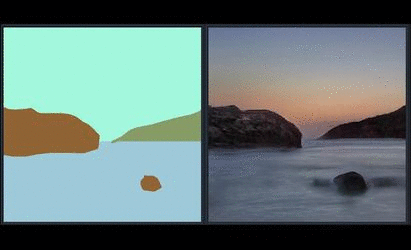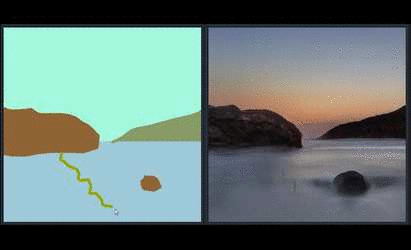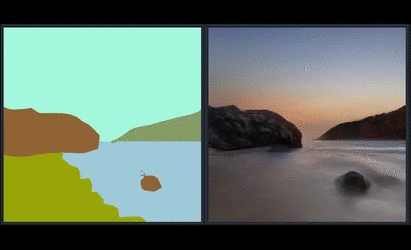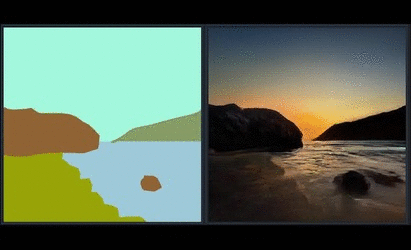
Generating Landscape Image using GauGAN
In the paper and the demo video, we showed GauGAN, our interactive app that generates realistic landscape images from the layout users draw. The model was trained on landscape images scraped from Flickr.com. We released an online demo that has the same features. Please visit https://www.nvidia.com/en-us/research/ai-playground/. The model weights are not released.
Training New Models
New models can be trained with the following commands.
-
Prepare dataset. To train on the datasets shown in the paper, you can download the datasets and use
--dataset_modeoption, which will choose which subclass ofBaseDatasetis loaded. For custom datasets, the easiest way is to use./data/custom_dataset.pyby specifying the option--dataset_mode custom, along with--label_dir [path_to_labels] --image_dir [path_to_images]. You also need to specify options such as--label_ncfor the number of label classes in the dataset,--contain_dontcare_labelto specify whether it has an unknown label, or--no_instanceto denote the dataset doesn't have instance maps. -
Train.
# To train on the Facades or COCO dataset, for example.
python train.py --name [experiment_name] --dataset_mode facades --dataroot [path_to_facades_dataset]
python train.py --name [experiment_name] --dataset_mode coco --dataroot [path_to_coco_dataset]
# To train on your own custom dataset
python train.py --name [experiment_name] --dataset_mode custom --label_dir [path_to_labels] -- image_dir [path_to_images] --label_nc [num_labels]
There are many options you can specify. Please use python train.py --help. The specified options are printed to the console. To specify the number of GPUs to utilize, use --gpu_ids. If you want to use the second and third GPUs for example, use --gpu_ids 1,2.
To log training, use --tf_log for Tensorboard. The logs are stored at [checkpoints_dir]/[name]/logs.
Testing
Testing is similar to testing pretrained models.
python test.py --name [name_of_experiment] --dataset_mode [dataset_mode] --dataroot [path_to_dataset]
Use --results_dir to specify the output directory. --how_many will specify the maximum number of images to generate. By default, it loads the latest checkpoint. It can be changed using --which_epoch.
Code Structure
train.py,test.py: the entry point for training and testing.trainers/pix2pix_trainer.py: harnesses and reports the progress of training.models/pix2pix_model.py: creates the networks, and compute the lossesmodels/networks/: defines the architecture of all modelsoptions/: creates option lists usingargparsepackage. More individuals are dynamically added in other files as well. Please see the section below.data/: defines the class for loading images and label maps.
Options
This code repo contains many options. Some options belong to only one specific model, and some options have different default values depending on other options. To address this, the BaseOption class dynamically loads and sets options depending on what model, network, and datasets are used. This is done by calling the static method modify_commandline_options of various classes. It takes in theparser of argparse package and modifies the list of options. For example, since COCO-stuff dataset contains a special label "unknown", when COCO-stuff dataset is used, it sets --contain_dontcare_label automatically at data/coco_dataset.py. You can take a look at def gather_options() of options/base_options.py, or models/network/__init__.py to get a sense of how this works.
VAE-Style Training with an Encoder For Style Control and Multi-Modal Outputs
To train our model along with an image encoder to enable multi-modal outputs as in Figure 15 of the paper, please use --use_vae. The model will create netE in addition to netG and netD and train with KL-Divergence loss.
Citation
If you use this code for your research, please cite our papers.
@inproceedings{park2019SPADE,
title={Semantic Image Synthesis with Spatially-Adaptive Normalization},
author={Park, Taesung and Liu, Ming-Yu and Wang, Ting-Chun and Zhu, Jun-Yan},
booktitle={Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition},
year={2019}
}
Acknowledgments
This code borrows heavily from pix2pixHD. We thank Jiayuan Mao for his Synchronized Batch Normalization code.