ADGCL : Adversarial Graph Augmentation to Improve Graph Contrastive Learning
Introduction
This repo contains the Pytorch [1] implementation of Adversarial Graph Contrastive Learning (AD-GCL) principle instantiated with learnable edge dropping augmentation. The paper is available on arxiv. 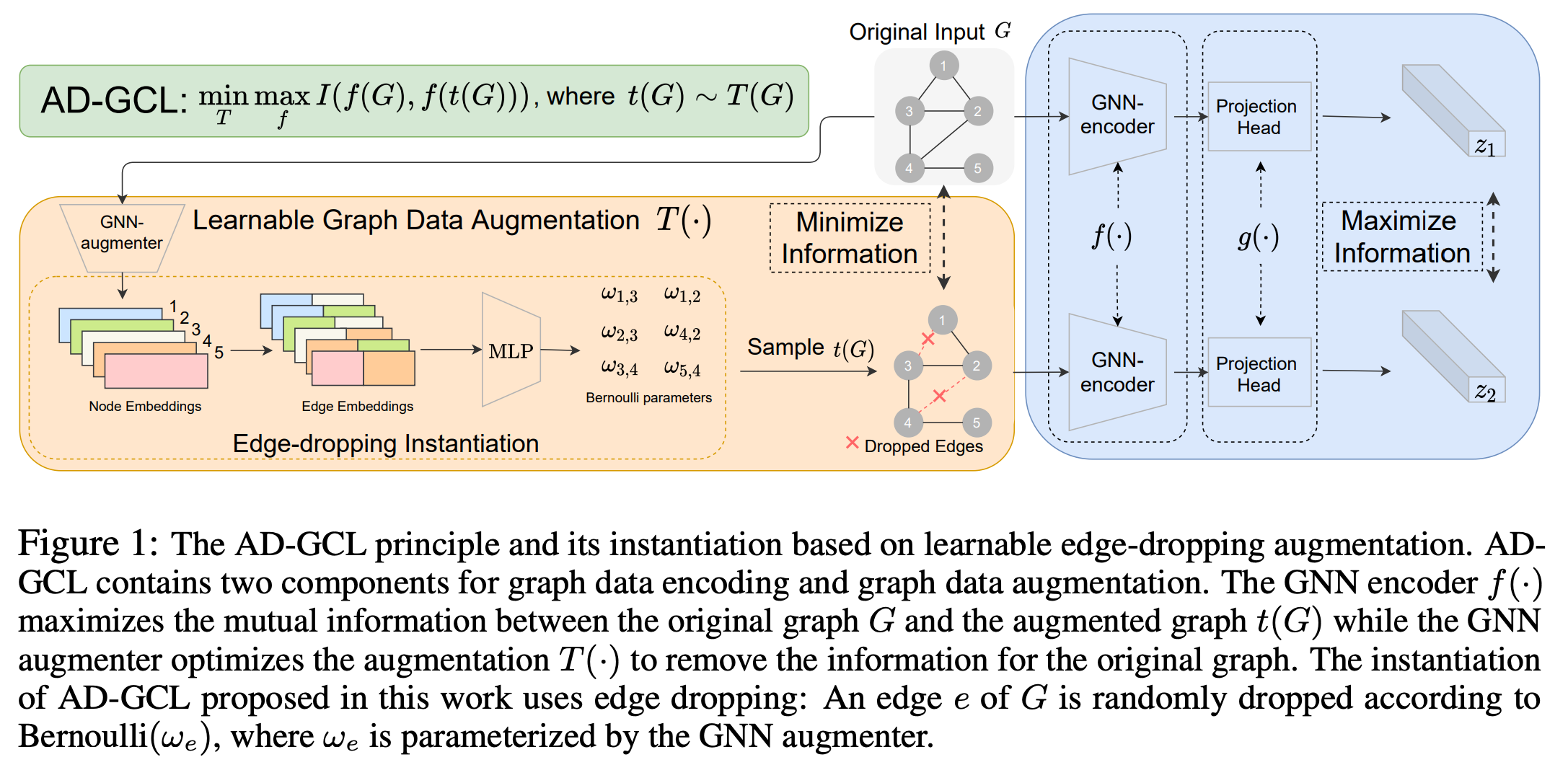
Requirements and Environment Setup
Code developed and tested in Python 3.8.8 using PyTorch 1.8. Please refer to their official websites for installation and setup.
Some major requirements are given below
numpy~=1.20.1
networkx~=2.5.1
torch~=1.8.1
tqdm~=4.60.0
scikit-learn~=0.24.1
pandas~=1.2.4
gensim~=4.0.1
scipy~=1.6.2
ogb~=1.3.1
matplotlib~=3.4.2
torch-cluster~=1.5.9
torch-geometric~=1.7.0
torch-scatter~=2.0.6
torch-sparse~=0.6.9
torch-spline-conv~=1.2.1
rdkit~=2021.03.1
Datasets
The package datasets contains the modules required for downloading and loading the TU Benchmark Dataset, ZINC and transfer learning pre-train and fine-tuning datasets.
Create a folder to store all datasets using mkdir original_datasets. Except for the transfer learning datasets all the others are automatically downloaded and loaded using the datasets package. Follow and download chem and bio datasets for transfer learning from here and place it inside a newly created folder called transfer within original_datasets.
The Open Graph Benchmark datasets are downloaded and loaded using the ogb library. Please refer here for more details and installation.
AD-GCL Training
For running AD-GCL on Open Graph Benchmark. e.g. CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 python test_minmax_ogbg.py --dataset ogbg-molesol --reg_lambda 0.4
usage: test_minmax_ogbg.py [-h] [--dataset DATASET] [--model_lr MODEL_LR] [--view_lr VIEW_LR] [--num_gc_layers NUM_GC_LAYERS] [--pooling_type POOLING_TYPE] [--emb_dim EMB_DIM] [--mlp_edge_model_dim MLP_EDGE_MODEL_DIM] [--batch_size BATCH_SIZE] [--drop_ratio DROP_RATIO]
[--epochs EPOCHS] [--reg_lambda REG_LAMBDA] [--seed SEED]
AD-GCL ogbg-mol*
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
--dataset DATASET Dataset
--model_lr MODEL_LR Model Learning rate.
--view_lr VIEW_LR View Learning rate.
--num_gc_layers NUM_GC_LAYERS
Number of GNN layers before pooling
--pooling_type POOLING_TYPE
GNN Pooling Type Standard/Layerwise
--emb_dim EMB_DIM embedding dimension
--mlp_edge_model_dim MLP_EDGE_MODEL_DIM
embedding dimension
--batch_size BATCH_SIZE
batch size
--drop_ratio DROP_RATIO
Dropout Ratio / Probability
--epochs EPOCHS Train Epochs
--reg_lambda REG_LAMBDA
View Learner Edge Perturb Regularization Strength
--seed SEED
Similarly, one can run for ZINC and TU datasets using for e.g. CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 python test_minmax_zinc.py and CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 python test_minmax_tu.py --dataset REDDIT-BINARY respectively. Adding a --help at the end will provide more details.
Pretraining for transfer learning
usage: test_minmax_transfer_pretrain_chem.py [-h] [--dataset DATASET] [--model_lr MODEL_LR] [--view_lr VIEW_LR] [--num_gc_layers NUM_GC_LAYERS] [--pooling_type POOLING_TYPE] [--emb_dim EMB_DIM] [--mlp_edge_model_dim MLP_EDGE_MODEL_DIM] [--batch_size BATCH_SIZE]
[--drop_ratio DROP_RATIO] [--epochs EPOCHS] [--reg_lambda REG_LAMBDA] [--seed SEED]
Transfer Learning AD-GCL Pretrain on ZINC 2M
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
--dataset DATASET Dataset
--model_lr MODEL_LR Model Learning rate.
--view_lr VIEW_LR View Learning rate.
--num_gc_layers NUM_GC_LAYERS
Number of GNN layers before pooling
--pooling_type POOLING_TYPE
GNN Pooling Type Standard/Layerwise
--emb_dim EMB_DIM embedding dimension
--mlp_edge_model_dim MLP_EDGE_MODEL_DIM
embedding dimension
--batch_size BATCH_SIZE
batch size
--drop_ratio DROP_RATIO
Dropout Ratio / Probability
--epochs EPOCHS Train Epochs
--reg_lambda REG_LAMBDA
View Learner Edge Perturb Regularization Strength
--seed SEED
usage: test_minmax_transfer_pretrain_bio.py [-h] [--dataset DATASET] [--model_lr MODEL_LR] [--view_lr VIEW_LR] [--num_gc_layers NUM_GC_LAYERS] [--pooling_type POOLING_TYPE] [--emb_dim EMB_DIM] [--mlp_edge_model_dim MLP_EDGE_MODEL_DIM] [--batch_size BATCH_SIZE]
[--drop_ratio DROP_RATIO] [--epochs EPOCHS] [--reg_lambda REG_LAMBDA] [--seed SEED]
Transfer Learning AD-GCL Pretrain on PPI-306K
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
--dataset DATASET Dataset
--model_lr MODEL_LR Model Learning rate.
--view_lr VIEW_LR View Learning rate.
--num_gc_layers NUM_GC_LAYERS
Number of GNN layers before pooling
--pooling_type POOLING_TYPE
GNN Pooling Type Standard/Layerwise
--emb_dim EMB_DIM embedding dimension
--mlp_edge_model_dim MLP_EDGE_MODEL_DIM
embedding dimension
--batch_size BATCH_SIZE
batch size
--drop_ratio DROP_RATIO
Dropout Ratio / Probability
--epochs EPOCHS Train Epochs
--reg_lambda REG_LAMBDA
View Learner Edge Perturb Regularization Strength
--seed SEED
Pre-train models will be automatically saved in a folder called models_minmax. Please use those when finetuning to initialize the GNN. More details below.
Fine-tuning for evaluating transfer learning
For fine-tuning evaluation for transfer learning.
usage: test_transfer_finetune_chem.py [-h] [--device DEVICE] [--batch_size BATCH_SIZE] [--epochs EPOCHS] [--lr LR] [--lr_scale LR_SCALE] [--decay DECAY] [--num_layer NUM_LAYER] [--emb_dim EMB_DIM] [--dropout_ratio DROPOUT_RATIO] [--graph_pooling GRAPH_POOLING] [--JK JK]
[--gnn_type GNN_TYPE] [--dataset DATASET] [--input_model_file INPUT_MODEL_FILE] [--seed SEED] [--split SPLIT] [--eval_train EVAL_TRAIN] [--num_workers NUM_WORKERS]
Finetuning Chem after pre-training of graph neural networks
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
--device DEVICE which gpu to use if any (default: 0)
--batch_size BATCH_SIZE
input batch size for training (default: 32)
--epochs EPOCHS number of epochs to train (default: 100)
--lr LR learning rate (default: 0.001)
--lr_scale LR_SCALE relative learning rate for the feature extraction layer (default: 1)
--decay DECAY weight decay (default: 0)
--num_layer NUM_LAYER
number of GNN message passing layers (default: 5).
--emb_dim EMB_DIM embedding dimensions (default: 300)
--dropout_ratio DROPOUT_RATIO
dropout ratio (default: 0.5)
--graph_pooling GRAPH_POOLING
graph level pooling (sum, mean, max, set2set, attention)
--JK JK how the node features across layers are combined. last, sum, max or concat
--gnn_type GNN_TYPE
--dataset DATASET dataset. For now, only classification.
--input_model_file INPUT_MODEL_FILE
filename to read the pretrain model (if there is any)
--seed SEED Seed for minibatch selection, random initialization.
--split SPLIT random or scaffold or random_scaffold
--eval_train EVAL_TRAIN
evaluating training or not
--num_workers NUM_WORKERS
number of workers for dataset loading
Similarly, for the bio dataset use python test_transfer_finetune_bio.py --help for details.
Please refer to the appendix of our paper for more details regarding hyperparameter settings.
Acknowledgements
This reference implementation is inspired and based on earlier works [2] and [3].
Please cite our paper if you use this code in your own work.
@article{suresh2021adversarial,
title={Adversarial Graph Augmentation to Improve Graph Contrastive Learning},
author={Suresh, Susheel and Li, Pan and Hao, Cong and Neville, Jennifer},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2106.05819},
year={2021}
}
References
[1] Paszke, Adam, et al. "PyTorch: An Imperative Style, High-Performance Deep Learning Library." Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 32 (2019): 8026-8037.
[2] Y. You, T. Chen, Y. Sui, T. Chen, Z. Wang, and Y. Shen, “Graph contrastive learning with augmentations”. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 33, 2020
[3] Weihua Hu*, Bowen Liu*, Joseph Gomes, Marinka Zitnik, Percy Liang, Vijay Pande, Jure Leskovec. "Strategies for Pre-training Graph Neural Networks". ICLR 2020