Overview
Prompt-learning is the latest paradigm to adapt pre-trained language models (PLMs) to downstream NLP tasks, which modifies the input text with a textual template and directly uses PLMs to conduct pre-trained tasks. This library provides a standard, flexible and extensible framework to deploy the prompt-learning pipeline. OpenPrompt supports loading PLMs directly from huggingface transformers. In the future, we will also support PLMs implemented by other libraries.
What Can You Do via OpenPrompt?
- Use the implementations of current prompt-learning approaches.* We have implemented various of prompting methods, including templating, verbalizing and optimization strategies under a unified standard. You can easily call and understand these methods.
- Design your own prompt-learning work. With the extensibility of OpenPrompt, you can quickly practice your prompt-learning ideas.
Installation
Using Git
Clone the repository from github:
git clone https://github.com/thunlp/OpenPrompt.git
cd OpenPrompt
pip install -r requirements.txt
python setup.py install
Modify the code
python setup.py develop
Use OpenPrompt
Base Concepts
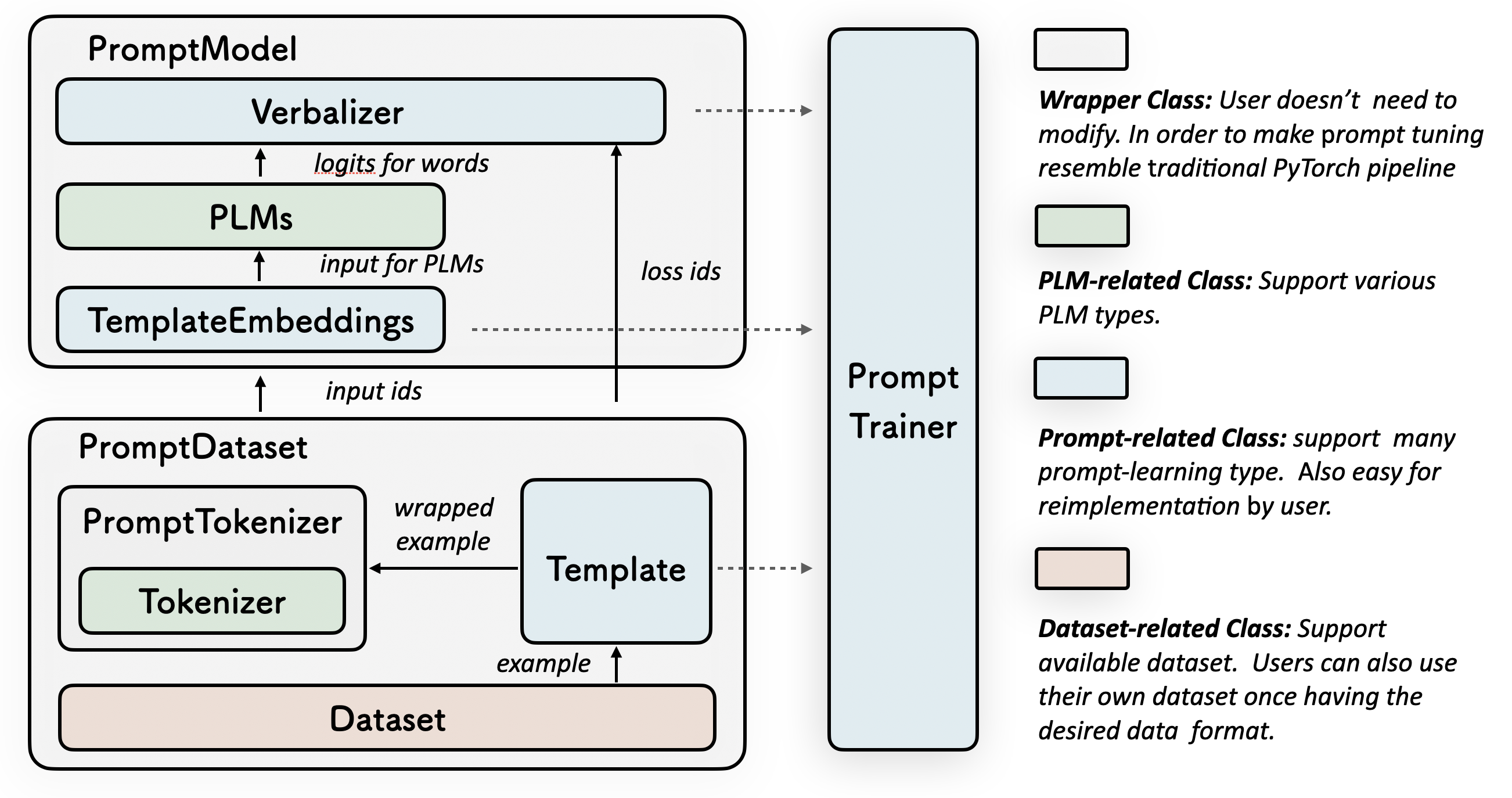
A Prompt class contains a (or multiple) Template and a (or multiple) Verbalizer, where the Template class is defined to wrap the original input with templates, and the Verbalizer class is to construct a projection between labels and target words in the current vocabulary.
A PromptModel class combines the Template, Verbalizer and PLM, practically participating in training and inference.
Introduction by a Simple Example
With the modularity and flexibility of OpenPrompt, you can easily develop a prompt-learning pipeline.
Step 1: Define a task
The first step is to determine the current NLP task, think about what’s your data looks like and what do you want from the data! That is, the essence of this step is to determine the classses and the InputExample of the task. For simplicity, we use Sentiment Analysis as an example. tutorial_task.
from openprompt.data_utils import InputExample
classes = [ # There are two classes in Sentiment Analysis, one for negative and one for positive
"negative",
"positive"
]
dataset = [ # For simplicity, there's only two examples
# text_a is the input text of the data, some other datasets may have multiple input sentences in one example.
InputExample(
guid = 0,
text_a = "Albert Einstein was one of the greatest intellects of his time.",
),
InputExample(
guid = 1,
text_a = "The film was badly made.",
),
]
Step 2: Define a Pre-trained Language Models (PLMs) as backbone.
Choose a PLM to support your task. Different models have different attributes, we encourge you to use OpenPrompt to explore the potential of various PLMs. OpenPrompt is compatible with models on huggingface.
from openprompt.plms import get_model_class
model_class = get_model_class(plm_type = "bert")
model_path = "bert-base-cased"
bertConfig = model_class.config.from_pretrained(model_path)
bertTokenizer = model_class.tokenizer.from_pretrained(model_path)
bertModel = model_class.model.from_pretrained(model_path)
Step 3: Define a Template.
A Template is a modifier of the original input text, which is also one of the most important modules in prompt-learning.
from openprompt.prompts import ManualTemplate promptTemplate = ManualTemplate( text = ["" , "It", "was", "" ], tokenizer = bertTokenizer, )
Step 4: Define a Verbalizer
A Verbalizer is another important (but not neccessary) in prompt-learning,which projects the original labels (we have defined them as classes, remember?) to a set of label words. Here is an example that we project the negative class to the word bad, and project the positive class to the words good, wonderful, great.
from openprompt.prompts import ManualVerbalizer
promptVerbalizer = ManualVerbalizer(
classes = classes,
label_words = {
"negative": ["bad"],
"positive": ["good", "wonderful", "great"],
},
tokenizer = bertTokenizer,
)
Step 5: Combine them into a PromptModel
Given the task, now we have a PLM, a Template and a Verbalizer, we combine them into a PromptModel. Note that although the example naively combine the three modules, you can actually define some complicated interactions among them.
from openprompt import PromptForClassification
promptModel = PromptForClassification(
template = promptTemplate,
model = bertModel,
verbalizer = promptVerbalizer,
)
Please refer to our documentation for more details.
Datasets
We provide a series of download scripts in the dataset/ folder, feel free to use them to download benchmarks.
Citation
We are working on the technical report...
Contributors
We thank all the contributors to this project, more contributors are welcome!


 hello, when I try to run the example in the readme, I found the download speed is too slow. I use miniconda with python3.8 and cuda11.1. Are there any ways to speed up the download?
hello, when I try to run the example in the readme, I found the download speed is too slow. I use miniconda with python3.8 and cuda11.1. Are there any ways to speed up the download?