当前位置:网站首页>groovy基础学习
groovy基础学习
2022-08-08 15:39:00 【bobo洁厕灵】
范围运算符
class HelloGroovy {
static void main(args) {
def range = 5..10; //定义一个简单的整数范围,存储一个局部变量,下限为0,上限为1
println(range);
println(range.get(2));
}
}Groovy 中的方法是使用返回类型或使用 def 关键字定义的。方法可以接收任意数量的参数。定义参数时,不必显式定义类型。可以添加修饰符,如 public,private 和 protected。默认情况下,如果未提供可见性修饰符,则该方法为 public。
class Example {
static def DisplayName() {
println("This is how methods work in groovy");
println("This is an example of a simple method");
}
static void main(String[] args) {
DisplayName();
}
}默认参数
如果没有值传递给方法的参数,则使用缺省值。 如果使用非默认和默认参数,则必须注意,默认参数应在参数列表的末尾定义。
groovy文件I/O
重点:file类
读取文件
import java.io.File
class Example {
static void main(String[] args) {
new File("E:/Example.txt").eachLine {
line -> println "line : $line";
}
}
}读取文件的内容到字符串
可以使用文件类的text属性
class Example {
static void main(String[] args) {
File file = new File("E:/Example.txt")
println file.text
}
}写入文件
使用write类
import java.io.File
class Example {
static void main(String[] args) {
new File('E:/','Example.txt').withWriter('utf-8') {
writer -> writer.writeLine 'Hello World'
}
}
}获取文件的大小
如果要获取文件的大小,可以使用文件类的length属性来获取
class Example {
static void main(String[] args) {
File file = new File("E:/Example.txt")
println "The file ${file.absolutePath} has ${file.length()} bytes"
}
}测试文件是否是目录
如果要查看路径是文件还是目录,可以使用File类的isFile和isDirectory选项
class Example {
static void main(String[] args) {
def file = new File('E:/')
println "File? ${file.isFile()}"
println "Directory? ${file.isDirectory()}"
}
}创建目录
如果要创建一个新目录,可以使用File类的mkdir函数。
class Example {
static void main(String[] args) {
def file = new File('E:/Directory')
file.mkdir()
}
}删除文件
如果要删除文件,可以使用File类的delete功能。
class Example {
static void main(String[] args) {
def file = new File('E:/Example.txt')
file.delete()
}
}复制文件
Groovy还提供将内容从一个文件复制到另一个文件的功能
class Example {
static void main(String[] args) {
def src = new File("E:/Example.txt")
def dst = new File("E:/Example1.txt")
dst << src.text
}
}获取目录内容
Groovy还提供了列出驱动器中的驱动器和文件的功能。
class Example {
static void main(String[] args) {
def rootFiles = new File("test").listRoots()
rootFiles.each {
file -> println file.absolutePath
}
}
}使用File类的eachFile函数列出特定目录中的文件。
class Example {
static void main(String[] args) {
new File("E:/Temp").eachFile() {
file->println file.getAbsolutePath()
}
}
}递归显示目录及其子目录中的所有文件,则可以使用File类的eachFileRecurse函数
class Example {
static void main(String[] args) {
new File("E:/temp").eachFileRecurse() {
file -> println file.getAbsolutePath()
}
}
} 特征
特征是语言的结构构造,允许 -
- 行为的组成。
- 接口的运行时实现。
- 与静态类型检查/编译的兼容性
它们可以被看作是承载默认实现和状态的接口。使用trait关键字定义 trait
可以使用 implement 关键字以类似于接口的方式实现 trait。
class Example {
static void main(String[] args) {
Student st = new Student();
st.StudentID = 1;
st.Marks1 = 10;
println(st.DisplayMarks());
}
}
trait Marks {
void DisplayMarks() {
println("Display Marks");
}
}
class Student implements Marks {
int StudentID
int Marks1;
}实现接口
Traits 可以实现接口,在这种情况下,使用 interface 关键字声明接口。
定义(interface)一个接口,
trait定义的Marks特征实现(继承)了Total接口,
Student类再继承Marks特征,拓展这个特征
实现类完成功能实现
class Example {
static void main(String[] args) {
Student st = new Student();
st.StudentID = 1;
st.Marks1 = 10;
println(st.DisplayMarks());
println(st.DisplayTotal());
}
}
interface Total {
void DisplayTotal()
}
trait Marks implements Total {
void DisplayMarks() {
println("Display Marks");
}
void DisplayTotal() {
println("Display Total");
}
}
class Student implements Marks {
int StudentID
int Marks1;
} 属性
特征可以定义属性。下面给出了具有属性的trait的示例。
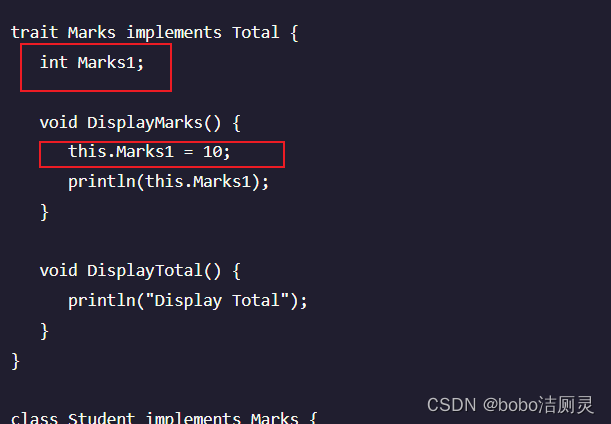
行为的构成
特征可以用于以受控的方式实现多重继承

扩展特征
特征可能扩展另一个特征,在这种情况下,必须使用extends关键字

Groovy闭包
闭包closure是一个短的匿名代码块。它通常跨越几行代码。一个方法甚至可以将代码块作为参数。它们是匿名的。
class Example {
static void main(String[] args) {
def clos = {println "Hello World"};
clos.call();
}
}代码行 - {println“Hello World”}被称为闭包。此标识符引用的代码块可以使用call语句执行。
执行后,输出Hello World
闭包也可以包含形式参数,以使它们更有用,就像Groovy中的方法一样。
class Example {
static void main(String[] args) {
def clos = {param->println "Hello ${param}"};
clos.call("World");
}
}使用$ {param},这导致closure接受一个参数。当通过clos.call语句调用闭包时,我们现在可以选择将一个参数传递给闭包。
运行后,输出Hello world
class Example {
static void main(String[] args) {
def clos = {println "Hello ${it}"}; //隐式单个参数
clos.call("World");
}
}包可以在定义闭包时引用变量。下面定义了一个str1变量,并在clos中引用
class Example {
static void main(String[] args) {
def str1 = "Hello";
def clos = {param -> println "${str1} ${param}"}
clos.call("World");
// We are now changing the value of the String str1 which is referenced in the closure
str1 = "Welcome";
clos.call("World");
}
}在方法中使用闭包
闭包也可以用作方法的参数。在Groovy中,很多用于数据类型(例如列表和集合)的内置方法都有闭包作为参数类型。
class Example {
//静态方法Display,以一个闭包为参数
def static Display(clo) {
// This time the $param parameter gets replaced by the string "Inner"
clo.call("Inner");
}
static void main(String[] args) {
def str1 = "Hello";
def clos = { param -> println "${str1} ${param}" }
clos.call("World");
// We are now changing the value of the String str1 which is referenced in the closure
str1 = "Welcome";
clos.call("World");
将定义的闭包作为参数传递到Dispaly方法中
// Passing our closure to a method
Example.Display(clos);
}
}边栏推荐
猜你喜欢

【Unity入门计划】制作RubyAdventure02-处理瓦片地图&碰撞
Create a 2D array

Iptables防火墙iprange模块扩展匹配规则

如何使用 Eolink 实现 API 文档自动生成

【kali-权限提升】(4.2.5)社会工程学工具包:PowerShell攻击向量(防报毒)

【服务器数据恢复】Ext4文件系统fsck后mount不上并报错的数据修复案例
带你玩转“超大杯”ECS特性及实验踩坑【华为云至简致远】

Elegantly detect and update web applications in real time

Introduction to Power BI

LED显示屏在会议室如何应用
随机推荐
【Unity入门计划】用双血条方法控制伤害区域减血速度
Redis RDB分析系统
瑞吉外卖学习笔记3
Share these new Blender plugins that designers must not miss in 2022
想要精准营销,从学习搭建一套对的标签体系开始丨 DTVision 分析洞察篇
pytorch安装过程中出现torch.cuda.isavailable()=False问题
Introduction to Recurrent Neural Network (RNN)
干货:从零设计高并发架构
Jingdong T9 pure hand type 688 pages of god notes, SSM framework integrates Redis to build efficient Internet applications
幂等性~~
【Unity入门计划】Unity实例-C#如何通过封装实现对数据成员的保护
C#/VB.NET 将PDF转为PDF/X-1a:2001
国泰君安证券新手开户、有安全保障吗?
codeforces 444C DZY Loves Colors
从洞察到决策,一文解读标签画像体系建设方法论丨DTVision分析洞察篇
Install Update(Patches) on ESXi
Elegantly detect and update web applications in real time
C#/VB.NET convert PDF to PDF/X-1a:2001
把酒言欢话聊天,基于Vue3.0+Tornado6.1+Redis发布订阅(pubsub)模式打造异步非阻塞(aioredis)实时(websocket)通信聊天系统
小实验:实现一个用于计算(包括加减乘除)的小程序