当前位置:网站首页>Shengxin experiment record (part2)--tf.reduce_sum() usage introduction
Shengxin experiment record (part2)--tf.reduce_sum() usage introduction
2022-08-11 01:40:00 【GoatGui】
学习笔记,仅供参考,有错必纠
参考自:tf.reduce_sum()用法介绍
前言
I came across this function while reproducing…emmm… Speaking of which, I really know very little about deep learning.
方法定义
tf.reduce_sum()The role of is to calculate the sum of the elements in the tensor in a certain way.
tf.reduce_sum(
input_tensor,
axis=None,
keepdims=None,
name=None)
参数解释:
input_tensoris the tensor to be processed.
axisSpecifies which dimension to sum by,All elements are added by default.
keepdimsIndicates that the dimensions of the original tensor are not maintained,默认为False,若为TrueThe original tensor dimensions are maintained, .
nameUsed to define the operation name.
示例
有形如(2,3,4)的三维张量:
import tensorflow as tf
a = tf.constant([[[1, 2, 3, 4],
[5, 6, 7, 8],
[9, 10, 9, 8]],
[[7, 6, 5, 4],
[3, 2, 1, 0],
[1, 2, 3, 4]]])
print(a.shape)
# (2, 3, 4)
分别设置axis为0,1,2The result of performing the addition is as follows:
b = tf.reduce_sum(a, axis = 0)
c = tf.reduce_sum(a, axis = 1)
d = tf.reduce_sum(a, axis = 2)
sess = tf.InteractiveSession()
b
b.eval()
<tf.Tensor 'Sum_18:0' shape=(3, 4) dtype=int32>
array([[ 8, 8, 8, 8],
[ 8, 8, 8, 8],
[10, 12, 12, 12]])
c
c.eval()
<tf.Tensor 'Sum_19:0' shape=(2, 4) dtype=int32>
array([[15, 18, 19, 20],
[11, 10, 9, 8]])
d
d.eval()
<tf.Tensor 'Sum_20:0' shape=(2, 3) dtype=int32>
array([[10, 26, 36],
[22, 6, 10]])
可以看到,The original tensor is three-dimensional,指定axis进行一次tf.reduce_sum()Then it becomes a two-dimensional tensor. 如果设置keepdims=True,则结果如下,It can be seen that the tensor after calculating the sum is still three-dimensional,其中指定axisThe number of elements in that dimension is 1,The other dimensions remain unchanged.
b = tf.reduce_sum(a, axis = 0, keepdims=True)
c = tf.reduce_sum(a, axis = 1, keepdims=True)
d = tf.reduce_sum(a, axis = 2, keepdims=True)
b
b.eval()
<tf.Tensor 'Sum_24:0' shape=(1, 3, 4) dtype=int32>
array([[[ 8, 8, 8, 8],
[ 8, 8, 8, 8],
[10, 12, 12, 12]]])
c
c.eval()
<tf.Tensor 'Sum_25:0' shape=(2, 1, 4) dtype=int32>
array([[[15, 18, 19, 20]],
[[11, 10, 9, 8]]])
d
d.eval()
<tf.Tensor 'Sum_26:0' shape=(2, 3, 1) dtype=int32>
array([[[10],
[26],
[36]],
[[22],
[ 6],
[10]]])
sess.close()
边栏推荐
- 成功解决raise TypeError(‘Unexpected feature_names type‘)TypeError: Unexpected feature_names type
- #yyds干货盘点#【愚公系列】2022年08月 Go教学课程 008-数据类型之整型
- Update chromedriver driver programming skills │ selenium
- 导入数据包上传宝贝提示“类目不能为空”是什么原因,怎么解决?
- WinForm (5) control and its members
- Deep Learning【第二章】
- 安装dlib库
- 22/8/9 贪心问题合集
- 二维数组实战项目--------《扫雷游戏》
- apache+PHP+MySQL+word press,安装word press时页面报错?
猜你喜欢

络达开发---自定义BLE服务(二):功能实现
Pico 4更多参数曝光:Pancake+彩色透视,还有Pro版本
![[21 Days Learning Challenge] Half Insertion Sort](/img/30/4971479a2fa08592e88f032bb23844.png)
[21 Days Learning Challenge] Half Insertion Sort
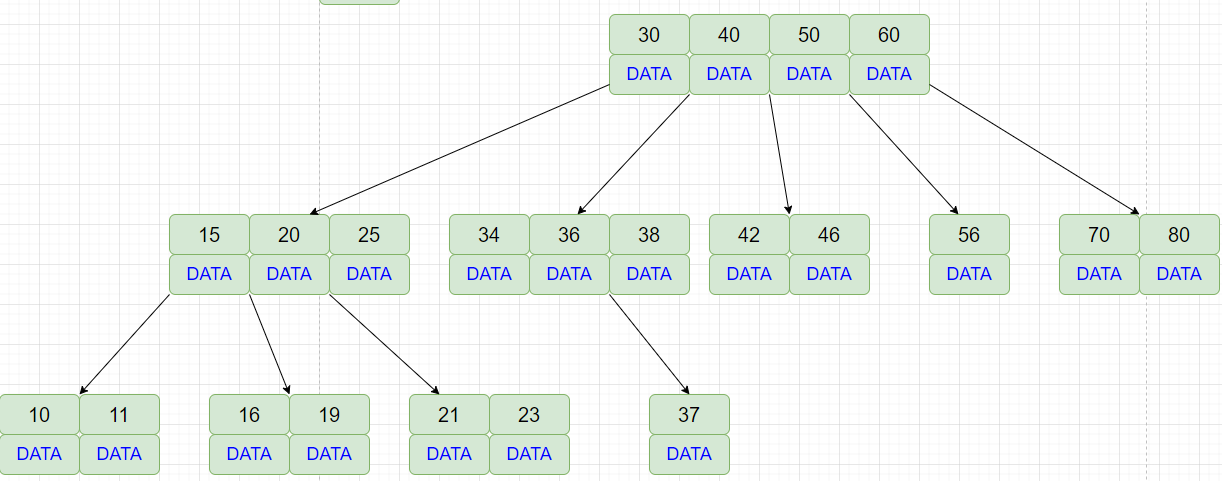
MySQL索引与事务

22-7-31
![[ASM] The relationship between the role of the bytecode operation ClassWriter COMPUTE_FRAMES and visitMaxs](/img/28/66370d46ebeb1e16b56ea2a36fe100.jpg)
[ASM] The relationship between the role of the bytecode operation ClassWriter COMPUTE_FRAMES and visitMaxs

两日总结九
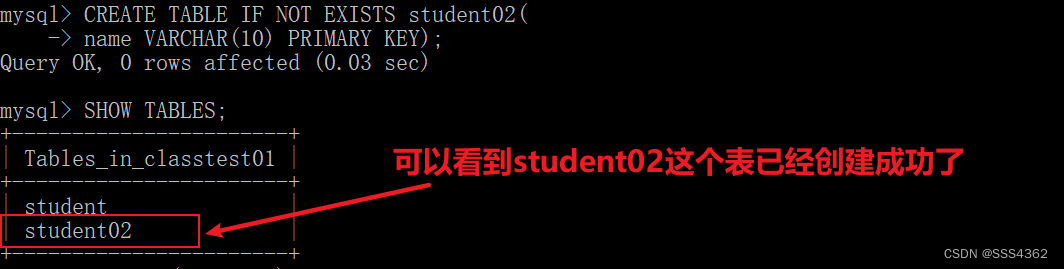
使用mysql语句操作数据表(table)
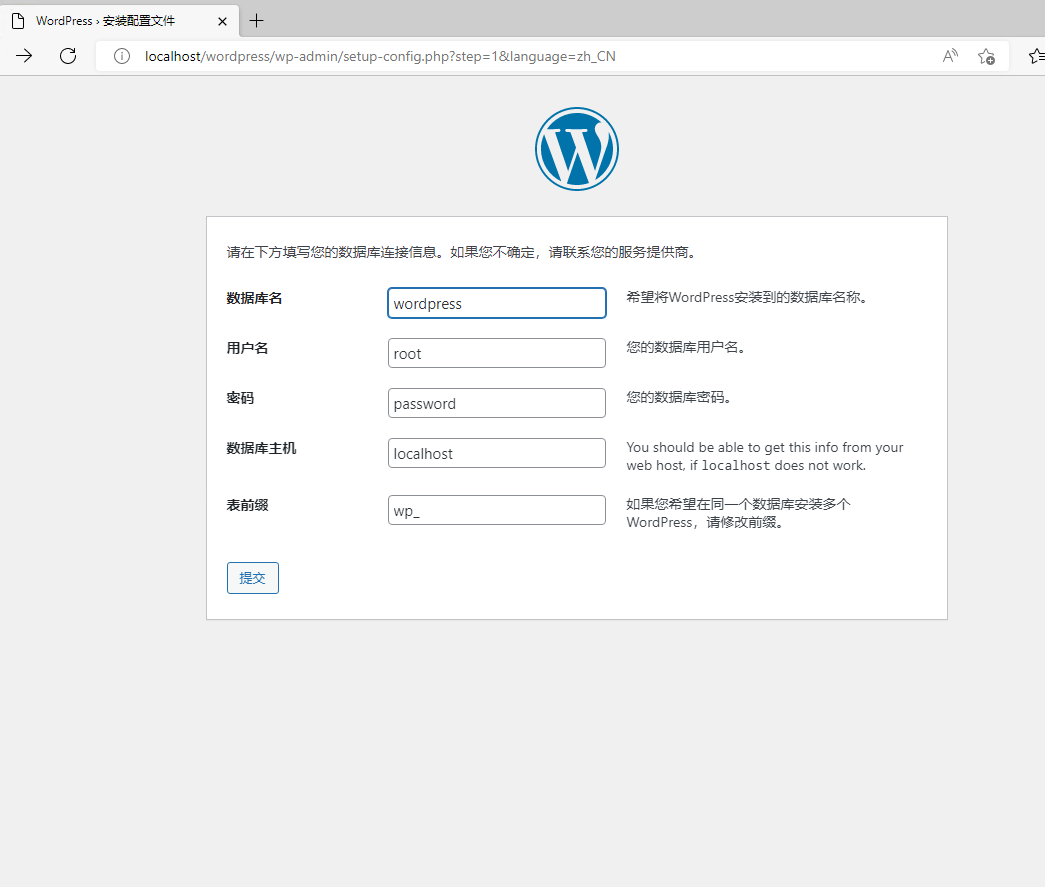
apache+PHP+MySQL+word press,安装word press时页面报错?

嵌入式软件打log的一些心得
随机推荐
FPGA学习专栏-串口通信(xinlinx)
Data Filters in ABP
SystemVerilog: 验证知识点点滴滴
Apache Commons Configuration Remote Code Execution Vulnerability (CVE-2022-33980) Analysis & Reproduction
数据库数据采集利器FlinkCDC
两日总结十一
异常:try catch finally throws throw
QT+VTK+PCL拟合圆柱并计算起始点、中止点
联盛德W801系列6-从微信小程序的角度来分析W801的蓝牙通信源码(indicate方式)
Linux install redis database
C#使用计时器
Ambari迁移Spark2到其它机器(图文教程)
颠覆性创新招商,链动2+1是个怎么样的制度模式?
Apache Commons Configuration远程代码执行漏洞(CVE-2022-33980)分析&复现
sed of the Three Musketeers of Shell Programming
联盛德W801系列5-微信小程序与W801蓝牙通信例程(阅读笔记)
Mysql数据库安装配置详细教程
【iframe父页面调用子页面的方法】踩坑:获取元素的时候需要用 `[x]`是关键,不能用`.eq(x)`否则获取不到。
Dual machine thermal for comprehensive experiment (VRRP + OSPF + + NAT + DHCP + VTP PVSTP + single-arm routing)
Two-dimensional array combat project -------- "Minesweeper Game"