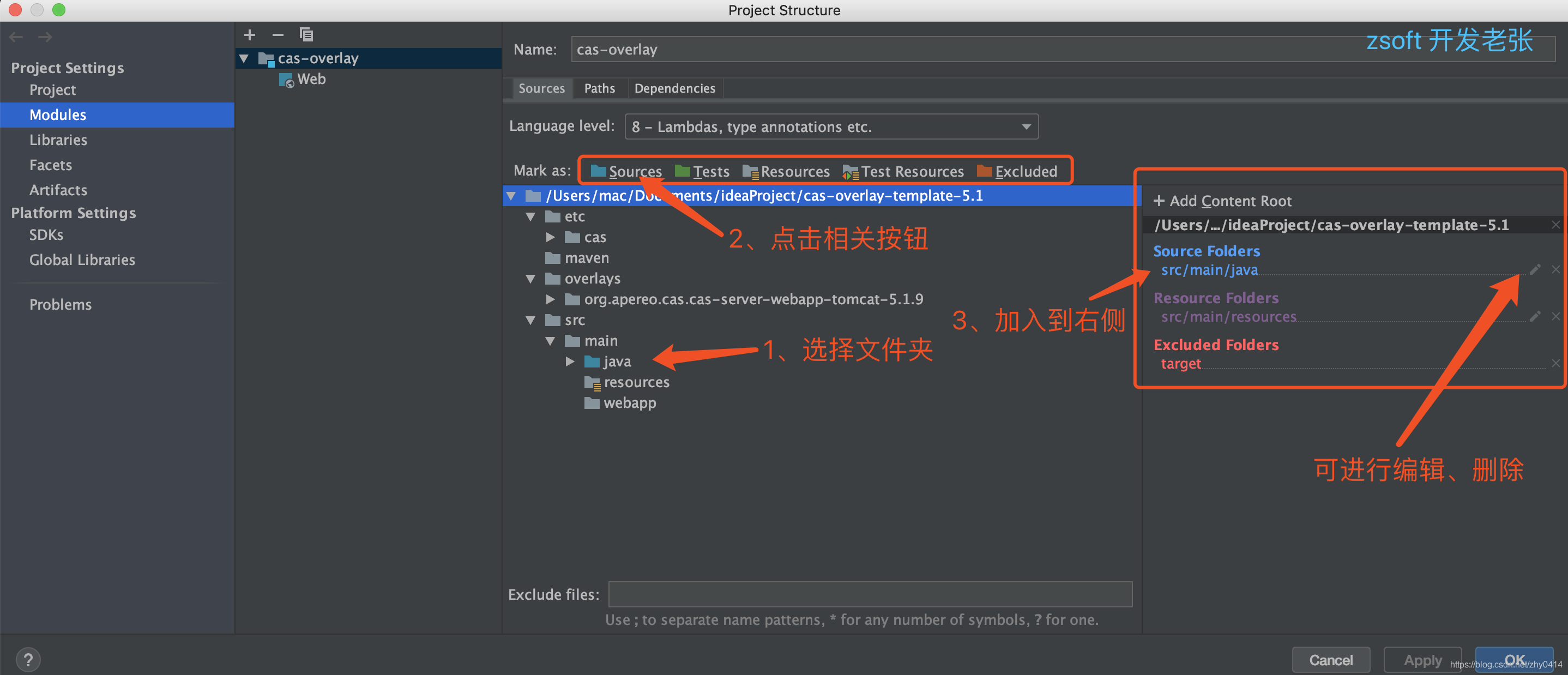
当前位置:网站首页>链表API设计
链表API设计
2022-08-10 05:32:00 【cbys-1357】
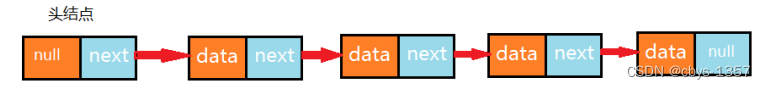
public class LinkList<T> implements Iterable<T>{
private Node head;
private int N;
// 结点类(内部类)
private class Node{
// 储存数据
T item;
// 下一个结点
Node next;
public Node(T item,Node next) {
this.item=item;
this.next=next;
}
}
// 构造方法
public LinkList(){
this.head=new Node(null,null);
this.N=0;
}
// 清空链表
public void clear() {
head.next=null;
this.N=0;
}
// 判断链表是否为空
public boolean isEmpty() {
return N==0;
}
// 获取链表的长度
public int length() {
return N;
}
// 获取指定位置i的元素
public T get(int i) {
Node n=head.next;
for(int index=0;index<i;index++) {
n=n.next;
}
return n.item;
}
// 向链表中添加元素
public void insert(T t) {
Node n=this.head;
// 获取链表中最后一个节点
while(n.next!=null) {
n=n.next;
}
Node newNode=new Node(t,null);
n.next=newNode;
N++;
}
// 向链表中指定位置添加元素
public void insert(int i,T t) {
Node pre=this.head;
//找到i位置的前一个节点
for(int index=0;index<i;index++) {
pre=pre.next;
}
// 找到i位置的节点
Node curr=pre.next;
// 创建新节点
Node newNode=new Node(t,curr);
pre.next=newNode;
N++;
}
// 删除指定位置的元素,并返回元素的值
public T remove(int i) {
Node pre=this.head;
for(int index=0;index<i;index++) {
pre=pre.next;
}
Node curr=pre.next;
Node nextNode=curr.next;
pre.next=nextNode;
N--;
return curr.item;
}
// 返回元素t在链表中第一次出现的位置
public int index(T t) {
Node node=this.head;
for(int i=0;node.next!=null;i++) {
node=node.next;
if(node.item==t) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
@Override
public Iterator<T> iterator() {
return new LIterator();
}
private class LIterator implements Iterator{
private Node n;
public LIterator(){
this.n=head;
}
@Override
public boolean hasNext() {
return n.next!=null;
}
@Override
public Object next() {
n=n.next;
return n.item;
}
}
// 整个链表反转
public void reverse() {
if(isEmpty()) {
return;
}
reverse(head.next);
}
// 单个节点之间顺序反转
public Node reverse(Node curr) {
if(curr.next==null) {
head.next=curr;
return curr;
}
Node pre=reverse(curr.next);
pre.next=curr;
curr.next=null;
return curr;
}
}
2.双向链表
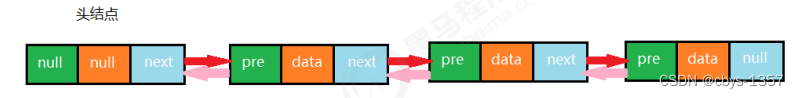
public class TowWayList<T> implements Iterable<T>{
private Node head;//首结点
private Node last;//最后一个结点
private int N;
public class Node {
private T item;//储存数据
private Node next;//下一个结点
private Node pre;//上一个结点
public Node(T t,Node pre,Node next) {
this.item=t;
this.next=next;
this.pre=pre;
}
}
// 构造方法
public TowWayList() {
this.head=new Node(null,null,null);
this.last=null;
this.N=0;
}
// 清空链表
public void clear() {
this.head.next=null;
this.head.item=null;
this.head=null;
this.N=0;
}
// 判断链表是否为空
public boolean isEmpty() {
return N==0;
}
// 返回链表的长度
public int length() {
return N;
}
// 获取链表中指定位置的元素
public T get(int i) {
Node n=head.next;
for(int index=0;index<i;index++) {
n=n.next;
}
return n.item;
}
// 向链表的末尾处添加元素
public void insert(T t) {
if(isEmpty()) {
Node newNode=new Node(t,head,null);
last=newNode;
head.next=last;
}else {
Node oldLast=last;
Node newNode=new Node(t,oldLast,null);
oldLast.next=newNode;
last=newNode;
}
N++;
}
// 向链表指定位置i处添加元素
public void insert(int i,T t) {
Node pre=head;
for(int index=0;index<i;i++) {
pre=pre.next;
}
Node curr=pre.next;
Node newNode=new Node(t,pre,curr);
pre.next=newNode;
N++;
}
// 删除链表指定位置i处的元素,并返回指定位置的元素值
public T remove(int i) {
Node pre=head;
for(int index=0;index<i;index++) {
pre=pre.next;
}
Node curr=pre.next;
Node nextNode=curr.next;
pre.next=nextNode;
return curr.item;
}
// 返回元素t在链表中第一次出现的位置
public int indexOf(T t) {
Node n=head;
for(int i=0;n.next!=null;i++) {
n=n.next;
if(n.item.equals(t)) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
// 获取第一个元素
public T getFirst() {
if(isEmpty()) {
return null;
}
return head.next.item;
}
// 获取最后一个元素
public T getLast() {
if(isEmpty()) {
return null;
}
return last.item;
}
@Override
public Iterator<T> iterator() {
return new TIterator();
}
private class TIterator implements Iterator<T>{
private Node n;
public TIterator() {
this.n=head;
}
@Override
public boolean hasNext() {
return n.next!=null;
}
@Override
// 正向遍历
public T next() {
n=n.next;
return n.item;
}
}
}
3.应用
1.快慢指针
1.中间值问题
原理:
代码实现:
public class FastSlowTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Node<String> first=new Node<String>("aa",null);
Node<String> second=new Node<String>("bb",null);
Node<String> third=new Node<String>("cc",null);
Node<String> forth=new Node<String>("dd",null);
Node<String> fifth=new Node<String>("ee",null);
Node<String> six=new Node<String>("ff",null);
Node<String> seven=new Node<String>("gg",null);
first.next=second;
second.next=third;
third.next=forth;
forth.next=fifth;
fifth.next=six;
six.next=seven;
String mid=getMid(first);
System.out.println("中间值:"+mid);
}
private static boolean isCircle(Node<String> first) {
Node<String> fast=first;
Node<String> Slow=first;
while(fast!=null&&fast.next!=null) {
fast=fast.next.next;
Slow=Slow.next;
if(fast.equals(Slow)) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
private static String getMid(Node<String> first) {
Node<String> fast=first;//快指针
Node<String> Slow=first;//慢指针
while(fast!=null&&fast.next!=null) {
fast=fast.next.next;
Slow=Slow.next;
}
return Slow.item;
}
private static class Node<T>{
T item;
Node next;
public Node(T item,Node next) {
this.item=item;
this.next=next;
}
}
}2.单向链表是否有环问题
原理:
代码实现:
public class FastSlowTest02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Node<String> first=new Node<String>("aa",null);
Node<String> second=new Node<String>("bb",null);
Node<String> third=new Node<String>("cc",null);
Node<String> forth=new Node<String>("dd",null);
Node<String> fifth=new Node<String>("ee",null);
Node<String> six=new Node<String>("ff",null);
Node<String> seven=new Node<String>("gg",null);
first.next=second;
second.next=third;
third.next=forth;
forth.next=fifth;
fifth.next=six;
six.next=seven;
// 产生环
seven.next=third;
//判断链表是否有环
boolean circle=isCircle(first);
System.out.println("first的链表是否有环:"+circle);
}
private static boolean isCircle(Node<String> first) {
Node<String> fast=first;
Node<String> Slow=first;
while(fast!=null&&fast.next!=null) {
fast=fast.next.next;
Slow=Slow.next;
if(fast.equals(Slow)) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
private static String getMid(Node<String> first) {
Node<String> fast=first;//快指针
Node<String> Slow=first;//慢指针
while(fast!=null&&fast.next!=null) {
fast=fast.next.next;
Slow=Slow.next;
}
return Slow.item;
}
//内部类
private static class Node<T>{
T item;
Node next;
public Node(T item,Node next) {
this.item=item;
this.next=next;
}
}
}
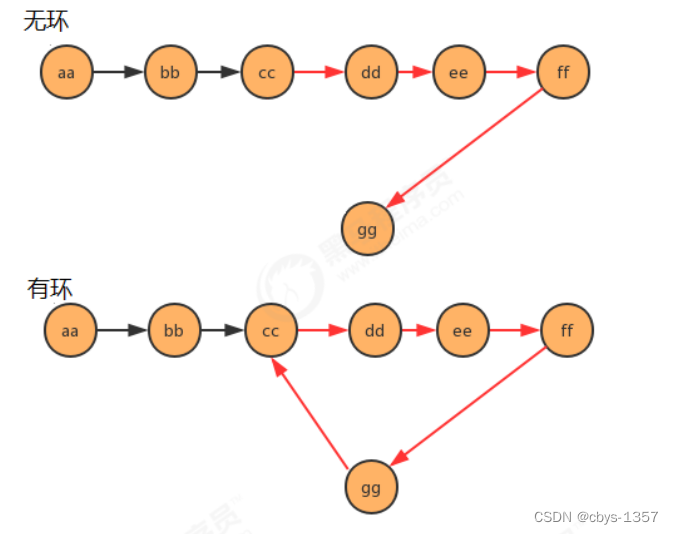
3.有环链表入口问题
原理:
public class CircleListInTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO 自动生成的方法存根
// 构建节点
Node<String> first=new Node<String>("aa",null);
Node<String> second=new Node<String>("bb",null);
Node<String> third=new Node<String>("cc",null);
Node<String> forth=new Node<String>("dd",null);
Node<String> fifth=new Node<String>("ee",null);
Node<String> six=new Node<String>("ff",null);
Node<String> seven=new Node<String>("gg",null);
// 构建链表
first.next=second;
second.next=third;
third.next=forth;
forth.next=fifth;
fifth.next=six;
six.next=seven;
// 产生环
seven.next=third;
// 判断链表是否有环
if(isCircle(first)) {
Node<String> entrance=getEntrance(first);
System.out.println("first链表环的入口节点元素:"+entrance.item);
}else {
System.out.println("该链表未形成环");
}
}
private static Node<String> getEntrance(Node<String> first) {
Node<String> fast=first;
Node<String> slow=first;
Node<String> tem=null;
// 遍历节点,先找到环(快慢指针相遇),准备临时指针,指向链表的首节点,继续遍历,直至那个慢指针和临时指针相遇,那个相遇的地方就是环的入口节点(要用数论来证明)
while(fast!=null&&fast.next!=null) {
fast=fast.next.next;
slow=slow.next;
if(fast.equals(slow)) {
tem=first;
continue;
}
if(tem!=null) {
tem=tem.next;
if(tem.equals(slow)) {
break;
}
}
}
return tem;
}
private static boolean isCircle(Node<String> first) {
// TODO 自动生成的方法存根
Node<String> fast=first;
Node<String> Slow=first;
while(fast!=null&&fast.next!=null) {
fast=fast.next.next;
Slow=Slow.next;
if(fast.equals(Slow)) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
private static class Node<T>{
T item;
Node next;
public Node(T item,Node next) {
this.item=item;
this.next=next;
}
}
}
代码实现:
public class JosephTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO 自动生成的方法存根
// 第一个结点(元素)
Node<Integer> first=null;
// 记录前一个结点
Node<Integer> pre=null;
// 1.构建循环链表
for(int i=1;i<=41;i++) {
if(i==1) {
first=new Node(i,null);
pre=first;
continue;
}
Node<Integer> newNode=new Node(i,null);
pre.next=newNode;
pre=newNode;
if(i==41) {
pre.next=first;//构建循环链表,让最后一个结点指向第一个结点
}
}
int count=0;
Node<Integer> n=first;
Node<Integer> before=null;
while(n!=n.next) {
count++;//4.判断count的值,如果是3,则从链表中删除这个结点并打印结点的值,把count重置为0;
if(count==3) {
// 删除当前结点
before.next=n.next;
System.out.print(n.item+",");
count=0;
n=n.next;
}else {
before=n;
n=n.next;
}
}
System.out.print(n.item);//打印剩余的最后那个人
}
private static class Node<T> {
T item;
Node next;
public Node(T item,Node next) {
this.item=item;
this.next=next;
}
}
}
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
定时器(setInterval)的开启与关闭
Operation table Function usage
文章复现:超分辨率网络-VDSR
Link reading good article: What is the difference between hot encrypted storage and cold encrypted storage?
The latest and most complete digital collection sales calendar-07.26
sqlplus displays the previous command and the available backspace key
视图【】【】【】【】
Small program wx.request simple Promise package
redis集群模式
先人一步,不再错过,链读APP即将上线!
Bifrost micro synchronous database implementation services across the library data synchronization
IDEA连接MySQL数据库并执行SQL查询操作
Mini Program Study Notes: Communication between Mini Program Components
cesium 添加点,移动点
R中设置图形参数--函数par()详解
The submenu of the el-cascader cascade selector is double-clicked to display the selected content
第二次实验
用Pytorch从0到1实现逻辑回归
Decentralized and p2p networks and traditional communications with centralization at the core
毫米波雷达数据集Scorp使用