当前位置:网站首页>刷题《剑指Offer》day12
刷题《剑指Offer》day12
2022-08-08 10:57:00 【吃豆人编程】
题目来源:力扣《剑指Offer》第二版
完成时间:2022/08/07
文章目录
30. 包含min函数的栈

题目链接:剑指 Offer 30. 包含min函数的栈 - 力扣(LeetCode)
我的题解
我的题解和书上的一样,用一个辅助栈。出栈的时候,两个栈同时出栈。入栈的时候,判断一下,如果入栈元素小于等于辅助栈栈顶元素,则直接入栈,如果大于则辅助栈的栈顶元素再入栈一次。这样可以保持辅助栈栈顶的元素最小。
class MinStack {
public:
/** initialize your data structure here. */
stack<int> min_stack;
stack<int> data_stack;
MinStack() {
}
void push(int x) {
if(min_stack.empty() || x < min_stack.top()){
min_stack.push(x);
}else {
min_stack.push(min_stack.top());
}
data_stack.push(x);
}
void pop() {
if(!data_stack.empty()){
min_stack.pop();
data_stack.pop();
}
}
int top() {
return data_stack.top();
}
int min() {
return min_stack.top();
}
};
/** * Your MinStack object will be instantiated and called as such: * MinStack* obj = new MinStack(); * obj->push(x); * obj->pop(); * int param_3 = obj->top(); * int param_4 = obj->min(); */
31. 栈的压入、弹出序列

题目链接:剑指 Offer 31. 栈的压入、弹出序列 - 力扣(LeetCode)
我的题解1
这道题我一开始稀里糊涂的,没考虑清楚直接就写了,然后居然也过了。思路就是先匹配入栈序列,入栈序列完事后,如果出栈序列还没完事,再检查出栈序列。
class Solution {
public:
bool validateStackSequences(vector<int>& pushed, vector<int>& popped) {
int index_push = 0, index_pop = 0;
stack<int> stack1;
while(index_push != pushed.size()){
if(stack1.empty()){
stack1.push(pushed[index_push]);
index_push++;
}
if(stack1.top() == popped[index_pop]){
stack1.pop();
index_pop++;
}else if(index_push != pushed.size()){
stack1.push(pushed[index_push]);
index_push++;
}else {
return false;
}
}
while(index_pop != popped.size()){
if(stack1.top() == popped[index_pop]){
stack1.pop();
index_pop++;
}else {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
};
我的题解2
后来我发现如果在第一次循环中没有清空栈的话,必定是不符合要求的。精简了一下,代码如下:
class Solution {
public:
bool validateStackSequences(vector<int>& pushed, vector<int>& popped) {
int index_push = 0, index_pop = 0;
stack<int> stack1;
while(true){
while(!stack1.empty() && stack1.top() == popped[index_pop]){
stack1.pop();
index_pop++;
}
if(index_push != pushed.size()){
stack1.push(pushed[index_push]);
index_push++;
}else {
break;
}
}
return stack1.empty();
}
};
我的题解3
好吧。。看了评论区大佬的题解,发现还可以进一步精简
class Solution {
public:
bool validateStackSequences(vector<int>& pushed, vector<int>& popped) {
int index = 0;
stack<int> stack1;
for(int i = 0;i < pushed.size();i++) {
stack1.push(pushed[i]);
while(!stack1.empty() && stack1.top() == popped[index]){
stack1.pop();
index++;
}
}
return stack1.empty();
}
};
leetcode 这个提交是真的迷

32 - I. 从上到下打印二叉树
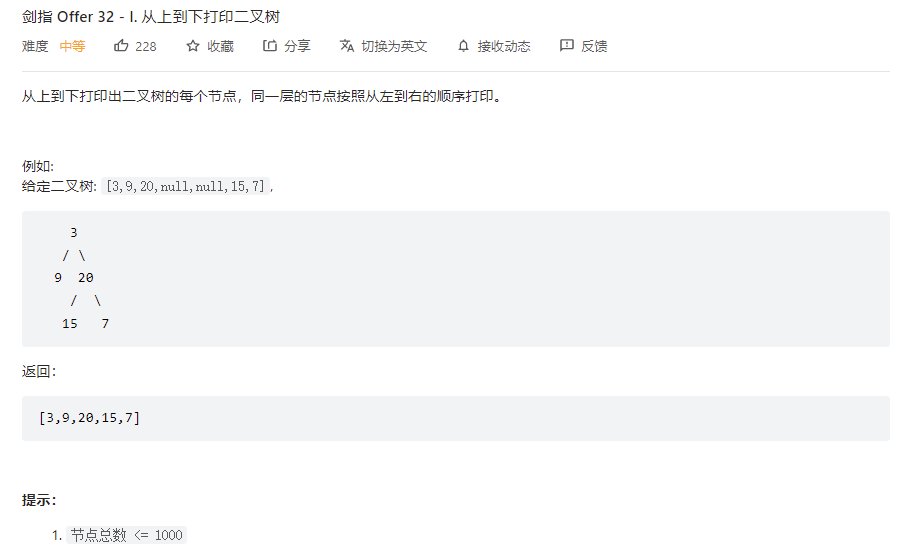
题目链接:剑指 Offer 32 - I. 从上到下打印二叉树 - 力扣(LeetCode)
我的题解
模板题,队列套就完事了
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {} * }; */
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> levelOrder(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> result;
if(root == nullptr) return result;
queue<TreeNode*> que;
que.push(root);
while(!que.empty()) {
TreeNode* tmp = que.front();
que.pop();
if(tmp->left) que.push(tmp->left);
if(tmp->right) que.push(tmp->right);
result.push_back(tmp->val);
}
return result;
}
};
32 - II. 从上到下打印二叉树 II

题目链接:剑指 Offer 32 - II. 从上到下打印二叉树 II - 力扣(LeetCode)
我的题解
这题也非常简单,直接在上题的基础上改就行了,在每次while循环中加入对当前队列元素个数的判断,即可得出某一层的节点熟练,遍历一遍即可。
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {} * }; */
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(TreeNode* root) {
vector<vector<int>> result;
if(root == nullptr) return result;
queue<TreeNode*> que;
que.push(root);
while(!que.empty()) {
int size = que.size();
vector<int> res;
for(int i = 0;i < size;i++) {
TreeNode* tmp = que.front();
que.pop();
if(tmp->left) que.push(tmp->left);
if(tmp->right) que.push(tmp->right);
res.push_back(tmp->val);
}
result.push_back(res);
}
return result;
}
};
32 - III. 从上到下打印二叉树 III

题目链接:剑指 Offer 32 - III. 从上到下打印二叉树 III - 力扣(LeetCode)
我的题解
这题也比较简单,上一题基础上加个count计数,如果是偶数,就把元素插入到vector的头部。
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {} * }; */
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(TreeNode* root) {
vector<vector<int>> result;
if(root == nullptr) return result;
int count = 1;
queue<TreeNode*> que;
que.push(root);
while(!que.empty()) {
int size = que.size();
vector<int> res;
for(int i = 0;i < size;i++) {
TreeNode* tmp = que.front();
que.pop();
if(tmp->left) que.push(tmp->left);
if(tmp->right) que.push(tmp->right);
if(count % 2 == 1) {
//res.push_front(tmp->val);
res.push_back(tmp->val);
}else {
res.insert(res.begin(),tmp->val);
}
}
result.push_back(res);
count++;
}
return result;
}
};
//res.push_front(tmp->val);
res.push_back(tmp->val);
}else {
res.insert(res.begin(),tmp->val);
}
}
result.push_back(res);
count++;
}
return result;
}
};
边栏推荐
- 苹果开发者账号申请流程完整版
- d切片示例
- Kubernetes资源编排系列之四: CRD+Operator篇
- CentOS MySQL体系管理
- 3 million tenders!Qingdao Medical Security Bureau host database middleware operation and maintenance service project
- Redis是持久化键值数据库嘛?
- .net开发中,C# DateTime.Now 取出的时间含有星期解决办法
- PG核心篇--物理存储结构
- One article to understand configuration management (CM)
- ReentrantLock源码分析和使用案例
猜你喜欢

Kubernetes资源编排系列之四: CRD+Operator篇
机器学习(十六)推荐系统

NLP和CV中的Local和Global建模

Postman使用简单演示
day02 -DOM—高级事件(注册事件、事件监听、删除事件、DOM事件流、事件对象、阻止默认行为、阻止事件冒泡、事件委托)—常用鼠标事件—常用的键盘事件
C语言详解系列——指针与结构体

#yyds干货盘点#【愚公系列】2022年08月 Go教学课程 005-变量

3 million tenders!Qingdao Medical Security Bureau host database middleware operation and maintenance service project

模式识别 学习笔记:第七章 特征选择

微服务分库分表
随机推荐
SCCM2012R2管理之版本更新
shell 创建LVM逻辑据卷
详细讲解修改allure报告自定义的logo和名称中文
基于ftp协议的上传与下载
便利贴--48{再次,适配屏幕宽高class}
关于mysql联合索引的最左前缀原则以及b+tree
C语言详解系列——指针与结构体
ssh 安全 之 密钥登录
(kali - elevated privileges 】 【 4.2.4) social engineering toolkit: remote control trojans use, set up and use
列存储数据库是什么呢?
Mysql的分布式事务原理理解
皕杰报表之数据校验与处理
MongoDB是什么,怎么用?
一起学习集合框架之 TreeSet
3D激光SLAM:LIO-SAM整体介绍与安装编译
持久化键值数据库的数据是保存在内存中吗?
使用C# 调用api接口获取法定节假日(百度api)
文档数据库是用来干什么的呢?
Machine learning model too slow?Look at Intel (R) extension to accelerate
有哪些典型的列存储数据库呢?