当前位置:网站首页>Openvx's immediate mode and graph mode and examples
Openvx's immediate mode and graph mode and examples
2022-04-22 21:08:00 【Banana Nicky】
OpenVX Of Immediate mode (immediate mode) And graph mode (graph mode)
openvx The execution model of is generally divided into Immediate mode and Graph pattern .
The direct mode is very simple , With vxu… The function at the beginning is similar to opencv, Accustomed to tradition opencv api Of , Can quickly experience openvx The function of , Call a function to get a result .
OpenCVX The real strength of is graph Pattern , He abstracts every function into a node, The function prototype is called kernel, One graph There can be more than one node, Friends who have learned about neural networks will know , This design structure is very consistent with the structure of neural network , every last layer Can be seen as a node, Although training a neural network is not openvx The function of , But in openvx Reasoning is one of its powerful functions . About openvx Description of neural network , Please refer to my previous article .
Immediate mode (immediate mode)
Sample explanation 1
Next, we will explain the application of immediate mode and graph mode in the form of code examples
The functions of the program are as follows :
- Create a OpenVX Context
- Create an image of a white rectangle on a black background
- Locate the corner in the image , Using non maximum suppression Fast Angle algorithm
vxuFastCorners() - Show results
To write openvx The first thing the program thinks of is to create a context. At the same time, think of release.
vx_context context = vxCreateContext();// establish
vxReleaseContext(&context); Release
The second thing is to think about how to verify the created context , To verify that the creation was successful . Generally speaking , We can call vxGetStatus() Function to test vx_reference Any type of return value .
void errorCheck(vx_context *context_p, vx_status status, const char *message)
{
if (status)
{
puts("ERROR! ");
puts(message);
vxReleaseContext(context_p);
exit(1);
}
}
errorCheck(&context, vxGetStatus((vx_reference)context), "Could notcreate a vx_context\n");
Then let's look at the next function , A graphic used to create a rectangular box on a black background , Used to do Fast Corner calculation .
vx_image makeInputImage(vx_context context)
{
// Create a 100*100 vx_image object
vx_image image = vxCreateImage(context, 100U, 100U, VX_DF_IMAGE_U8);
vx_rectangle_t rect = {
.start_x = 20, .start_y = 40, .end_x=80, .end_y = 60
};
if (VX_SUCCESS == vxGetStatus((vx_reference)image))
{
// obtain image Of ROI
vx_image roi = vxCreateImageFromROI(image, &rect);
vx_pixel_value_t pixel_white, pixel_black;
pixel_white.U8 = 255;
pixel_black.U8 = 0;
// Set up ROI Pixel value
if (VX_SUCCESS == vxGetStatus((vx_reference)roi) &&
VX_SUCCESS == vxSetImagePixelValues(image, &pixel_black) &&
VX_SUCCESS == vxSetImagePixelValues(roi, &pixel_white))
vxReleaseImage(&roi);
else
vxReleaseImage(&image);
}
return image;
}
We make a black background by filling all the images , Then by filling in a ROI( Areas of interest ) To make a white rectangle . When we finish ROI after , We release it , Because we don't need it anymore . Be careful , If we encounter an error when creating an image , We will not touch the image further or ROI, If we don't create ROI Or copy data , Then we will release the image and return a null pointer .
Calling Fast Before corner detection function , We also need other parameters
// Threshold for corner detection ( When the pixel value of the center point is greater than most of the surrounding pixels 16 Pixel value of a point , Then the pixel is considered to be a corner )
vx_float32 strength_thresh_value = 128.0;
vx_scalar strength_thresh = vxCreateScalar(context, VX_TYPE_FLOAT32,&strength_thresh_value);
// Save an array of coordinate points
vx_array corners = vxCreateArray(context, VX_TYPE_KEYPOINT, 100);
vx_array corners1 = vxCreateArray(context, VX_TYPE_KEYPOINT, 100);
vx_size num_corners_value = 0;
vx_scalar num_corners = vxCreateScalar(context, VX_TYPE_SIZE,
&num_corners_value);
vx_scalar num_corners1 = vxCreateScalar(context, VX_TYPE_SIZE,
&num_corners_value);
vx_keypoint_t *kp = calloc( 100, sizeof(vx_keypoint_t));
The last part is to perform the control of non maximum suppression and non maximum suppression Fast Focus detection , Then display the coordinates .
All the codes are as follows :
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <VX/vx.h>
#include <VX/vxu.h>
// Error detection function
void errorCheck(vx_context *context_p, vx_status status, const char *message)
{
if (status)
{
puts("ERROR! ");
puts(message);
vxReleaseContext(context_p);
exit(1);
}
}
// Image creation function
vx_image makeInputImage(vx_context context)
{
// Create a 100*100 Of image object
vx_image image = vxCreateImage(context, 100U, 100U, VX_DF_IMAGE_U8);
// coordinate
vx_rectangle_t rect = {
.start_x = 20, .start_y = 40, .end_x=80, .end_y = 60
};
if (VX_SUCCESS == vxGetStatus((vx_reference)image))
{
// Create a ROI Area
vx_image roi = vxCreateImageFromROI(image, &rect);
vx_pixel_value_t pixel_white, pixel_black;
pixel_white.U8 = 255;
pixel_black.U8 = 0;
// Pixel fill
if (VX_SUCCESS == vxGetStatus((vx_reference)roi) &&
VX_SUCCESS == vxSetImagePixelValues(image, &pixel_black) &&
VX_SUCCESS == vxSetImagePixelValues(roi, &pixel_white))
vxReleaseImage(&roi);
else
vxReleaseImage(&image);
}
return image;
}
int main(void)
{
// Create context
vx_context context = vxCreateContext();
errorCheck(&context, vxGetStatus((vx_reference)context), "Could not create a vx_context\n");
// Create test image
vx_image image1 = makeInputImage(context);
errorCheck(&context, vxGetStatus((vx_reference)image1), "Could not create image");
// Fast corner detection threshold
vx_float32 strength_thresh_value = 128.0;
vx_scalar strength_thresh = vxCreateScalar(context, VX_TYPE_FLOAT32, &strength_thresh_value);
vx_array corners = vxCreateArray(context, VX_TYPE_KEYPOINT, 100);
vx_array corners1 = vxCreateArray(context, VX_TYPE_KEYPOINT, 100);
vx_size num_corners_value = 0;
vx_scalar num_corners = vxCreateScalar(context, VX_TYPE_SIZE, &num_corners_value);
vx_scalar num_corners1 = vxCreateScalar(context, VX_TYPE_SIZE, &num_corners_value);
vx_keypoint_t *kp = calloc( 100, sizeof(vx_keypoint_t));
errorCheck(&context,
kp == NULL ||
vxGetStatus((vx_reference)strength_thresh) ||
vxGetStatus((vx_reference)corners) ||
vxGetStatus((vx_reference)num_corners) ||
vxGetStatus((vx_reference)corners1) ||
vxGetStatus((vx_reference)num_corners1),
"Could not create parameters for FastCorners");
// Using non maximum shift suppression Fast Corner detection operator
errorCheck(&context, vxuFastCorners(context, image1, strength_thresh, vx_true_e, corners, num_corners), "Fast Corners function failed");
// Non maximum shift suppression is not used Fast Corner detection operator
errorCheck(&context, vxuFastCorners(context, image1, strength_thresh, vx_false_e, corners1, num_corners1), "Fast Corners function failed");
// Number of corners
errorCheck(&context, vxCopyScalar(num_corners, &num_corners_value, VX_READ_ONLY, VX_MEMORY_TYPE_HOST), "vxCopyScalar failed");
printf("Found %zu corners with non-max suppression\n", num_corners_value);
// Coordinate save array
errorCheck(&context, vxCopyArrayRange( corners, 0, num_corners_value, sizeof(vx_keypoint_t), kp,VX_READ_ONLY, VX_MEMORY_TYPE_HOST), "vxCopyArrayRange failed");
// Show coordinates
for (int i=0; i<num_corners_value; ++i)
{
printf("Entry %3d: x = %d, y = %d\n", i, kp[i].x, kp[i].y);
}
// Number of corners
errorCheck(&context, vxCopyScalar(num_corners1, &num_corners_value, VX_READ_ONLY, VX_MEMORY_TYPE_HOST), "vxCopyScalar failed");
printf("Found %zu corners without non-max suppression\n", num_corners_value);
// Coordinate save array
errorCheck(&context, vxCopyArrayRange( corners1, 0, num_corners_value, sizeof(vx_keypoint_t), kp,VX_READ_ONLY, VX_MEMORY_TYPE_HOST), "vxCopyArrayRange failed");
// Show coordinates
for (int i=0; i<num_corners_value; ++i)
{
printf("Entry %3d: x = %d, y = %d\n", i, kp[i].x, kp[i].y);
}
free(kp);
vxReleaseContext(&context);
return 0;
}
Calculation results : Non maximum suppression is adopted , detected 4 Corner points , Do not use detected 24 Corner points .

Sample explanation 2
Next, let's enrich some examples 1 The content of , We can use vxuWarpAffine Affine transformation rotates the input image 90 degree , then vxuOr() Logic or process two images , Create a white cross on a black background , So we see 12 It's a corner .
About what is affine transformation , Interested friends can refer to some links : Affine transformation

Affine transformation is a kind of rotation , Each of these outputs x and y The pixel is obtained from the pixel at the address given by the linear combination of the input address ; If the input address is not an integral , Interpolation is performed as specified . The coefficients given in the code are used as matrix_values Just a simple exchange x and y, There is no offset ;
// Required for affine transformation Mtrix
vx_matrix warp_matrix = vxCreateMatrix(context, VX_TYPE_FLOAT32, 2U,3U);
vx_float32 matrix_values[3][2] = {
/* Rotate through 90 degrees */
{
0.0, 1.0}, /* x coefficients */
{
1.0, 0.0}, /* y coefficients */
{
0.0, 0.0} /* offsets */
};
errorCheck(&context, vxCopyMatrix(warp_matrix, matrix_values,VX_WRITE_ONLY,VX_MEMORY_TYPE_HOST), "Could not initialize thematrix");
/* Now image2 set to image 1 rotated */
// Affine transformation
errorCheck(&context, vxuWarpAffine(context, image1, warp_matrix,VX_INTERPOLATION_NEAREST_NEIGHBOR, image2) ||
/* image3 set to logical OR of images 1 and 2 */
// Logic or
vxuOr(context, image1, image2, image3) ||
/*And now count the corners */
//Fast Corner detection
vxuFastCorners(context, image3, strength_thresh, vx_true_e,corners, num_corners),"Image functions failed");
Instance to explain 3
Further optimization , We add image processing , Use Sobel、Magnitude and Dilate filters( Expansion filter ) Replace the white cross with the outline of the White Cross , Calculate and count the inner and outer corners .
Sobel The filter is an edge detection filter , It is applied to cross to get two output images ,x The gradient of the direction and y Directional gradient .
take x and y Graphic Magnitude, We get a single pixel solid line that outlines the intersection . Be careful ,vxuMagnitude The function accepts two as vxuSobel Output 16 Output of bit signed image , And generate a 16 Bit signed image as output . However , Most others OpenVX Functions only operate on 8 Bit unsigned image , So we use vxu Convert the depth function to generate such an image ,VX_CONVERT_POLICY_SATURATE Specifies that values below zero should be set to zero , higher than 255 The value of should be set to 255.
Last ,vxuDilate3x3 Function application expansion filter , Make the thin outline more substantial .
/* Now image2 set to image 1 rotated */
vx_status status = vxuWarpAffine(context, image1, warp_matrix, VX_INTERPOLATION_NEAREST_NEIGHBOR, image2);
/* image3 set to logical OR of images 1 and 2 and then processed as described above */
errorCheck(&context, vxuOr(context, image1, image2, image3) ||
vxuSobel3x3(context, image3, grad_x, grad_y) ||
vxuMagnitude(context, grad_x, grad_y, magnitude) ||
vxuConvertDepth(context, magnitude, converted, VX_CONVERT_POLICY_SATURATE, 1) ||
vxuDilate3x3(context, converted, dilated) ||
/* And now count the corners */
vxuFastCorners(context, dilated, strength_thresh, vx_true_e, corners, num_corners),"Image functions failed");
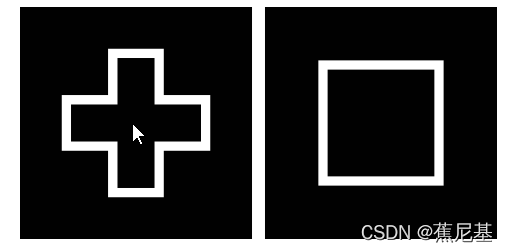
The following code is the overall code after several optimizations
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "VX/vx.h"
#include "VX/vxu.h"
void errorCheck(vx_context *context_p, vx_status status, const char *message)
{
if (status)
{
puts("ERROR! ");
puts(message);
vxReleaseContext(context_p);
exit(1);
}
}
vx_image makeInputImage(vx_context context)
{
vx_image image = vxCreateImage(context, 100U, 100U, VX_DF_IMAGE_U8);
vx_rectangle_t rect = {
.start_x = 20, .start_y = 40, .end_x=80, .end_y = 60
};
if (VX_SUCCESS == vxGetStatus((vx_reference)image))
{
vx_image roi = vxCreateImageFromROI(image, &rect);
vx_pixel_value_t pixel_white, pixel_black;
pixel_white.U8 = 255;
pixel_black.U8 = 0;
if (VX_SUCCESS == vxGetStatus((vx_reference)roi) &&
VX_SUCCESS == vxSetImagePixelValues(image, &pixel_black) &&
VX_SUCCESS == vxSetImagePixelValues(roi, &pixel_white))
vxReleaseImage(&roi);
else
vxReleaseImage(&image);
}
return image;
}
int main(void)
{
vx_context context = vxCreateContext();
errorCheck(&context, vxGetStatus((vx_reference)context), "Could not create a vx_context\n");
vx_image image1 = makeInputImage(context);
errorCheck(&context, vxGetStatus((vx_reference)image1), "Could not create first image");
vx_image image2 = vxCreateImage(context, 100U, 100U, VX_DF_IMAGE_U8);
vx_image image3 = vxCreateImage(context, 100U, 100U, VX_DF_IMAGE_U8);
vx_image grad_x = vxCreateImage(context, 100U, 100U, VX_DF_IMAGE_S16);
vx_image grad_y = vxCreateImage(context, 100U, 100U, VX_DF_IMAGE_S16);
vx_image magnitude = vxCreateImage(context, 100U, 100U, VX_DF_IMAGE_S16);
vx_image converted = vxCreateImage(context, 100U, 100U, VX_DF_IMAGE_U8);
vx_image dilated = vxCreateImage(context, 100U, 100U, VX_DF_IMAGE_U8);
vx_image image4 = vxCreateImage(context, 100U, 100U, VX_DF_IMAGE_U8);
vx_matrix warp_matrix = vxCreateMatrix(context, VX_TYPE_FLOAT32, 2U, 3U);
vx_float32 matrix_values[3][2] = {
/* Rotate through 90 degrees */
{
0.0, 1.0}, /* x coefficients */
{
1.0, 0.0}, /* y coefficients */
{
0.0, 0.0} /* offsets */
};
vx_float32 strength_thresh_value = 128.0;
vx_scalar strength_thresh = vxCreateScalar(context, VX_TYPE_FLOAT32, &strength_thresh_value);
vx_array corners = vxCreateArray(context, VX_TYPE_KEYPOINT, 100);
vx_size num_corners_value = 0;
vx_scalar num_corners = vxCreateScalar(context, VX_TYPE_SIZE, &num_corners_value);
vx_keypoint_t *kp = calloc( 100, sizeof(vx_keypoint_t));
errorCheck(&context,
kp == NULL ||
vxGetStatus((vx_reference)strength_thresh) ||
vxGetStatus((vx_reference)corners) ||
vxGetStatus((vx_reference)num_corners) ||
vxGetStatus((vx_reference)image2) ||
vxGetStatus((vx_reference)image3) ||
vxGetStatus((vx_reference)grad_x) ||
vxGetStatus((vx_reference)grad_y) ||
vxGetStatus((vx_reference)magnitude) ||
vxGetStatus((vx_reference)converted) ||
vxGetStatus((vx_reference)dilated) ||
vxGetStatus((vx_reference)image4) ||
vxGetStatus((vx_reference)warp_matrix),
"Could not create objects");
errorCheck(&context, vxCopyMatrix(warp_matrix, matrix_values, VX_WRITE_ONLY, VX_MEMORY_TYPE_HOST), "Could not initialise the matrix");
/* Now image2 set to image 1 rotated */
vx_status status = vxuWarpAffine(context, image1, warp_matrix, VX_INTERPOLATION_NEAREST_NEIGHBOR, image2);
/* image3 set to logical OR of images 1 and 2 and then processed as described above */
errorCheck(&context, vxuOr(context, image1, image2, image3) ||
vxuSobel3x3(context, image3, grad_x, grad_y) ||
vxuMagnitude(context, grad_x, grad_y, magnitude) ||
vxuConvertDepth(context, magnitude, converted, VX_CONVERT_POLICY_SATURATE, 1) ||
vxuDilate3x3(context, converted, dilated) ||
/* And now count the corners */
vxuFastCorners(context, dilated, strength_thresh, vx_true_e, corners, num_corners),
"Image functions failed");
errorCheck(&context, vxCopyScalar(num_corners, &num_corners_value, VX_READ_ONLY, VX_MEMORY_TYPE_HOST), "vxCopyScalar failed");
printf("Found %zu corners with non-max suppression\n", num_corners_value);
errorCheck(&context, vxCopyArrayRange( corners, 0, num_corners_value, sizeof(vx_keypoint_t), kp,
VX_READ_ONLY, VX_MEMORY_TYPE_HOST), "vxCopyArrayRange failed");
for (int i=0; i<num_corners_value; ++i)
{
printf("Entry %3d: x = %d, y = %d\n", i, kp[i].x, kp[i].y);
}
free(kp);
vxReleaseContext(&context);
return 0;
}
We use a lot of image object , in fact , Most of these images really don't need to be preserved , Because we are not interested in intermediate data . The only image of interest is actually the input image we created . After that , We only use the output from the final corner detector .
Graph pattern (Graph mode)
About Graph mode Use , We can compare the above patterns ,graph How patterns are implemented and executed .
Go straight to the code first , You can see the difference between the two modes of programs that realize the same function , Then I will explain the meaning of the main functions one by one .
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "VX/vx.h"
void errorCheck(vx_context *context_p, vx_status status, const char *message)
{
if (status)
{
puts("ERROR! ");
puts(message);
vxReleaseContext(context_p);
exit(1);
}
}
vx_image makeInputImage(vx_context context, vx_uint32 width, vx_uint32 height)
{
vx_image image = vxCreateImage(context, 100U, 100U, VX_DF_IMAGE_U8);
if (width > 48)
width = 48;
if (height > 48)
height = 48;
vx_rectangle_t rect = {
.start_x = 50 - width, .start_y = 50 - height, .end_x = 50 + width, .end_y = 50 + height
};
if (VX_SUCCESS == vxGetStatus((vx_reference)image))
{
vx_image roi = vxCreateImageFromROI(image, &rect);
vx_pixel_value_t pixel_white, pixel_black;
pixel_white.U8 = 255;
pixel_black.U8 = 0;
if (VX_SUCCESS == vxGetStatus((vx_reference)roi) &&
VX_SUCCESS == vxSetImagePixelValues(image, &pixel_black) &&
VX_SUCCESS == vxSetImagePixelValues(roi, &pixel_white))
vxReleaseImage(&roi);
else
vxReleaseImage(&image);
}
return image;
}
vx_graph makeTestGraph(vx_context context)
{
vx_graph graph = vxCreateGraph(context);
int i;
vx_image imagesU8[5], imagesS16[3];
vx_image input = vxCreateImage(context, 100U, 100U, VX_DF_IMAGE_U8);
// The virtual image object required by the node
for (i = 0; i < 5; ++i)
imagesU8[i] = vxCreateVirtualImage(graph, 100, 100, VX_DF_IMAGE_U8);
for (i = 0; i < 3; ++i)
imagesS16[i] = vxCreateVirtualImage(graph, 0, 0, VX_DF_IMAGE_VIRT);
// Create the required parameters
vx_matrix warp_matrix = vxCreateMatrix(context, VX_TYPE_FLOAT32, 2U, 3U);
vx_float32 matrix_values[6] = {
0.0, 1.0, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0 }; /* Rotate through 90 degrees */
vx_float32 strength_thresh_value = 128.0;
vx_scalar strength_thresh = vxCreateScalar(context, VX_TYPE_FLOAT32, &strength_thresh_value);
vx_array corners = vxCreateArray(context, VX_TYPE_KEYPOINT, 100);
vx_size num_corners_value = 0;
vx_int32 shift_value = 1;
vx_scalar num_corners = vxCreateScalar(context, VX_TYPE_SIZE, &num_corners_value);
vx_scalar shift = vxCreateScalar(context, VX_TYPE_INT32, &shift_value);
vxCopyMatrix(warp_matrix, matrix_values, VX_WRITE_ONLY, VX_MEMORY_TYPE_HOST);
// Node connection : The connection mode of nodes is supported by data
/* Create the nodes to do the processing, order of creation is not important */
vx_node last_node = vxFastCornersNode(graph, imagesU8[4], strength_thresh, vx_true_e, corners, num_corners);
vxDilate3x3Node(graph, imagesU8[3], imagesU8[4]);
vxConvertDepthNode(graph, imagesS16[2], imagesU8[3], VX_CONVERT_POLICY_SATURATE, shift);
vxMagnitudeNode(graph, imagesS16[0], imagesS16[1], imagesS16[2]);
vxSobel3x3Node(graph, imagesU8[2], imagesS16[0], imagesS16[1]);
vxOrNode(graph, imagesU8[0], imagesU8[1], imagesU8[2]);
vxWarpAffineNode(graph, imagesU8[0], warp_matrix, VX_INTERPOLATION_NEAREST_NEIGHBOR, imagesU8[1]);
// Set up grpah Input ,Index: The first few parameters of the node
/* Setup input parameter using a Copy node */
vxAddParameterToGraph(graph, vxGetParameterByIndex(vxCopyNode(graph, (vx_reference)input, (vx_reference)imagesU8[0]), 0));
// Set up grpah Output ,Index: The first few parameters of the node
/* Setup the output parameters from the last node */
vxAddParameterToGraph(graph, vxGetParameterByIndex(last_node, 3)); /* array of corners */
vxAddParameterToGraph(graph, vxGetParameterByIndex(last_node, 4)); /* number of corners */
/* Release resources */
vxReleaseImage(&input);
for (i = 0; i < 5; ++i)
vxReleaseImage(&imagesU8[i]);
for (i = 0; i < 3; ++i)
vxReleaseImage(&imagesS16[i]);
vxReleaseMatrix(&warp_matrix);
vxReleaseScalar(&strength_thresh);
vxReleaseScalar(&num_corners);
vxReleaseScalar(&shift);
vxReleaseArray(&corners);
return graph;
}
// obtain Graph Parameters of
vx_reference getGraphParameter(vx_graph graph, vx_uint32 index)
{
vx_parameter p = vxGetGraphParameterByIndex(graph, index);
vx_reference ref = NULL;
vxQueryParameter(p, VX_PARAMETER_REF, &ref, sizeof(ref));
vxReleaseParameter(&p);
return ref;
}
void showResults(vx_graph graph, vx_image image, const char * message)
{
vx_status status;
// Create context
vx_context context = vxGetContext((vx_reference)graph);
puts(message);
// Set up Graph The output parameters of ,Index:0 The first 0 Parameters
vxSetGraphParameterByIndex(graph, 0, (vx_reference)image);
//graph authentication
errorCheck(&context,vxVerifyGraph(graph),"Graph verify fail!");
//graph perform
status = vxProcessGraph(graph);
if (VX_SUCCESS == status)
{
vx_size num_corners_value = 0;
vx_keypoint_t *kp = calloc( 100, sizeof(vx_keypoint_t));
// After successful execution , take scaler Parameter copy value num_corners_value
errorCheck(&context, vxCopyScalar((vx_scalar)getGraphParameter(graph, 2), &num_corners_value,
VX_READ_ONLY, VX_MEMORY_TYPE_HOST), "vxCopyScalar failed");
printf("Found %zu corners with non-max suppression\n", num_corners_value);
/* Array can only hold 100 values */
if (num_corners_value > 100)
num_corners_value = 100;
// After successful execution , take scaler Parameter copy value vx_keypoint_t Array
errorCheck(&context, vxCopyArrayRange((vx_array)getGraphParameter(graph, 1), 0,
num_corners_value, sizeof(vx_keypoint_t), kp,
VX_READ_ONLY, VX_MEMORY_TYPE_HOST), "vxCopyArrayRange failed");
for (int i=0; i<num_corners_value; ++i)
{
printf("Entry %3d: x = %d, y = %d\n", i, kp[i].x, kp[i].y);
}
free(kp);
}
else
{
printf("Graph processing failed[%d]!\n",status);
}
}
int main(void)
{
vx_context context = vxCreateContext();
errorCheck(&context, vxGetStatus((vx_reference)context), "Could not create a vx_context\n");
vx_graph graph = makeTestGraph(context);
vx_image image1 = makeInputImage(context, 30, 10);
vx_image image2 = makeInputImage(context, 25, 25);
showResults(graph, image1, "Results for Image 1");
showResults(graph, image2, "Results for Image 2");
vxReleaseContext(&context);
return 0;
}
The meaning and explanation of each function
vx_graph graph = vxCreateGraph(context);
Create a based on context graphvxCreateVirtualImage( )
This function is used to create a virtual image, We often don't care about intermediate data , However, the connection of nodes should be supported by data objects , therefore , Virtual object technology is born from application .vxCreateMatrix( )
Create a matrix objectvxCreateScalar( )
Create a scalar objectvxCreateArray( )
Create an array objectvxCopyNode( )
Copy a nodevxGetParameterByIndex(vx_node node, vx_uint32 index)
Get the parameters of the node , Among them index, Is the index of the parameters of the node , A few is to get rid of graph The number of parameters other than parameters .vxAddParameterToGraph(vx_graph graph, vx_parameter param)
Add parameters to graphvxVerifyGraph(graph)
Node authentication , Main verification graph Whether the structure is legal
-vxProcessGraph(graph)
graph perform , This function will execute graph All in node The functionality .
版权声明
本文为[Banana Nicky]所创,转载请带上原文链接,感谢
https://yzsam.com/2022/04/202204222101015165.html
边栏推荐
- 2022 R2 mobile pressure vessel filling training test questions and online simulation test
- 容联云携手中国信通院,开启办公即时通信软件系列标准研制
- 解数独[Pre-DS-hash结构 + component-DFS | Pre-hash-1-9特性--二进制状态压缩 + DFS]
- Application value of smart agriculture app software
- 站长工具大全-站长软件网站-站长工具网站-站长必备工具免费
- QT使用windeployqt.exe打包程序
- 自媒体运营中千万不能做的四件事情
- 蜥蜴书学习day1-机器学习概述
- Reflection and annotation
- . 102 keyboard move div
猜你喜欢
![[radar] point target simulation of simulated synthetic aperture radar (SAR)](/img/65/12a9a76c5e5590e0008bdc00f3148c.png)
[radar] point target simulation of simulated synthetic aperture radar (SAR)

Rong Lianyun joined hands with China Academy of information and communications to start the development of a series of standards for office instant messaging software

nodejs笔记3

Minio基本使用与原理

2、 Linear regression

JMeter data and software

QT使用windeployqt.exe打包程序
![解数独[Pre-DS-hash结构 + component-DFS | Pre-hash-1-9特性--二进制状态压缩 + DFS]](/img/06/295b26f1389da3d90ad211dc447123.png)
解数独[Pre-DS-hash结构 + component-DFS | Pre-hash-1-9特性--二进制状态压缩 + DFS]

软件测试知识点 | Jmeter实现接口关联小结

机器视觉需要掌握的知识
随机推荐
Smart agriculture has become a development path, give full play to intelligence and liberate manpower
统计字符数C
BLE---Advertisement data format & service
TC process addition status
Question bank and simulation examination of work permit for safety management personnel of hazardous chemical business units in 2022
k8s部署mysql
大量mapper IO优化(使用多线程异步+CountDownLatch)
Ali Interviewer: you'd better not write glide on your resume. It's not as simple as asking for the source code
LeetCode刷题日记 - 剑指 Offer II 070. 排序数组中只出现一次的数字
SDF accelerate trace
[noip2012] borrow classroom
Get specified TC rule
jmeter整套资料
2022年G3锅炉水处理国家题库及在线模拟考试
蜥蜴书学习day1-机器学习概述
智慧农业成为发展道路,充分发挥智能化,解放人力
Jingdong new product Intelligence Bureau spoilers oppo K10 series or linkage Guoman IP surprise?
Use of dSPACE simulation platform
DSPACE仿真平台的使用
How to install monitoring without network in rural areas, and what kind of monitoring without WiFi at home