当前位置:网站首页>Concepts of objects and classes
Concepts of objects and classes
2022-04-23 03:34:00 【Chen Yu】
Java Summary of knowledge points : You can enter from here if you want to see
1、 object-oriented programming
java The core idea is object-oriented (OOP Object-Oriented Programming). Object oriented is suitable for dealing with complex problems , Suitable for dealing with multi person cooperation . For a problem , The first is to classify the problems , Then think about the class alone , Finally, process oriented analysis is carried out for each class .
The essence of object-oriented programming is : Organize code as a class , Encapsulating data in the form of objects .
A program is seen as a collection of objects , The object is the smallest unit . A set of related objects form a complex system .
1.1 The concept of object
So what is an object ?
Anything in real life can be regarded as an object , We usually use the static part ( attribute ) And the dynamic part ( Behavior ), To understand things .
All things are objects , Entities and concepts in the problem domain can be abstracted as objects . In the field of school : Student 、 teacher 、 Course 、 Classes and so on are all objects .
- Objects are unique in a system
- Objects have properties and behaviors : Static part ( attribute ) And the dynamic part ( Behavior )
How do we describe a person in reality ? Usually through his height, fat and thin 、 Gender 、 Age and other attributes . In addition, it usually describes what he is currently doing : speak 、 running 、 Crying and other behaviors . Through these aspects, we can fully understand a person . - Object has state : After a certain behavior occurs, the value of the attribute may be changed .
- Objects are the concrete implementation of a class .
How do we describe a student who is studying in the computer A?
1、 First, we abstract the student entity as an object , Then consider the attributes and specific behaviors of students .
2、 attribute : Student number 、 full name 、 Age 、 Gender 、 Class, etc . Behavior : Study 、 game 、 Sports and so on
3、 Specific to this student through attributes A.
4、 Describe the students A Is learning .
Therefore, by analyzing the static part and dynamic part of students, we can determine a specific student object .
1.2 The concept of class
Class can actually be seen as a template , And the object is the entity created through this template . In reality, we print paper money , You need to make a template first ( class ), Then the paper money is quickly generated through the template ( object ).
So the essence of a class is the carrier that encapsulates the properties and behaviors of an object , An object is an instance of a class . A class is a general term for a series of objects with the same characteristics . The properties of the object are defined in the form of member variables in the class , And behavior is defined as specific methods .
2、 Classes and objects
2.1、 package
stay java In, we need to create different classes , Create objects based on classes to write programs , So when our program gets bigger and bigger , If you put all the classes together , The difficulty of management can be imagined , I think anyone who sees a lot of classes together will have a headache .
So in java Package is introduced in (package) The concept of . It is similar to a folder , Multiple namespaces can be provided .
Bag 3 The two functions are as follows :
- It is convenient for us to distinguish classes with the same name
- It is more convenient to manage and maintain classes
- It is more convenient to control the access rights of classes
The first line in the code is the package definition statement , By keyword package. The following import statement of follow-up package , Keyword is import

package Package name (com.*****); // first line , And only one
import Package name + Class name ; // stay package after , There can be multiple
2.2 、 class
class (Class) It is the carrier that encapsulates the properties and behaviors of objects , Is one for creating java Templates for objects , It abstracts the common features and behaviors of objects , Use member variables to represent the properties of things , Describe the behavior in a specific way , So as to form a class . adopt new Keyword instantiates a class , That is to create an object with such characteristics and behavior .
We define a student's class :

2.2.1 attribute
Java The properties of an object are member variables , Member variables can be set to various data types , The initial value can be assigned , You can also assign no value ( Have default values ). Usually, attributes use keywords private Set up , Expressed as private , Other classes are not visible , Provide some operation methods through .

2.2.2 Method
There are generally two methods : Construction methods and common methods .
1、 Construction method
Constructor( Constructors ) Is a special method in a class , Execute only once when the object is created , Some operations used for initialization , Class will have a parameterless constructor by default , You can also define , But once you define yourself , The default constructor will be overridden . The construction method can be overridden , The corresponding construction method will be selected according to different parameters passed .
- characteristic
- No return value , nothing void
- The name of the method is exactly the same as the name of the class
- effect
- It is mainly used to initialize properties
public class Student{
private String name;
// Construction method . No return value , The method name and type are the same
public Student(String name){
this.name = namel
}
// The construction method with parameters is defined , Also want to use a parameterless construct , You have to define it manually
public Student(){
}
}

2、 Common method
-
Method definition
// Common method Permission modifier return type Method name ( Parameter type Parameter name ......){ // No return value is void, If there is a return value, it is the corresponding data type Method body ; return Return value ; // When there is a return value , Use keywords return return } /** 1、 Modifier : It's optional , Tell the compiler how to call the method . Defines the access type of the method . 2、 return type : Method may return a value . Or there may be no return value . When there is a return value, it indicates the return value type , And use return return . Use when not in use void keyword 3、 Parameter type : Parameters passed to the method when the method is called , This parameter can be used in the method body . 4、 Method body : The method body contains specific statements , Define the function of the method . 5、 keyword return: Code execution to return End directly after , The subsequent code will not execute .return Followed by the corresponding return value */Methods pass parameters in addition to ordinary parameters , There is also a variable parameter :
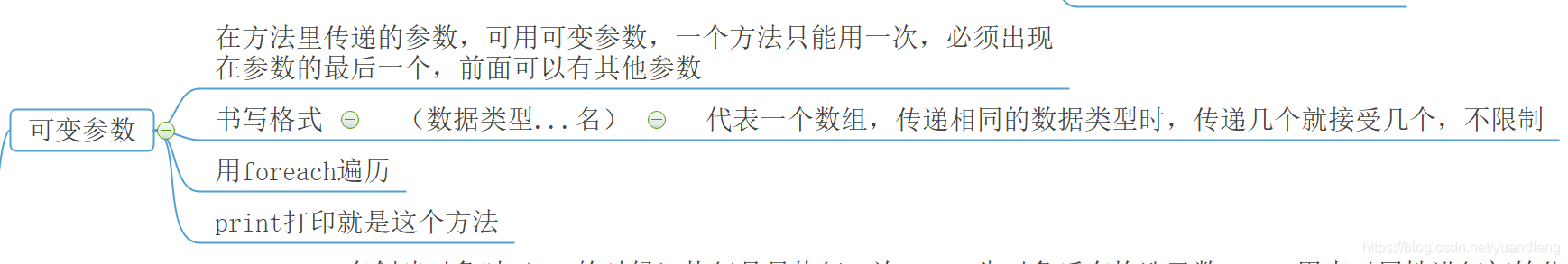
-
Method call
- The type of parameters passed by the called method must be consistent with the parameters of the method
- Static methods : keyword static The method of decoration , When the class is loaded, it will produce
- Class name . Method name ();
- Non static methods : Only when the object is created
- Instantiate the object first : Class name Object name = new Class name ();
- Object name . Method name ();
// Create a class about people , Describe a person by attributes , People have their own specific behavior
package **; // Package of class
import **; // Import other classes
//class The keyword is represented as a class ,public For permissions ,Person For class name
public class Person(){
// attribute , What are the characteristics of a person . People have names 、 With age 、 There's sex
private String name; // full name
private int age; // Age
private String sex; // Gender
// Constructors , Each class has a default constructor , You can define , After definition, it defaults to custom
public Person(String name,int age,String sex){
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.sex = sex;
}
public Person(){
}
// Common method , People can talk
public void say(){
System.out.printf(" My name is %s, This year, %d year , Gender %s",name,age,sex);
}
}
2.2.4 Inner class

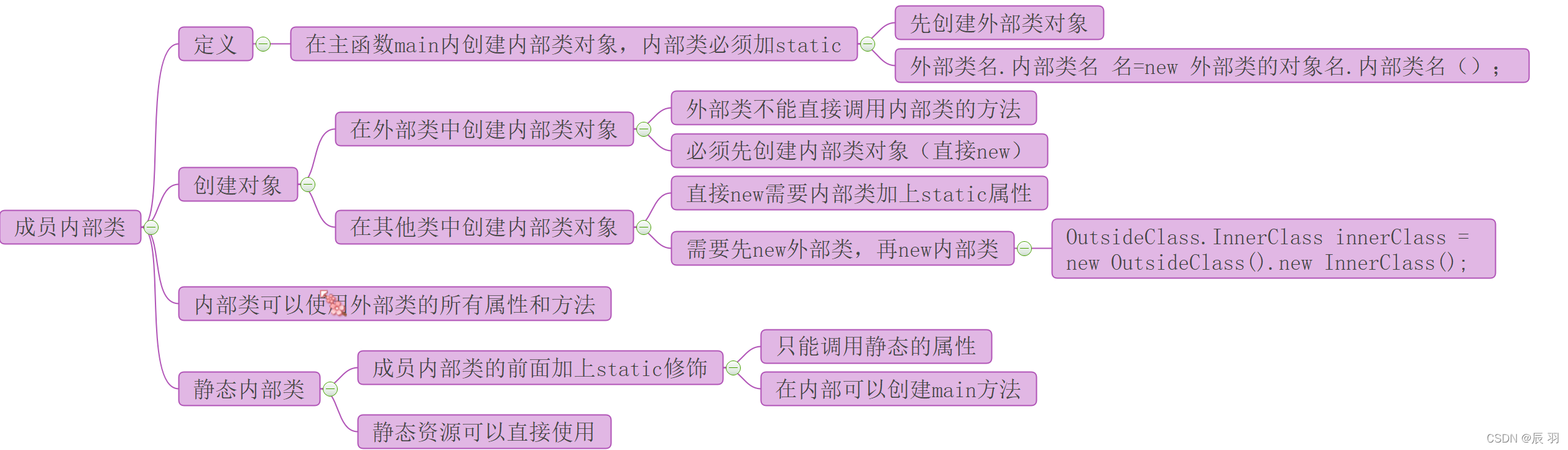
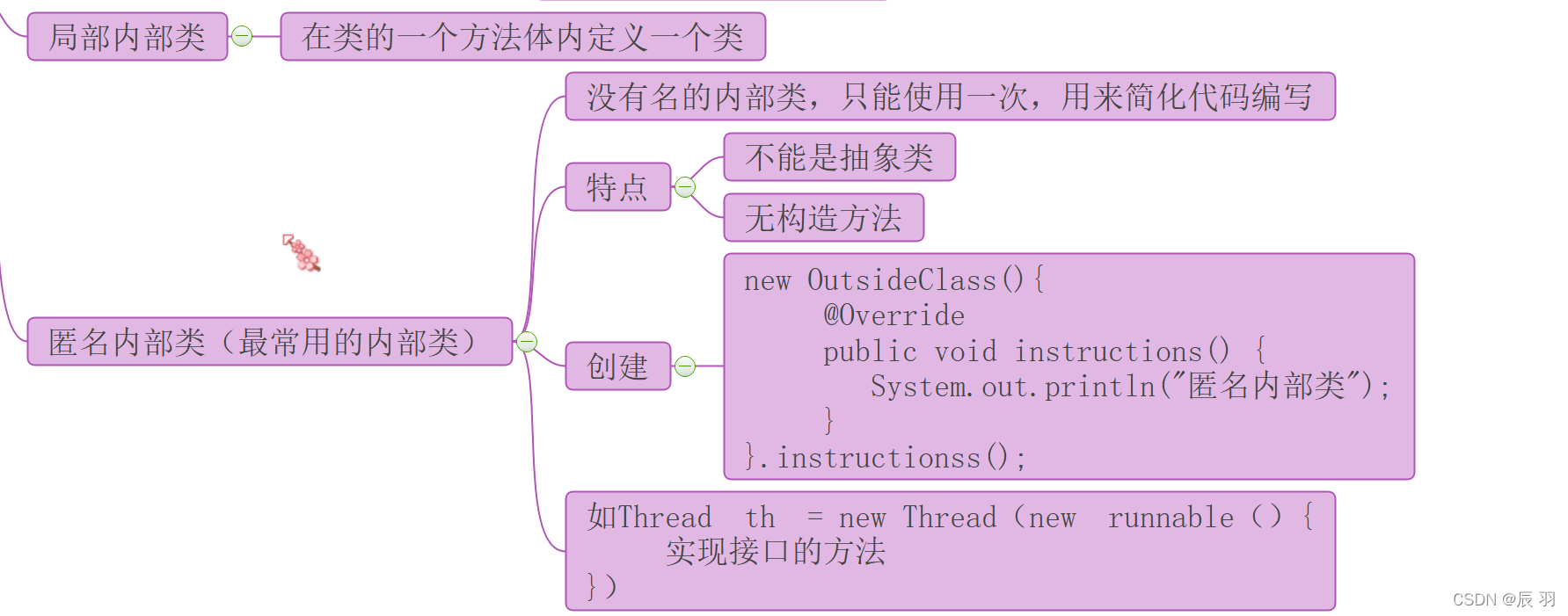

2.3、 object
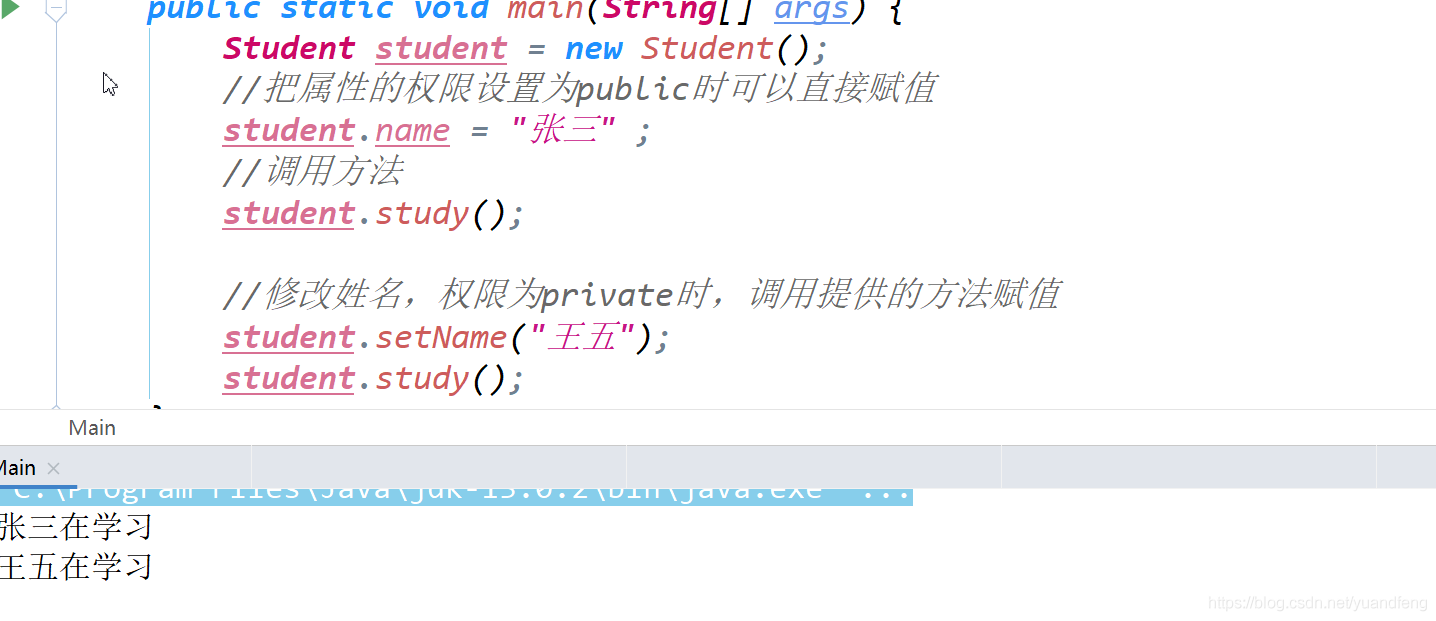
2.3.1 Object creation
Steps to generate an object :
1、 Statement : Declare an object , That is, declare the type and name of the object .
2、 Instantiation : adopt new Keyword to create an object .
3、 initialization : When using new When you create an object , The constructor will be called to initialize the object .
Syntax for creating objects : Class name name = new Class name (); Create a student object Student student = new Student(); student It's actually a reference to an object , It doesn't save the object itself , It's the address of the object ( The data of the object is stored in heap memory , Stack memory is the address in heap memory ).
Different objects created by the same class are independent of each other , Allocate memory address when creating , When the object is no longer used , Object by Java Garbage collection and disposal mechanism of virtual machine .

2.3.2 Use of objects
-
Access properties : Property cannot be set to private
Object name . Property name = value ;
-
Calling method
Object name . Method name ( Parameters );
版权声明
本文为[Chen Yu]所创,转载请带上原文链接,感谢
https://yzsam.com/2022/04/202204230332246332.html
边栏推荐
- Design and implementation of redis (1): understand data structures and objects
- 淺學一下I/O流和File類文件操作
- Using swagger in. Net5
- ThreadLocal test multithreaded variable instance
- 2022 团体程序设计天梯赛 模拟赛 L2-4 哲哲打游戏 (25 分)
- QT learning summary
- Application and definition of interface
- Design and implementation of redis (2): how to handle expired keys
- you need to be root to perform this command
- Section 2 map and structure in Chapter 6
猜你喜欢
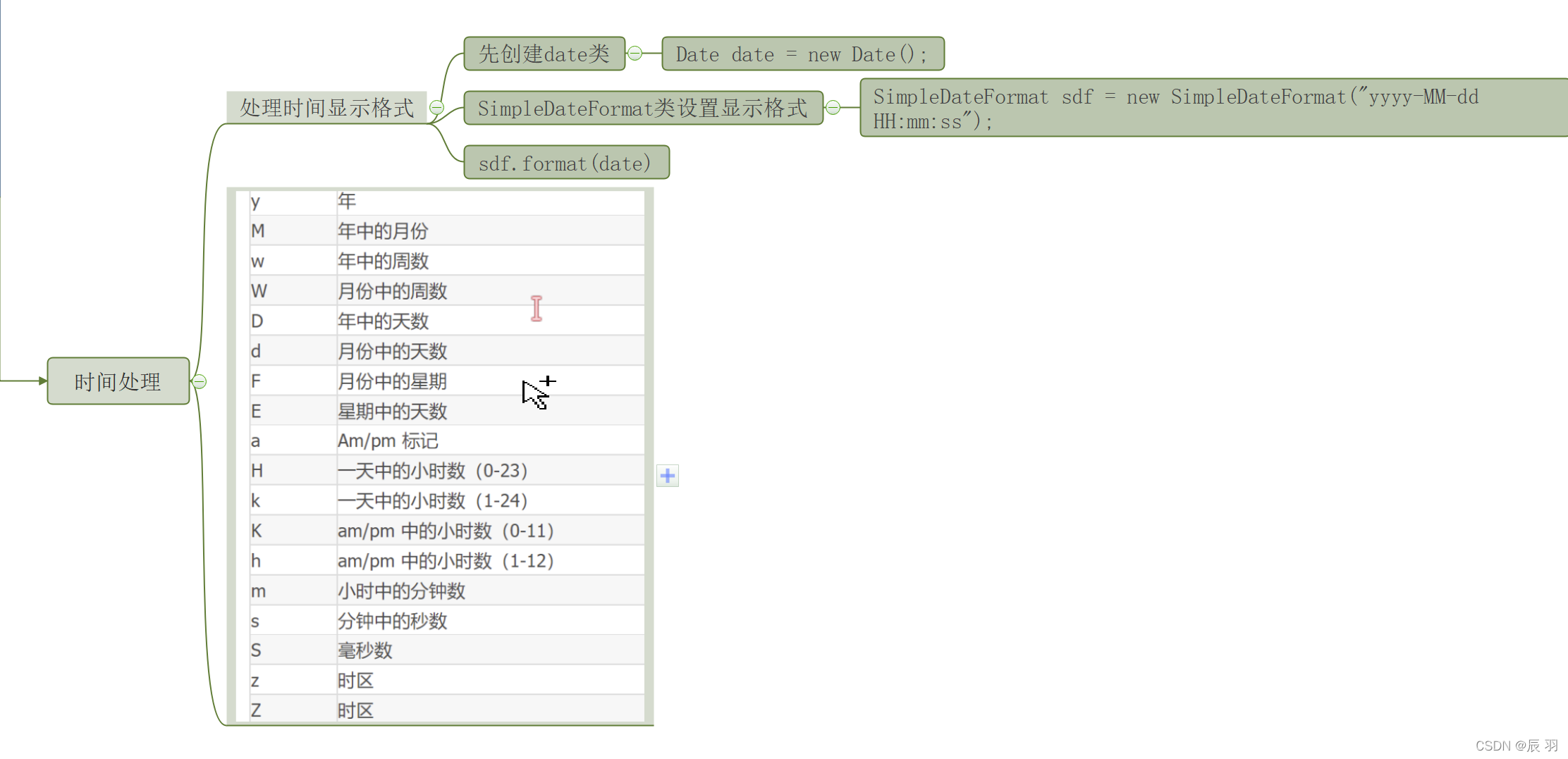
常用的辅助类
![Super easy to use [general excel import function]](/img/9b/ef18d1b92848976b5a141af5f239b5.jpg)
Super easy to use [general excel import function]
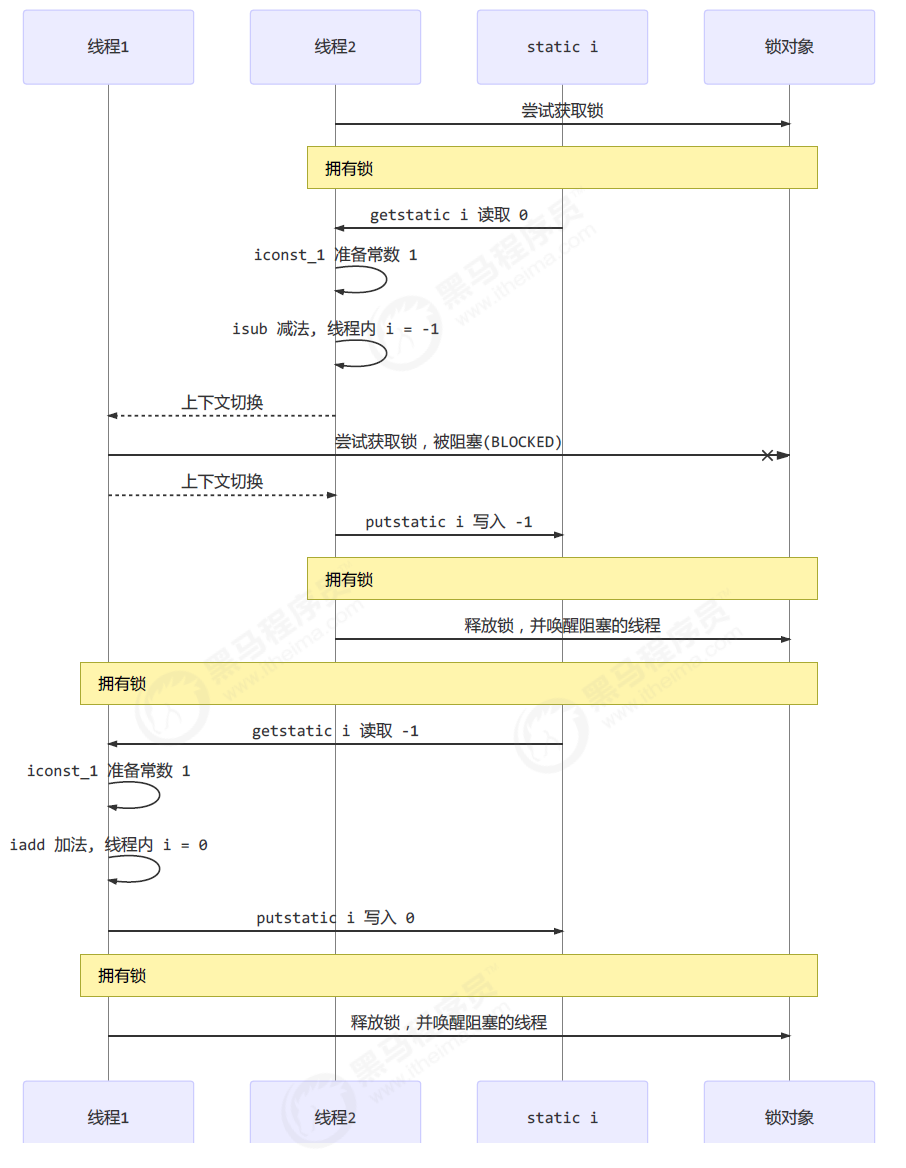
The art of concurrent programming (2): synchronized usage scenarios
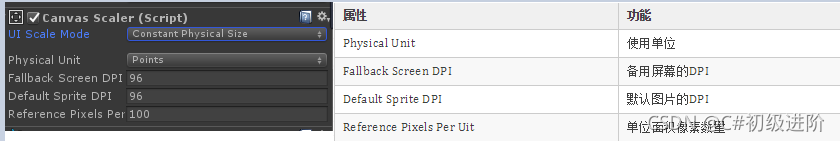
Unity knowledge points (ugui)
Unity knowledge points (ugui 2)
2022 group programming ladder simulation match 1-8 are prime numbers (20 points)

Unity games and related interview questions

Database - MySQL -- Navicat import SQL error 1067 - invalid default value for 'paydate‘
Design and implementation of redis (6): how redis achieves high availability

Codeforces round 784 (Div. 4) (AK CF (XD) for the first time)
随机推荐
JS calculates the display date according to the time
第四次作业
浅学一下I/O流和File类文件操作
Problem B: small challenge
MySQL keyword group_ Concat, combined connection query
Leetcode 617 merge binary tree
C-11 problem I: find balloon
Leetcode punch in diary day 01
JS changes the words separated by dashes into camel style
Section 2 map and structure in Chapter 6
打卡:4.22 C语言篇 -(1)初识C语言 - (11)指针
Supersocket is Used in net5 - command
Romantic silhouette of L2-3 of 2022 group programming ladder Simulation Competition (25 points)
There is no index in the database table. When inserting data, SQL statements are used to prevent repeated addition (Reprint)
Supersocket is Use in net5 - startup
"Visual programming" test paper
The principle and solution of not allowing pasting in an English Network
Design and implementation of redis (4): what is the event driver of redis
批量下載文件----壓縮後再下載
Design and implementation of redis (6): how redis achieves high availability