当前位置:网站首页>Go reflection rule
Go reflection rule
2022-04-23 04:33:00 【Heavy dust】
Go The law of reflection
Reflection is Go One of the more important features of language , Although not common in most applications and services , But many frameworks rely on Go The reflection mechanism of language realizes some dynamic functions . As a static language ,Golang It's very simple in design , So in fact, there is no strong expression ability in grammar , however Go What language offers us reflect The dynamic features provided by the package can make up for some of its syntactic disadvantages .
reflect The reflection ability of runtime is realized , To be able to make Golang Programs that operate on different types of objects , We can use the functions in the package TypeOf From static type interface{} Get the dynamic type information from ValueOf Get the runtime representation of the data , With these two functions and other tools in the package, we can get more powerful expressive power .
summary
stay go In language , The key to reflection is reflect package , Enables programs to manipulate different types of objects . among , In the reflection package, there are two very important type and function , The two functions are :
reflect.TypeOf- Can get information about the type of objectreflect.ValueOf- Can get the data of the object
The two types are reflect.Type and reflect.Value, They correspond to functions one by one :
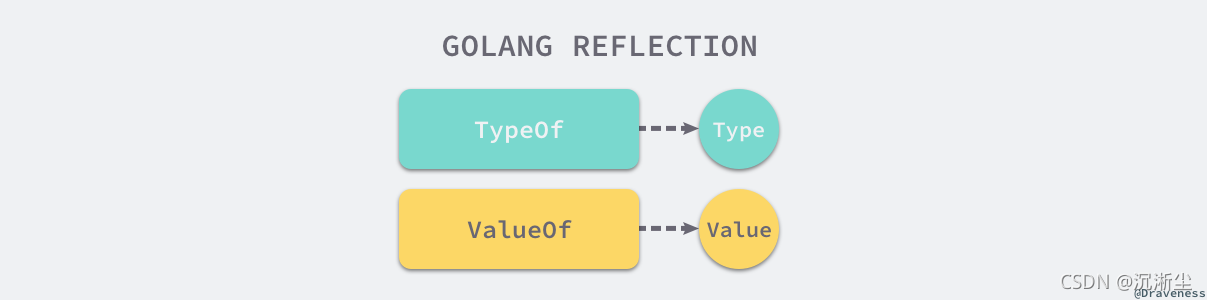
The law of reflection
Runtime reflection is a way for a program to check its own structure during runtime , It is Metaprogramming A kind of , But the flexibility it brings is also a double-edged sword , Excessive use of reflection will make our program logic difficult to understand and slow , We will introduce in this section Go The three laws of language reflection , This can help us better understand the role of reflection .
- Reflection objects can be reflected from interface values ;
- The interface value can be reflected from the reflection object ;
- To modify the reflection object , Its value must be settable ;
First rule
The first law of reflection is , We can Go Interface type variables in the language are converted to reflection objects , As mentioned above reflect.TypeOf and reflect.ValueOf That's the two most important ways to accomplish this transformation , If we think Go There are two differences between types and reflective types in language 『 The world 』 Words , So these two ways are bridges between the two worlds .

Let's briefly introduce the functions of these two methods through the following examples , among TypeOf Gets the variable author The type of string and ValueOf Get the value of the variable draven, If we know the type and value of a variable , So that means we have all the information about this variable .
package main
import (
"fmt"
"reflect"
)
func main() {
author := "draven"
fmt.Println("TypeOf author:", reflect.TypeOf(author))
fmt.Println("ValueOf author:", reflect.ValueOf(author))
}
$ go run main.go
TypeOf author: string
ValueOf author: draven
From the type of variable, we can get the method that the current type can execute Method And the interface implemented by the current type ;
- For structures , You can get the number of fields and get the fields by subscript and field name
StructField; - For hash tables , Can get the hash table
Keytype ; - For functions or methods , You can get the types of input parameters and return values ;
- …
To make a long story short , Use TypeOf and ValueOf To be able to Go The variables in the language are converted into reflection objects , At this time, we can get almost all the data and operations related to the current type , Then you can use these runtime structures to dynamically execute some methods .
Many readers may be confused by this subtitle , Why from Interface To reflect objects , If called directly
reflect.ValueOf(1), It seems to be from the basic typeintTo the reflection type , howeverTypeOfandValueOfThe input parameters of the two methods are actuallyinterface{}type .We've been in before Function call In this section ,Go Language function calls are value passing , Variables are typed before method calls , That is to say
intThe basic variable of type is converted tointerface{}type , That's the first rule, from interfaces to reflective objects .
The second rule
Now that we can convert a variable of an interface type to a reflection object type , Then you also need some other methods to restore the reflection object to a variable of interface type ,reflect Medium Interface The way to do it :
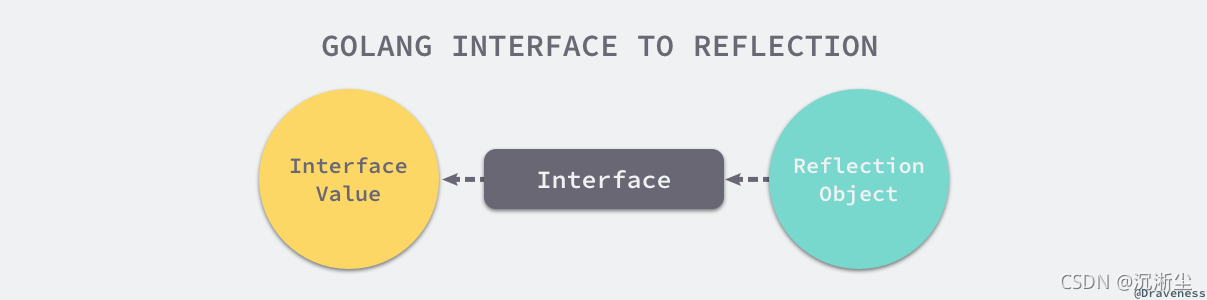
But call Interface Methods we can only get interface{} Interface variables of type , If you want to restore it to its original type, you need to go through a forced type conversion , As shown below :
v := reflect.ValueOf(1)
v.Interface{
}.(int)
The process from the reflective object to the interface value is the mirror process from the interface value to the reflective object , Both processes need to go through two transformations :
- From interface value to reflection object :
- Type conversion from basic type to interface type ;
- Conversion from interface type to reflection object ;
- From reflection object to interface value :
- Convert reflection object to interface type ;
- Change to the original type by explicit type conversion ;

Of course, not all variables need type conversion , If it is interface{} Type of , So it doesn't really need to be typed , For most variables , The process of type conversion is often implicit , Only when we need to convert the reflection object back to the basic type, we need to do the conversion operation of display .
The third rule
Go The last rule of language reflection is related to whether values can be changed , If we want to update one reflect.Value, Then the value it holds must be updatable , Suppose we have the following code :
func main() {
i := 1
v := reflect.ValueOf(i)
v.SetInt(10)
fmt.Println(i)
}
$ go run reflect.go
panic: reflect: reflect.flag.mustBeAssignable using unaddressable value
goroutine 1 [running]:
reflect.flag.mustBeAssignableSlow(0x82, 0x1014c0)
/usr/local/go/src/reflect/value.go:247 +0x180
reflect.flag.mustBeAssignable(...)
/usr/local/go/src/reflect/value.go:234
reflect.Value.SetInt(0x100dc0, 0x414020, 0x82, 0x1840, 0xa, 0x0)
/usr/local/go/src/reflect/value.go:1606 +0x40
main.main()
/tmp/sandbox590309925/prog.go:11 +0xe0
Running the above code causes the program to panic And report reflect: reflect.flag.mustBeAssignable using unaddressable value error , If you think about it carefully, you can actually find out the cause of the mistake ,Go Linguistic Function call It's all about value transmission , So the reflection object we get has nothing to do with the initial variable , No variables hold the copied values , So modifying it directly can lead to a crash .
If we want to modify the original variables, we can only use the following method , First, through reflect.ValueOf Get the variable pointer , And then through Elem Method to get the variable pointed to by the pointer and call SetInt Method to update the value of a variable :
func main() {
i := 1
v := reflect.ValueOf(&i)
v.Elem().SetInt(10)
fmt.Println(i)
}
$ go run reflect.go
10
This kind of getting pointer corresponds to reflect.Value And pass Elem Method roundabout way to get variables that can be set , This complicated process is mainly due to Go Language function calls are value passing , We can interpret the above code as :
func main() {
i := 1
v := &i
*v = 10
}
If you can't operate directly i A variable modifies the value it holds , We can only get i Variable address and use *v Modify the whole tree stored in the address .
版权声明
本文为[Heavy dust]所创,转载请带上原文链接,感谢
https://yzsam.com/2022/04/202204230413460324.html
边栏推荐
- 减治思想——二分查找详细总结
- Effects of antibiotics on microbiome and human health
- VSCode配置之Matlab极简配置
- 補:注解(Annotation)
- [mapping program design] coordinate azimuth calculation artifact (version C)
- Basic use of shell WC (counting the number of characters)
- win10, mysql-8.0.26-winx64.zip 安装
- Network principle | connection management mechanism in TCP / IP important protocol and core mechanism
- 无线键盘全国产化电子元件推荐方案
- Coinbase:关于跨链桥的基础知识、事实和统计数据
猜你喜欢

Alibaba cloud IOT transfer to PostgreSQL database scheme
zynq平臺交叉編譯器的安裝

Phishing for NFT

win10, mysql-8.0.26-winx64. Zip installation

AWS EKS添加集群用户或IAM角色

VSCode配置之Matlab极简配置

【论文阅读】【3d目标检测】Voxel Transformer for 3D Object Detection
![[BIM introduction practice] wall hierarchy and FAQ in Revit](/img/95/e599c7547029f57ce23ef4b87e8b9a.jpg)
[BIM introduction practice] wall hierarchy and FAQ in Revit

协程与多进程的完美结合
![[AI vision · quick review of NLP natural language processing papers today, issue 31] Fri, 15 APR 2022](/img/40/72fdf9c89ed7d063cc368e6e052d0f.png)
[AI vision · quick review of NLP natural language processing papers today, issue 31] Fri, 15 APR 2022
随机推荐
Alibaba cloud IOT transfer to PostgreSQL database scheme
Bacterial infection and antibiotic use
无线键盘全国产化电子元件推荐方案
zynq平臺交叉編譯器的安裝
MYSQL去重方法汇总
【论文阅读】【3d目标检测】point transformer
那些年我面试过的Android开发岗总结(附面试题+答案解析)
Inverse system of RC low pass filter
Go反射—Go语言圣经学习笔记
Kotlin. The binary version of its metadata is 1.6.0, expected version is 1.1.15.
Go 语言中的 logger 和 zap 日志库
Hard core chip removal
Set经典小题目
Express middleware ① (use of Middleware)
【BIM+GIS】ArcGIS Pro2.8如何打开Revit模型,BIM和GIS融合?
QML进阶(四)-绘制自定义控件
IDE idea automatic compilation and configuration of on update action and on frame deactivation
VHDL语言实现32位二进制数转BCD码
用D435i录制自己的数据集运行ORBslam2并构建稠密点云
阿里十年技术专家联合打造“最新”Jetpack Compose项目实战演练(附Demo)