当前位置:网站首页>Introduction to Cortex-M3 register set, assembly language and C language interface
Introduction to Cortex-M3 register set, assembly language and C language interface
2022-04-23 04:00:00 【Chenxr32】
learn uCOS The task switching of involves assembly code . In order to understand assembly code , I learned about it online Cortex-M3 Register group 、C Knowledge of interface with assembly , Share it here .
Let's first introduce Cortex-M3 Register group :

Cortex-M3 Have 16 General registers R0-R15.
R0-R12 All are 32 Bit general register , For data manipulation .
R13 It's a stack pointer . stay CM3 There are two stack pointers in the processor core , So it supports two stacks . When referencing R13(SP) when , You are referring to the one currently in use , The other must be accessed with special instructions . The two stack pointers are :
- Main stack pointer (MSP): This is the default stack pointer , It consists of OS kernel 、 Exception service program and application code requiring privileged access .
- Process stack pointer (PSP): For general application code .
R14 Is the connection register (LR). Store the returned address when the function is called .
R15 Program counter (PC). Point to the address of the current program . If you change its value , Will change the execution order of the program ( Many advanced operations are here ).
Next, the compilation and C The interface of :
Give Way C When a program and an assembler interact with each other , We must know how parameters are passed , And how the value is returned , In this way, we can coordinate the work between the main function and the subroutine . These interaction mechanisms are ARM There are clear provisions in , By document 《ARM Architecture Procedure Call Standard(AAPCS,Ref5)》( I haven't seen it ) give . Although I didn't read the official documents , I still read it on Baidu C Mixed programming with assembly , And make the following summary :
1、 When a function call occurs , The entry parameters pass through R0-R3 Register transfer , among R0 Pass on the first ,R1 Pass on section 2 individual ……, When more than 4 When the parameters , Other parameters are passed through the stack . The return value of the function passes through R0 Register returns . Before the function is called ,R0-R3 The value in will be automatically stacked .
2、R4-R11 For ordinary general purpose registers , When a function call occurs , The data will not be automatically stacked , If the called function needs to use these registers , The called function needs to store the data in these registers on the stack first, and then use these registers . Before the called function returns , You need to take the data out of the stack and reply R4-R11 Value , And then it returns to the main function .
3、R12(IP) You can record calls to subroutines .
R13-R15 The role of is introduced in the previous section , Stop talking .
Last , I use C And compiled a program of running water lamp , This is a demonstration C Language calls assembly functions , among LED The switching between on and off is realized by assembly code . Some codes are attached below : Code download address :https://download.csdn.net/download/qdchenxr/10887924
/******************led.h*******************/
#ifndef __LED_H
#define __LED_H
#include "stm32f10x.h"
void LED_Init(void);//GPIO initialization
void LED_Change(unsigned char index);// Assembler function in C Declaration in language header file
#endif
/******************main.c*******************/
#include "delay.h"
#include "led.h"
int main(void)
{
unsigned char index=1;
delay_init();
LED_Init();
while(1)
{
LED_Change(index);// Call the assembly function , Pass a parameter
index=!index;
delay_ms(300);
}
}
/******************led.s*******************/
; Global function
EXPORT LED_Change ; The functions defined in this file
; Constant
GPIOB_BASE EQU 0x40010C00 ;GPIOB The base address
GPIOB_BRR EQU GPIOB_BASE+0x14 ;GPIOB_BRR The address of the register
GPIOB_BSRR EQU GPIOB_BASE+0x10 ;GPIOB_BSRR The address of the register
GPIOE_BASE EQU 0x40011800 ;GPIOE The base address
GPIOE_BRR EQU GPIOE_BASE+0x14 ;GPIOE_BRR The address of the register
GPIOE_BSRR EQU GPIOE_BASE+0x10 ;GPIOE_BSRR The address of the register
LED_LIGHT EQU 0x0020
; Code generation instructions
PRESERVE8
THUMB
AREA CODE, CODE, READONLY
;LED Switching function
LED_Change
CBZ R0, LED1_Light ; A parameter consists of R0 Pass on , Judge R0, If the value is 0 Jump to LED1_Light
LED2_Light
; Lighten up LED2
LDR R1, =GPIOE_BRR ;R1=GPIOE_BRR;//R1 Zhongcun GPIOE_BRR The address of the register
LDR R2, =LED_LIGHT ;R2=0x0020;
STR R2, [R1] ;*R1=R2;
; Extinguish LED1
LDR R1, =GPIOB_BSRR
LDR R2, =LED_LIGHT
STR R2, [R1]
BX LR ; The function returns
LED1_Light
; Lighten up LED1
LDR R1, =GPIOB_BRR
LDR R2, =LED_LIGHT
STR R2, [R1]
; Extinguish LED2
LDR R1, =GPIOE_BSRR
LDR R2, =LED_LIGHT
STR R2, [R1]
BX LR ; The function returns
NOP
END ; End of assembly file
The effect is as follows :( Turn into GIF The back is reversed , I don't know why I'm coming )
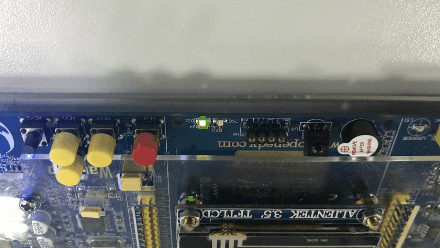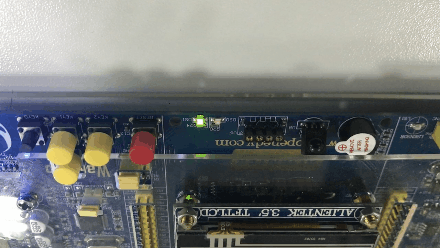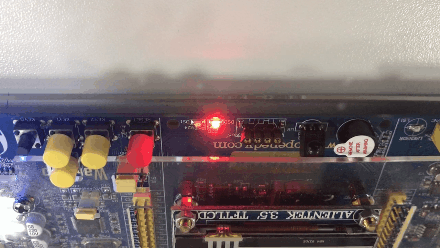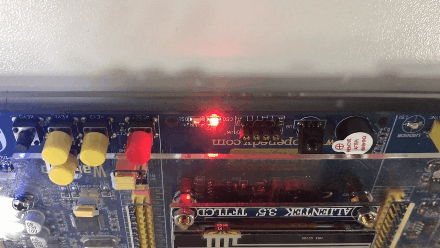
版权声明
本文为[Chenxr32]所创,转载请带上原文链接,感谢
https://yzsam.com/2022/04/202204230356325276.html
边栏推荐
- QT program integration easyplayer RTSP streaming media player screen flicker what is the reason?
- VS Studio 修改C語言scanf等報錯
- Jupiter notebook modify configuration file setting startup directory is invalid
- ROS series (IV): ROS communication mechanism series (6): parameter server operation
- matlab讀取多張fig圖然後合並為一張圖(子圖的形式)
- (valid for personal testing) compilation guide of paddedetection on Jetson
- According to the category information and coordinate information of the XML file, the category area corresponding to the image is pulled out and stored in the folder.
- 【NeurIPS 2019】Self-Supervised Deep Learning on Point Clouds by Reconstructing Space
- A function second kill 2sum 3sum 4sum problem
- vscode删除卸载残余
猜你喜欢

Paddlepaddle does not support arm64 architecture.

作为一名码农,女友比自己更能码是一种什么体验?

The great gods in acmer like mathematics very much

The whole process of connecting the newly created unbutu system virtual machine with xshell and xftp

MATLAB lit plusieurs diagrammes fig et les combine en un seul diagramme (sous forme de sous - Diagramme)
![[BIM introduction practice] wall hierarchy and FAQ in Revit](/img/95/e599c7547029f57ce23ef4b87e8b9a.jpg)
[BIM introduction practice] wall hierarchy and FAQ in Revit
Writing latex with vscode - the latest tutorial 2022 / 4 / 17

A sword is a sword. There is no difference between a wooden sword and a copper sword
Express middleware ② (classification of Middleware)
【NeurIPS 2019】Self-Supervised Deep Learning on Point Clouds by Reconstructing Space
随机推荐
列表、元组、字典和集合的区别
ROS series (IV): ROS communication mechanism series (3): parameter server
Basic introduction to spot gold
Nel ASA:挪威Herøya设施正式启用
ROS series (I): rapid installation of ROS
Vs studio modifies C language scanf and other errors
[AI vision · quick review of today's sound acoustic papers issue 1] Thu, 14 APR 2022
Jupiter notebook modify configuration file setting startup directory is invalid
为什么推荐你学嵌入式
【Echart】echart 入门
CRF based medical entity recognition baseline
Matlab reads multiple fig graphs and then combines them into one graph (in the form of sub graph)
Network principle | connection management mechanism in TCP / IP important protocol and core mechanism
[AI vision · quick review of robot papers today, issue 28] wed, 1 Dec 2021
Source code and update details of new instance segmentation network panet (path aggregation network for instance segmentation)
Hard core chip removal
硬核拆芯片
[latex] differences in the way scores are written
【测绘程序设计】坐标方位角推算神器(C#版)
【李宏毅2022 机器学习春】hw6_GAN(不懂..)