当前位置:网站首页>DAY25: Logic Vulnerability
DAY25: Logic Vulnerability
2022-08-10 08:32:00 【EdmunDJK】
DAY25: Logic Vulnerability
1. Introduction to Logic Vulnerabilities
Logic loopholes refer to the fact that some logic branches cannot properly handle or handle errors due to imprecise program logic or too complicated logic.In layman's terms: After a system has too many functions, it is difficult for program developers to think comprehensively, and there may be omissions in some places, or they may not be handled correctly, resulting in logical loopholes.Logic loopholes can also be said to be errors in the thinking of program developers and loopholes in the logic of program developers.
1.1, Vulnerability Type
(1) traversal
(2) Urban
(3) Payment
(4) Conditional competition
1.2, Features
Very hidden and dangerous
2, unauthorized vulnerability
2.1, Vulnerability Overview
Ultra vires is beyond the scope of authority or power.Most web applications have permission division and control, but if there are flaws in the design of permission control functions, attackers can use these flaws to access unauthorized functions or data, which is what we usually call ultra-privilege vulnerabilities.After the attacker oversteps his authority, he can perform some operations, such as viewing sensitive information, performing some operations such as addition, deletion, modification, and inspection.An unauthorized vulnerability is a very common logical security vulnerability.It is because the server side trusts the data operation request put forward by the client too much and ignores the judgment of the user's operation authority. As a result, modifying the relevant parameters can have the functions of adding, deleting, checking, and changing other accounts, resulting in an unauthorized vulnerability.
2.2, Vulnerability Type
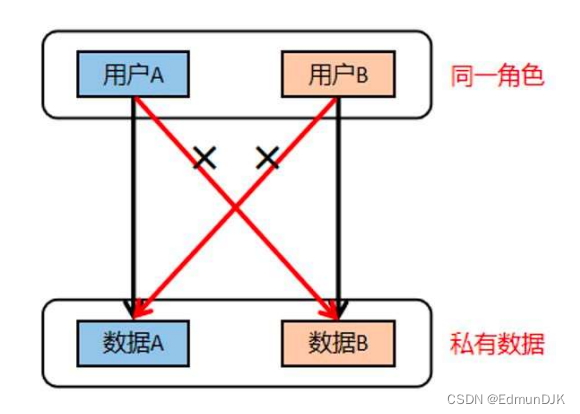
(1) Horizontal override
Refers to an attacker attempting to access a user resource that has the same permissions as him.
(2) Vertical override
Vertical override is a loophole caused by the design flaw of "URL-based access control". Vertical override can be divided into two types, namely upward override and downward override.

3. Payment loopholes
3.1, Vulnerability Overview
Payment loopholes are loopholes at the business logic level in the payment process of the system.There may be payment loopholes in all functions involving purchase, payment, etc.

You can also use some conditional competition or weak type comparison

4, verification code vulnerability
4.1, Vulnerability Overview
As a means of distinguishing between humans and machines, CAPTCHA plays an important role in the field of computer security.Without the verification code, attackers can illegally take over user accounts through brute force cracking, or perform arbitrary user registration on the website.The purpose of setting the verification code is to prevent automatic attacks, but if it is not designed well, it will be useless, so understanding the principle of verification code and the reasons for the loopholes will help to improve the security index of the website in a more comprehensive way
4.2. Mechanism of verification code
Step1: Client initiates a request
Step2: The server responds and creates a new SessionID and generates a random verification code
Step3: Return the verification code and SessionID to the client together
Step4: The client submits the verification code together with the SessionID to the server
Step5: The server verifies the verification code and destroys the current session and returns the result to the client
4.3, verification code classification
(1) Picture verification code
(2) SMS verification code
(3) Behavioral verification code
(4) Voice verification code
(5) Video verification code

4.4. Use of verification code
(1) The verification code can be blasted
(2) The verification code will be echoed back
(3) Fixed verification code
(4) The verification code can be guessed
(5) The verification code can be bypassed
(6) The verification code is invalid
(7) The verification code is generated and verified by the client
5, verification code vulnerability
(1) Use a strong verification code
(2) The verification code should not be generated by the client or returned to the client
(3) During development, the system pays attention to the verification and identification and destroys the verification code in the session
(4) Restricting the verification code submitted by the user cannot be empty, and the server will perform a secondary verification of the verification code on the mobile phone/email. Strong security verification code
(2) The verification code should not be generated by the client or returned to the client
(3) During development, the system pays attention to the verification and identification and destroys the verification code in the session
(4) The verification code submitted by the user is restricted from being empty, and the server performs a secondary verification on the verification code of the mobile phone/email
边栏推荐
- [深入研究4G/5G/6G专题-56]: L3信令控制-5-无线承载管理
- 1499. 满足不等式的最大值 堆/双端队列
- In the SQL SERVER database, if the data of the table is added, deleted, or modified, will the index of the table be recorded in the ldf log?
- 问下cdc mysql to doris.不显示具体行数,怎么办?
- js reduce
- PHP笔记 28 29 30 31
- Rust learning: 6.3_ Tuples of composite types
- 1-31部 1-31套 和硬件工程师90天学习资料及笔记汇总
- Guys, may I ask, the oraclecdc error report is not serialized, but I see that the source code does not inherit serialization, what is the reason?
- CV-人脸识别-2018:ArcFace
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
占位占位1
速卖通卖家如何抓住产品搜索权重
【FAQ】【Push Kit】推送服务,回执配置一直报错、回执过期修改、怎么删除配置的回执
【OAuth2】二十、OAuth2扩展协议 PKCE
MySQL的用户临时表与内部临时表
winget包管理器
每日一题,二叉树中增加一行
mySQL增删改查进阶
NPU architecture and force analysis
js--------对象数组转换成二维数组(excel表格导出)
Introduction to the C language to realize bubble sort
Synchronization lock synchronized traces the source
明明加了唯一索引,为什么还是产生重复数据?
PTA 习题2.2 数组循环左移
UGUI - Events, iTween Plugin
短视频同城流量宣传小魔推有何优势?如何给实体商家带来销量?
Rust学习:6.4_复合类型之枚举
The precise effect of network integration promotion outsourcing in the era of Internet of Things-Shenzhen Win-Win World News
Day37 LeetCode
[Learn Rust together | Advanced articles | RMQTT library] RMQTT message server - installation and cluster configuration