当前位置:网站首页>Huashu "deep learning" and code implementation: 01 Linear Algebra: basic concepts + code implementation basic operations
Huashu "deep learning" and code implementation: 01 Linear Algebra: basic concepts + code implementation basic operations
2022-04-23 02:40:00 【LiBiGor】
1 Scalar 、 vector 、 Matrices and tensors
2 Matrix and vector multiply
3 Identity matrix and inverse matrix
3.0 Unit matrix
a = np.identity(3) # Three row and three column identity matrix 3.1 The matrix of the inverse
A = [[1.0,2.0],[3.0,4.0]]
A_inv = np.linalg.inv(A)
print("A The inverse matrix ", A_inv)3.1 Transposition
A = np.array([[1.0,2.0],[1.0,0.0],[2.0,3.0]])
A_t = A.transpose()
print("A:", A)
print("A The transpose :", A_t)3.2 Matrix addition
a = np.array([[1.0,2.0],[3.0,4.0]])
b = np.array([[6.0,7.0],[8.0,9.0]])
print(" Matrix addition : ", a + b)3.3 Matrix multiplication
m1 = np.array([[1.0,3.0],[1.0,0.0]])
m2 = np.array([[1.0,2.0],[5.0,0.0]])
print(" According to the rules of matrix multiplication : ", np.dot(m1, m2))
print(" Multiply by element : ", np.multiply(m1, m2))
print(" Multiply by element : ", m1*m2)
v1 = np.array([1.0,2.0])
v2 = np.array([4.0,5.0])
print(" Vector inner product : ", np.dot(v1, v2))4 Linear correlation and generating subspace
5 norm
5.0 Code implementation
5.0.1 Vectorial L1 L2 The infinite norm
a = np.array([1.0,3.0])
print(" vector 2 norm ", np.linalg.norm(a,ord=2))
print(" vector 1 norm ", np.linalg.norm(a,ord=1))
print(" Vector infinite norm ", np.linalg.norm(a,ord=np.inf))5.0.2 Matrix F norm
a = np.array([[1.0,3.0],[2.0,1.0]])
print(" matrix F norm ", np.linalg.norm(a,ord="fro"))5.1 The general definition of norm
A norm is a function that maps a vector to a nonnegative value . Intuitively speaking , vector x From the origin to the point x Distance of .
5.1.1 Definition

5.1 L1 norm
5.1.1 Definition
When the difference between zero and non-zero elements in machine learning is very important , In these cases , Instead, use the same slope at each position , You usually use L1 norm , It is also often used as an alternative function to represent the number of non-zero elements .
5.1.2 Mathematical expression

5.2 L2 norm / Euclid Norm
Represents starting from the origin to the vector x Euclidean distance of a certain point .
5.2.1 square L2 norm
It is also often used to measure the size of vectors , It can be calculated simply by point product , It grows very slowly near the origin .
5.2.2 square L2 Norm and L2 Norm comparison
square L2 Norm pair x The derivative of each element in depends only on the corresponding element .
L2 The derivative of the norm for each element is related to the entire vector .
5.3 Maximum norm
5.3.1 meaning
Represents the absolute value of the element with the largest amplitude in the vector :
5.3.2 Definition
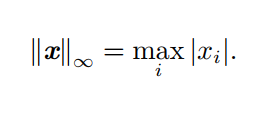
5.4 F norm
5.4.1 meaning
F Norm is used to measure the size of the matrix
5.4.2 Mathematical definition

5.5 Use norm to express dot product

6 Special matrix
6.1 Diagonal matrix
Contains only non-zero elements on the main diagonal , All other positions are zero .
6.1.1 The meaning of diagonal matrix
By limiting some matrices to diagonal matrices , We can get a lower computational cost ( And to the point ) Algorithm .
6.1.2 Multiplication calculation of nonstandard diagonal matrix

6.2 Symmetric matrix

6.3 Orthogonal matrix
Row vector and column vector are square matrices which are respectively standard orthogonal :

6.4 Unit vector and orthogonal

6.5 Orthonormal
If these vectors are not only orthogonal to each other , And the norm is 1, So we call them orthonormal .
7 Characteristics of decomposition
7.0 Code implementation : Characteristics of decomposition
A = np.array([[1.0,2.0,3.0],
[4.0,5.0,6.0],
[7.0,8.0,9.0]])
# Calculate eigenvalues
print(" The eigenvalue :", np.linalg.eigvals(A))
# Calculate the eigenvalues and eigenvectors
eigvals,eigvectors = np.linalg.eig(A)
print(" The eigenvalue :", eigvals)
print(" Eigenvector :", eigvectors)7.1 Definition
The matrix is decomposed into a set of eigenvectors and eigenvalues .
7.2 computing method

7.3 Tip
Not every matrix can be decomposed into eigenvalues and eigenvectors .
Every real symmetric matrix can be decomposed into real eigenvector and real eigenvalue .

7.4 Positive definite 、 Semi positive definite 、 Negative definite 、 Seminegative definite matrix
- A matrix in which all eigenvalues are positive is called a positive definite matrix .
- A matrix whose eigenvalues are nonnegative is called a positive semidefinite matrix .
- A matrix in which all eigenvalues are negative is called a negative definite matrix .
- A matrix whose eigenvalues are all non positive numbers is called a semi negative definite matrix .
8 Singular value decomposition (singular value decomposition, SVD)
8.0 The code realizes singular value decomposition
A = np.array([[1.0,2.0,3.0],
[4.0,5.0,6.0]])
U,D,V = np.linalg.svd(A)
print("U:", U)
print("D:", D)
print("V:", V)8.1 meaning
The matrix is decomposed into singular vectors and singular values .
8.1 Decomposition calculation method

9 Pseudo inverse
9.1 Problem solved

If matrix A The number of rows is greater than the number of columns , Then the above equation may not have a solution . If matrix A The number of rows is less than the number of columns , Then the above matrix may have multiple solutions .
9.2 The calculation process

10 Trace operation
10.1 The definition of trace

10.2 Trace operation provides a description matrix Frobenius The way of norm :
10.3 Operational rules
10.3.1 Trace operation is invariant under transpose operation

10.3.2 Trace of square matrix obtained by multiplication of multiple matrices , It's the same trace that multiplies the last of these matrices when they're moved to the front .

10.3.3 After cyclic permutation, the shape of the matrix obtained by the matrix product changes , The result of trace operation remains unchanged .

10.3.4 Scalar is still itself after trace operation

11 determinant
11.1 Definition
determinant , Write it down as det(A), It's a general square A Functions mapped to real numbers .
11.2 The characteristics of determinant
- Determinant is equal to the product of matrix eigenvalue .
- The absolute value of determinant can be used to measure the expansion or reduction of space after matrix multiplication .
- If the determinant is 0, Then space shrinks completely along at least one dimension , Make it lose all its volume .
- If the determinant is 1, So this transformation keeps the volume of space constant .
版权声明
本文为[LiBiGor]所创,转载请带上原文链接,感谢
https://yzsam.com/2022/04/202204220810526212.html
边栏推荐
- 在MySQL Workbench中执行外部的SQL脚本,报错
- Intelligent agricultural management model
- Leetcode cooking
- 一、序列模型-sequence model
- 每日一题冲刺大厂第十六天 NOIP普及组 三国游戏
- php+mysql对下拉框搜索的内容修改
- Niuke hand speed monthly race 48 C (I can't understand the difference. It belongs to yes)
- Day 4 of learning rhcsa
- php+mysql對下拉框搜索的內容修改
- Web learning record (medium)
猜你喜欢

How to solve the complexity of project document management?

一、序列模型-sequence model
Flink stream processing engine system learning (III)

013_ Analysis of SMS verification code login process based on session

php+mysql对下拉框搜索的内容修改
RT_ Thread ask and answer
005_ redis_ Set set

RT_Thread自问自答

Those years can not do math problems, using pyhon only takes 1 minute?

使用Go语言构建Web服务器
随机推荐
windows MySQL8 zip安装
grain rain
005_ redis_ Set set
Class initialization and instance initialization interview questions
MySQL JDBC编程
leetcode 烹飪料理
【无标题】
Understanding process (multithreading primary)
智能辅助功能丰富,思皓X6安全配置曝光:将于4月23日预售
打靶narak
SQL server2019 cannot download the required files, which may indicate that the version of the installer is no longer supported. What should I do
JVM class loader
Jupyter for local and remote access to ECS
How to solve the complexity of project document management?
IAR嵌入式开发STM32f103c8t6之点亮LED灯
C语言中*与&的用法与区别 以及关键字static和volatile 的含义
Synchronized lock and its expansion
Deploying sbert model based on torchserve < semantic similarity task >
WordPress calls the specified page content. 2 get_ children()
C语言 171. 最近回文数
