当前位置:网站首页>Android interview Online Economic encyclopedia [constantly updating...]
Android interview Online Economic encyclopedia [constantly updating...]
2022-04-23 07:12:00 【Drink dichlorvos alone】
Preface
This article is for my interview and free time to sort out the common questions of network interview . For my review . Share with you . You can comment and add !
Because the common questions in the interview are usually the network layer , Transport layer and application layer . So I went from top to bottom , To share
Last updated time :2021.12.30
One 、 Application layer FAQs
1.DNS How to get ip Address
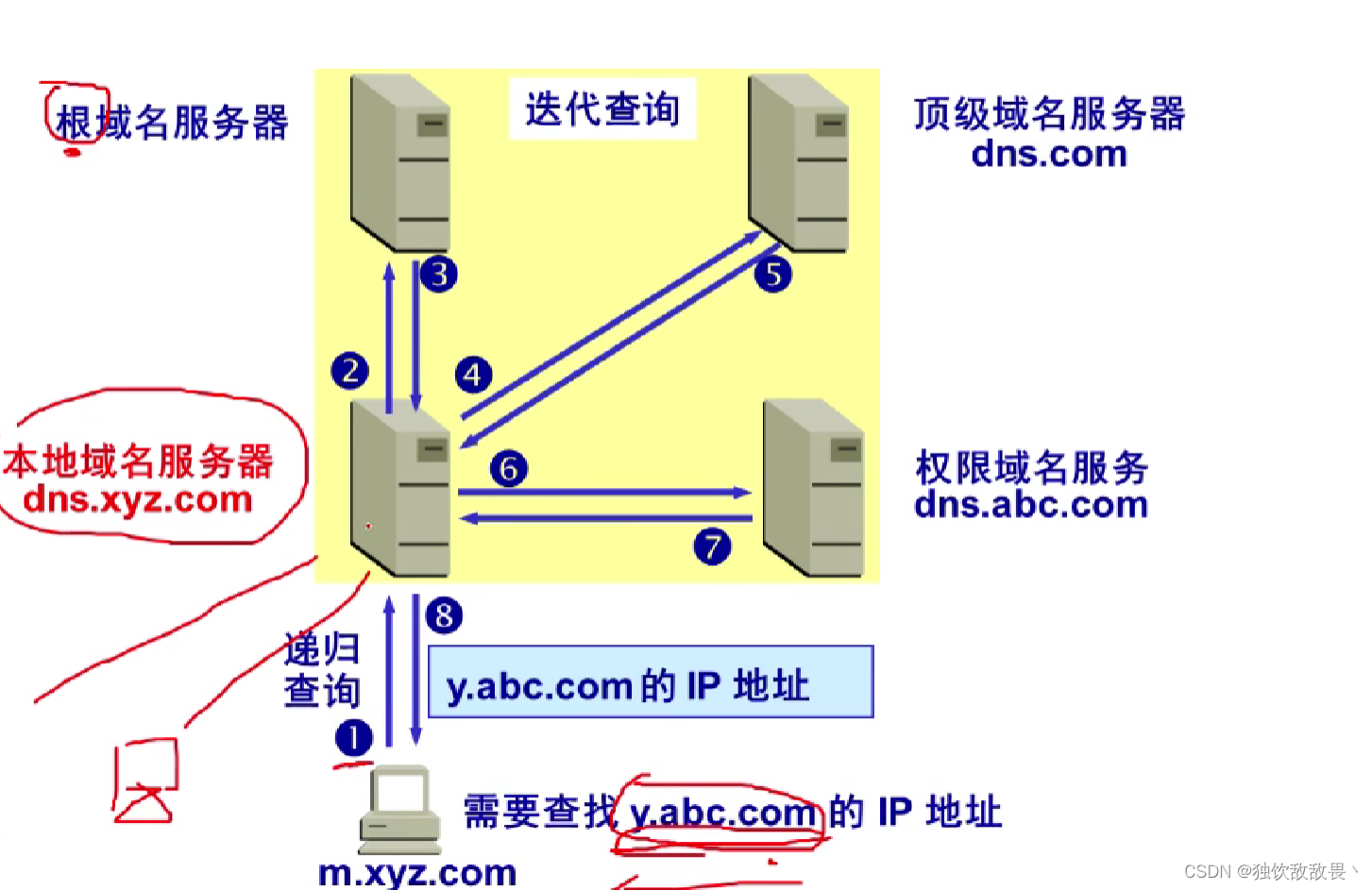
Suppose the domain name is m.xyz.com Your host wants to know another host ( The domain name is y.abc.com ) Of IP Address . for example , host m.xyz.com Plan to send mail to the host y.abc.com. At this time, you must know the host y.abc.com Of IP Address . Query steps :
① host m.xyz.com First to its local domain name server dns.xyz.com Make recursive queries .
② Local domain name server adopts iterative query . It first queries a root domain name server .
③ Root domain name server tells local domain name server , The next top-level domain name server to query dns.com Of IP Address .
④ Local domain name server to top-level domain name server dns.com The query .
⑤ Top-level domain server dns.com Tell local domain name server , The domain name server that should be queried next time dns.abc.com Of IP Address .
⑥ The local domain name server to the permission domain name server dns.abc.com The query .
⑦ Domain name server dns.abc.com Tell local domain name server , Of the host being queried IP Address .
⑧ The local domain name server finally tells the host the query result m.xyz.com
notes :
① Used 8 individual UDP message .
②m.xyz.com The host name of is m. Top level domain name is com
③ The benefits of using iterative queries : It can greatly reduce the load of the root domain name server , Make... On the Internet DNS The number of query requests and reply messages is greatly reduced .
Upper figure
2.http and https The difference between
① The biggest difference is https Based on the ssl above , The transmitted data is encrypted ( Combination of symmetric encryption and asymmetric encryption ). and http No,
②https You need to apply for a certificate , Generally, there are fewer free certificates , So there will be some expenses
③https and http The ports of are respectively 443 and 80
④ Generally speaking http Page response speed ratio https fast . because HTTP Use TCP Three handshakes to establish a connection , Client and server need to exchange 3 A package , and HTTPS except TCP Three bags of , Plus ssl Handshake needs 9 A package , So the total is 12 A package .
3.http1.0、http1.1、http2.0 The difference between
(1)
HTTP 1.0 The browser and the server only maintain a short connection , Each request requires a connection with the server TCP Connect . If you need to establish a long connection , You need to set a non-standard field ,keep-alive
(2)
①HTTP1.1 in , Long connection is supported by default (Connection: keep-alive)
②HTTP 1.1 It also allows the client not to wait for the result of the last request to return , You can make the next request . But the server must send back the response results in the order of receiving the client's requests , To ensure that the client can distinguish the response content of each request
③HTTP1.1 Added more request headers and response headers . And new request methods , Such as put.
(3)
①HTTP/2.0 Support multiplexing . Reuse TCP Connect , In a connection , Both the client and the browser can send multiple requests or responses at the same time , And it doesn 't have to be 11 in sequence , This avoids ” The team's head is jammed ”
(http1.1 Although reuse is allowed TCP Connect , But the same TCP Connect the inside , All data communication is in order , The server can only process one request , Then the next request will be processed . If the front processing is particularly slow , There will be a lot of requests waiting in line .HTTP2.0 Is fully multiplexed , Not ordered and blocked .)
②HTTP2.0 Support header compression . That is, using the header table . Store previously sent key value pairs , For the same data , No longer sends per request and response .
③HTTP2.0 Support server push .
4. Enter... In the browser www.baidu.com After the implementation of the whole process
① Browser direction DNS The server sends a request to resolve the domain name ;(ip agreement 、UDP agreement ,ARP agreement ,OSPF agreement )
②DNS The server resolves the domain name to the corresponding IP Address , And return it to the client ;
③ Browser and server setup TCP Connect ( The default port is 80,https by 443);
④ The browser sends out HTTP Request message ;
⑤ Server reply HTTP response message ;
⑥ Browser parse response message , And displayed in Web On the web ;
⑦ End of receiving and sending message , Release TCP Connect .
Two 、 Common problems of transportation layer
1.TCP How to achieve reliable transmission
① Establishing a connection : Three handshakes
② send data :
use window To send and receive data ( The data has serial number ), Yes Acknowledgement mechanism , Timeout retransmission mechanism . besides , also Flow control and congestion control .
③ Connection release : Four handshakes
2.TCP Three handshake process
Just look at the picture
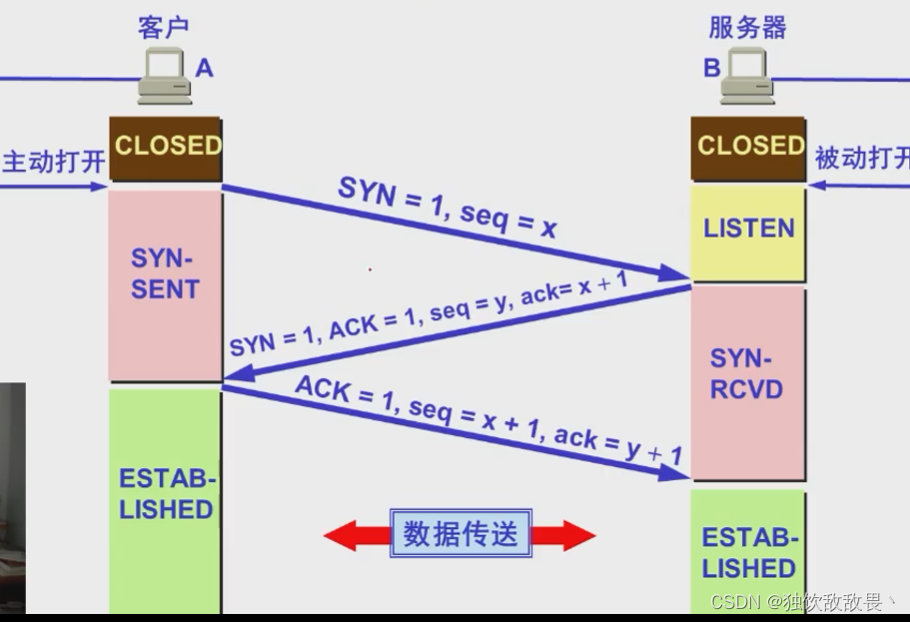
Why use 3 The second handshake , instead of 2 And then ?
The triple handshake is used to prevent invalid connection request segments from suddenly being transmitted to the host B, So there's a mistake . The invalid connection request segment refers to : host A The connection request made was not received by the host B The confirmation of , So after a while , host A Again to the host B Send a connection request , And it's built successfully , Complete data transmission in sequence . Consider such a special case , host A The first connection request sent was not lost , It's because the network node causes delays to reach the host B, host B Thought it was the mainframe A New connections started again , So the host B Agree to connect , And to the host A Send back confirmation , But at this point the host A Don't pay any attention to , host B Just waiting for the host A send data , Lead to a host B Waste of resources .
3.TCP The whole process of four waves
Just look at the picture

Be careful :
(1) Why do you need to wave four times ? because TCP It's full duplex , Client to server FIN When , It means that the client does not send data to the server , But the server can send data to the client , The client can also receive data .
(2) Four waves , Not necessarily four times , Middle two steps , It is possible to merge
(3) Why TIME_WAINTING state ?
① be in TIME_WAINTING In the state of , Application is not allowed to release port , etc. TIME_WAINTING Time for , The server will transmit all the data , Release again at this time
② If the client sends a breakup confirmation signal , The fourth wave , lost , Then the server will send again , If the range TIME_WAINTING Time for , Then the third wave sent by the server , The client cannot accept
4.TCP Congestion control
(1) How to judge congestion ? let me put it another way , What will reduce the congestion window ?
① Retransmission timer timeout ( It means it's congested )
② Received three identical ACK( It indicates that there may be congestion )
(2) When congestion occurs , How to control , Or how to prevent congestion ?
The way : Slow start , Congestion avoidance , Fast retransmission , Fast recovery
5.TCP The difference between flow control and congestion control
Flow control is realized through the receiving window , Generally, the receiver , The receiver sends a confirmation message , To regulate the sending window of the sender . It's not a global .
Congestion control is realized through congestion window , Generally, the line is considered . To control the overall situation , Both the receiver and the receiver are considered , Also consider the sender , Also consider the line between the receiver and the sender . When the line is congested , The line will regulate the congestion window .
So the final sending window is The receiving window of the receiver and the congestion window of the line minimum value decision
6.TCP unpacking / What is a sticky bag
unpacking , Just more than one point , Sticky package , It's all in one . That is to say TCP Reuse and reuse
How to solve TCP Sticking and unpacking characteristics of ?
① The message was made into a fixed length
② Or the message header includes the length of the message
③ Use special delimiters ( such as ftp agreement , No messages , Use carriage return line feed , To distinguish between different messages )
7.UDP Where to use it
① need multicast Of ,TCP Only unicast
② Packet loss does not affect the normal use of software
③ Software that requires high real-time performance
UDP Implemented software , Don't want him to lose his bag , What do I do ?
The upper layer uses itself to realize reliable transmission . Such as UDT. It is said that HTTP3 Will use UDT To achieve
8.TCP and UDP What's the difference
TCP Connection oriented , There are three handshakes and four waves ,UDP No connection , So it can also be used for broadcasting
TCP It's reliable , Specifically, timeout retransmission ( Calculate how long to wait for retransmission according to the round-trip delay ) And response confirmation
TCP There is data sorting , That is, at the opposite end , When the groups are combined , How to sort by number
TCP With flow control ( The sliding window ) And congestion control
Generally speaking ,UDP Send data faster , Real time is better than TCP stronger
9.socket What is it
The operating system hides all the details related to network communication at the bottom , use socket To operate , It's a facade pattern , call connect Method is connected .TCP use The host IP Address plus port number on the host As TCP End of connection , This kind of endpoint is called a socket .
It can be understood as the transport layer , And the following agreements , It's all encapsulated . From the perspective of application layer to the next layer , Namely socket
3、 ... and 、 Network layer FAQs
1.IP Classification of addresses
A Class address : With 0 start , First byte range :1~126(1.0.0.0 - 126.255.255.255);
B Class address : With 10 start , First byte range :128~191(128.0.0.0 - 191.255.255.255);
C Class address : With 110 start , First byte range :192~223(192.0.0.0 - 223.255.255.255);
D Class address : With 1110 start , First byte range :224~239(224.0.0.0 - 239.255.255.255);( Use as multicast )
All host numbers are 1 Of is the broadcast address
ip The address and subnet mask are bitwise AND , Get the network number
2.ARP How the protocol works
① First , Each host will be on its own ARP Create a... In the buffer ARP list , To indicate that IP Address and MAC Correspondence between addresses .
② When the source host wants to send data , First check ARP Is there a corresponding... In the list IP Address of the destination host MAC Address , If there is , Send data directly , without , Send... To all hosts of this network segment ARP Data packets , The data package includes : The source host IP Address , The source host MAC Address , Of the destination host IP Address .
③ When all hosts of the network receive the ARP Packet time , First check... In the packet IP Is the address your own IP Address , If not , Then ignore the packet , If it is , First, take out the... Of the source host from the packet IP and MAC Address written to ARP In the list , If it already exists , Coverage , Then put your own MAC Address write ARP Response package , Tell the source host that it is what it is looking for MAC Address .
④ Source host received ARP After responding to the package . Will target the host's IP and MAC Address write ARP list , And use this information to send data . If the source host has not received ARP Response packets , Express ARP The query fails .
Broadcast transmission ARP request , Single broadcast to send ARP Respond to .
3. Problems related to routing protocol
RIP,OSPF,BGP Which floor do they belong to , In fact, it is still controversial . In my submission RIP,BGP It should be in the application layer ,OSPF It's better at the transport layer . because RIP use UDP,BGP use TCP,OSPF use IP. So it's divided like this
(1) Internal gateway protocol
①RIP It's the internal gateway protocol . It believes that a good route is that it passes through a small number of routers , Short distance . Not more than 15 jump .
Three characteristics
regular And the only Adjacent routers Exchange each other's All information
Update algorithm : Drawing interpretation
②OSPF It's for customer service RIP Disadvantages of R & D . namely “ Shortest path first ”, Using the dijestra algorithm
RIP It can only be applied to small-scale networks ,OSPF It can be applied to large-scale networks . It divides an autonomous system into several smaller areas .
(2) External gateway protocol
BGP It is a routing protocol between different autonomous systems , Will choose something similar to “ Spokesman ” To exchange routing information .
Four 、 General questions
1. Equipment on each floor
The physical layer : Repeater , A hub
Data link layer : bridge , Switch
The network layer : Router
Transport layer : gateway
2. agreement
OSI layered (7 layer ): The physical layer 、 Data link layer 、 The network layer 、 Transport layer 、 The session layer 、 The presentation layer 、 application layer .
TCP/IP layered (4 layer ): Network interface layer 、 The layer 、 Transport layer 、 application layer .
Five layer agreement (5 layer ): The physical layer 、 Data link layer 、 The network layer 、 Transport layer 、 application layer .
Network security related issues
1. All kinds of hijackings
DNS hijacked , It means putting DNS Parsed ip Address , Replace it with a wrong ip Address , It could be a phishing website
HTTP hijacked , It means hijacking http Request message or response message . terms of settlement : use https
2. Flooding attack
Flooding attack is the message sent by the client for the first time , Source ip The address is false , So after the server sends the confirmation message , There has been no response , Just waiting for , Wasting resources

版权声明
本文为[Drink dichlorvos alone]所创,转载请带上原文链接,感谢
https://yzsam.com/2022/04/202204230606380165.html
边栏推荐
- Exception record-9
- MySQL笔记5_操作数据
- 组件化学习
- Oracle和mysql批量查询用户下所有表名和表名注释
- MarkDown基础语法笔记
- 【2021年新书推荐】Effortless App Development with Oracle Visual Builder
- iTOP4412 FramebufferNativeWindow(4.0.3_r1)
- MySQL notes 2_ data sheet
- Viewpager2 realizes Gallery effect. After notifydatasetchanged, pagetransformer displays abnormal interface deformation
- this.getOptions is not a function
猜你喜欢

mysql和pgsql时间相关操作

JVM basics you should know
取消远程依赖,用本地依赖

【2021年新书推荐】Practical Node-RED Programming
this. getOptions is not a function
C connection of new world Internet of things cloud platform (simple understanding version)

【2021年新书推荐】Learn WinUI 3.0

Bottomsheetdialogfragment conflicts with listview recyclerview Scrollview sliding

Ffmpeg common commands

常用UI控件简写名
随机推荐
利用队列实现栈
Oracle Job定时任务的使用详解
oracle 修改默认临时表空间
Android清除应用缓存
Ffmpeg common commands
Abnormal record-22
实习做了啥
几款电纸书阅读器参数对比
Tiny4412 HDMI display
Bottom navigation bar based on bottomnavigationview
一款png生成webp,gif, apng,同时支持webp,gif, apng转化的工具iSparta
第三篇:docker安装mysql容器(自定义端口)
js时间获取本周一、周日,判断时间是今天,今天前、后
Abnormal record-15
【机器学习】笔记 4、KNN+交叉验证
[Andorid] 通过JNI实现kernel与app进行spi通讯
Itop4412 HDMI display (4.4.4_r1)
Explore how @ modelandview can forward data and pages through the source code
MarkDown基础语法笔记
组件化学习(2)Arouter原理学习