当前位置:网站首页>MySQL基础知识
MySQL基础知识
2022-08-08 23:53:00 【Lora_0925】
字段类型分类
char和varchar类型区别
char:底层会先留出所有空位
varchar:底层不会留空位,输入多少个字符就会计算多少个字符的空位
创建多种字段类型的表
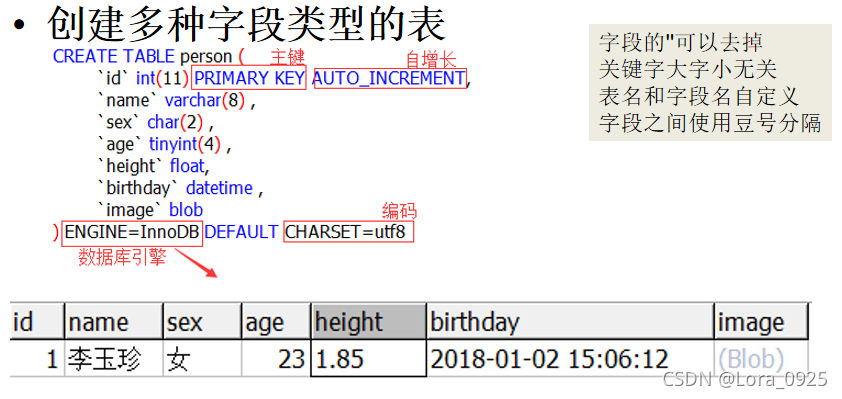
create table husband
(
id int primary key auto_increment,
no char(12) unique,
name char(20) ,
age int
)ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
create table wife
(
id int primary key auto_increment,
no char(12) unique,
name char(20) ,
age int,
`h_id` int,
FOREIGN KEY(`h_id`) REFERENCES `husband` (`id`)
)ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
# FOREIGN KEY(`h_id`)创建wife表的外键值 REFERENCES `husband` (`id`)husband表的主键值
# drop table if exists `husband` 删除表格,如过有其他表格引用此表内容则无法删除什么是主表,什么是从表
没有外键叫主表,有外键叫从表
增加:insert into 表(字段) values(值); 字符串和时间用引号引起来
insert into stu(id, name, sex, age) values (13,'小十三','男', 20);
insert into stu values (14, '小十四', '男', 20);
insert into stu(age)values (20);删除:delete from 表 #where 后面加条件
delete from stu where id=1;
修改:update 表 set 属性1=值1,......,属性n=值n ,修改多个用逗号隔开 #where 后面加条件
update stu set sex='G' where sex='女';
update stu set sex='男' where id>5 and id<10;
update stu set name='小花',sex='G' where sex='女';查询
1.无序查找
2.有条件查找
* 多个条件是按照写的先后排序
select * from zystu order by sex , name;
order by 排序
desc:从大到小
asc: 从小到大(默认值)
select * from table ordery by字段 ---asc:默认升序 desc:降序
可以order by 字段1,字段2,......
select * from stu order by name desc, age desc
运算符 描述
= 等于
<> 不等于,该操作符可被写成 !=
> 大于
< 小于
>= 大于等于
in 多个可能值
not in 不个排除值
between...and... 数值型范围
is null 为空
is not null 不为空
and/&& 并且
or/|| 或
like 搜索某种模式
REGEXP 正则表达式
% 匹配0到多个字符
_ 匹配1个字符
select * from zystu where id=1 or id =2 ;
select * from zystu where id in(2,1,4) ;
select * from zystu where name like '%王';函数
标量函数:对表的计算
as:修改名字(起别名)
UCASE( )查出找后将字母改为大写
NGTH() - 返回某个文本字段的长度 |
ROUND() - 对某个数值字段进行指定小数位数的四舍五入 |
NOW() - 返回当前的系统日期和时间 |
FORMAT() - 格式化某个字段的显示方式 timestampdiff()-时间差 |
now() :
select now();date_format(now);
select name ,sex, date_format(now(),'%Y') from zystu;select name ,sex, date_format(now(),'%Y年 %m月%d日') from zystu;# 结果 2020年 07月28日
格式 | 描述 |
%d | 月的天,数值(00-31) |
%Y | 年 |
%H | 小时 (00-23) |
%h | 小时 (01-12) |
%i | 分钟,数值(00-59) |
%j | 年的天 (001-366) |
%M | 月名 |
%m | 月,数值(00-12) |
%S | 秒(00-59) |
%u | 周 (00-53) 星期一是一周的第一天 |
select * from stu where timestampdiff (year,brith,now())>20;select * from stu order by rand();#将顺序打乱--随机排序
分页查询:
limit a,b : 第一页a从索引0开始(每页首条索引),b每页显示的行数(此时一页两行)最多显示的行数
a=(页数-1)*b
select * from stu limit 0,2; 聚合函数:对组的计算
分组查询:
having avg(age) >20;avg() 聚合函数,统计平均值
where 前面必须是表,对符合条件的表进行筛选
having前面必须是组,对符合条件的组进行筛选
聚合函数:
AVG() - 返回平均值 |
COUNT() - 返回行数 |
FIRST() - 返回第一个记录的值(mysql不支持) |
LAST() - 返回最后一个记录的值(mysql不支持) |
MAX() - 返回最大值 |
MIN() - 返回最小值 |
SUM() - 返回总和 |
分组查询步骤:
1.from
2.where
3.group
4.having
5.select
6.order by
7.limit
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢

Risk Control Modeling 1: Definition of Good and Bad Labels

TensorFlow learning path deep learning 】 【 5: several methods to prevent a fitting and within DNN TensorFlow implementation
测试用例的原则、缺陷报告怎么写你都知道吗?

OSPF实验
postgresql源码学习(35)—— 检查点⑤-检查点中的XLog清理机制
HCIP2--RIP实验

第三章 传输层

并发编程第5篇,Synchronized的原理
Introduction to basic grammar and the foundation of freemarker

RHCSA--第二天
随机推荐
弹出PopupWindow后让背景变暗的方法
pytorch常用代码
测试计划包括哪些内容?目的和意义是什么?
神经网络学习笔记(1)
风控建模四:逻辑回归评分卡开发
并发编程第11篇,线程池的一些常用用法和使用
北斗网络同步时钟与GPS卫星时钟同步设备的区别
了解CI/CD流水线
重发布实验
TensorFlow learning path deep learning 】 【 3: gradient disappear \ explosion and solution
[QNX Hypervisor 2.2用户手册]10.13 shmem - 更新中
pytorch 使用torch.autograd.grad 求导
jira操作流程
win10电脑:电脑触摸板控制
时间对象的格式化
mysql 高级知识【order by 排序优化】
03 Spark on 读取内部数据分区策略(源码角度分析)
深入理解计算系统第三章程序的机器级表达总结
ABP中的数据过滤器
TensorFlow learning path deep learning 】 【 5: several methods to prevent a fitting and within DNN TensorFlow implementation
