当前位置:网站首页>Principle of synchronized implementation
Principle of synchronized implementation
2022-04-23 09:09:00 【MARIO ODYSSEY】
List of articles
One Basic use
1 Three functions
-
Atomicity : Ensure that threads are mutually exclusive to access synchronization code , That is, only one thread will enter the synchronous code block at the same time
-
visibility : Ensure that changes to shared variables are visible in time , Depend on JMM For a variable unlock Before the operation , Must be synchronized to main memory ; On a variable lock operation , The working memory will be emptied ( Thread private ) The value of this variable in , Re from main memory load or assign Initialize variable values
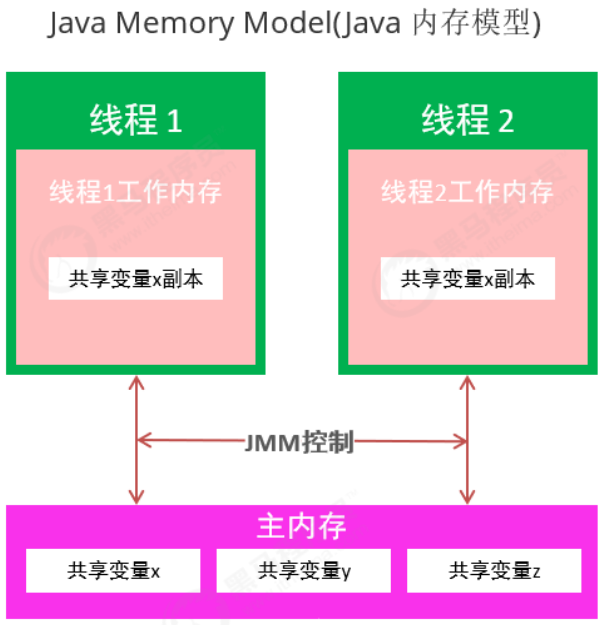
-
Orderliness : Despite the reordering , There is only one block of code that will be synchronized , Instruction rearrangement under single thread is safe
2 Three uses
- lock Example method when , Monitor lock (monitor) Object instance (this)
- lock Static methods when , Monitor lock (monitor) It's the object Class example , That is, all instances of this class are locked
- lock Object instances when , Monitor lock (monitor) It's an example of an object enclosed in parentheses
Two Synchronization principle
The synchronization of data depends on the lock , How to realize lock synchronization ?
synchronizedRely on... At the software level JVM Realize lock synchronizationJUC.LockAt the hardware level, it depends on special CPU Instructions
1 The monitor Monitor
- Each object corresponds to a monitor lock (monitor), Used to implement Heavyweight lock
synchronizedstay JVM The implementation in is based on entry and exit Monitor Object to synchronize methods and code blocks- Every Java Object header of the object Mark Word There are corresponding Monitor References to objects , So any object can be used as a lock
- Monitor Object contains two queues
_EntryListand_WaitSet, Store separately and not get Monitor Object's thread , And once got and waited again Monitor Object's thread- When multiple threads access a piece of synchronous code at the same time, they will first enter
_EntryListaggregate , When the thread gets the monitor after , Get into_OwnerArea and put monitor Medium owner Variable set to current thread , meanwhile monitor The counter in count++ - If the thread calls
wait()Method , Will release what is currently held monitor,owner The variable returns to null,count–, At the same time, the thread enters_WaitSetWaiting to be awakened - If the current thread is finished , Release monitor And reset count, So that other threads can get in monitor

- When multiple threads access a piece of synchronous code at the same time, they will first enter
2 synchronized Used to synchronize code blocks
After decompilation, you can get monitorenter、monitorexit Two instructions are implemented
-
monitorenter: When monitor It will be locked when occupied , Threads executemonitorenterAn attempt was made to get the name of the object while executing the monitor The ownership of the , The process is as follows :- If monitor The number of entries is 0, Then the thread enters monitor, Then set the number of entries to 1, This thread is monitor Owner
- If the thread already owns the monitor, Just re-enter , entering monitor The number of entries plus 1 ( Reentrancy )
- If other threads are already occupied monitor, Then the thread enters the blocking state , until monitor The number of entries is 0, Try again to get monitor The ownership of the
-
monitorexit: performmonitorexitThe thread of must be monitor Owner . Instruction execution ,monitor The number of entries minus 1, If less 1 The last in number is 0, The thread exits monitor, It's not this anymore monitor Owner .monitorexitInsert at the end of the method and at the exception ,JVM Make sure that eachmonitorenterThere must be a correspondingmonitorexit
3 synchronized Method for synchronization
- Method synchronization did not go through the instructions
monitorenterandmonitorexitTo complete , There is essentially no difference between the two synchronization modes , But method synchronization is an implicit way to achieve , No bytecode required - Compared with asynchronous methods , There are too many constants in the constant pool of the synchronization method
ACC_SYNCHRONIZEDIdentifier - When a method is called , The call instruction will check the method's
ACC_SYNCHRONIZEDWhether the access flag is set , If set , Execution thread will get first monitor, Method body can only be executed after obtaining success , Release after method execution monitor . During method execution , No other thread can get the same monitor object
3 Mark Word
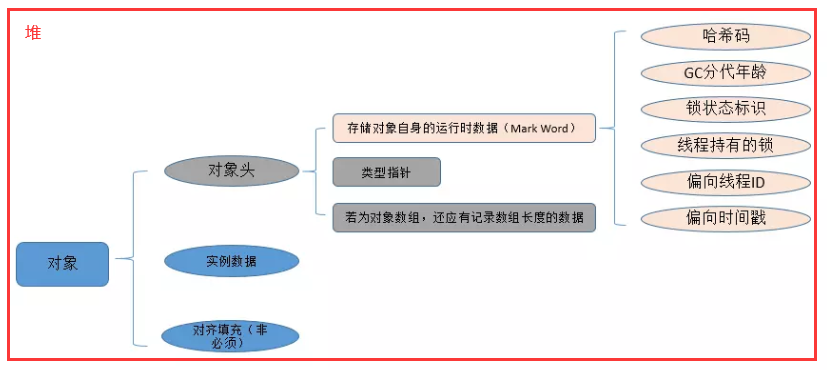
Class Pointer( Type a pointer ): Object to its class metadata , The virtual machine uses this pointer to determine which class instance this object isMark Word( Tag field ): Used to store runtime data of the object itself , It's the realization of Lightweight lock and Biased locking The key to .- Every Java Object header of the object Mark Word There are corresponding Monitor References to objects , So any object can be used as a lock . In order to store as much data as possible in a small memory , Its structure will change as the program runs
4 The head of the object Mark Word And thread Lock Record
- When a thread enters a synchronized code block , If the synchronization object is not locked , Then the virtual machine will first be in the current Threads Created in the stack called “ Lock record (Lock Record)” Space , This space is thread private , be used for Stores the name of the lock object Mark Word A copy of the
- Of every locked object Mark Word And the thread that gets the lock Lock Record relation ( The head of the object Mark Word Medium Lock Word Point to Lock Record From )
- Lock Record There is one of them. Owner Field holds the unique ID of the thread that owns the lock , Indicates that the lock is occupied by this thread
3、 ... and Lock optimization
1 spinlocks
- spinlocks : When a thread tries to acquire a lock , If the lock is occupied by another thread , Just loop through the lock to see if it's released , Instead of going into thread suspend or sleep state
- Reasons for using spin locks :CPU Switching between user state and core state of mind consumes resources ; In most cases, the duration of the lock state is very short
- spinlocks It is applicable to the case that the critical area of lock protection is very small , If the critical area is small , The lock takes a short time . Spin waiting can't replace blocking , Although it can avoid the cost of thread switching , But it takes up CPU Processor time , So we need to specify the appropriate number of spins
- Adaptive spin lock : If the thread spins successfully , So the next spin will be more ; On the contrary, it will reduce the number of spins or even cancel
2 Lock elimination
- In some cases ,JVM No shared data race detected , At this time, these synchronization locks will be eliminated
- When you run this code ,JVM Variables can be detected clearly vector There is no way to escape , So you can vector The internal locking operation is eliminated
public void vectorTest(){
Vector<String> vector = new Vector<String>();
for(int i = 0 ; i < 10 ; i++){
vector.add(i + "");
}
System.out.println(vector);
}
3 Lock coarsening
- If a series of successive lock unlock operations , May cause unnecessary performance loss , Lock coarsening locks multiple consecutive 、 Unlock operations are linked together , Expand to a larger range of locks
- The above example vector Every time add All need to be locked ,JVM Continuous locking of the same object detected 、 Unlock operation , Will merge a larger range of locks 、 Unlock operation , That is, the locking and unlocking operation will move out of the cycle
4 Biased locking
There are four main states of locks , In turn, is : No lock state 、 Biased lock state 、 Lightweight lock state 、 Heavyweight lock state , Locks can be upgraded from biased locks to lightweight locks , Upgrade the heavyweight lock . But lock upgrade is one-way , That is to say, it can only be upgraded from low to high , There will be no lock degradation
- The deflection lock is in Single thread The mechanism used when executing code blocks , If In the environment of multithreading concurrency, it will be transformed into lightweight lock or heavyweight lock
- The main purpose of introducing biased locks is : In order to be in Without multithreading competition Minimize unnecessary lightweight lock execution paths
- Lightweight locks are designed to work on threads Execute synchronization blocks alternately Time to improve performance , The deflection lock is in Only one thread executes the synchronization block Further improve performance
5 Lightweight lock 、 Heavyweight locks and the comparison of three locks *
- If it's single threaded , The cost of biased locking is the least , Just compare object headers in memory , There is no need to CAS
- If other threads compete , Then the biased lock will be upgraded to a lightweight lock
- If other threads go through a certain number of CAS The attempt failed , Then enter the heavyweight lock

版权声明
本文为[MARIO ODYSSEY]所创,转载请带上原文链接,感谢
https://yzsam.com/2022/04/202204230718011675.html
边栏推荐
- Go language self-study series | initialization of golang structure
- Output first order traversal according to second order and middle order traversal (25 points)
- Valgrind and kcache grind use run analysis
- 考研线性代数常见概念、问题总结
- Chris LATTNER, father of llvm: the golden age of compilers
- 政务中台研究目的建设目标,建设意义,技术创新点,技术效果
- To remember the composition ~ the pre order traversal of binary tree
- Is Zhongyan futures safe and reliable?
- Summary of common concepts and problems of linear algebra in postgraduate entrance examination
- What is augmented reality technology? Where can it be used?
猜你喜欢

NPM reports an error: operation not allowed, MKDIR 'C: \ program files \ node JS \ node_ cache _ cacache’

调包求得每个样本的k个邻居
![[SQL Server fast track] view and cursor of database](/img/2c/8edd92ecef11932c982db56af76c3f.png)
[SQL Server fast track] view and cursor of database

Mini - exercice MySQL (seulement pour les débutants, pas pour les non - débutants)

Distributed message oriented middleware framework selection - Digital Architecture Design (7)

I don't understand time, timestamp and time zone. Look at this article

Node installation

Detailed explanation of delete, truncate and drop principles in MySQL database

Pctp test experience sharing

112. 路径总和
随机推荐
【SQL server速成之路】数据库的视图和游标
Go language self-study series | golang method
Brush classic topics
Star Trek's strong attack opens the dream linkage between metacosmic virtual reality
爬虫使用xpath解析时返回为空,获取不到相应的元素的原因和解决办法
基于点云凸包的凹包获取方法
kettle实验
[boutique] using dynamic agent to realize unified transaction management II
npm ERR! network
员工试用期转正申请书(泸州老窖)
Wechat: get the owner of a single tag
政务中台研究目的建设目标,建设意义,技术创新点,技术效果
Non duplicate data values of two MySQL query tables
Kettle实验
PLC的点表(寄存器地址和点表定义)破解探测方案--方便工业互联网数据采集
Illegal character in scheme name at index 0:
机器学习(六)——贝叶斯分类器
ONEFLOW learning notes: from functor to opexprinter
Valgrind and kcache grind use run analysis
Find the sum of simple types of matrices