当前位置:网站首页>Establishment of binary tree and its cueing
Establishment of binary tree and its cueing
2022-04-21 13:24:00 【If sad wave】
Catalog
The binary tree is n( n ⩾ \geqslant ⩾ 0 ) A finite set of nodes , The set is either empty ( It's called an empty binary tree ), Or a root node and two disjoint nodes 、 They are called the left subtree of the root node and the binary tree of the right subtree .
Binary list
Because of the binary number, each node has at most two children , So we can express by linked list , The linked list consists of one data field and two pointer fields .
| lchild | data | rchild |
|---|---|---|
| Pointer to left child | Data fields | Pointer to right child |
typedef struct BiTNode
{
char data;
struct BiTNode *lchild, *rchild;
}BiTNode, *BiTree;
Binary tree creation
Usually create a binary tree in the way of previous order , That is, write the data of a node first , Write the data again , Finally, write its right child data .
/********************************************************************************************\ *function: Create a binary tree by entering the previous order on the keyboard *intput: BiTree *Tree -- BiTNode Second level pointer of ( The pointer to a function passes only its contents , So use the pointer to apply for memory , Secondary pointers should be used ) *output: none *return: void \********************************************************************************************/
void CreateBiTree(BiTree *Tree)
{
char str;
scanf("%c", &str); // Read characters from the keyboard
if (str == '#') // With # Represents an empty node
{
*Tree = NULL;
}
else
{
*Tree = (BiTree )malloc(sizeof(BiTNode)); // Apply for memory for the new node
if(*Tree == NULL)
{
exit(1); // Failed to apply for memory , Interrupt program operation
}
(*Tree)->data = str; // Write this node data
CreateBiTree(&(*Tree)->lchild); // Write left child data
CreateBiTree(&(*Tree)->rchild); // Write right child data
}
}
Binary tree traversal
Usually there are 3 Two ways to traverse a binary tree , I.e. preamble 、 Middle preface 、 Post order method .
Before the order : Read the node data first , Read the data of the left child again , Finally, read the data of the right child ;
Middle preface : First read the data of the left child , Read the data of the node again , Finally, read the data of the right child ;
In the following order : First read the data of the left child , Read the data of the right child again , Finally, read the data of the node .
Let's take preorder traversal as an example , The middle order and the post order only need to exchange the traversal order of the node data and its children .
/********************************************************************************************\ *function: Traversing a binary tree in the way of previous order , And print it *intput: BiTree Tree -- BiTNode The first level pointer of *output: none *return: void \********************************************************************************************/
void PreOrderTraverse(BiTree Tree)
{
if (Tree == NULL) // Determine whether it is a null pointer
{
return;
}
printf("%c ", Tree->data); // Output the data of this node
PreOrderTraverse(Tree->lchild); // The left child
PreOrderTraverse(Tree->rchild); // The right child
}
We can try to compile binary tree creation and traversal functions :
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main(void)
{
BiTree OneTree; // Create node pointer
CreateBiTree(&OneTree); // Create a binary tree in the previous order
printf(" The former sequence traversal :");
PreOrderTraverse(OneTree); // Preorder traversal binary tree
printf("\n In the sequence traversal :");
InOrderTraverse(OneTree); // Middle order ergodic binary tree
printf("\n After the sequence traversal :");
PostOrderTraverse(OneTree); // Post order traversal binary tree
return 0;
}
Output :
abc###de##f##
The former sequence traversal :a b c d e f
In the sequence traversal :c b a e d f
After the sequence traversal :c b e f d a
a
/ \
b d
/ / \
c e f
Clue binary tree
There are a large number of null pointers in the binary tree established by using the linked list above , every last # Are null pointers , It's a big waste of space . Therefore, we can use these null pointers to represent the precursor and successor of a node .
In order to distinguish whether the pointer field points to its child or precursor or successor , Therefore, two flag fields are added . If the left flag field is 0, Then the left pointer field points to the left child , If 1, It points to the precursor , The right flag field is the same .
| lchild | lflag | data | rflag | rchild |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pointer to left child | Left flag field | Data fields | Right flag field | Pointer to right child |
The following figure , In the way of middle order traversal , The solid line indicates the child pointing to the node , The dotted line indicates the precursor or successor to the node .

Creation of clue binary tree
The structure of nodes is defined as follows :
typedef enum
{
Link = 0,
Thread
}PointerFlag;
typedef struct BiThrNode
{
char data; // Data fields
struct BiThrNode *lchild, *rchild; // Left and right child pointer
PointerFlag LFlag; // Left sign
PointerFlag RFlag; // Right sign
}BiThrNode, *BiThrTree;
BiThrTree Pre = NULL; // Precursor pointer
First, create a binary tree in the order of precedence :
/********************************************************************************************\ *function: First, create a binary tree *intput: BiThrTree *T -- BiThrNode Second level pointer of *output: none *return: void \********************************************************************************************/
void CreateBiTree(BiThrTree *T)
{
char str;
scanf("%c", &str);
if (str == '#')
{
*T = NULL;
}
else
{
*T = (BiThrTree )malloc(sizeof(BiThrNode));
if(*T == NULL)
{
exit(1);
}
(*T)->data = str;
(*T)->LFlag = Link; // Creation time , First, make the flag bits indicate pointing to the child
(*T)->RFlag = Link;
CreateBiTree(&(*T)->lchild);
CreateBiTree(&(*T)->rchild);
}
}
Then in the way of medium order traversal , Clue binary tree :
/********************************************************************************************\ *function: Middle order clue binary tree *intput: BiThrTree T -- BiThrNode The first level pointer of *output: none *return: void \********************************************************************************************/
void InThreading(BiThrTree T)
{
if (T == NULL)
{
return;
}
InThreading(T->lchild); // Clue left subtree
if (T->lchild == NULL) // The current node has no left child
{
T->LFlag = Thread; // The flag field is changed to precursor clue
T->lchild = Pre; // The left child's pointer points to the front wheel
}
if (Pre->rchild == NULL) // The precursor node has no right child
{
Pre->RFlag = Thread; // Change the flag field to follow-up clue
Pre->rchild = T; // The right child's pointer points to the successor
}
Pre = T; //T About to point to the next node , Therefore, it is necessary to make Pre Point to the current node
InThreading(T->rchild); // Clue right subtree
}
Finally, define the header pointer , And connect the head pointer with the binary tree :
/********************************************************************************************\ *function: Create header pointer , And connect the head pointer with the binary tree *intput: BiThrTree T -- BiThrNode The first level pointer of *output: none *return: BiThree ThrHead -- The head pointer ( If it's an empty tree , Then the header pointer is a null pointer ) \********************************************************************************************/
BiThrTree CreatInHreading(BiThrTree T)
{
BiThrTree ThrHead;
ThrHead = (BiThrNode *)malloc(sizeof(BiThrNode));// Request memory for header pointer
if (T == NULL)
{
ThrHead = NULL; // If the root node is empty , be ThrHead It's empty
}
else
{
Pre = ThrHead; // take ThrHead Assign to pre,pre Traverse the precursor of the current node for the middle order
InThreading(T); // In binary tree, order is threaded
ThrHead->LFlag = Link;
ThrHead->lchild = T; // The left child of the head pointer points to the head node of the binary tree
Pre->RFlag = Thread;
Pre->rchild = ThrHead; // The last node of the middle order clue tree is followed by ThrHead The head pointer
ThrHead->RFlag = Thread;
ThrHead->rchild = Pre; // The head pointer ThrHead The right child points to the last node
}
return ThrHead; // Return to header node
}
Traversing the clue binary tree in the middle order
/********************************************************************************************\ *function: Traversing the clue binary tree in the middle order *intput: BiThrTree Head -- The head pointer of the clue binary tree *output: none *return: void \********************************************************************************************/
void InOrderTraverse_Thr(BiThrTree Head)
{
BiThrTree p;
p = Head->lchild;
while (p != Head) // At the end of traversal ,p Will point to the head pointer
{
while (p->LFlag == Link) // The first node traversed in middle order
{
p = p->lchild;
}
printf("%c ", p->data);// Print the first node
while ((p->RFlag == Thread) && (p->rchild != Head)) // There are subsequent nodes , And the subsequent node is not a header pointer
{
p = p->rchild;
printf("%c ", p->data); // Print subsequent nodes
}
p = p->rchild; //p Point to its right subtree
}
}
The main function is as follows :
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main(void)
{
BiThrTree R;
CreateBiTree(&R); // Create a binary tree
BiThrTree Head;
Head = CreatInHreading(R); // Middle order clue binary tree
InOrderTraverse_Thr(Head); // Traversing the clue binary tree in the middle order
return 0;
}
Output :
AB#D##C##
B D A C
The threaded binary tree makes full use of the space of the pointer field , Realize the function of two-way traversal , You can traverse backward from the first node , You can traverse forward from the last node .
版权声明
本文为[If sad wave]所创,转载请带上原文链接,感谢
https://yzsam.com/2022/04/202204211322494293.html
边栏推荐
- 百度地图开发自定义信息窗口openInfoWindow样式
- 网络的构成要素
- Shell programming learning (II) variables and operations
- Interface advanced actual combat (unfinished)
- 【数字信号处理】相关系数 ( 相关系数概念解析 | 信号能量常数 | 共轭序列 | 序列在相同时刻的相关性 )
- Algorithem_ Merge Two Binary Trees
- 一文读懂Faster RCNN
- Village vlog harvest 8000w + play, another flow ceiling?
- Wanzi dry goods! Help you master the knowledge of "light and shadow" in design
- Detailed explanation and demonstration of 3-4dom shaped XSS
猜你喜欢

In depth analysis of focal loss loss function
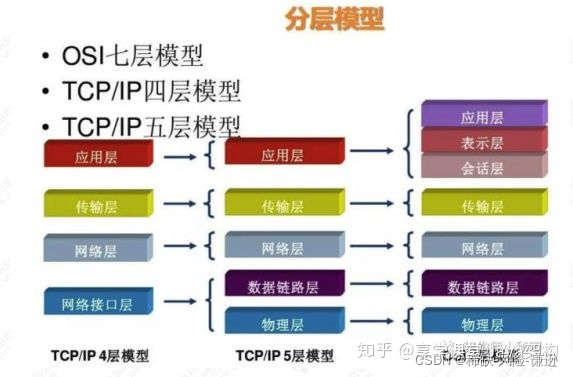
网络通信协议模型
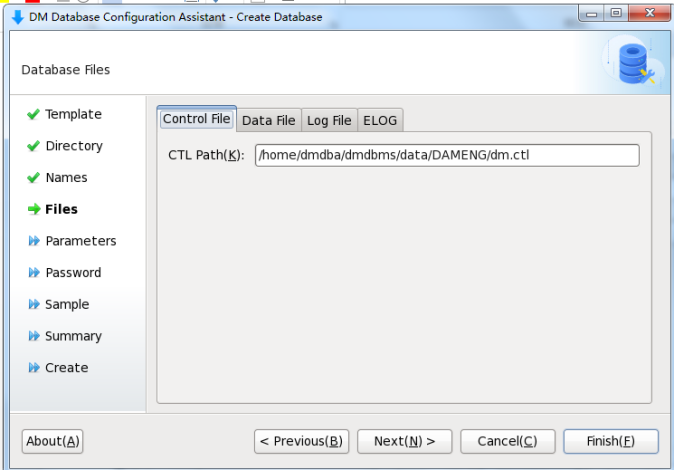
How to install the database of Dameng 8 version in Kirin V10 SP2

Small and medium-sized manufacturing enterprises transformation capacity-building sharing

Detailed explanation and demonstration of 3-4dom shaped XSS

Which brand of running headphones is good and suitable for sports
20210812

What kind of comfortable sports earphones are recommended

twenty million two hundred and ten thousand eight hundred and twelve

Redis data persistence
随机推荐
HCIP之路OSPF拓展配置
【数字信号处理】线性常系数差分方程 ( 使用 matlab 求解 “ 线性常系数差分方程 “ 示例 | A 向量分析 | B 向量分析 | 输入序列分析 | matlab 代码 )
English word analysis of communication protocol
OJ每日一练——数组倒序输出新数组
Wang Baiping: my way to envoy maintainer
Flink相关API开发及运行架构和实现原理详解
Network communication protocol model
20210818日记
UGUI-- Button 按钮组件
L2-013 red alarm (25 points)
大才能否小用?OceanBase一体化场景测试
leetcode:824. 山羊拉丁文【简单字符串操纵】
Interface advanced actual combat (unfinished)
Revit secondary development - creating and switching tags (issue 16)
Revit secondary development - creating grids (phase 9)
Village vlog harvest 8000w + play, another flow ceiling?
Mysql 浅析行锁如何减少冲突提高性能
Meichuang technology was invited to carry out data security training for Haidian District academy of Educational Sciences
一文读懂Faster RCNN
Navlinkmatch of blazor's navlink What does prefix do