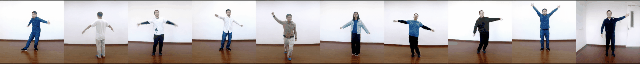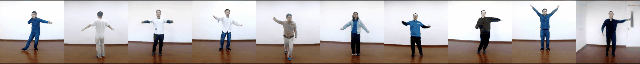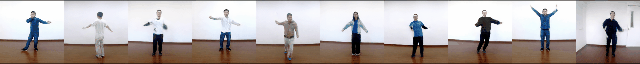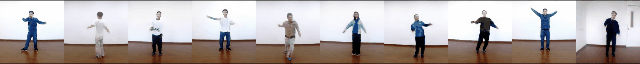
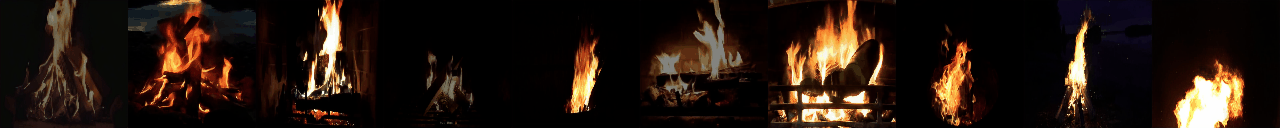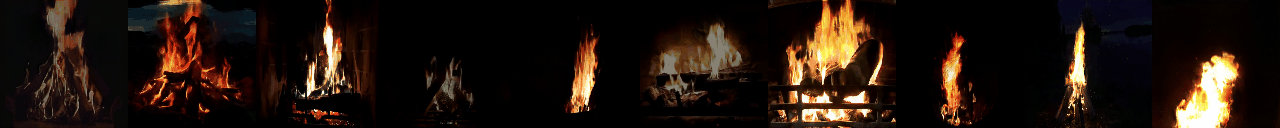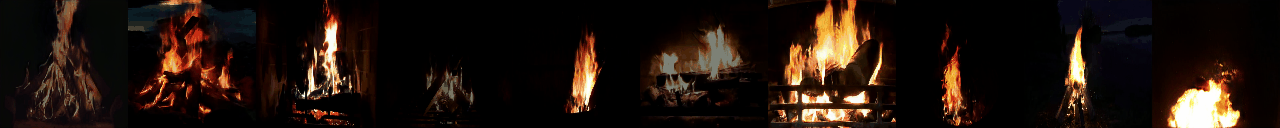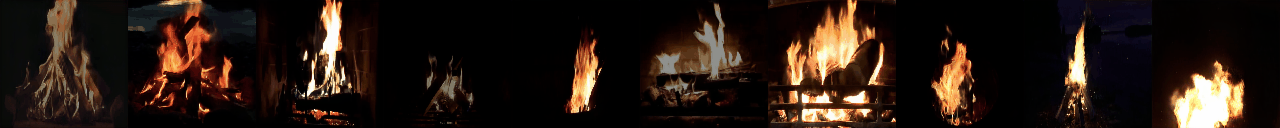Stochastic Image-to-Video Synthesis using cINNs
Official PyTorch implementation of Stochastic Image-to-Video Synthesis using cINNs accepted to CVPR2021.
teaser.mp4
Arxiv | Project Page | Supplemental | Pretrained Models | BibTeX
Michael Dorkenwald, Timo Milbich, Andreas Blattmann, Robin Rombach, Kosta Derpanis*, Björn Ommer*, CVPR 2021
tl;dr We present a framework for both stochastic and controlled image-to-video synthesis. We bridge the gap between the image and video domain using conditional invertible neural networks and account for the inherent ambiguity with a learned, dedicated scene dynamics representation.
For any questions, issues, or recommendations, please contact Michael at m.dorkenwald(at)gmail.com. If our project is helpful for your research, please consider citing.
Table of Content
Requirements
A suitable conda environment named i2v can be created and activated with
conda env create -f environment.yaml
conda activate i2v
For this repository cuda verion 11.1 is used. To suppress the annoying warnings from kornia please run all python scripts with -W ignore.
Running pretrained models
One can test our method using the scripts below on images placed in assets/GT_samples after placing the pre-trained model weights for the corresponding datasets e.g. bair in the models folder like models/bair/.
python -W ignore generate_samples.py -dataset landscape -gpu <gpu_id> -seq_length <sequence_length>
Moreoever, one can also transfer an observed dynamic from a given video (first row) to an arbitrary starting frame using
python -W ignore generate_transfer.py -dataset landscape -gpu <gpu_id>
python -W ignore generate_samples.py -dataset bair -gpu <gpu_id>
Our model can be extended to control specific factors e.g. the endpoint location of the robot arm. Note, to run this script you need to download the BAIR dataset.
python -W ignore visualize_endpoint.py -dataset bair -gpu <gpu_id> -data_path <path2data>
| Sample 1 | Sample 2 |
|---|---|
 |
 |
or look only on the last frame of the generated sequence, which is similar since all videos were conditioned on the same endpoint
| Sample 1 | Sample 2 |
|---|---|
 |
 |
python -W ignore generate_samples.py -dataset iPER -gpu <GPU_ID>
python -W ignore generate_samples.py -dataset DTDB -gpu <GPU_ID> -texture fire
python -W ignore generate_samples.py -dataset DTDB -gpu <GPU_ID> -texture vegetation
python -W ignore generate_samples.py -dataset DTDB -gpu <GPU_ID> -texture clouds
python -W ignore generate_samples.py -dataset DTDB -gpu <GPU_ID> -texture waterfall
Data preparation
BAIR
To download the dataset to a given target directory <TARGETDIR>, run the following command
sh data/bair/download_bair.sh <TARGETDIR>
In order to convert the tensorflow records file run the following command
python data/bair/convert_bair.py --data_dir <DATADIR> --output_dir <TARGETDIR>
traj_256_to_511 is used for validation and traj_0_to_255 for testing. The resulting folder structure should be the following
$bair/train/
├── traj_512_to_767
│ ├── 1
| ├── ├── 0.png
| ├── ├── 1.png
| ├── ├── 2.png
| ├── ├── ...
│ ├── 2
│ ├── ...
├── ...
$bair/eval/
├── traj_256_to_511
│ ├── 1
| ├── ├── 0.png
| ├── ├── 1.png
| ├── ├── 2.png
| ├── ├── ...
│ ├── 2
│ ├── ...
$bair/test/
├── traj_0_to_255
│ ├── 1
| ├── ├── 0.png
| ├── ├── 1.png
| ├── ├── 2.png
| ├── ├── ...
│ ├── 2
│ ├── ...
Please cite the corresponding paper if you use the data.
Landscape
Download the corresponding dataset from here using e.g. gdown. To use our provided data loader all images need to be renamed to frame0 to frameX to alleviate the problem of missing frames. Therefore the following script can be used
python data/landscape/rename_images.py --data_dir <DATADIR>
In data/landscape we provide a list of videos that were used for training and testing. Please cite the corresponding paper if you use the data.
iPER
Download the dataset from here and run
python data/iPER/extract_iPER.py --raw_dir <DATADIR> --processed_dir <TARGETDIR>
to extract the frames. In data/iPER we provide a list of videos that were used for train, eval, and test. Please cite the corresponding paper if you use the data.
Dynamic Textures
Download the corrsponding dataset from here and unzip it. Please cite the corresponding paper if you use the data. The original mp4 files from DTDB can be downloaded from here.
Evaluation
After storing the data as described, the evaluation script for each dataset can be used.
Synthesis quality
We use the following metrics to measure synthesis quality: LPIPS, FID, FVD, DTFVD. The latter was introduced in this work and is a specific FVD for dynamic textures. Therefore, please download the weights of the I3D model from here and place it in the models folder like /models/DTI3D/. For more details on DTFVD please see Sec. C3 in supplemental. To compute the mentioned metrics for a given dataset please run
python -W ignore eval_synthesis_quality.py -gpu <gpu_id> -dataset <dataset> -data_path <path2data> -FVD True -LPIPS True -FID True -DTFVD True
for DTDB please specify the dynamic texture you want to evalute e.g. fire
python -W ignore eval_synthesis_quality.py -gpu <gpu_id> -dataset DTDB -data_path <path2data> -texture fire -FVD True -LPIPS True -FID True -DTFVD True
Please cite our work if you use DTFVD in your work. If you place the chkpts outside this repository please specify the location using the argument -chkpt <path_to_chkpt>.
Diversity
We measure diversity by comparing different realizations of an example using a pretrained VGG, I3D and DTI3D backbone. The last two consider the temporal property of the data whereas for the VGG diversity score compared images framewise. To evaluate diversity for a given dataset please run
python -W ignore eval_diversity.py -gpu <gpu_id> -dataset <dataset> -data_path <path2data> -DTI3D True -VGG True -I3D True -seq_length <length>
for DTDB please specify the dynamic texture you want to evalute e.g. fire
python -W ignore eval_diversity.py -gpu <gpu_id> -dataset DTDB -data_path <path2data> -texture fire -DTI3D True -VGG True -I3D True
Training
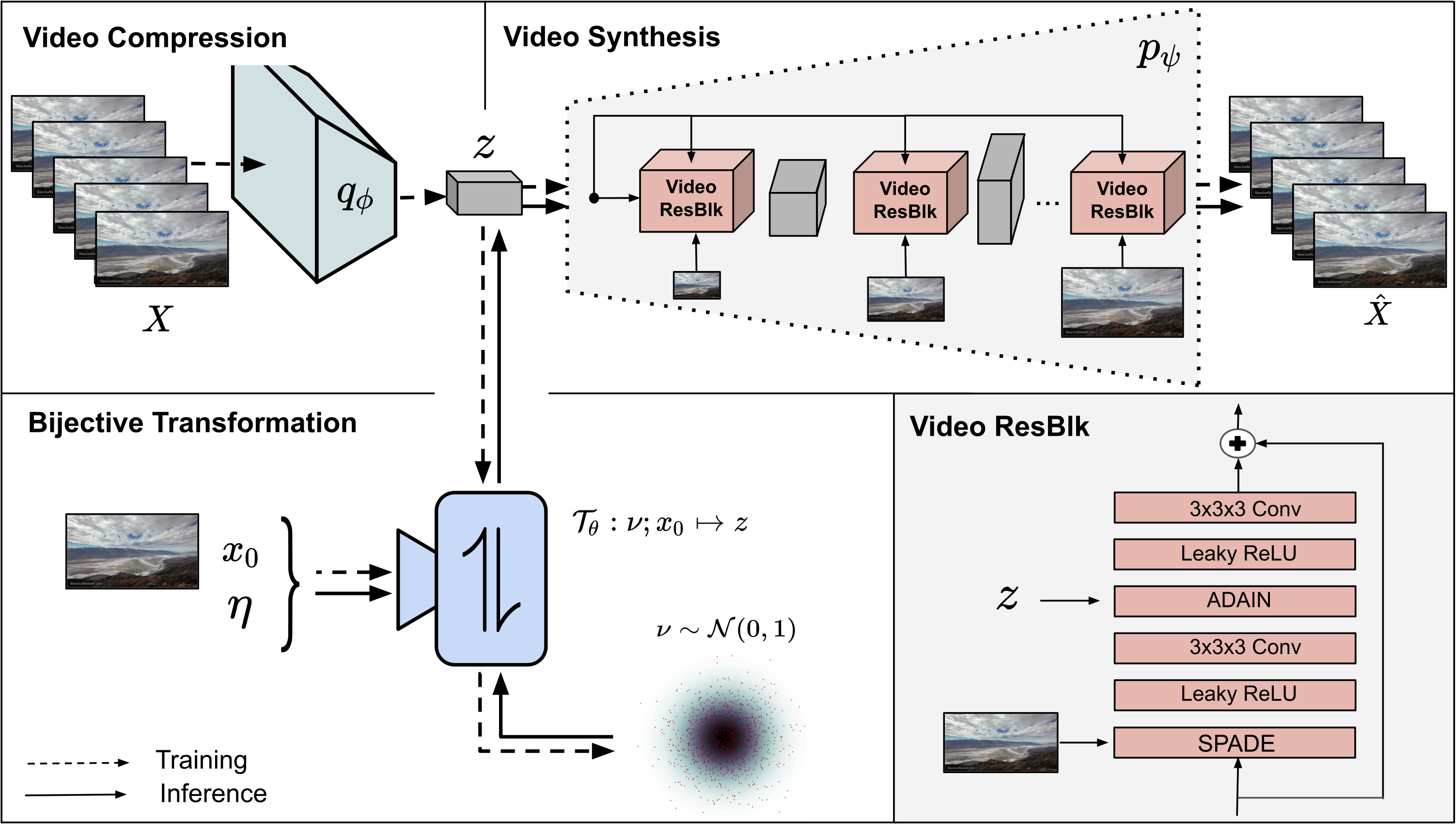
The training of our models is divided into two consecutive stages. In stage 1, we learn an information preserving video latent representation using a conditional generative model which reconstructs the given input video as best as possible. After that, we learn a conditional INN to map the video latent representation to a residual space depicting the scene dynamics conditioned on the starting frame and additional control factors. During inference, we now can sample new scene dynamics from the residual distribution and synthesize novel videos due to the bijective nature of the cINN. For more details please check out our paper.
For logging our runs we used and recommend wandb. Please create a free account and add your username to the config. If you don't want to use it, the metrics are also logged in a csv file and samples are written out in the specified chkpt folder. Therefore, please set logging mode to offline. For logging (PyTorch) FVD please download the weights of a PyTorch I3D from here and place it in models like /models/PI3D/. For logging DTFVD please download the weights of the DTI3D model from here and place it in the models folder like /models/DTI3D/. Depending on the dataset please specify either FVD or DTFVD under FVD in the config. For each provided pretrained model we left the corresponding config file in the corresponding folder. If you want to run our model on a dataset we did not provide please create a new config. Before you start a run please specify the data path, save path, and the name of the run in the config.
Stage 1: Video-to-Video synthesis
To train the conditional generative model for video-to-video synthesis run the following command
python -W ignore -m stage1_VAE.main -gpu <gpu_id> -cf stage1_VAE/configs/<config>
Stage 2: cINN for Image-to-Video synthesis
Before we can train the cINN, we need to train an AE to obtain an encoder to embed the starting frame for the cINN. You can use the on provided or train your own by running
python -W ignore -m stage2_cINN.AE.main -gpu <gpu_id> -cf stage2_cINN/AE/configs/<config>
To train the cINN, we need to specify the location of the trained encoder as well as the first stage model in the config. After that, training of the cINN can be started by
python -W ignore -m stage2_cINN.main -gpu <gpu_id> -cf stage2_cINN/configs/<config>
To reproduce the controlled video synthesis experiment, one can specify the control True in the bair_config.yaml to additional condition the cINN on the endpoint location.
Shout-outs
Thanks to everyone who makes their code and models available. In particular,
- The decoder architecture is inspired by SPADE
- The great work and code of Stochastic Latent Residual Video Prediction SRVP
- The 3D encoder and discriminator are based on 3D-Resnet and spatial discriminator is adapted from PatchGAN
- The metrics which were used LPIPS PyTorch FID FVD
BibTeX
@misc{dorkenwald2021stochastic,
title={Stochastic Image-to-Video Synthesis using cINNs},
author={Michael Dorkenwald and Timo Milbich and Andreas Blattmann and Robin Rombach and Konstantinos G. Derpanis and Björn Ommer},
year={2021},
eprint={2105.04551},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.CV}
}