OpenSA
Aiming at the common training datsets split, spectrum preprocessing, wavelength select and calibration models algorithm involved in the spectral analysis process, a complete algorithm library is established, which is named opensa (openspectrum analysis).
系列文章目录
“光晰本质,谱见不同”,光谱作为物质的指纹,被广泛应用于成分分析中。伴随微型光谱仪/光谱成像仪的发展与普及,基于光谱的分析技术将不只停留于工业和实验室,即将走入生活,实现万物感知,见微知著。本系列文章致力于光谱分析技术的科普和应用。
@TOC
前言
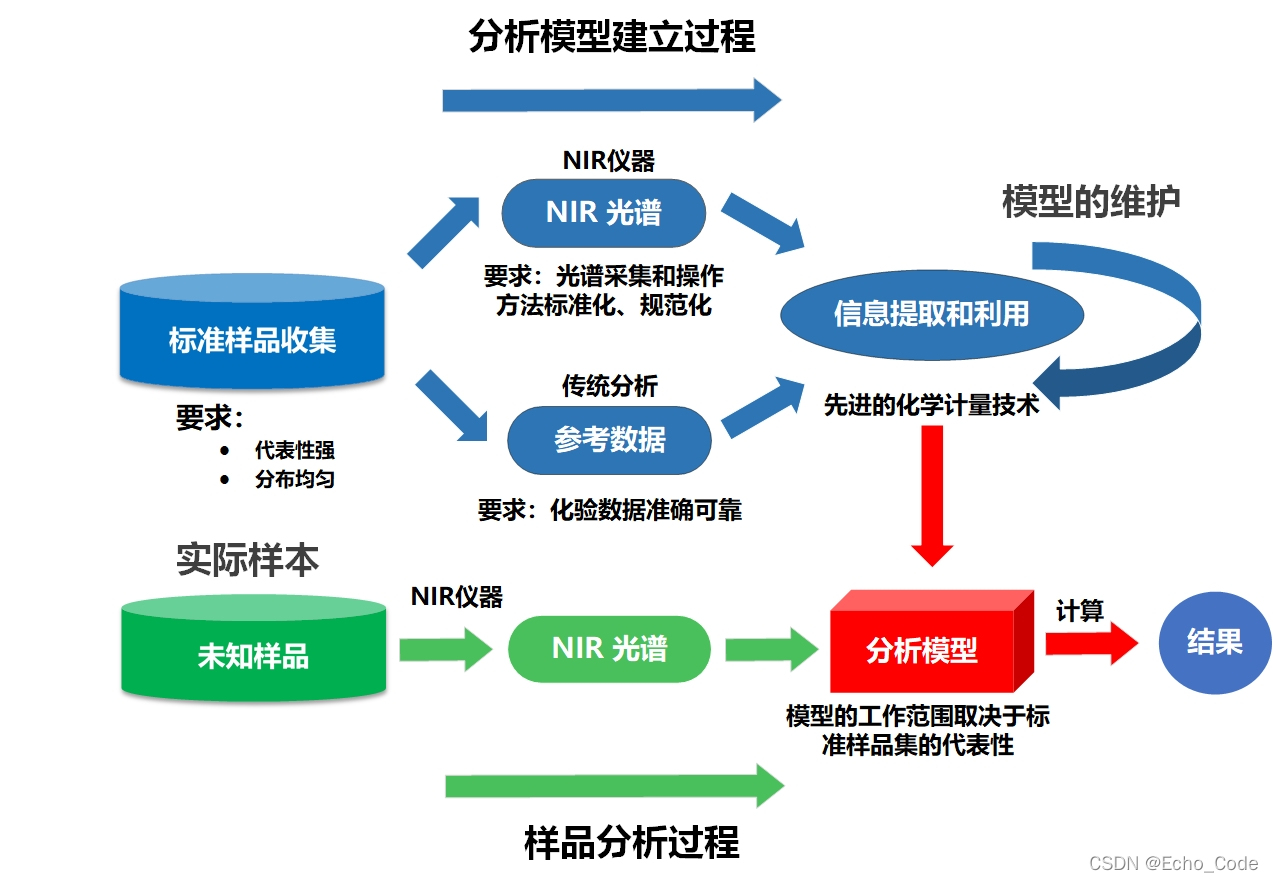
典型的光谱分析模型(以近红外光谱作为示意,可见光、中远红外、荧光、拉曼、高光谱等分析流程亦相似)建立流程如下所示,在建立过程中,需要使用算法对训练样本进行选择,然后使用预处理算法对光谱进行预处理,或对光谱的特征进行提取,再构建校正模型实现定量分析,最后针对不同测量仪器或环境,进行模型转移或传递。因此训练样本的选择、光谱的预处理、波长筛选、校正模型、模型传递以及上述算法的参数都影响着模型的应用效果。
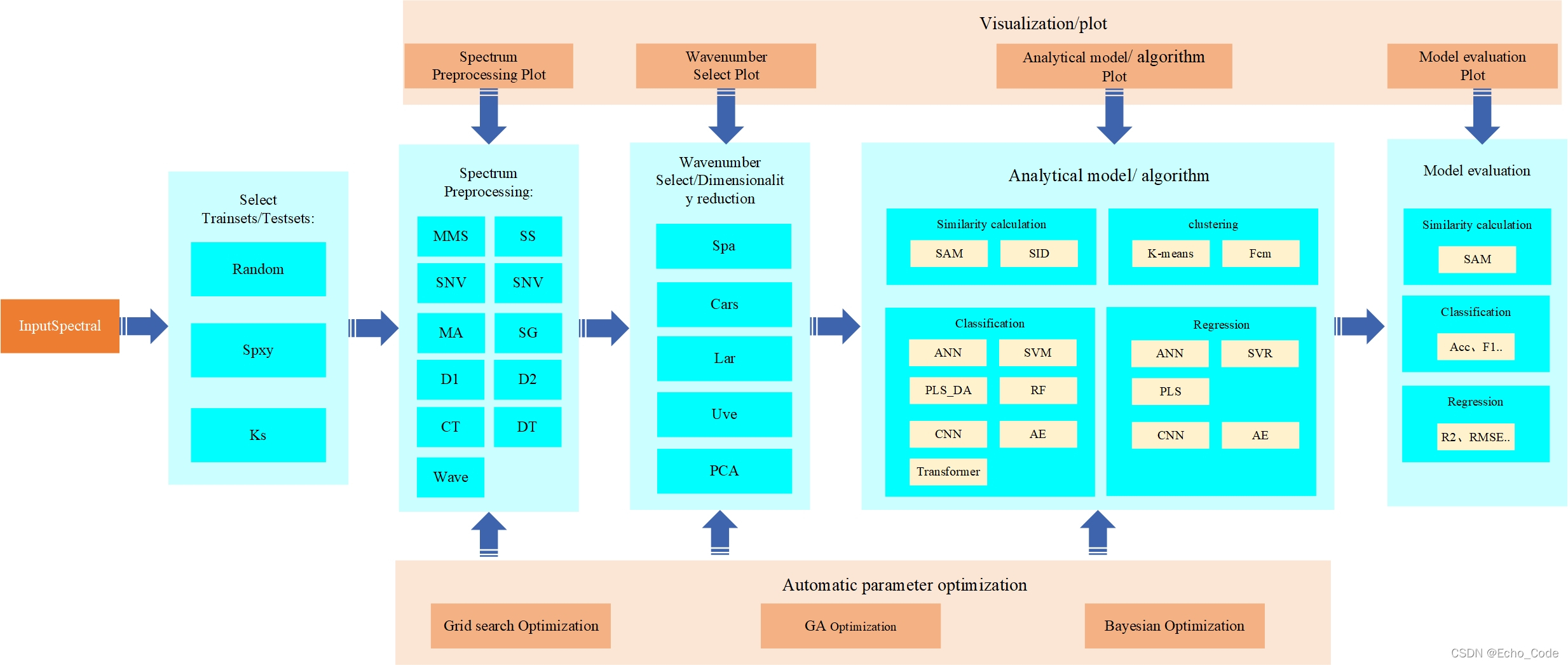
本篇针对OpenSA的光谱预处理模块进行代码开源和使用示意。
一、光谱数据读入
提供两个开源数据作为实列,一个为公开定量分析数据集,一个为公开定性分析数据集,本章仅以公开定量分析数据集作为演示。
1.1 光谱数据读入
# 分别使用一个回归、一个分类的公开数据集做为example
def LoadNirtest(type):
if type == "Rgs":
CDataPath1 = './/Data//Rgs//Cdata1.csv'
VDataPath1 = './/Data//Rgs//Vdata1.csv'
TDataPath1 = './/Data//Rgs//Tdata1.csv'
Cdata1 = np.loadtxt(open(CDataPath1, 'rb'), dtype=np.float64, delimiter=',', skiprows=0)
Vdata1 = np.loadtxt(open(VDataPath1, 'rb'), dtype=np.float64, delimiter=',', skiprows=0)
Tdata1 = np.loadtxt(open(TDataPath1, 'rb'), dtype=np.float64, delimiter=',', skiprows=0)
Nirdata1 = np.concatenate((Cdata1, Vdata1))
Nirdata = np.concatenate((Nirdata1, Tdata1))
data = Nirdata[:, :-4]
label = Nirdata[:, -1]
elif type == "Cls":
path = './/Data//Cls//table.csv'
Nirdata = np.loadtxt(open(path, 'rb'), dtype=np.float64, delimiter=',', skiprows=0)
data = Nirdata[:, :-1]
label = Nirdata[:, -1]
return data, label
1.2 光谱可视化
#载入原始数据并可视化
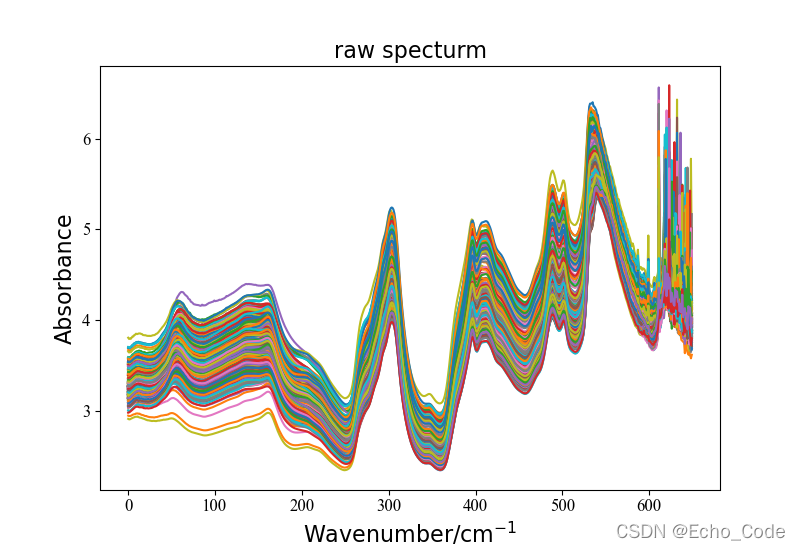
data, label = LoadNirtest('Rgs')
plotspc(data, "raw specturm")
二、光谱预处理
2.1 光谱预处理模块
将常见的光谱进行了封装,使用者仅需要改变名字,即可选择对应的光谱分析,下面是光谱预处理模块的核心代码
"""
-*- coding: utf-8 -*-
@Time :2022/04/12 17:10
@Author : Pengyou FU
@blogs : https://blog.csdn.net/Echo_Code?spm=1000.2115.3001.5343
@github :
@WeChat : Fu_siry
@License:
"""
import numpy as np
from scipy import signal
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
from sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScaler, StandardScaler
from copy import deepcopy
import pandas as pd
import pywt
# 最大最小值归一化
def MMS(data):
"""
:param data: raw spectrum data, shape (n_samples, n_features)
:return: data after MinMaxScaler :(n_samples, n_features)
"""
return MinMaxScaler().fit_transform(data)
# 标准化
def SS(data):
"""
:param data: raw spectrum data, shape (n_samples, n_features)
:return: data after StandScaler :(n_samples, n_features)
"""
return StandardScaler().fit_transform(data)
# 均值中心化
def CT(data):
"""
:param data: raw spectrum data, shape (n_samples, n_features)
:return: data after MeanScaler :(n_samples, n_features)
"""
for i in range(data.shape[0]):
MEAN = np.mean(data[i])
data[i] = data[i] - MEAN
return data
# 标准正态变换
def SNV(data):
"""
:param data: raw spectrum data, shape (n_samples, n_features)
:return: data after SNV :(n_samples, n_features)
"""
m = data.shape[0]
n = data.shape[1]
print(m, n) #
# 求标准差
data_std = np.std(data, axis=1) # 每条光谱的标准差
# 求平均值
data_average = np.mean(data, axis=1) # 每条光谱的平均值
# SNV计算
data_snv = [[((data[i][j] - data_average[i]) / data_std[i]) for j in range(n)] for i in range(m)]
return data_snv
# 移动平均平滑
def MA(data, WSZ=11):
"""
:param data: raw spectrum data, shape (n_samples, n_features)
:param WSZ: int
:return: data after MA :(n_samples, n_features)
"""
for i in range(data.shape[0]):
out0 = np.convolve(data[i], np.ones(WSZ, dtype=int), 'valid') / WSZ # WSZ是窗口宽度,是奇数
r = np.arange(1, WSZ - 1, 2)
start = np.cumsum(data[i, :WSZ - 1])[::2] / r
stop = (np.cumsum(data[i, :-WSZ:-1])[::2] / r)[::-1]
data[i] = np.concatenate((start, out0, stop))
return data
# Savitzky-Golay平滑滤波
def SG(data, w=11, p=2):
"""
:param data: raw spectrum data, shape (n_samples, n_features)
:param w: int
:param p: int
:return: data after SG :(n_samples, n_features)
"""
return signal.savgol_filter(data, w, p)
# 一阶导数
def D1(data):
"""
:param data: raw spectrum data, shape (n_samples, n_features)
:return: data after First derivative :(n_samples, n_features)
"""
n, p = data.shape
Di = np.ones((n, p - 1))
for i in range(n):
Di[i] = np.diff(data[i])
return Di
# 二阶导数
def D2(data):
"""
:param data: raw spectrum data, shape (n_samples, n_features)
:return: data after second derivative :(n_samples, n_features)
"""
data = deepcopy(data)
if isinstance(data, pd.DataFrame):
data = data.values
temp2 = (pd.DataFrame(data)).diff(axis=1)
temp3 = np.delete(temp2.values, 0, axis=1)
temp4 = (pd.DataFrame(temp3)).diff(axis=1)
spec_D2 = np.delete(temp4.values, 0, axis=1)
return spec_D2
# 趋势校正(DT)
def DT(data):
"""
:param data: raw spectrum data, shape (n_samples, n_features)
:return: data after DT :(n_samples, n_features)
"""
lenth = data.shape[1]
x = np.asarray(range(lenth), dtype=np.float32)
out = np.array(data)
l = LinearRegression()
for i in range(out.shape[0]):
l.fit(x.reshape(-1, 1), out[i].reshape(-1, 1))
k = l.coef_
b = l.intercept_
for j in range(out.shape[1]):
out[i][j] = out[i][j] - (j * k + b)
return out
# 多元散射校正
def MSC(data):
"""
:param data: raw spectrum data, shape (n_samples, n_features)
:return: data after MSC :(n_samples, n_features)
"""
n, p = data.shape
msc = np.ones((n, p))
for j in range(n):
mean = np.mean(data, axis=0)
# 线性拟合
for i in range(n):
y = data[i, :]
l = LinearRegression()
l.fit(mean.reshape(-1, 1), y.reshape(-1, 1))
k = l.coef_
b = l.intercept_
msc[i, :] = (y - b) / k
return msc
# 小波变换
def wave(data):
"""
:param data: raw spectrum data, shape (n_samples, n_features)
:return: data after wave :(n_samples, n_features)
"""
data = deepcopy(data)
if isinstance(data, pd.DataFrame):
data = data.values
def wave_(data):
w = pywt.Wavelet('db8') # 选用Daubechies8小波
maxlev = pywt.dwt_max_level(len(data), w.dec_len)
coeffs = pywt.wavedec(data, 'db8', level=maxlev)
threshold = 0.04
for i in range(1, len(coeffs)):
coeffs[i] = pywt.threshold(coeffs[i], threshold * max(coeffs[i]))
datarec = pywt.waverec(coeffs, 'db8')
return datarec
tmp = None
for i in range(data.shape[0]):
if (i == 0):
tmp = wave_(data[i])
else:
tmp = np.vstack((tmp, wave_(data[i])))
return tmp
def Preprocessing(method, data):
if method == "None":
data = data
elif method == 'MMS':
data = MMS(data)
elif method == 'SS':
data = SS(data)
elif method == 'CT':
data = CT(data)
elif method == 'SNV':
data = SNV(data)
elif method == 'MA':
data = MA(data)
elif method == 'SG':
data = SG(data)
elif method == 'MSC':
data = MSC(data)
elif method == 'D1':
data = D1(data)
elif method == 'D2':
data = D2(data)
elif method == 'DT':
data = DT(data)
elif method == 'WVAE':
data = wave(data)
else:
print("no this method of preprocessing!")
return data
2 .2 光谱预处理的使用
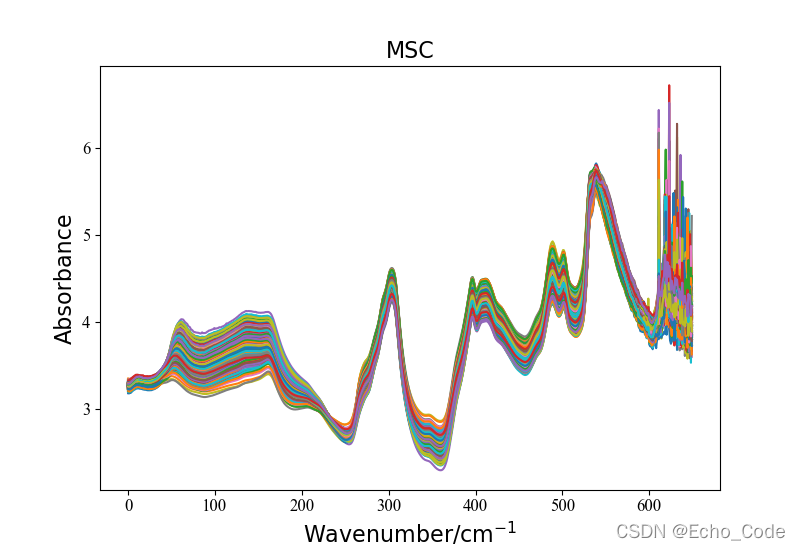
在example.py文件中,提供了光谱预处理模块的使用方法,具体如下,仅需要两行代码即可实现所有常见的光谱预处理。 示意1:利用OpenSA实现MSC多元散射校正
#载入原始数据并可视化
data, label = LoadNirtest('Rgs')
plotspc(data, "raw specturm")
#光谱预处理并可视化
method = "MSC"
Preprocessingdata = Preprocessing(method, data)
plotspc(Preprocessingdata, method)
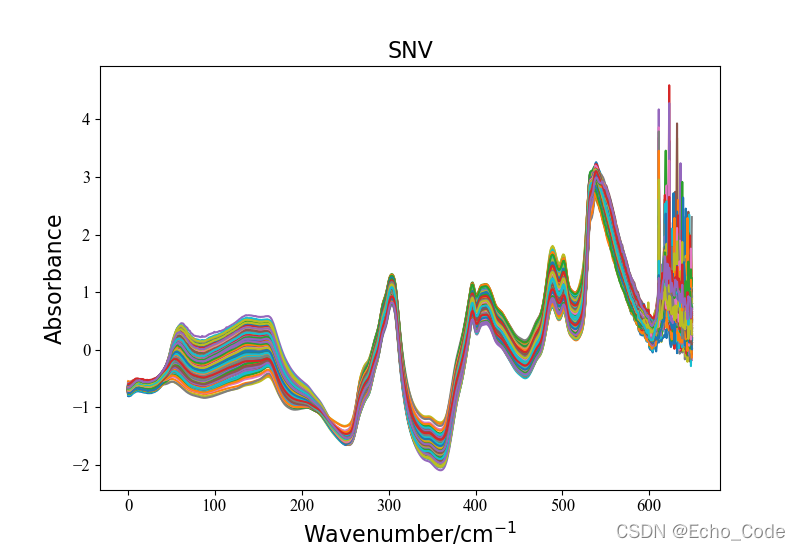
示意2:利用OpenSA实现SNV预处理
#载入原始数据并可视化
data, label = LoadNirtest('Rgs')
plotspc(data, "raw specturm")
#光谱预处理并可视化
method = "SNV"
Preprocessingdata = Preprocessing(method, data)
plotspc(Preprocessingdata, method)
总结
利用OpenSA可以非常简单的实现对光谱的预处理,完整代码可从获得GitHub仓库 如果对您有用,请点赞! 代码现仅供学术使用,若对您的学术研究有帮助,请引用本人的论文,同时,未经许可不得用于商业化应用,欢迎大家继续补充OpenSA中所涉及到的算法,如有问题,微信:Fu_siry