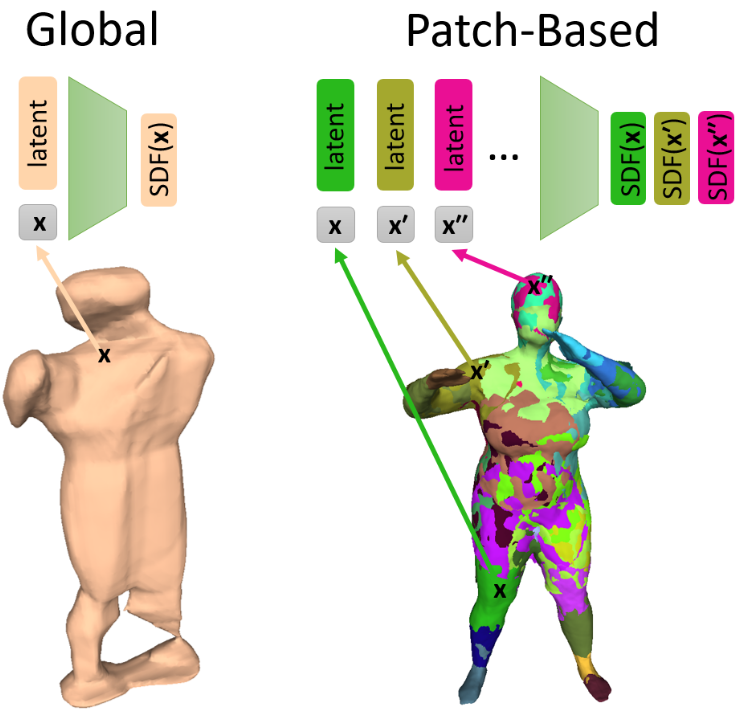
PatchNets
This is the official repository for the project "PatchNets: Patch-Based Generalizable Deep Implicit 3D Shape Representations". For details, we refer to our project page, which also includes supplemental videos.
This code requires a functioning installation of DeepSDF, which can then be modified using the provided files.
(Optional) Making ShapeNet V1 Watertight
If you want to use ShapeNet, please follow these steps:
- Download Occupancy Networks
- On Linux, follow the installation steps from there:
conda env create -f environment.yaml
conda activate mesh_funcspace
python setup.py build_ext --inplace
- Install the four external dependencies from
external/mesh-fusion:- for
libfusioncpuandlibfusiongpu, runcmakeand thensetup.py - for
libmcubesandlibrender, runsetup.py
- for
- Replace the original OccNet files with the included slightly modified versions. This mostly switches to using
.objinstead of.off - Prepare the original Shapenet meshes by copying all objs as follows: from
02858304/1b2e790b7c57fc5d2a08194fd3f4120d/model.objto02858304/1b2e790b7c57fc5d2a08194fd3f4120d.obj - Use
generate_watertight_meshes_and_sample_points()fromuseful_scripts.py. Needs to be run twice, see comment atgenerate_command. - On a Linux machine with display,
activate mesh_funcspace - Run the generated
command.sh. Note: this preprocessing crashes frequently because some meshes cause issues. They need to be deleted.
Preprocessing
During preprocessing, we generate SDF samples from obj files.
The C++ files in src/ are modified versions of the corresponding DeepSDF files. Please follow the instruction on the DeepSDF github repo to compile these. Then run preprocess_data.py. There is a special flag in preprocess_data.py for easier handling of ShapeNet. There is also an example command for preprocessing ShapeNet in the code comments. If you want to use depth completion, add the --randomdepth and --depth flags to the call to preprocess_data.py.
Training
The files in code/ largely follow DeepSDF and replace the corresponding files in your DeepSDF installation. Note that some legacy functions from these files might not be compatible with PatchNets.
- Some settings files are available in
code/specs/. The training/test splits can be found incode/examples/splits/. TheDataSourceand, if used, thepatch_network_pretrained_pathandpretrained_depth_encoder_weightsneed to be adapted. - Set a folder that collects all experiments in
code/localization/SystemSpecific.py. - The code uses
code/specs.jsonas the settings file. Replace this file with the desired settings file. - The code creates a results folder, which also includes a backup. This is necessary to later run the evaluation script.
- Throughout the code,
metadatarefers to patch extrinsics. mixture_latent_modecan be set toall_explicitfor normal PatchNets mode or toall_implicitfor use with object latents.- Some weights automatically change in
deep_sdf_decoder.pydepending on whetherall_explicitorall_implicitis used.
- Some weights automatically change in
- For all_implicit/object latents, please set
sdf_filenameunderuse_precomputed_bias_initindeep_sdf_decoder.pyto an.npzfile that was obtained via Preprocessing and for whichinitialize_mixture_latent_vector()fromtrain_deep_sdf.pyhas been run (e.g. by including it in the training set and training a normal PatchNet).MixtureCodeLengthis the object latent size andPatchCodeLengthis the size of each of the regressed patch codes. - For all_explicit/normal PatchNets,
MixtureCodeLengthneeds to be compatible withPatchCodeLength. SetMixtureCodeLength = (PatchCodeLength + 7) x num_patches. The 7 comes from position (3) + rotation (3) + scale (1). Always use 7, regardless of whether scale and/or rotation are used. Consider keeping the patch extrinsics fixed at their initial values instead of optimizing them with the extrinsics loss, see the second stage ofStagedTraining. - When using staged training,
NumEpochsand the total Lengths of eachStagedschedule should be equal. Also note that bothStagedschedules should have the exact sameLengthslist.
Evaluation
- Fit PatchNets to test data: Use
train_deep_sdf.pyto run the trained network on the test data. Getting the patch parameters for a test set is almost the same workflow as training a network, except that the network weights are initialized and then kept fixed and a few other settings are changed. Please see included testspecs.jsonfor examples. In all cases, settest_time = True,train_patch_network = False,train_object_to_patch = False. Setpatch_network_pretrained_pathin the testspecs.jsonto the results folder of the trained network. Make sure thatScenesPerBatchis a multiple of the test set size. Adjust the learning rate schedules according to the testspecs.jsonexamples included. - Get quantitative evaluation: Use
evaluate_patch_network_metrics()fromuseful_scripts.pywith the test results folder. Needs to be run twice, see comment atgenerate_meshes. Running this script requires an installation of Occupancy Networks, see comments inevaluate_patch_network_metrics(). It also requires theobjfiles of the dataset that were used for Preprocessing.
Applications, Experiments, and Mesh Extraction
useful_scripts.py contains code for the object latent applications from Sec. 4.3: latent interpolation, the generative model and depth completion. The depth completion code contains a mode for quantitative evaluation. useful_scripts.py also contains code to extract meshes.
code/deep_sdf/data.py contains the code snippet used for the synthetic noise experiments in Sec. 7 of the supplementary material.
Additional Functionality
The code contains additional functionalities that are not part of the publication. They might work but have not been thoroughly tested and can be removed.
- wrappers to allow for easy interaction with a trained network (do not remove, required to run evaluation)
_setup_torch_network()inuseful_scripts.py
- a patch encoder
- Instead of autodecoding a patch latent code, it is regressed from SDF point samples that lie inside the patch.
Encoderinspecs.json. Check that this works as intended, later changes to the code might have broken something.
- a depth encoder
- A depth encoder maps from one depth map to all patch parameters.
use_depth_encoderinspecs.json. Check that this works as intended, later changes to the code might have broken something.
- a tiny PatchNet version
- The latent code is reshaped and used as network weights, i.e. there are no shared weights between different patches.
dimsinspecs.jsonshould be set to something small like [ 8, 8, 8, 8, 8, 8, 8 ]use_tiny_patchnetinspecs.json- Requires to set
PatchLatentCodecorrectly, the desired value is printed by_initialize_tiny_patchnet()indeep_sdf_decoder.py.
- a hierarchical representation
- Represents/encodes a shape using large patches for simple regions and smaller patches for complex regions of the geometry.
hierarchical_representation()inuseful_scripts.py. Never tested. Later changes to the network code might also have broken something.
- simplified curriculum weighting from Curriculum DeepSDF
use_curriculum_weightinginspecs.json. Additional parameters are intrain_deep_sdf.py. This is our own implementation, not based on their repo, so mistakes are ours.
- positional encoding from NeRF
positional_encodinginspecs.json. Additional parameters are intrain_deep_sdf.py. This is our own implementation, not based on their repo, so mistakes are ours.
- a Neural ODE deformation model for patches
- Instead of a simple MLP regressing the SDF value, a velocity field first deforms the patch region and then the z-value of the final xyz position is returned as the SDF value. Thus the field flattens the surface to lie in the z=0 plane. Very slow due to Neural ODE. Might be useful to get UV maps/a direct surface parametrization.
use_odeandtime_dependent_odeinspecs.json. Additional parameters are intrain_deep_sdf.py.
- a mixed representation that has explicit patch latent codes and only regresses patch extrinsics from an object latent code
- Set
mixture_latent_modeinspecs.jsontopatch_explicit_meta_implicit.posrot_latent_sizeis the size of the object latent code in this case.mixture_to_patch_parametersis the network that regresses the patch extrinsics. Check that this works as intended, later changes to the code might have broken something.
- Set
Citation
This code builds on DeepSDF. Please consider citing DeepSDF and PatchNets if you use this code.
@article{Tretschk2020PatchNets,
author = {Tretschk, Edgar and Tewari, Ayush and Golyanik, Vladislav and Zollh\"{o}fer, Michael and Stoll, Carsten and Theobalt, Christian},
title = "{PatchNets: Patch-Based Generalizable Deep Implicit 3D Shape Representations}",
journal = {European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV)},
year = "2020"
}
@InProceedings{Park_2019_CVPR,
author = {Park, Jeong Joon and Florence, Peter and Straub, Julian and Newcombe, Richard and Lovegrove, Steven},
title = {DeepSDF: Learning Continuous Signed Distance Functions for Shape Representation},
booktitle = {The IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR)},
month = {June},
year = {2019}
}
License
Please note that this code is released under an MIT licence, see LICENCE. We have included and modified third-party components, which have their own licenses. We thank all of the respective authors for releasing their code, especially the team behind DeepSDF!