Prototype-based Incremental Few-Shot Semantic Segmentation
Fabio Cermelli, Massimiliano Mancini, Yongqin Xian, Zeynep Akata, Barbara Caputo -- BMVC 2021 (Poster) Link
Official PyTorch Implementation
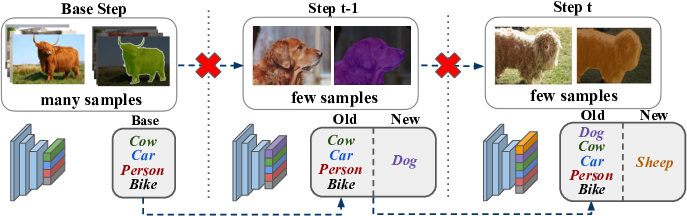
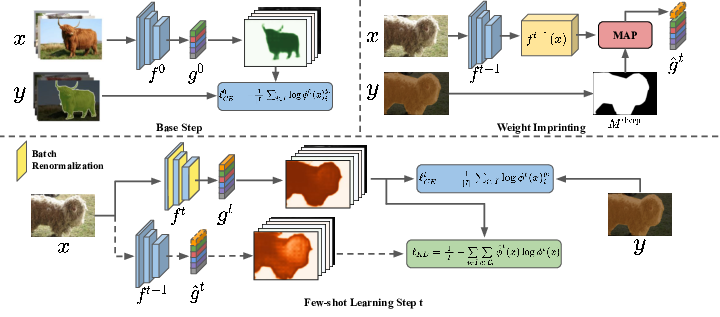
Semantic segmentation models have two fundamental weaknesses: i) they require large training sets with costly pixel-level annotations, and ii) they have a static output space, constrained to the classes of the training set. Toward addressing both problems, we introduce a new task, Incremental Few-Shot Segmentation (iFSS). The goal of iFSS is to extend a pretrained segmentation model with new classes from few annotated images and without access to old training data. To overcome the limitations of existing models iniFSS, we propose Prototype-based Incremental Few-Shot Segmentation (PIFS) that couples prototype learning and knowledge distillation. PIFS exploits prototypes to initialize the classifiers of new classes, fine-tuning the network to refine its features representation. We design a prototype-based distillation loss on the scores of both old and new class prototypes to avoid overfitting and forgetting, and batch-renormalization to cope with non-i.i.d.few-shot data. We create an extensive benchmark for iFSS showing that PIFS outperforms several few-shot and incremental learning methods in all scenarios.
How to run
Requirements
We have simple requirements: The main requirements are:
python > 3.1
pytorch > 1.6
If you want to install a custom environment for this codce, you can run the following using conda:
conda install pytorch torchvision cudatoolkit=10.1 -c pytorch
conda install tensorboard
conda install jupyter
conda install matplotlib
conda install tqdm
conda install imageio
pip install inplace-abn
conda install -c conda-forge pickle5
Datasets
In the benchmark there are two datasets: Pascal-VOC 2012 and COCO (object only). For the COCO dataset, we followed the COCO-stuff splits and annotations, that you can see here.
To download dataset, follow the scripts: data/download_voc.sh, data/download_coco.sh
To use the annotations of COCO-Stuff in our setting, you should preprocess it by running the provided script.
Please, remember to change the path in the script before launching it! python data/coco/make_annotation.py
Finally, if your datasets are in a different folder, make a soft-link from the target dataset to the data folder. We expect the following tree:
/data/voc/dataset
/annotations
<Image-ID>.png
/images
<Image-ID>.png
/data/coco/dataset
/annotations
/train2017
<Image-ID>.png
/val2017
<Image-ID>.png
/images
/train2017
<Image-ID>.png
/val2017
<Image-ID>.png
ImageNet Pretrained Models
After setting the dataset, you download the models pretrained on ImageNet using InPlaceABN. Download the ResNet-101 model (we only need it but you can also download other networks if you want to change it). Then, put the pretrained model in the pretrained folder.
Run!
We provide different scripts to run the experiments (see run folder). In the following, we describe the basic structure of them.
First, you should run the base step (or step 0).
exp --method FT --name FT --epochs 30 --lr 0.01 --batch_size 24
In this example, we are running the fine-tuning method (FT). For other methods (COS, SPN, DWI, RT) you can change the method name. WI and PIFS rely on the COS in the step 0, while FT, AMP, LWF, ILT, MIB rely on the FT one.
After this, you can run the incremental steps. There are a few options: (i) the task, (ii) the number of images (n_shot), and (iii) the sampling split (i_shot).
i) The list of tasks is:
voc:
5-0, 5-1, 5-2, 5-3
coco:
20-0, 20-1, 20-2, 20-3
For multi-step, you can append an m after the task (e.g., 5-0m)
ii) We tested 1, 2, and 5 shot. You can specify it with the nshot option.
iii) We used three random sampling. You can specify it with the ishot option.
The training will produce both an output on the terminal and it will log on tensorboard at the logs/<Exp_Name> folder. After the training, it will append a row in the csv file logs/results/<dataset>/<task>.csv.
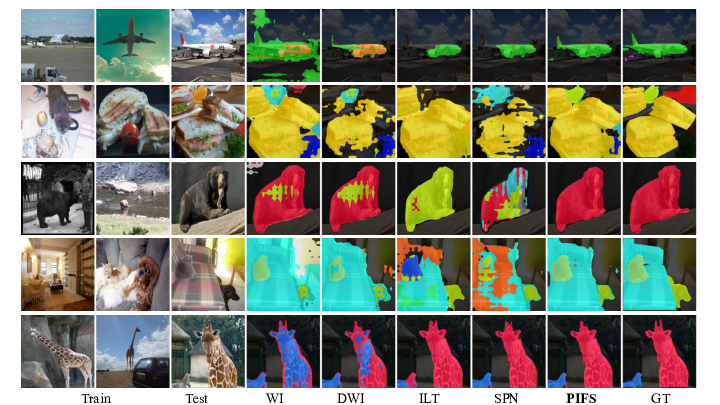
Qualitative Results
Cite us!
Please, cite the following article when referring to this code/method.
@InProceedings{cermelli2020prototype,
title={Prototype-based Incremental Few-Shot Semantic Segmentation },
author={Cermelli, Fabio and Mancini, Massimiliano and Xian, Yongqin and Akata, Zeynep and Caputo, Barbara},
booktitle={Proceedings of the 32nd British Machine Vision Conference},
month={November},
year={2021}
}