CLIPPER: A Graph-Theoretic Framework for Robust Data Association
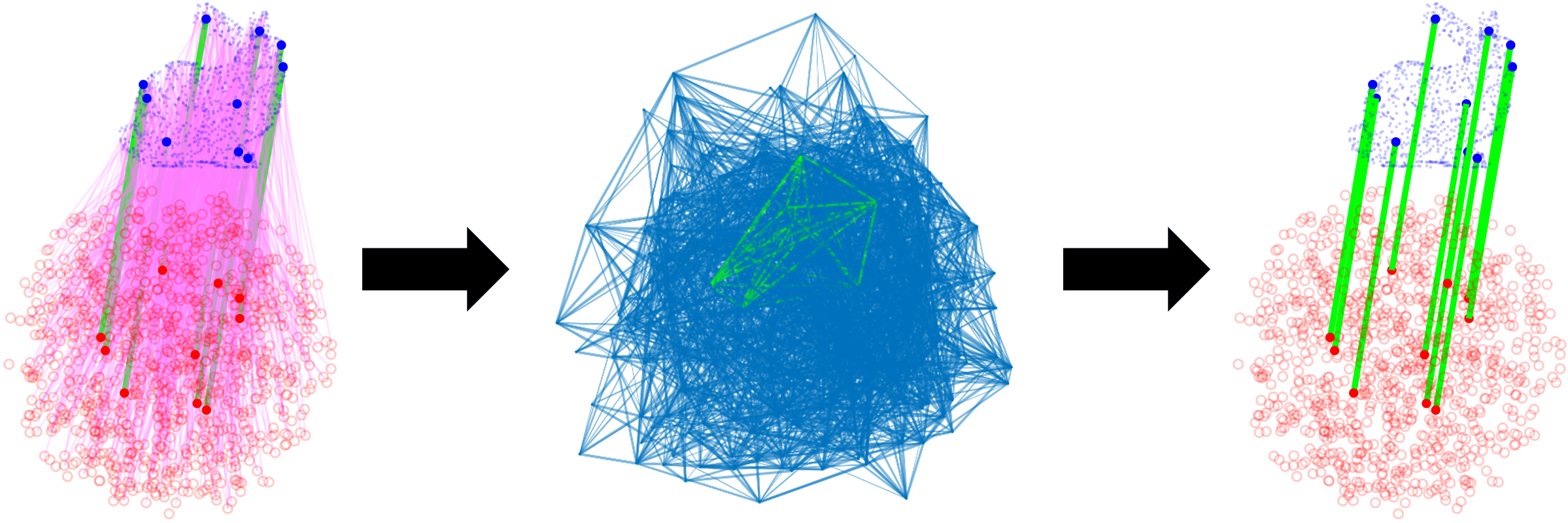
Data association is a fundamental problem in robotics and autonomy. CLIPPER provides a framework for robust, pairwise data association and is applicable in a wide variety of problems (e.g., point cloud registration, sensor calibration, place recognition, etc.). By leveraging the notion of geometric consistency, a graph is formed and the data association problem is reduced to the maximum clique problem. This NP-hard problem has been studied in many fields, including data association, and solutions techniques are either exact (and not scalable) or approximate (and potentially imprecise). CLIPPER relaxes this problem in a way that (1) allows guarantees to be made on the solution of the problem and (2) is applicable to weighted graphs, avoiding the loss of information due to binarization which is common in other data association work. These features allow CLIPPER to achieve high performance, even in the presence of extreme outliers.
This repo provides both MATLAB and C++ implementations of the CLIPPER framework. In addition, Python bindings, Python, C++, and MATLAB examples are included.
Citation
If you find this code useful in your research, please cite our paper:
- P.C. Lusk, K. Fathian, and J.P. How, "CLIPPER: A Graph-Theoretic Framework for Robust Data Association," arXiv preprint arXiv:2011.10202, 2020. (pdf) (presentation)
@inproceedings{lusk2020clipper,
title={CLIPPER: A Graph-Theoretic Framework for Robust Data Association},
author={Lusk, Parker C and Fathian, Kaveh and How, Jonathan P},
booktitle={IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA)},
year={2021}
}
Getting Started
After cloning this repo, please build using cmake:
$ mkdir build
$ cd build
$ cmake ..
$ make
Once successful, the C++ tests can be run with ./test/tests (if -DBUILD_TESTS=ON is added to cmake .. command).
Python Bindings
If Python bindings are built (see configuration options below), then the clipper Python module will need to be installed before using. This can be done with
$ cd build
$ make pip-install
# or directly using pip (e.g., to control which python version)
$ python3 -m pip install build/bindings/python # 'python3 -m' ensures appropriate pip version is used
Note: if using Python2 (e.g., < ROS Noetic), you must tell pybind11 to use Python2.7. Do this with adding the flag -DPYBIND11_PYTHON_VERSION=2.7 to the cmake .. command. You may have to remove your build directory and start over to ensure nothing is cached. You should see that pybind11 finds a Python2.7 interpreter and libraries.
A Python example notebook can be found in examples.
MATLAB Bindings
If MATLAB is installed on your computer and MATLAB bindings are requested (see configuration options below), then cmake will attempt to find your MATLAB installation and subsequently generate a set of MEX files so that CLIPPER can be used in MATLAB.
Note that in addition to the C++/MEX version of CLIPPER's dense cluster finder, we provide a reference MATLAB version of our projected gradient ascent approach to finding dense clusters.
Please find MATLAB examples here.
Configuring the Build
The following cmake options are available when building CLIPPER:
| Option | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
BUILD_BINDINGS_PYTHON |
Uses pybind11 to create Python bindings for CLIPPER |
ON |
BUILD_BINDINGS_MATLAB |
Attempts to build MEX files which are required for the MATLAB examples. A MATLAB installation is required. Gracefully fails if not found. | ON |
BUILD_TESTS |
Builds C++ tests | OFF |
ENABLE_MKL |
Attempts to use Intel MKL (if installed) with Eigen for accelerated linear algebra. | OFF |
ENABLE_BLAS |
Attempts to use a BLAS with Eigen for accelerated linear algebra. | OFF |
Note: The options ENABLE_MKL and ENABLE_BLAS are mutually exclusive.
These cmake options can be set using the syntax cmake -DENABLE_MKL=ON .. or using the ccmake . command (both from the build dir).
Performance with MKL vs BLAS
On Intel CPUs, MKL should be preferred as it offers superior performance over other general BLAS packages. Also note that on Ubuntu, OpenBLAS (sudo apt install libopenblas-dev) provides better performance than the default installed blas.
With MKL, we have found an almost 2x improvement in runtime over the MATLAB implementation. On an i9, the C++/MKL implementation can solve problems with 1000 associations in 70 ms.
Note: Currently, MATLAB bindings do not work if either BLAS or MKL are enabled. Python bindings do not work if MKL is enabled.
Including in Another C++ Project
A simple way to include clipper as a shared library in another C++ project is via cmake. This method will automatically clone and build clipper, making the resulting library accessible in your main project. In the project CMakeLists.txt you can add
set(CLIPPER_DIR "${CMAKE_CURRENT_BINARY_DIR}/clipper-download" CACHE INTERNAL "CLIPPER build dir" FORCE)
set(BUILD_BINDINGS_MATLAB OFF CACHE BOOL "")
set(BUILD_TESTS OFF CACHE BOOL "")
set(ENABLE_MKL OFF CACHE BOOL "")
set(ENABLE_BLAS OFF CACHE BOOL "")
configure_file(cmake/clipper.cmake.in ${CLIPPER_DIR}/CMakeLists.txt IMMEDIATE @ONLY)
execute_process(COMMAND "${CMAKE_COMMAND}" -G "${CMAKE_GENERATOR}" . WORKING_DIRECTORY ${CLIPPER_DIR})
execute_process(COMMAND "${CMAKE_COMMAND}" --build . WORKING_DIRECTORY ${CLIPPER_DIR})
add_subdirectory(${CLIPPER_DIR}/src ${CLIPPER_DIR}/build)
where cmake/clipper.cmake.in looks like
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.10)
project(clipper-download NONE)
include(ExternalProject)
ExternalProject_Add(clipper
GIT_REPOSITORY "https://github.com/mit-acl/clipper"
GIT_TAG master
SOURCE_DIR "${CMAKE_CURRENT_BINARY_DIR}/src"
BINARY_DIR "${CMAKE_CURRENT_BINARY_DIR}/build"
CONFIGURE_COMMAND ""
BUILD_COMMAND ""
INSTALL_COMMAND ""
TEST_COMMAND ""
)
Then, you can link your project with clipper using the syntax target_link_libraries(yourproject clipper).
This research is supported by Ford Motor Company.